When making the settings, the router is connected to a laptop. For this purpose, a network cable is provided with the router. After completing the settings, the cable is disconnected.

Wi-Fi Speed: what affects and can be improved

What does it depend on? Wi-Fi speed depends on a number of factors, and not always the most advanced routers can give the expected performance. Most often, the problem is in the external environment: interference, congestion of channels, improper installation of the device, etc.
How to improve? However, the Wi-Fi standard will also be an important factor. If the device runs on an outdated protocol, you should not expect maximum performance from it. In this case, firmware or replacement can help.
Impact of Wi-Fi standard on speed
WI-FI .
The first standard for wireless data transmission appeared back in 1996. It didn't have any symbol and was used for 3 years. That protocol provided the ability to transmit information wirelessly at 1 Mbit/sec. Of course, for today's mobile gadgets, this is negligible.
Let me remind you that back then people could not even think that it was possible to connect to the "World Wide Web" from portable equipment. Even WAP was not developed back then, the size of online pages was up to 20 Kb.

WI-FI 802.11A
The first project of the Wi-Fi Alliance, an association of the largest computer vendors, was the 802.11a protocol. The technology did not become very widespread. The difference of the new protocol was that computer devices could now use the 5 GHz frequency. This increased the speed of Wi-Fi to 54 Mbit/s.
Except that this standard did not support the 2.4 GHz frequency that had been used previously, which led to its failure. To work in networks with different frequency characteristics, manufacturers of computer equipment had to provide a double transceiver. This led to an increase in the size of the equipment.
WI-FI 802.11B
Since the 2.4 GHz frequency has the distinct advantage of wide coverage, manufacturers decided to revisit its use when creating the WI-FI 802.11B protocol. Gadget designers were able to provide data transfer rates of 5.5 to 11 Mbps. All routers supported the protocol.
All of the most popular portable devices eventually began to work with WI-FI 802.11B. For example, this option appeared in the Nokia E65 smartphone. It is important that Wi-Fi Alliance managed to achieve compatibility of the new protocol with the first version of the standard, so the transition occurred without much trouble.
IEEE 802.11 standards are Wi-Fi
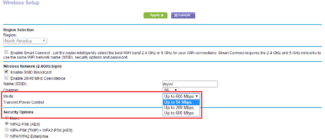
Developers of routers are aware of the issue of the changing market and offer combined devices (Mixed) for a guaranteed connection of the user to the Internet. Before proceeding to the settings, you need to determine which mode to choose for your Wi-Fi router.
Read more about IEEE 802.11 standards set, Wi-Fi bgn – what does this combination mean?
Pay attention! Wi-Fi b, g, n differ in the speed of information transfer. Each subsequent one connects to the previous one without any additional settings.
Another newest standard – 802.11ac – works only on dual-band routers with speeds up to 6.77 Gbps, the 5 GHz band, the presence of 8 antennas provides MU-MIMO.
Aspect Wi-Fi mode broadcasts the network in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
Pay attention! Modes of operation of the router – the letter values that the device supports are spelled out in the specifications for the device next to the mark Wi-Fi 802.11.
A complete list of standards has more than 30 items. The rest are not basic. They are amendments or additions to functions. Two of these standards are of interest precisely because of their additional features.
802.11.y offers a data transmission range of up to 5 km and uses pure bandwidth.
802.11.ad offers super speeds over short distances.
Wi-Fi Channel List
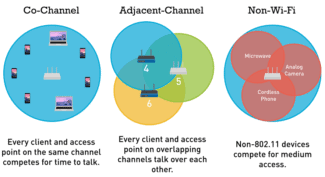
Typical routers receive 1-14 channels. The number depends on the router model, frequency, and country. Channel represents a "sub-frequency" of the main frequency on which the device operates. A kind of "air corridor" from the router to the receiver wi-fi.
Note! The more devices are on the same channel, the more interference and the lower the bandwidth.
802.11b/g/n
Channels 1-14 are the 14 channels for 802.11b/g/n. Radio frequency bands 2400-2483.5 MHz, transmitter emission power not more than 100 mW. Small range.
802.11a/h/j/n/ac
Channels 34-180 are 38 channels for 802.11a/h/j/n/ac frequencies. The frequency is 5170-5905 MHz.
802.11y
Channels 131-138 are 14 channels for 802.11y. Operates at 3.65-3.70 MHz up to 5000 m (open space). Additional communication channel. In the U.S., channels are available at 5;10;20 MHz.
Please note! Before you decide to change the channel, you need to check what channels are busy, collect statistics on the signal strength, the protocols used, and only then switch the router to the right position. Acrylic Wi-Fi Home program (free download) will help to gather statistics.