So, we don't know if our router supports the second frequency. The easiest way to check this information is in the settings (or configurator) of the router. You do not need to install anything, just being connected to the router's network (by cable or Wi-Fi) you should type the IP or DNS address of the router into the address bar of any browser. It can be found on a label underneath the device. Very often such addresses are used:

Why change the Wi-Fi frequency on my smartphone?
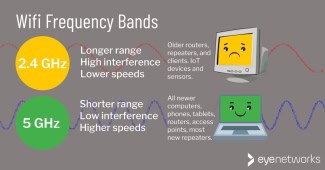
Since many other devices, as well as most routers and mobile devices, operate on the 2.4 GHz frequency, this frequency can cause interference and connection failures. The 5 GHz band is not used as often, which means interference will occur much less frequently. Therefore, it is recommended to change the Wi-Fi frequency on the phone if the user has started to experience sudden connection interruptions and loss of connection frequently.
Change the frequency from 2.4 GHz to 5 GHz when distributing Internet from the phone, i.e. with the access point on the mobile device turned on. In this way, the user can avoid connection problems while streaming.

How do I know if my phone supports 5 GHz?
There are several ways to find out if your cell phone can work with 5 GHz frequency:
- From the technical specifications of the phone. You can find out them on the official site of the manufacturer or in the instruction manual. It should indicate the possibility of 802.11ac. If this information is available, it means that your phone supports 5 GHz.
- Using the Wi-Fi Info app. It can be downloaded for free via Google Play. Next to the bottom line labeled "5Ghz Support" will either show true (5Ghz support is present) or false (no 5Ghz support).
Intel Processors
The leading position in manufacturing processors is occupied by Intel. It manufactures three types of CPUs.
1. Celeron is a relatively inexpensive processor with low performance. It has been created as a "budget brother" of more powerful CPUs.
2. Atom – microprocessors with low power consumption. They are designed for mobile devices: tablets, smartphones, netbooks. 3.
3. Core i – the CPUs used by all computer and notebook manufacturers. They are integrated into most IBM and Mac architecture computers. The processors produced are:
- Core i3 (the weakest of the family; have 2 physical cores and clock speeds of 2.93 to 3.8 GHz);
- Core i5 (more powerful CPUs, with 4 physical cores; i5 CPUs clocked up to 3.5 GHz, except the 2-core i5-661 clocked at 3.33 GHz);
- Core i7 (4-core processors; CPU clock speeds in this family range from 2.8 GHz to 5 MHz).
AMD processors
The second largest processor company in terms of sales is AMD (Advanced Micro Devices). They have proven themselves in the microprocessor market as inexpensive but powerful – AMD is the main competitor to Intel.
To date, the main AMD processor lines are:
- Budget E series (E1 models with 2 cores and E2 with 4 cores);
- APU – series with integrated graphics core (A4, A6 models with 2 cores; A8, A10 models with 4 cores);
- Athlon – the same APU, but with disabled graphics core and at a lower cost (X4 model with four cores, X8 – eight cores);
- FX – the most powerful series of processor models, all with eight cores.
The third prominent manufacturer of 32 and 64-bit ARM Limited. ARM processors are used in most mobile devices, either alone or in combination with other processors. ARM processors are rarely installed in computers. Apple developers have plans to create a generation of laptops based on ARM, but so far laptops and desktop Macs contain Core i5 and i7.
When you buy a computer or other device, information about the specifications (the computer's guts) can be found in the included manual. Laptops often have many stickers that show the type of CPU, graphics card model, display options, and operating system.
STEP 2: Setup
Now we come to the question of how to switch and configure a 5 GHz router. Again, routers have different firmware because they are released by different manufacturers. Also, the operating systems may be different for the same manufacturer due to different hardware versions of the routers. I have tried to list all the possible ones. But before we get started, let me give you a quick rundown on some of the 5 GHz network parameters you might encounter:
- Mode or standards – three popular standards can be found:
- N– works also on the 2.4 GHz frequency. It has the lowest speed in the 5GHz range.
- AC . – 5th generation Wi-Fi. Has a fairly high speed. In the average of 400 to 500 Mbit per second.
- AX – 6th generation Wi-Fi. The highest speed and high reliability. Read more…
- WPA – The most unreliable and old method. It is used only on old devices.
- WPA2 – is the most popular and sufficiently reliable.
- WPA3 – is only supported by Wi-Fi The most secure.
