The good news is that most modern routers as Dual- or tri-band routers.

- Which WiFi Channel to Choose and How to Change to 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz on a Router?
- How do I check for congestion and find the best free WiFi channel?
- What's the difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi?
- 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi – Interference
- The choice between 2.4 or 5 GHz on my devices
- Advantages and disadvantages of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
- Speed or range
- How to choose the best range
- 1. The size of your home
- 2. Interference and Obstacles
- 3. type and scope of client devices
- 1. Power and Sensitivity
- 2. Number and type of obstacles
- Advantages and disadvantages of each band
- 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz: Which should I choose?
- 5GHz on the Apple Airport router
- Something about Wi-Fi
Which WiFi Channel to Choose and How to Change to 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz on a Router?
This article is about how to find a free WiFi channel on your router and how to change it in your router's settings. We'll also talk about what wireless channel width to choose in the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz band. With the proliferation of wireless technology every year, network utilization is getting higher and higher, which means that the topic of changing the channel and changing its width is becoming more and more relevant. So next I will show you how to check the airwaves with an Android or iPhone smartphone using a scanner program. Then analyze and find the best free WiFi channel, configure and change it on different frequencies on routers TP-Link, Asus, D-Link, Zyxel Keenetic, Tenda, Netis, Upvel, Mercusys, Huawei and Apple.
As you know, wireless Internet is now available almost everywhere in cities and towns. But despite the fact that the 5 GHz frequency range has long appeared and is slowly developing, most devices are still sitting on the 2.4 GHz frequency, which is "full of it" (you can read more about the difference between these ranges in my other publication).
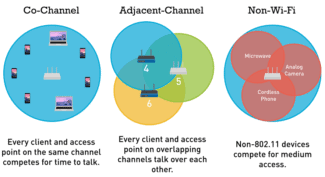
The number of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz routers running simultaneously is steadily increasing. It appears that there are many local networks operating in the same band on different WiFi channels at the same time. They interfere with each other by their overlapping signals. And in 99% of cases the routers are set to select the channel in automatic mode and do not always do so adequately. As a result, the signals mix up, create interference and interfere with each other. Because of this the speed and quality of the Internet decreases.
But everything is not so bad, because there are several wifi channels in this range, which means we can choose the one that is more free, and configure your router to it. In Russia and CIS countries there are 13 channels available for use.
Read More:That is why I advise that after the initial router setup, it is imperative that you find a free wifi channel and change it. Especially if you plan to work on 2.4 GHz.
How do I check for congestion and find the best free WiFi channel?
In order for you to have everything working steadily and without interference, you should first check which channels are used on your neighbors' access points. To find the freest wifi channel and choose the best one for your specific situation, we will use a free application – wifi channel scanner for smartphone, called Home WiFi Alert. It is free for Android users, but for the iPhone I could only find paid analogues.
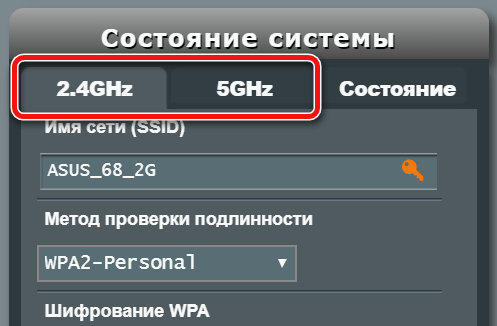
Install it and run it, then go to the section "Structure of the TD" and select the 2.4 Ghz band checkbox here.
Many people will have the same picture as I did – you will find a lot of parallel networks from different access points with different reception strengths. The number next to their name is the channel on which they are operating. Three on "10", three on "1", one each on "6" and "7".
What's the difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi?
Both are. 2 GHz Wi-Fi and 5 GHz – should be evaluated with the factors already mentioned in mind, namely the number of channels and signal strength, popularity of use and possible speed.
First of all, when comparing 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi, you can see the difference in the popularity of using a particular Wi-Fi band. The 2.4 GHz band is much more popular and most devices can be connected to it. The 5 GHz band, on the other hand, is still rare these days.
