Wi-Fi frequency band 20 or 40 is chosen based on the number of connected devices and the specifics of communication. The user can either set the default frequency band or take advantage of his router and change it to a more optimal one in the current circumstances.
- Basic frequencies for Wi-Fi
- What is the Wi-Fi signal width
- What is the channel width in Wi-Fi router settings
- What frequency to set the "bandwidth" to
- Which mode to choose
- How to set or change the channel width on your router
- TP-Link
- Asus .
- How to configure?
- Instructions for different models to change
- To read in
- Connecting secure Wi-Fi without a password (WPS button)
- Read on.
- Connecting secure Wi-Fi without a password (WPS button)
Basic frequencies for Wi-Fi

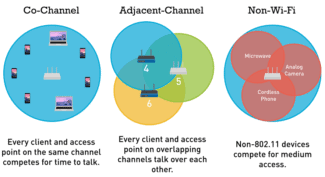
The specificity of wireless technology is that the connection goes through the provider indirectly – through channels operating on certain frequencies . The following topics are dealt with: what is the signal width, how to find out what frequency Wi-Fi works, whether you need to change it.

What is the Wi-Fi signal width
Each modem transmits digital streams of information from one to another point or points. The signal appears as an electrical pulse with 2 basic characteristics – Wi-Fi wavelength and frequency. Since wireless technology belongs to the category of radio waves, it works according to similar laws as light.
Wi-Fi frequencies are the number of periods of alternating current per second, otherwise the number of waves going to a particular location in space. The voltage frequency determines the total length of the radio wave.
Other bands are found – 0.9, 3.6, 10, 24 GHz. They are rarely used when the normal frequencies are busy and only if the user has a license for them. Each frequency has individual properties. And even a weak signal can travel great distances, but in such a situation a special antenna or Wi-Fi gun will be needed to amplify the pulse.
To communicate using wireless technology you need to have an access point (equipment) and at least 1-2 Wi-Fi clients. Sometimes there is a point-to-point connection, i.e. users communicate directly. At the same time, the standard provides a significant degree of freedom in choosing the adapter and radio channel settings.
What is the channel width in Wi-Fi router settings
Channel width in the settings of the router is its bandwidth, it may differ on different models. Standard for household networks and, in particular, a modem, supports 20 or 40 MHz. Wireless Wi-Fi uses a frequency range of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
In turn, channels or so-called frequency lines are identified in the range. Their presence makes it possible to place different electrical devices within one band, each of which will be able to work effectively and not affect the others. So, within 2.4 GHz there are 13 such channels allocated, but only three of them do not overlap; in 5 GHz their number is higher and the total width is an order of magnitude greater.
Visually, the channel width can be represented as arcs with a lower and upper bound of 22 MHz thickness, some of which may have common points of intersection. In a practical sense, this means that the wireless networks of other tenants in the house interfere with each other and can cause disruptions in Internet access.
That is why it is so important to choose a quality provider from the beginning and to be able to change the bandwidth. Then there will be no question, 20 or 40 MHz Wi-Fi, which is better.
Interesting! In upgraded modems that support 5 GHz, you can set not only the width of 20 and 40, but also 80 MHz.

What frequency to set the "bandwidth" to
At first glance, a 40 MHz Wi-Fi bandwidth is preferable to a 20 MHz bandwidth because the bandwidth determines the speed of your Internet connection. But not everything is unambiguous about their performance.
- At 20 MHz bandwidth there are three channels that do not overlap. Thanks to their free positioning independently of each other, no interference enters the common range. In this case you can easily connect up to three different devices without worrying that they will interact negatively.
- The 40 MHz band allows only one non-overlapping channel to be placed. Therefore, if you connect multiple devices to Wi-Fi, each will create an obstacle and limit the overall access speed. Wireless devices are particularly susceptible to interference.
- If you use outdated hardware, pure modes (40 MHz and above) are not suitable for continuous operation according to technical standards, because they can provoke incompatibility.
