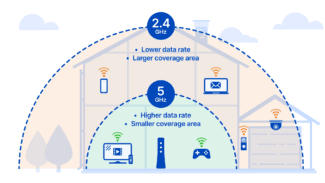
Don't get too hung up on the number of antennas sticking out of the Wi-Fi box.

Explaining high dBi and Wi-Fi gain antennas – what that means
This post is in addition to my other article on dBm. I'll explain another specification related to Wi-Fi coverage here – dBi – the high values of which are usually indicated on, so called, Wi-Fi antennas with high gain.
As it turns out, dBi by itself usually doesn't mean much for Wi-Fi. It's something you shouldn't pay much attention to, or ignore altogether.
That's why most equipment vendors don't list this value on home devices, and those that do are doing it purely for marketing purposes..
Bottom line: don't use dBi as a factor when choosing a home router or access point.
You can save that knowledge and move on or continue – this post can be a fun read on a quiet day.

What is dBi
To understand dBi, we first need to understand dB or decibels. Again, I detailed this in a post about dBm and Wi-Fi signal strength, but here's the gist:
- dB is a logarithmic measurement. It increases and decreases exponentially, not sequentially.
- In addition to sound level, dB is a logarithmic way of conveying other material properties.
- dBm (decimal milliwatt) is an example where dB is used to measure the power level or sensitivity of a signal.
In this case, dBi is isotropic decibels.. This is a logarithmic way of conveying the physical properties of an object measured in different directions. Specifically, 0 dBi means that the object radiates radio waves equally in all directions. It is similar to a sphere with a radiator right in the center.
Since we cannot see radio waves, you can think of 0 dBi as light emitted from a single source, such as the sun or a light bulb. It comes out equally in all directions or omnidirectionally.
Theoretically, the moment you increase the dBi above zero, the signal sphere begins to change its shape-it is no longer a perfect sphere. In fact, it depends on the circumstances.
That's because in our case, the object is the Wi-Fi antenna, and the property is the radio signals it emits. And it's all very complicated.
What is dBi.
To begin with, it's worth saying what a decibel is. This quantity is often used in telecommunications, acoustics, radio engineering, and in the theory of automatic control systems. It is a relative value that is calculated according to a formula, so that decibels can have different values in different scientific fields. In general, they indicate how many times stronger or weaker a signal is than another.
dBi (Russian dBi) – isotropic decibel (decibel relative to an isotropic radiator). It indicates the signal power gain relative to an ideal isotropic antenna. An isotropic antenna radiates perfectly over the entire range of the signal. That is, it has a perfectly circular sphere of signal propagation, where the signal goes in all directions with equal strength.
A reference antenna, the so-called isotropic radiator, is an ideal antenna whose radiation pattern represents a sphere whose gain is unity and whose efficiency is 100%. It is a virtual object whose parameters are worth aspiring to in order to achieve the greatest efficiency.
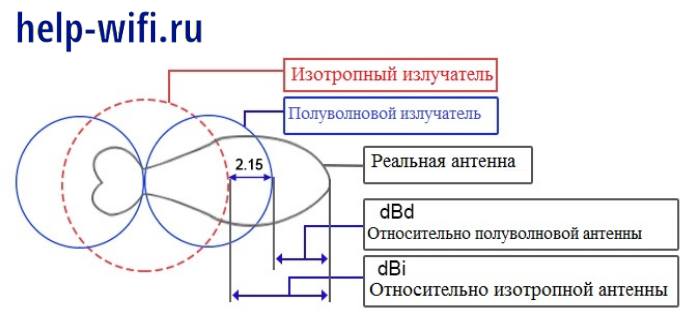
In real life, there are no such antennas. Each device has a certain antenna directivity, so that the signal is more active in one direction and weaker in the other directions than an isotropic antenna. Here in the characteristics and specifies this gain relative to the ideal antenna in the format dBi.
The formula is
There is a formula for calculating the dBi value itself, but for the user of any device such as a Wi-Fi router, 3G or 4G modems or other transmitting devices, it does not make sense by itself. Everything has already been calculated for you, and the specifications show dBi gain or dBi or something like that. But you can use the formula to calculate how much the antenna will amplify the original signal.
The formula looks like this: G(dBi) = 10log(G), where:
The difference between dBi and dBm
Also when selecting a router or other device you may see the dBm parameter. It is a different parameter and refers to the transmitter and not the antenna or the amplifier. It is also not as simple as it seems to a person unfamiliar with the topic.
dBm (dBm) – created for the convenience of designating characteristics. It was decided to take this parameter as a reference (zero level) and relative to it to measure the level in decibels. So, if we take as a zero level – 1mW and relative to it measured, then there is such a unit of measurement as dBm (1mW = 0 dBm).
| dBm | mW | dBm | mW |
| -18,0 | 0,0158 | 7 | 5,01 |
| -17,0 | 0,0200 | 8 | 6,31 |
| -16,0 | 0,0251 | 9 | 7,94 |
| -15,0 | 0,0316 | 10 | 10,0 |
| -14,0 | 0,0398 | 11 | 12,6 |
| -13,0 | 0,0501 | 12 | 15,8 |
| -12,0 | 0,0631 | 13 | 20,0 |
| -11,0 | 0,0794 | 14 | 25,1 |
| -10,0 | 0,100 | 15 | 31,6 |
| -9,0 | 0,126 | 16 | 38,8 |
| -8,0 | 0,158 | 17 | 50,1 |
| -7,0 | 0,200 | 18 | 63,1 |
| -6,0 | 0,251 | 19 | 79,4 |
| -5,0 | 0,316 | 20 | 100 |
| -4,0 | 0,398 | 21 | 126 |
| -3,0 | 0,501 | 22 | 158 |
| -2,0 | 0,631 | 23 | 200 |
| -1,0 | 0,794 | 24 | 251 |
| 0 | 1,00 | 25 | 316 |
| 1 | 1,26 | 26 | 398 |
| 2 | 1,58 | 27 | 501 |
| 3 | 2,00 | 28 | 631 |
| 4 | 2,51 | 29 | 794 |
| 5 | 3,16 | 30 | 1000 |
| 6 | 3,98 | 31 | 1300 |