As for the number of channels, a larger number of channels is characterized by 5 GHz. This makes the router work faster, because more channels means less interference in the network.
It is very important to emphasize the ability of the generated signal to overcome physical obstacles. The 2.4 GHz band definitely has an advantage here, because it will work much better in conditions where you need the equipment to work seamlessly in different rooms.
When choosing any of the available frequencies, you have to consider the factors that guide your network usage. If you want to work easily or use the Internet for a variety of purposes, think about mobility or speed.
The 5 GHz Internet is definitely the best option for anyone who needs a fast connection when you need to use multiple resources or transfer more files without problems. However, as far as mobility is concerned, the 2.4 GHz band will allow you to use the Internet in rooms other than the one in which the router is located without many obstacles.
It's worth noting that it's currently advantageous to purchase dual-band routerwhich operates on two frequencies simultaneously.
2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi – Interference
If you have a lot of devices in your area using the same Wi-Fi band, you could have interference. The 5 GHz band, less popular and less common on devices, has no serious problems.
Wi-Fi frequencies classified as 2.4 GHz, which have fewer channels, are prone to more interference due to the fact that the signals being radiated overlap. Due to the fact that 2.4 GHz is a fairly popular band, the risk of certain connectivity limitations will be more likely. You may not feel this while surfing the Internet, but certainly the quality and buffering speed of the FullHD movie you are watching will be low and unsatisfactory.
In today's world of the Internet and various technologies, a great solution is to use the previously mentioned dual-band router.
The choice between 2.4 or 5 GHz on my devices
If your device supports a wired Ethernet connection, and you have no problem connecting a cable to your device, we highly recommend using a wired connection instead of a wireless network. Wired connections offer lower latency, no disconnects due to interference, and simply faster speeds than a wireless connection.
Nevertheless, we're here to talk about wireless connections. If you're currently using 2.4GHz Wi-Fi and are wondering if you need to upgrade to 5GHz, this is really something you need to do. If you often experience dropped connections or need more speed to watch videos or play games, you probably need to upgrade to 5 GHz.. On a 2.4 GHz network, you'll only be able to get that speed under ideal conditions.
If you live in a crowded apartment complex with dozens of wireless routers, baby monitors and other 2.4 GHz devices, you definitely need to upgrade to 5 GHz.
If you're already using a dual-band or tri-band router, you'll need to make some decisions about how to connect your devices. It's tempting to just use 5 GHz Wi-Fi for any device that supports it, and use 2.4 GHz for the rest-you can do that, but it's not always the best strategy.
Instead, think about how you use each device. If the device only supports 2.4 GHz, your decision is already made. If the device supports both, consider whether you really need to use 5 GHz. Does this device require faster speeds, or are you only checking email and browsing the Internet? Does the device experience connection failures on the 2.4 GHz network and do you need it to be more reliable?
Advantages and disadvantages of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
Although the 2.4 GHz standard is much older, it has some advantages over the newer 5 GHz band.
First of all, the 2.4 GHz router does a little better with signal propagation through walls. In theory, the range of the 2.4 GHz network is also higher, but in practice it usually looks different because of the many interferences. If you use a lot of older devices, support for the 2.4 GHz band is also necessary because not all gadgets support 5 GHz.
Due to the small number of channels (only 13), in theory the 2.4 GHz network has only 3 channels without overlap. This is a huge disadvantage compared to the 5 GHz network, which provides up to 19 channels without overlap and thus more fault-tolerant operation. In addition, other devices (such as Bluetooth gadgets) operate at 2.4 GHz and thus interfere with the network.
Speed or range
The main difference between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands comes down to the difference in wireless speed and range (coverage) of the network: if you want more range, use 2.4 GHz; if faster connections are a priority, use 5 GHz.
The technical capabilities of the newer 5 GHz band reduce interference with a large number of devices served and maximize network performance. Which makes this band preferable, for example, for games where it is important that latency is as low as possible.