Which mode to choose
The so-called non-intersecting channels, which have certain numbers, will work best. You can determine them yourself by looking at the broadcast diagram of, for example, the 2.4 GHz band:
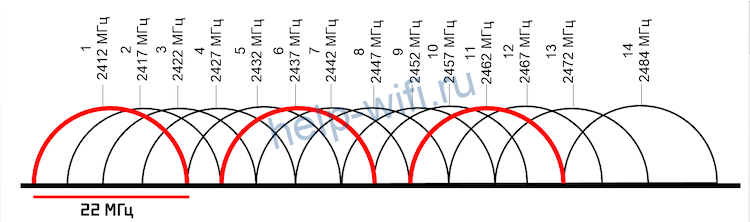
Initially, routers with this frequency mode can broadcast on all 14 channels, but some of them are reserved for social and government needs. For example, 11 channels are officially used in the USA. Formally, the laws of the U.S. do not prohibit citizens to use the 12th and 13th segments of the 2.4 GHz band in low-power mode. All channels except 14 are available in Russia and Ukraine. Devices purchased in different countries can see only those frequency band segments, the use of which is approved by the relevant legislation.
Based on the number of 13 channels available to Russians and Ukrainians, channels 1, 6 and 11 will work best. The width of the network segment also determines the wireless standard, which is also useful to consider when choosing this parameter.
For example, the minimum conditional channel width of 802.11g and 802.11n specifications is 20 MHz, while its actual value has decreased to 16.25 MHz. This is due to modern modulation technology. The channel spectrum of the 2.4 GHz band with a bandwidth of 16.25 MHz has no longer 3, but 4 minimally overlapping segments with the numbers 1, 5, 9 and 13.
Broadcasting at 5 GHz provides a much larger number of channels with an identical initial bandwidth. This more advanced wireless technology allows you to choose from 23 non-overlapping segments available depending on the region of use. These channels are usually highlighted in bold in the router's settings.
How to set or change the channel width on your router
Any router can broadcast in 2.4 GHz mode. The most modern devices also support 5 GHz operating mode. Few of the wireless standards work only in this band, but they are also backwards compatible with 2.4GHz gadgets. Before specifying bandwidth, you should pay attention to the Wi-fi specification in the settings. The wrong communication standard may make the configuration of the desired bandwidth unavailable.
The location of the channel width, channel number, and wireless standard settings in the router configuration depends on the firmware version.
Older equipment may not be able to access the Internet after configuration if the Wi-fi channel width is 40 MHz or more. If the router is not working in a suitable mode, the devices are able to recognize the network without actually accessing it. Such a connection is only suitable for exchanging system data between the router and the device.
To change the bandwidth value, you must first open the router settings. To do this, connect it to the system unit, turn it on, and enter the IP address of the device in the address bar. It is usually listed along with the default username and password on the bottom or back of the case.
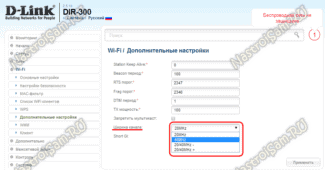
The bandwidth settings are determined by the router model, version and localization of the firmware. The Channel Width or Bandwidth settings may also be named Channel Width and Bandwidth.