TP-Link
In newer routers, you need to go to Advanced Settings – Wireless Mode – Configuration…. Here you can see two or even three networks (some models have support for two 5 GHz Wi-Fi). To disable wifi broadcasting, uncheck the "Enable wireless broadcasting" checkbox.
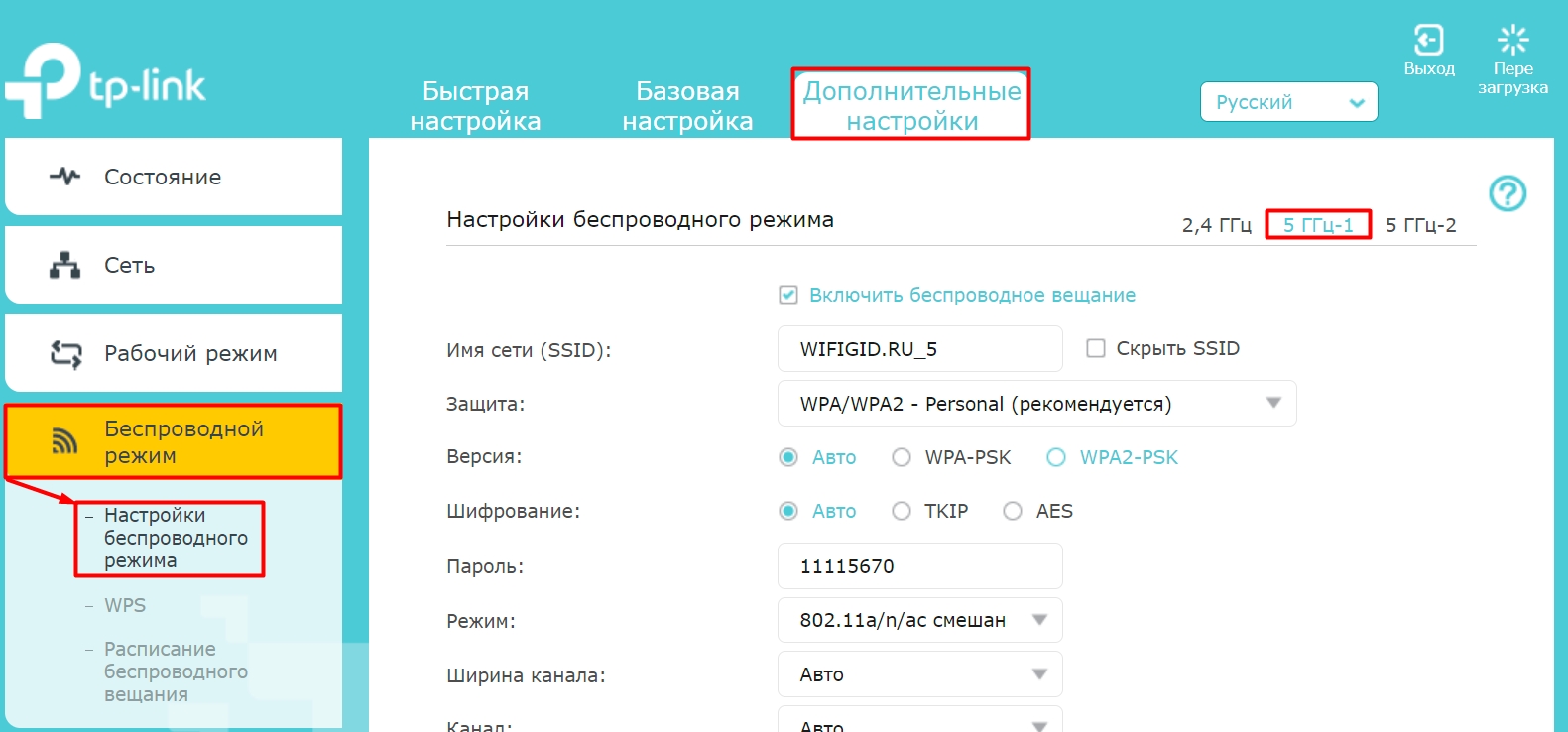
On some newer models, "Smart Connection" is enabled by default – when there is only one network on the air, and the router itself chooses which wave to connect devices to. That is, both frequencies are kind of paired. You can leave this configuration or turn it off to put the router in dual-band 2.4 and 5 GHz mode. Next, two wi-fi will begin to appear below, one of which you can turn off if necessary.