The 5 GHz band offers more communication channels, and it generally does not have significant problems serving many potentially competing devices. But technically, the 5 GHz band does not offer as much range as 2.4 GHz. Newer routers are usually dual-band and give you the choice of using 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz.
How to choose the best range
1. The size of your home
Larger homes need more coverage, so 2.4 GHz is the best option here.
For smaller homes or apartments, the 5 GHz band will not only provide faster connections, but also reduce interference from neighboring networks.
If you want to take full advantage of the 5 GHz band while increasing your Wi-Fi network coverage, it makes sense to consider Wi-Fi extenders.
2. Interference and Obstacles
The 2.4 GHz band is more susceptible to interference since many types of devices operate in this frequency. These include older models of routers, microwaves, Bluetooth devices, baby monitors, garage door openers, etc.
From this perspective, 5 GHz is the best option if the subscriber device is close enough to the router/access point. In addition, a large number of dedicated subscriber channels are available in the 5 GHz band. Less overlap between these channels means better interference immunity, which ultimately means better Wi-Fi network efficiency.
3. type and scope of client devices
The 2.4 GHz band uses longer wavelengths that are better suited for long-range signal transmission, including through walls and other solid objects in the signal path. The 2.4 GHz band would be ideal for connecting customers who do not require high bandwidth connections; it is a suitable option for Web surfing, for example.
The 5 GHz band, on the other hand, is better suited for high bandwidth client devices and loads such as online gaming or HDTV broadcasts.
1. Power and Sensitivity
The transmitter power allowed by the IEEE 802.11 standard for wireless Wi-Fi equipment should not exceed 20 dBm, which is equivalent to 100 milliwatts. The average power value of real equipment is in the range from 15 to 18 dBm. This is mostly due to the manufacturer's unwillingness to "take risks", because a device with more than 20 dBm power simply will not pass certification.
There are two things to pay attention to: firstly, you need to understand what part and in which direction the Wi-Fi adapter, or rather its antenna, radiates. The vast majority of home-version access points have omni-antenna with a circular radiation pattern in the form of a torus (a first approximation), Figure 1.
Figure 1 – Appearance and radiation pattern of the omni-antenna
Torus has a radiation pattern in the angular plane in the form of figure 8, and in the azimuthal plane – in the form of a circle. To ensure the most favorable reception conditions, the user of the network should be positioned in the direction of maximum radiation. Given that the antenna in question is omni-directional, it simply must be placed parallel to the receiver (receiver antenna). This condition is illustrated by figure 2.
Figure 2 – Illustration of the dependence of the reception quality on the mutual orientation of the transmitter and receiver
Thus if the location of your laptop corresponds to the direction of "minimal radiation" (Fig. 2) you should not be surprised with the low quality of reception. Considering that the antennas, coming with the router, have a "rotation system" in the base, then what kind of antenna orientations you can not meet in the apartments of everyday people.
2. Number and type of obstacles
The motto of the section: use logic in the placement of equipment.
Of course, without special equipment it is difficult to take into account the number and type of obstacles in the way of radio signal propagation, but there are some rules, following which you can "save" a few decibels of power.
The length of the Wi-Fi wave in the 2.4 GHz band is an average of 12.5 centimeters and for the 5 GHz band – 6 centimeters, so for large objects (walls, floors, cabinets, doors, etc.) you can use the principle of geometric optics, assuming that the signal propagates in a straight line (partially reflecting and refracting). This is, of course, a rough assumption, but at any rate it will make it possible to "by eye" estimate the direction of signal propagation and clear (if possible) its path.
The first thing to keep in mind is that the signal passes very poorly through metalized surfaces and respectively reinforced concrete slabs. Once it hits a metal object, the electromagnetic wave continues to propagate along its surface, scattering. Therefore, ideally, the access point should be placed away from safe doors, iron tables and so on. If it is necessary to ensure the passage of the signal through a thick wall (the type of material is not important), we must try to ensure that the path from the source to the receiver through this obstacle was minimal. This condition is demonstrated by the illustration in Figure 3.