TP-Link
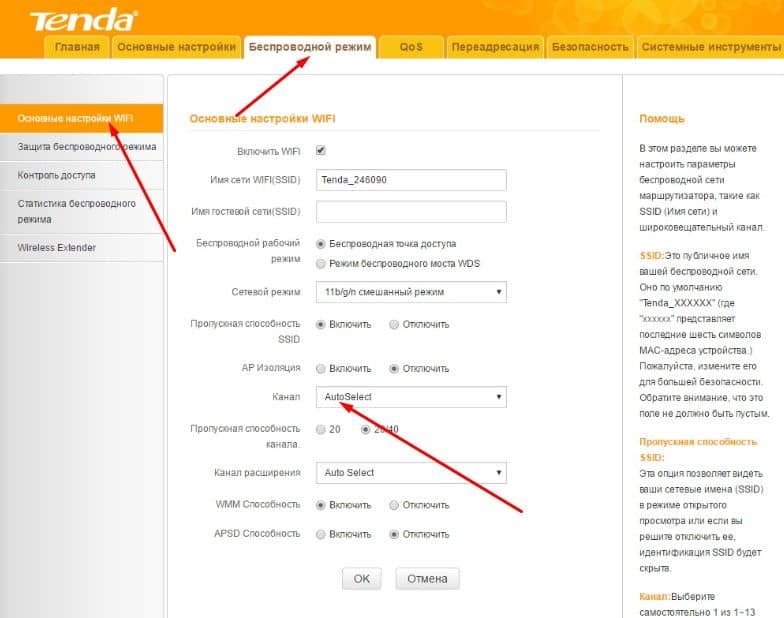
To set the wifi channel width in the TP-Link interface, one has to go to the "Wireless Mode" tab in the left-hand menu and choose "Wireless Mode Settings".

Asus .
Configuration of the frequency band for devices of this company can be found in the item "Wireless network" of the list "Advanced settings".
How to configure?
Well and the main question: how to increase the width of the WiFi channel – the setting is made, using the web interface or with the help of special programs, if the user is more convenient to work with them. Below we will give general instructions, but if you encounter any problems, there is an article on our website about how to change the channel on a Wi-Fi router. So, in order to open the web interface, you will need:
- Type in the browser in the address bar 192.168.1.1 (192.168.0.1 is used somewhat less frequently) and enter the username (admin), for the password is also preset (either 1234 or admin). The authorization data may be different if the user has changed the preset settings.
If the signal with the new settings became worse or the difference is not felt – you can make the changes again.
Instructions for different models to change
With the help of special programs, we have figured out which WiFi channel is better to use to protect against interference and improve the speed of the connection. If the user has not previously changed the settings, the default setting is automatic detection of the desired subfrequency. Each time you reboot or make a new connection, the router determines a new channel based on the current load.
Knowing how to select the correct channel for WiFi, you can manually determine the required parameter and set it in the settings. The general algorithm of actions has the following steps:
- Go to the router settings to make changes. You can find the necessary login information on the bottom of the router or on its box.
- In the settings section, enter the WiFi settings. If the router operates with two frequencies at 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz, you may need separate settings.
- In the settings, look for the number you want and select it.
- Save your changes and restart your router.
Most devices use the IP address 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 to enter the configuration mode. As for the authorization data, it is sufficient to enter the word admin in the login and password section. In some situations, the second field is left blank. You can also choose the width of the WiFi channel on the router and make other changes in the settings.
Approaches to channel configuration are individual for each router. Let's highlight recommendations for several models:
- TP-Link (old interface). To make adjustments, enter Wireless mode, and there in the Main settings. Find the Channel link and set the desired value. Then click the Save button and restart the router.
For the new interface, enter Wireless mode, and then click on Wireless settings. In the main field, there should be a Channel WiFi item with the option to set a new value. As in the last case, save the data and reboot.
To read in
Wi-Fi is a wireless LAN technology with devices based on IEEE 802.11. The Wi-Fi logo is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance. Under the acronym for Wi-Fi (from the English word combination Wireless Fidelity, which can be literally translated as "wireless fidelity") is now a whole family of standards for transmitting digital data streams over the radio Main generations of WiFi standards Name Year of creation Transmission Rate Generation 802.11a 1999 to 54 Mbps 802.11b 1999 to 11 Mbps 802.11g 2003 to 54 Mbps 802.11n 2009 to 150 Mbps per stream or 600 Mbps per 4 antenna Wi-Fi.
