Knowing how to use an ad hoc network probably isn't going to change your life. However, it is something that can come in handy, especially if you do not have a designated workspace and use coworking spaces or you travel a lot for work and stay at hotels that do not have free Wi-Fi. Even so, you do need to be careful about the security and who has access to that network.
What is Ad Hoc on a Wi-Fi network, what is it for and how do I configure it on Windows 10, 7 and XP?

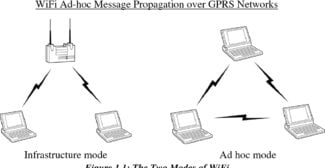
Hello! Ad hoc is the mode of a wireless network that does not have a permanent structure and is built "on the fly" through the pairing of devices. This mode is also called IBSS (Independent Basic Service Set) or point-to-point P2P. In order to implement this mode, it is sufficient for both devices to be equipped with Wi-Fi adapters and for the operating system through which they can communicate with, to have the drivers installed.
How Ad hoc works
Ad hoc mode requires a minimum of equipment. The most important thing is that each station is equipped with a WiFi–adapter .. You do not need to create a network.
This mode means that each node participates in routing by transiting data to other nodes. You can see which nodes send information based on the routing algorithm used. Ad Hoc is usually implemented to create temporary networks. For example, when a PC with an external Wi-Fi adapter and a laptop (with an internal wireless module) must be connected.
How to connect? It all depends on what version of Windows is installed on your computer. Let's start the report with the most modern one – Windows 10.
What Is Adhoc 11n?
An ad hoc wireless network is a temporary thing. It is created for specific purposes that will occur once and then the wireless network will cease to exist. People will often use this when they are working together on a specific document or project.
It can also be useful for people who are trying to work on the same creative project. Everyone connects to the network and it stays open. The second the last user logs out of the ad hoc network, the network will cease to exist. In order to get back on an ad hoc network, another one will have to be created. You will never get the “same” network back again.
To set up an ad hoc network, someone needs to go into the Network Sharing Center on any Microsoft Windows computer and do it from there. There are some questions surrounding the safety and security of these networks but if someone knows what they are doing, it is perfectly safe.
Wireless Ad Hoc Network Benefits
So why would someone choose to use an ad hoc network? There are many reasons to set one up, including:
- You can work pretty much anywhere you go.
- There isn’t a single point of failure when you use an ad hoc network.
- You won’t need to purchase expensive equipment to set up a network.
- Ad hoc networks quickly and safely allow you to share files or data directly from one computer to another when you don’t have access to a Wi-Fi network. You won’t have to use data from your phone to send documents that may be destroyed in the transfer.
- Ad hoc networks can be used in emergency situations where there isn’t an available wireless connection, the wireless connection goes down, or you only need it for a few seconds and the wireless is expensive (ie in hotels).
- Most ad hoc networks are easy to set up and take only seconds to launch.
- You can connect more than one laptop to the ad hoc network as long as everyone configures their computers for it. You do need to be within 100 meters of each other.
- Use ad hoc networks to troubleshoot potential problems.
- There is no need for a central management hub.
Everyone who uses an ad hoc network will come up with their own benefits for it, however, these are just some of the perks that most people enjoy.
Changing Mode
As you have probably already guessed, now we will try to change the mode to the highest speed mode. In this case we will change from "11bgn" to "11n". In this case the module will work only with the "n" standard without sputtering. The speed should theoretically increase inside the wireless network. Exactly inside – that is the local network. Internet speed will not increase – only if there is no loss in the "local network".