Figure 3 – Illustration of signal power level after passing through an obstacle
Advantages and disadvantages of each band
Each of the wi-fi bands has its pros and cons. The main advantage of 2.4 GHz is the wider coverage. That said, it's not as fast as its counterpart, the 5 GHz band.
Another disadvantage of the 2.4 GHz band is the limited number of simultaneous devices that can be connected to a single router. In addition, the 2.4 GHz band tends to be crowded because of the large number of devices that use it. This leads to connection problems such as slower than expected Wi-Fi speeds, dropped connections, interference, etc.
With that said, the 2.4 GHz frequency is ideal if you need broad Wi-Fi coverage throughout your home. Lower frequencies can penetrate hard objects better, so you'll be able to use your Wi-Fi from a greater distance.
The 5 GHz band supports higher speeds. Supporting more channels means you can connect many more devices. This band also tends to be less busy, hence less interference since not many devices use it. You will also have a stable internet connection.
The main drawback of the 5 GHz band is the coverage. Also, this band is not supported by many devices, especially older devices.
2.4 GHz or 5 GHz: Which should I choose?
Your choice depends primarily on your needs. Choose the 2.4 GHz band if you need wide coverage or if you live in a house with thick concrete walls that can cause interference. The 2.4 GHz band is also ideal for surfing the Internet without claiming high speeds.
The 5 GHz band is ideal for streaming video and online gaming. You should also use this band if you want to connect a lot of home devices to your wifi.
If a wide range of Wi-Fi is not required, 5 GHz would be ideal to use. But you can also use Wi-Fi signal repeaters to extend your coverage.
5GHz on the Apple Airport router
Now let's talk about one of the most expensive dual-band models – Apple Airport. It would be silly to buy a modern, cool router for 8,000 rubles and not use it to its full potential. The 5G standard, on the other hand, will help to eliminate the problem with wifi channel congestion, thereby increasing the speed of the Internet and the stability of your wireless network as a whole. By default, only one 2.4 GHz network is activated during the quick setup. But to enable a more advanced and high-speed wireless signal, you will need to do something else.
Launch the Airport Utility program on your computer and enter "Manual Settings".
Open the "Wireless" tab and click on the "Wireless Network Options" button
Here, activate the checkbox "5G" and set the name for the new wifi network. The password and encryption type will be copied from the main 2.4 G network
Save the settings by clicking "Update" and enjoy a more stable and faster signal.
As you can see, the advantages of wifi in the 5GHz band are many and there is nothing complicated about starting to use it. If you have any questions, I'll answer them in the comments!
Something about Wi-Fi
I recently attended a conference on "Building Wireless Networks". Despite the fact that I have been an administrator for a long time, it is not every day that I have to deploy wireless networks. I am hastening to share with you some of the nuances. I invite all interested readers under the hood.
Wi-Fi does not have a clear boundary of propagation.
That means that without proper evaluation no one can give you a guarantee that the connection will work even within a single office or room.
There were cases when in the office once a day the connection was lost for about half an hour. A tech-support staff member of the access point manufacturer was very experienced, therefore after finding out the time when the connection was down most often (which usually happened from 12-00 to 14-00), suggested that the blame lies in the microwave oven. In this office there was no microwave, but it was in the next, just behind the wall to which was screwed access point.
Here we should also remember all kinds of Wi-Fi jammers, which can be used by your competitors who pay their neighbors to turn it on from time to time.Because of this, it is not recommended to use wireless networks as a substitute for a corporate LAN with twisted pair or fiber. Or do it as a last resort when laying cable is not possible. For example, if you need to connect two nearby offices in the country.
Wireless network is best seen as a wonderful addition to the "traditional" networks. For example, to organize guest access for their customers.You should also keep in mind that Wi-Fi networks may not work equally well with different transport layer protocols. So, for example, TCP and UDP may work fine, but IPX is out of hand.
In order to understand exactly how to build a network and to try to determine the possible cause of the failure it is necessary to understand a little bit about the existing standards and their vulnerabilities.
At this point I think it makes sense to look at 802.11g and 802.11n.