(Read entire. )
Windows 7 writes, "The WiFi network settings stored on this computer do not meet the requirements of this network." The main thing is that it is absolutely unclear what it is and why. The main reason is that the router settings have changed from the previous connection. Namely: change password, change encryption type AES or TKIP, change band selection a/b/g/n/ac How to correct error "WiFi network parameters saved on this computer do not meet the requirements of this network"? go to the list of saved wireless networks, delete the specified network, reconnect to this network IMPORTANT. In some budget laptops the 802.11n option.
(Read more. )
Connecting secure Wi-Fi without a password (WPS button)
WPS is an acronym for Wi-Fi Protected Setup. A special technology for simplifying connection of devices to the router via Wi-Fi. This technology also has a second name from the company TP-link -> QSS (Quick Security Setup). Yes: the connection is secured, you do not need to enter a password, the devices "agree" with each other a password of 8 digits (the one on the bottom roof of the router) WPS authorization options: – PBC mode (Push Button Configuration) – Authorization with PIN code (allows you to configure individual router settings) Now more details. Often this button is combined with a reset button for the router (usually 5.
(Read more. )
Which WiFi channel width should I choose? The picture from the router settings is usually this. Which is better – 20 MHz channel width or 40 MHz channel width? And why should the user make this choice? Of course 40 MHz is better, because with this bandwidth both 802.11n and 802.11ac will work at their maximum speed. But that's the theory. In practice it works if you (or rather your router) are the only one on the air. Let's see what really happens on the air at 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. This is 2.4 GHz This is 5 GHz Yes, both 802.11n and 802.11ac can operate on two frequencies. It's just that routers have been released on both frequencies mainly since the introduction of 802.11ac. You can see that the 2.4 GHz frequencies are wanting.
(Read entire. )
Read on.
Wi-Fi is a wireless LAN technology with devices based on IEEE 802.11. The Wi-Fi logo is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance. Under the acronym for Wi-Fi (from the English word combination Wireless Fidelity, which can be literally translated as "wireless affection") is now a whole family of standards for transmitting digital data streams over radio channels The main generations of Wi-Fi standards Name Year of creation Transmission Rate Generation 802.11a 1999 to 54 Mbps 802.11b 1999 to 11 Mbps 802.11g 2003 to 54 Mbps 802.11n 2009 to 150 Mbps per stream or 600 Mbps per 4 antenna Wi-Fi.
(Read full. )
Windows 7 writes the following: "The WiFi settings stored on this computer do not meet the requirements of this network. The main thing is that it is absolutely unclear what this is and why. The main reason is that the router settings have changed compared to the previous connection. Namely: change the password, change the encryption type AES or TKIP, change the range selection a/b/g/n/ac How to fix the error "WiFi network settings stored on the computer do not match the requirements of the network"? go to the list of saved wireless networks, delete the specified network, reconnect to that network IMPORTANT. In some budget laptops the 802.11n option.
(Read more. )
Connecting secure Wi-Fi without a password (WPS button)
WPS is an acronym for Wi-Fi Protected Setup. A special technology for simplifying connection of devices to the router via Wi-Fi. This technology also has a second name from the company TP-link -> QSS (Quick Security Setup). Yes: the connection is secured, you do not need to enter a password, the devices "agree" with each other a password of 8 digits (the one on the bottom roof of the router) WPS authorization options: – PBC mode (Push Button Configuration) – Authorization with PIN code (allows you to configure individual router settings) Now more details. Often this button is combined with a reset button for the router (usually 5.
(Read more. )
What affects the actual WiFi connection speed? The easiest mystery is the 54 Mbps connection speed. There are two main possibilities here: either the device has the 802.11n band cut (blocked) or it uses the TKIP encryption protocol Let's look at the more complicated options. Router mode is 802.11n, AES encryption. Should it be like 300 Mbps with two antennas (150 Mbps per stream)? No? Options for real smartphone connections: 65 Mbps or 72 Mbps What to do and what to check? In fact, this is how it should be. The first and most important reason is interference in the communication channel, a lot of those who want to use in a residential building.
(Read completely. )