Part 4: Can I use both frequency settings on the same router?

Since both radio frequencies meet different network requirements, many people also want to know if 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies can be set simultaneously. Fortunately, the answer is yes! Today, you can buy a dual-band router that allows you to transmit both frequencies at the same time.
After setting up these routers, you will see two different SSIDs (with the same name) on your devices. The only difference between the two networks will be that they transmit the Internet on different frequencies. This means that you will be able to choose the right frequency according to your current network requirements.
For example, if you are sitting in the same room with a Wi-Fi router, you can choose the 5 GHz frequency and enjoy fast & uninterrupted internet speeds. However, if you are in another room of the building, you can easily switch to the 2.4 GHz radio frequency and surf the Internet at optimal speed.
Note: Some of today's Wi-Fi routers even have an auto-switching feature between 2.4GHz and 5GHz, making it easy for the user to get the best speed for their current environment.
Part 5: Are 2G and 5G Wi-Fi Harmful?

Now that you know the basic differences between 2G and 5G radio frequencies and their features, let's look at one of the most frequently asked questions about them, namely, are 2G and 5G Wi-Fi harmful. The answer is no; both of these radio frequencies are completely safe for humans.
Although many platforms on the Internet scare people with the term "harmful radiation" from Wi-Fi networks, using 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz radio frequencies has no ill effects. Both of these bands transmit frequencies at extremely low speeds and are not harmful to people at all. In fact, their frequency is much lower than visible light.
So, if you've been afraid to install Wi-Fi routers in your home because of their harmful effects, don't panic at all. At any rate, both of these radio frequencies are completely safe and will help you enjoy a high-speed Internet connection.
How do I connect?
The connection procedure on both your computer and phone is the same. The only question that remains open is support. Something that was purchased recently probably supports this 5 GHz frequency. Older devices may not work.
Look in the specifications of your device for the standard – if it says 802.11ac, you're fine. If it doesn't say 802.11ac, then nothing will work.
Your phone is usually hard to change, and you don't need to for the sake of speed. But a laptop or computer can also connect to home devices via waffle. Some modern laptops even allow you to change the built-in Wi-Fi module (they already come as modular cards), but the easiest way is to buy an external USB adapter:
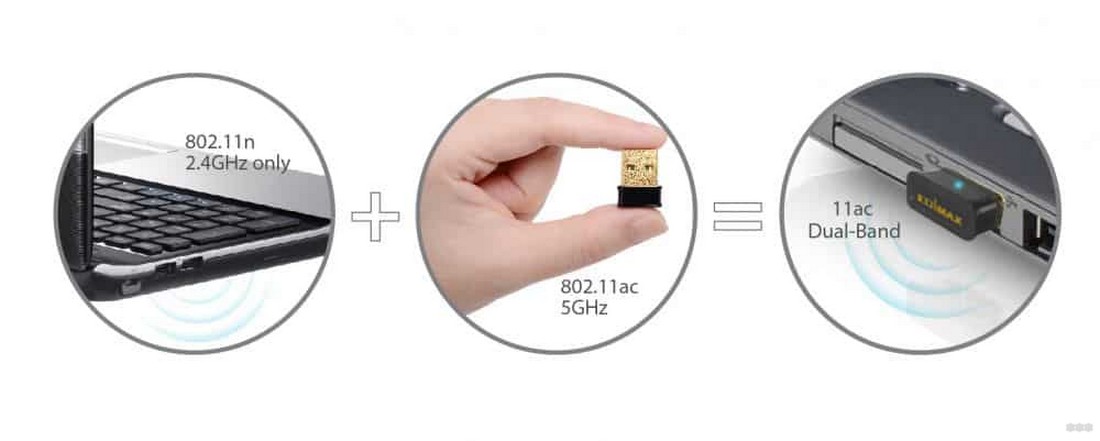
Put yourself such a whistle and work in peace. There are a lot of variants of these devices, and the price tag is also very affordable, from very affordable to incomprehensibly expensive. I should note that they also usually work in two bands of Wi-Fi frequencies – 2.4 and 5 GHz.

For a desktop computer, you can take not a USB adapter, but a full-fledged card into a PCI slot:

With TVs, however, things are much more complicated. Not all of them understand external USB adapters, so it will be easier to buy a set-top box. But is it really necessary to bother? Personally I didn't, the old one is enough for now.
How to switch it on?
Activation of the second Wi-Fi access point in 5 GHz occurs in the modem. I recommend to search settings for your model on our site via search (just enter into the search form on our site the exact name of your model and most likely you'll find an article with settings). If anything – write in comments, we'll look into it.
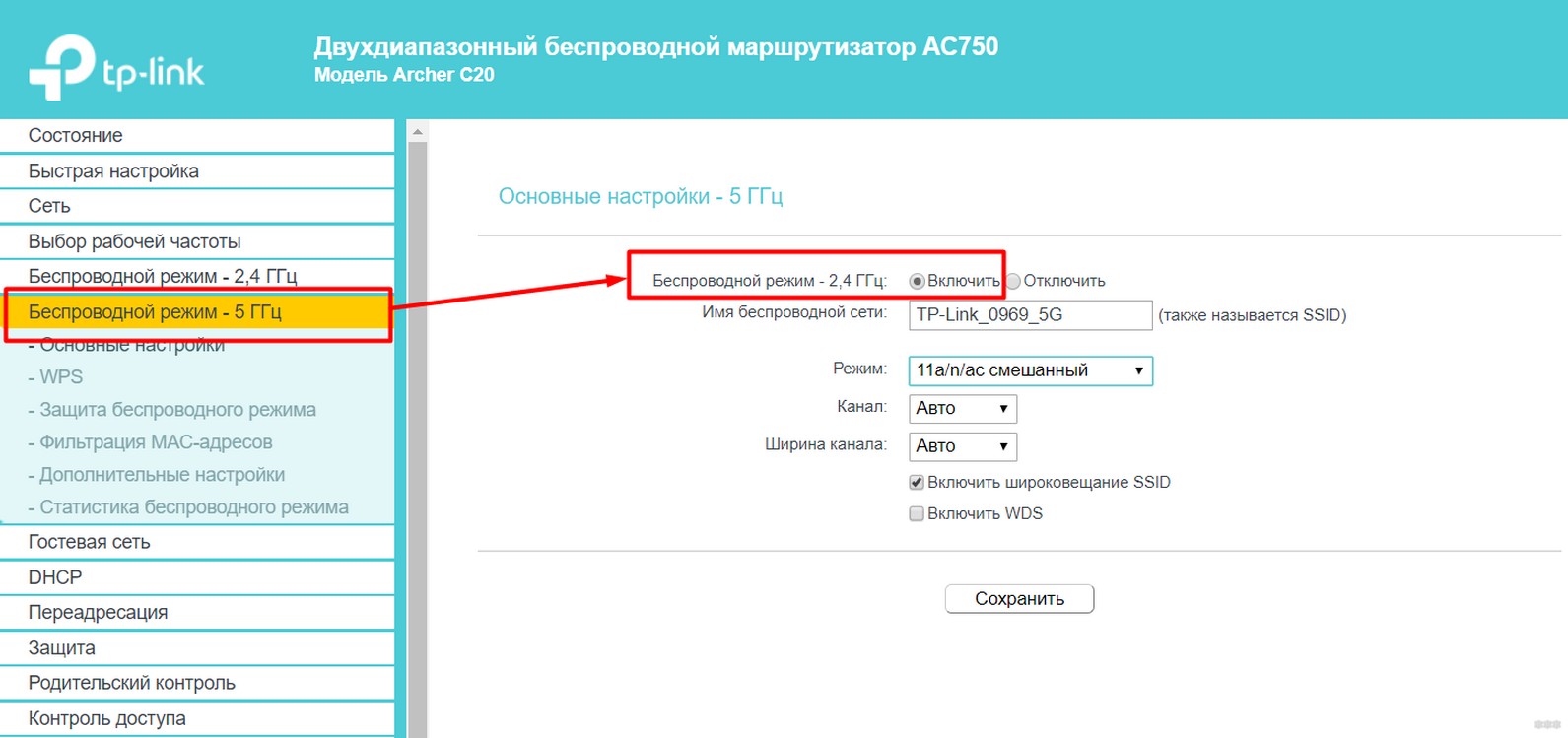
The picture above is an example for a TP-Link Archer C20. Those who are experienced will see that there is a duplication of tabs for different networks and for each band to enter its own settings. By the way, the networks will also be visible to two, if you activate both modes.
Some models in their settings support the simultaneous operation of only one network, and instead of enabling it you have to switch the range beforehand. This is done in about the same tab in the router settings – you must first go to the router configurator (look for your model on our website).