To change the mode we have to go to the settings of Web-configurator or admin panel of the device. To do this you must connect to the network of the device. You can do this over the wire or via Wi-Fi from any device. Then you open the browser and enter the address of the Internet center. Address, login and password by default are under the body on a special paper. The following instructions will vary depending on the company that released the router.
TP-Link
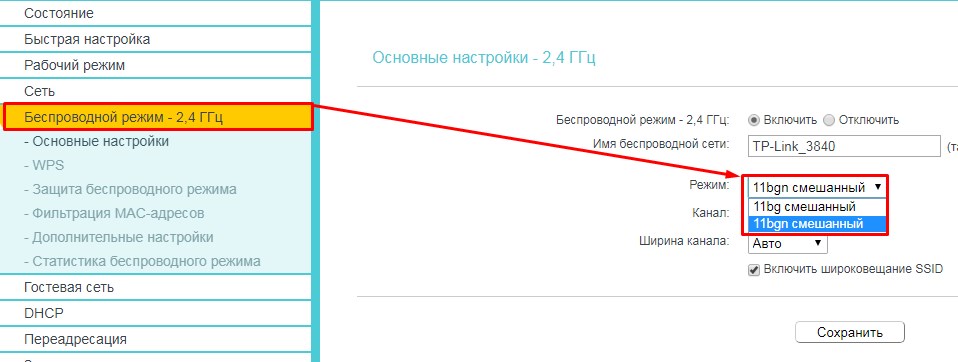
On the old firmware, find the "Wireless Mode" section on the left and select "Mode". Also see that there may be different modes for 2.4 and 5 GHz.
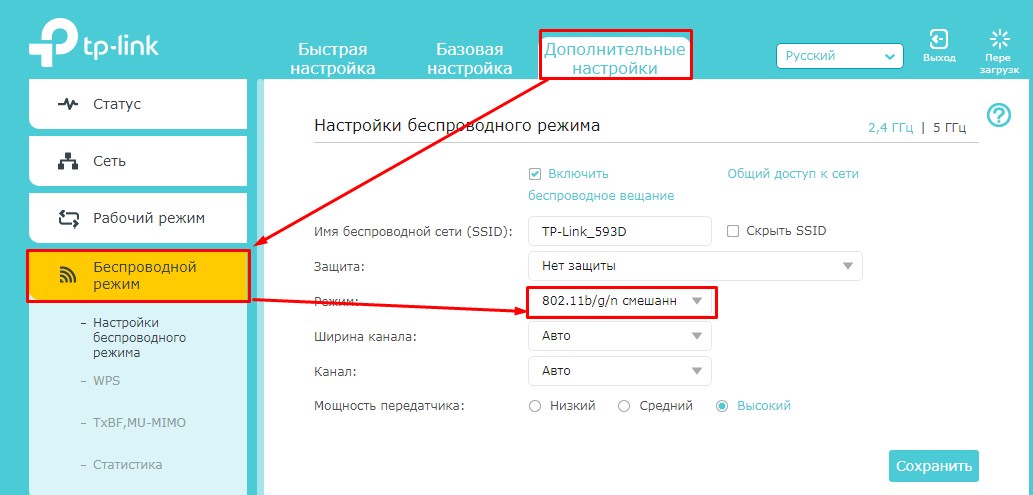
If you have newer firmware, you have to first select the "Advanced Settings" tab, then click on "Wireless Mode". In the upper right corner, don't forget to select the frequency as well.
D-Link
For the classic firmware: "Wi-Fi" – "Basic settings".
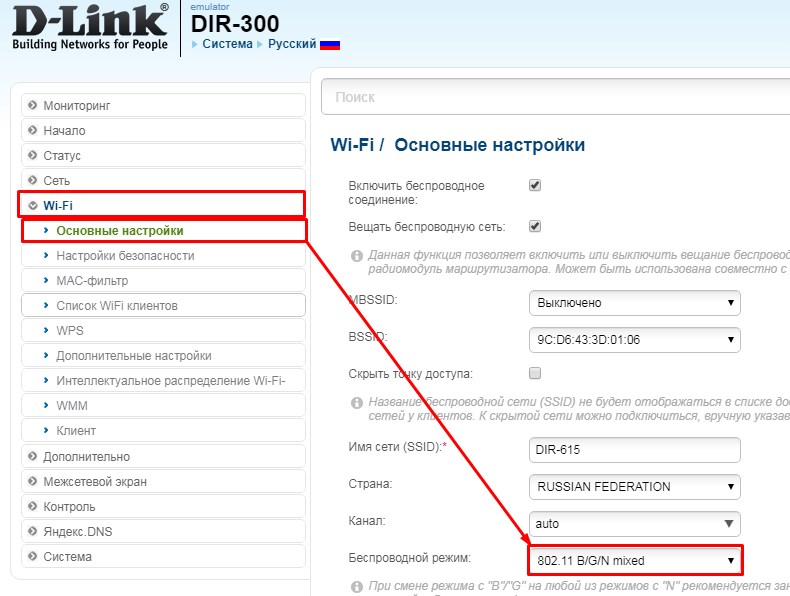
In the new firmware everything is a little more confusing. First at the bottom choose "Advanced settings", and then in the section "Wi-Fi" you need to click on the item "Basic settings".
Ad Hoc Networks
An ad hoc wireless network, unlike a standard wireless network, is a temporary network created for a specific purpose, such as a group of colleagues meeting in the same place to work together on an online document. When the last user exits the ad hoc network, the network is automatically deleted. You can set up a temporary ad hoc network from the Network Sharing Center on your Microsoft Windows computer.
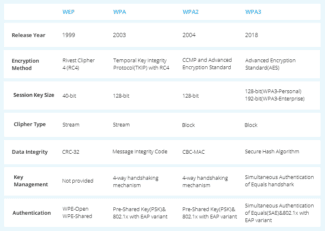
Most home networks use the standard 802.11b, 802.11g or 802.11n Wi-Fi network mode. Wireless modes offer different connection speeds, usually 11 megabits per second, or Mbps, for 802.11b connections, up to 54 Mbps for 802.11g and up to 150 Mbps for 802.11n. Routers that use 802.11n mode also offer compatibility with 802.11g to ensure that devices without 802.11n capabilities can still access the network.
Wireless adapters.
The advanced "Ad hoc 11n" setting on the device's wireless adapter allows the device to connect to the dedicated network created on the router in 802.11n Wi-Fi mode. The advantage of enabling this feature is a faster connection when connecting to a dedicated network. 802.11n mode can also extend the range of your wireless network, allowing you to connect to your router at a greater distance than is possible with 802.11g or 802.11b.
Make sure that enabling "Ad hoc 11n" improves the network performance of your wireless device by setting up a dedicated network. Open the Windows Network and Sharing Center from your computer's control panel. Click "Set up a new connection," then click "Set up a wireless ad hoc network (computer-to-computer)," and then click "Next." Windows launches the network setup wizard. When prompted, enter your Windows login password. You can also set a secret security code for the ad hoc network to prevent unauthorized access.

Some wireless adapters on desktops, mobile devices, and other wireless gadgets support the ad-hoc 11n feature, which you can turn on and off at will. Activating this feature allows you to use any device to connect to the network, based on the wireless router's 802.11n Wi-Fi technology.
"Ad Hoc" network, just like a standard wireless network, is a temporary network created for specific needs, such as various social events, seminars and conferences held in one compact location – where the rapid transfer of electronic documents between the participants of the event is required. As soon as the last user is disconnected from the Ad Hoc network, it will automatically shut down. FYI, you can deploy such a network yourself using the Network Sharing Center service on the Microsoft Windows platform.
Read More: