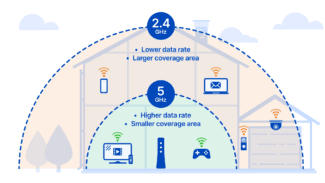
Deploying your home network in the 5 GHz band gives you more channels (available band sections) to isolate yourself from networks other than WiFi operating in the 2.4 GHz band.

Pros and cons of 5 GHz WiFi – Is it worth upgrading your router
5 GHz 802.11ac WiFi has many advantages over traditional 2.4 GHz WiFi. Here are the pros and cons of 802.11ac 5 GHz WiFi.
Back in 1999, we had the beginnings of a wireless future as Wi-Fi. The first was called 802.11a and operated in the 5 GHz band (later the 3.7 GHz band was supported). Previously, 5 GHz devices were more expensive than 2.4 GHz, and the 802.11b standard quickly surpassed the popularity of 802.11a. For years we enjoyed web surfing, listening to music and watching videos on the 2.4 GHz band.
Another technology that is beginning to compete for wireless connectivity with Wifi is Bluetooth. It promises to bring the Personal Area Network to mobile devices and into our lives. At first we were limited to wireless headsets, but then wireless keyboards and mice became popular. You can transfer files, schedule meetings, and more.
Other devices began to focus on the 2.4 GHz band, and the number of devices connected to Wi-Fi began to increase dramatically.
Nowadays, the average family will have many devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers connected to Wifi routers. They even have several streaming devices (Chromecast and Roku) connected to the router. Thanks to the Internet, the number of wireless devices is increasing.
802.11ac 5 GHz WiFi.
You can see dozens of wireless networks in your apartment (yours + your neighbor's). And if you have the same number of wireless devices connected to each of these Wi-Fi networks, you can imagine the level of congestion in the 2.4 GHz band.
The more devices in the band, the slower and less reliable the signal. So what's the solution? Increase the capacity? A bigger antenna? No, that doesn't help much. We need another band – WiFi 802.11ac at 5 GHz.

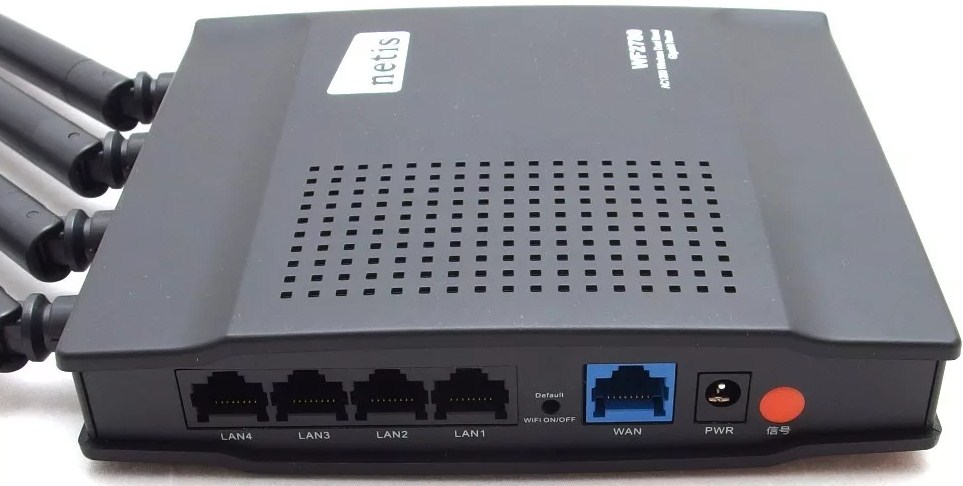
NETIS WF2710.
The cheapest device, costs about 1400 rubles on the market. It has support for all known standards, but after reading the comments I was convinced that it works extremely poorly. And the whole thing in a weak iron. These "cheap" transmitters usually have very weak hardware, which simply can not withstand normal operation. Oh yeah – it has all the ports at 100 – so you should not take it. I gave you an example of a bad transmitter so you don't have to buy one of these.

NETIS WF2780.
This is the model you can already buy. It's cheap, only 2,500 bucks. It has 4 antennas, which in itself increases the range of coverage, in conjunction with a high gain. Transmitter power 20 dBM. Local network speed ranges from 300 to 867 Mbps. There is nothing supernatural except for the price, but for a budget version it is the best. From the disadvantages it can be noted – the lack of USB port, but it is not always needed. From the picture you can see that all ports are Gigabit.

Standard channels

Standard channels in Russia
The standard 802.11as allows the use of channels of 20-160 MHz with a continuous dimension of 20, 40 and 80 MHz. To get the maximum channel width of 160 MHz two 80 MHz channels are added together.
The speed changes according to the channel width. When using the standard 802.11 n/as in Russia, the frequency ranges of 5150-5350 and 5650-5850 MHz (channels 36-64, 132-165) are available. In other words, 17/8/4/2 channels of 20/40/80/160 MHz are allowed.
5 GHz and 2.4 GHz WiFi bandwidth – what is the difference in practice?
In practice, the difference between the 5 GHz band and the 2.4 GHz band is the ability to connect a larger number of devices without losing signal quality. It also has a higher maximum speed and bandwidth.
Equipment that supports the 5 GHz standard is more expensive, but not by much. In addition to the high speed to the pluses of wifi 5 GHz can be attributed to the fact that at the moment it almost nobody uses, and therefore there is no interference. While the frequency range of 2.4 GHz is heavily littered, because it operates not only routers and network devices, but also all the devices of the smart home. Just look at the number of simultaneously working networks in the access area from my apartment.
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
What else is bad for Wi-Fi connectivity
Regardless of the device used, the following factors negatively affect wireless data transmission:
- Microwaves. We are talking about kitchen appliances. For example, a microwave works on a frequency of 2.45 GHz, like a number of routers. This circumstance will interfere with the router, will lead to instability of Internet distribution, will lower the speed of its functioning. Therefore, it is not necessary to place router in the kitchen next to the microwave.
- Working Bluetooth. Near the Wi-Fi transmitter, it is not recommended to use Bluetooth devices, turn on this technology. Bluetooth works on the same band as the router, which will cause these devices to conflict. Interference is formed, preventing the spread and normal functioning of the wireless connection.
- Garland. New Year's Eve garlands have a negative effect on wi-fi performance. Flashing devices emit an electromagnetic field that drowns out the transmitter signal. Therefore, such items should not be placed in close proximity to the router.
- Router firmware. If after purchasing the transmitter the Internet began to work poorly, then it is recommended to flash the device, i.e. to update its firmware. This can be done by downloading a special file from the Internet.
- Synchronizing the router with your computer. If the router is connected to a PC, it will provide it with the Internet, as well as distribute the network to other devices. In this case, the speed of data transfer to gadgets will be lower.
Pay attention! Stabilize the work of Wi-Fi helps to update the driver for the laptop network adapter.

How to update the driver for the laptop Wi-Fi module
Often the laptop does not catch 5G Wi-Fi because of an outdated network driver. To update it you need to:
- connect the laptop to the Internet;
- Open the "Start" menu and enter the phrase "Device Manager" in the search box;
- Expand the line "Network adapters" as described above;
- Click on the name of the module installed in the PC and click on the "Update" line;
- Select the option to search for a suitable driver on the Internet and left-click on it;
- Wait for the update procedure to complete and check the results.
After the driver update, you will need to reboot the operating system for the changes to take effect.

Thus, the 802.11ac standard operating at a frequency of 5 GHz is not supported by all devices and gadgets. This fact should be considered when buying a Wi-Fi router. If one wants a laptop to support the 5 GHz band, one can buy an external adapter. The above information allows you to understand why the computer does not see the 5 GHz Wi-Fi network.
Read More: