Notes
1. After changing the required parameters, press the "Apply" button, then the device will reboot.
2. During the application of the parameters, the device will be temporarily (1. 5 sec.) unavailable for connection.

Seb access point what it means
Greetings to our readers! The topic today is general education, more for those who are new to the Wi-Fi world. I'll explain what Access Point Mode, in Russian, means. And at the same time we will learn how to enable it on the router. Let's go!
Before we talk about Access Point Mode we have to remember what it is. An Access Point (AP) is a wireless station designed to connect "over the air" to an existing network or to create a new one.
APs are most often used to provide local network access to mobile devices – tablets, smartphones, laptops, etc. A set of communication standards for wireless LAN communication – IEEE 802.11 – is used to transmit information.
All routers can operate in Access Point mode. In addition, there are devices on the network equipment market that work exclusively as access points. This comes in handy if, for example, you have a large house and your router does not cover the necessary area with a signal. Then the access point will play the role of a repeater and expand the Wi-Fi zone.
So, an AP is just an access point. And a router is a multifunctional device that not only receives and transmits data, but also redistributes it according to the rules, and also performs a number of tasks.
I wrote about the differences between an access point and a router in detail here.
Features
What is an Access Point (AP) Mode? We will talk about features in the context of a comparison with the router mode.

- Let's take a look at the following situation. At home there is a wired network, cable to the router connected computers, printer, TV set-top box – all LAN ports are busy. And we need to connect another smartphone and laptop, and they stand in another room where the existing network signal is bad. We switch on the additional router to the access point mode, connect both devices, and the problem is solved – without unnecessary wires, all home devices are connected to the same network and get Internet access.
- In order to connect to the Internet, you may need to configure the connection settings. For Access Point Mode, you will have to make them on each device. In Router Mode, you set up once – you create a wireless network and then you can connect to it.
- A router, unlike an access point, has network protection against attacks and the ability to limit traffic. Of course, you have to make the appropriate settings, but it's worth it – you get protection against network attacks, you can determine the speed for certain devices and enable traffic prioritization.
- Router mode has more options, but that means it's more complicated to set up. You can name your wireless network and make up a password for it. You can do port forwarding, enable parental control, many devices have the ability to create a guest network, and more.
- The access point as an independent device doesn't distribute IP, doesn't connect to the ISP – it just gets the Internet from the router and distributes it further "over the air". However, some can do it all, but there are nuances, and the cost of such access points will be comparable with the price of routers. Therefore, in this situation, it is still better to buy a full-fledged router.
In this section I would also like to briefly describe the modes in which the router can operate:
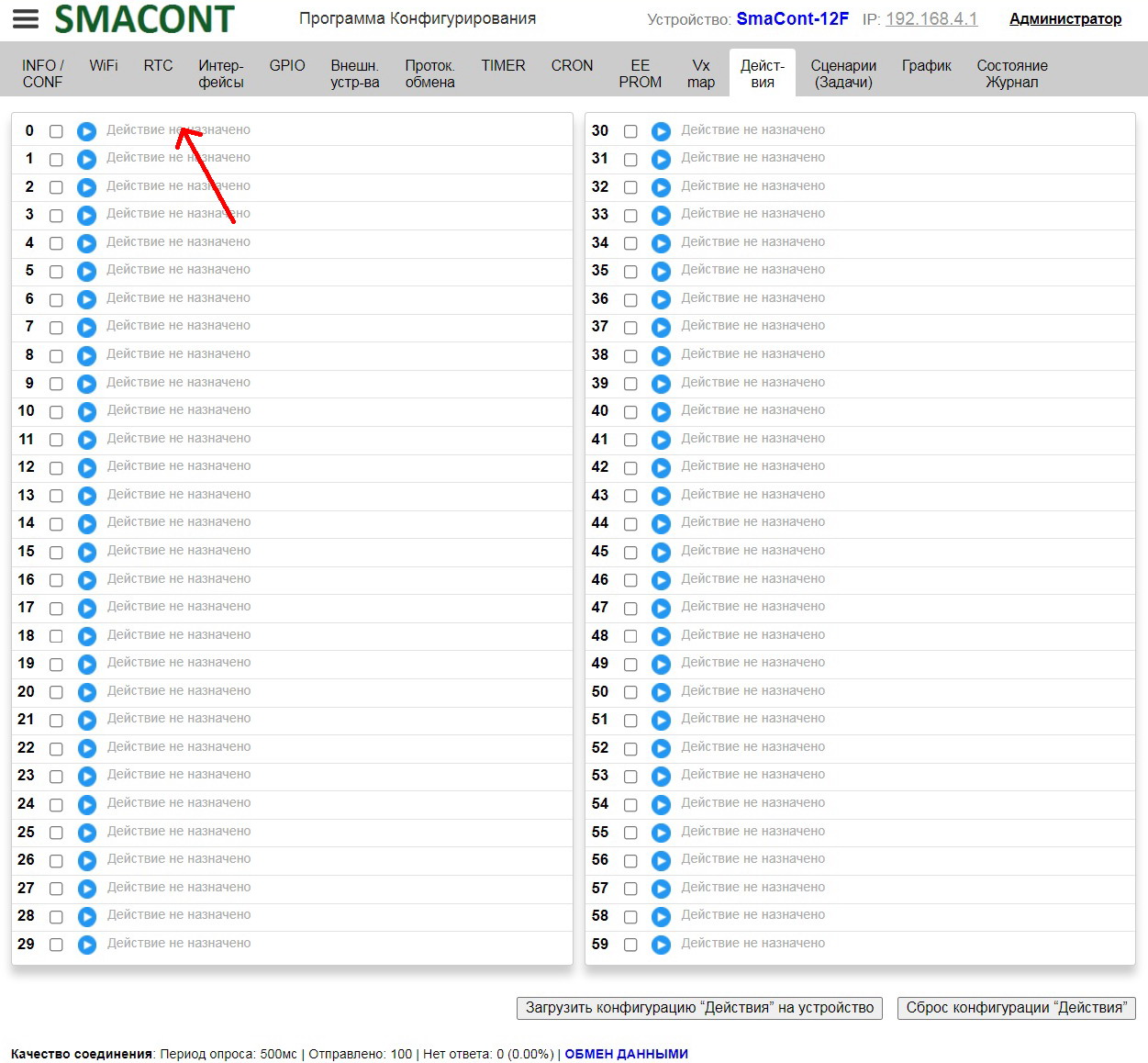
Changing the WiFi mode
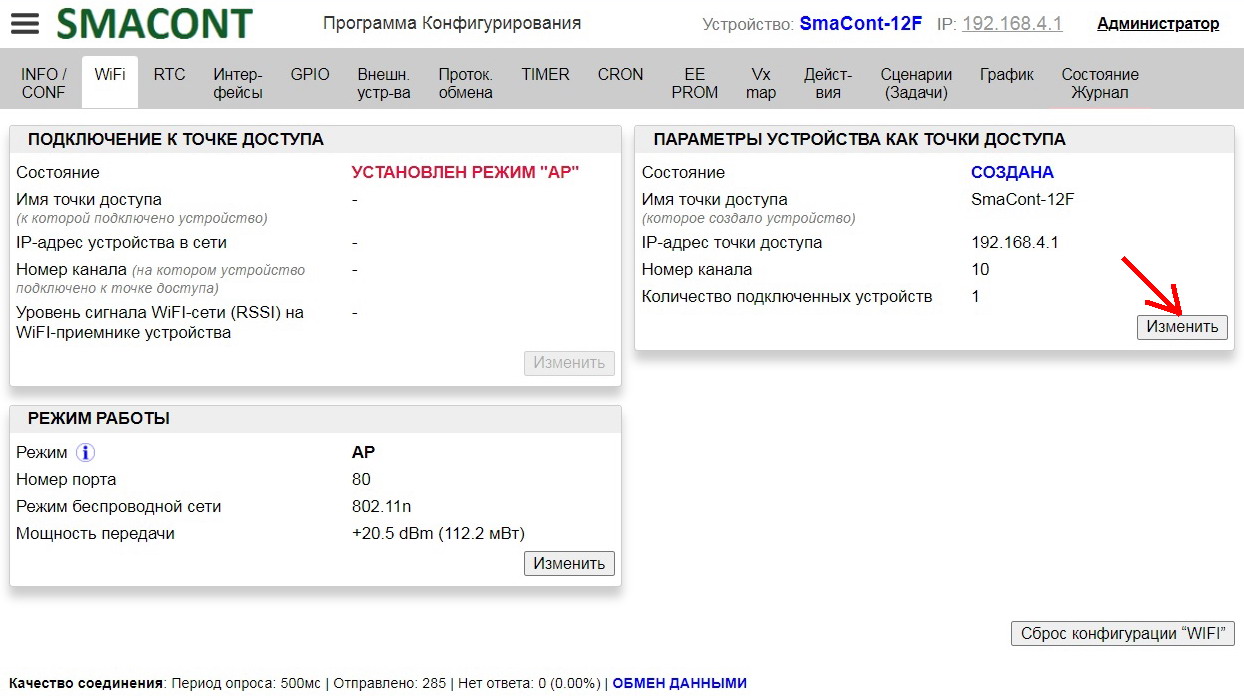
Changing the WiFi operation mode is done using the "Configuration software" in the "WiFi" tab.
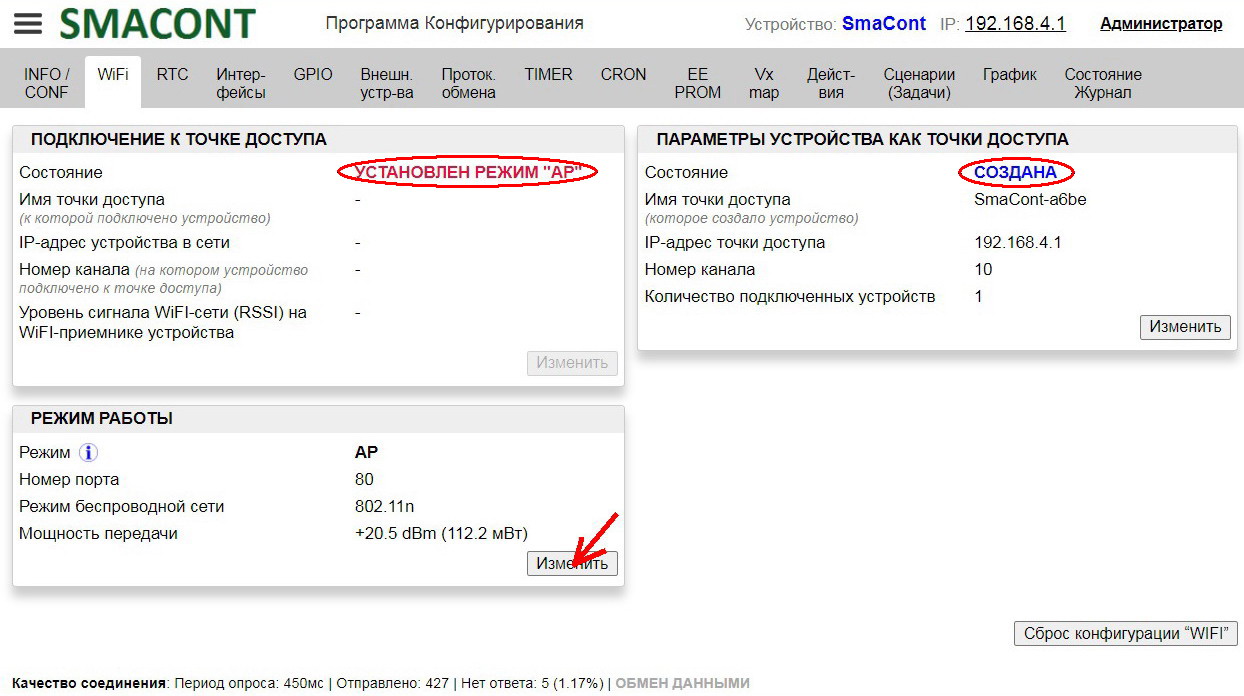
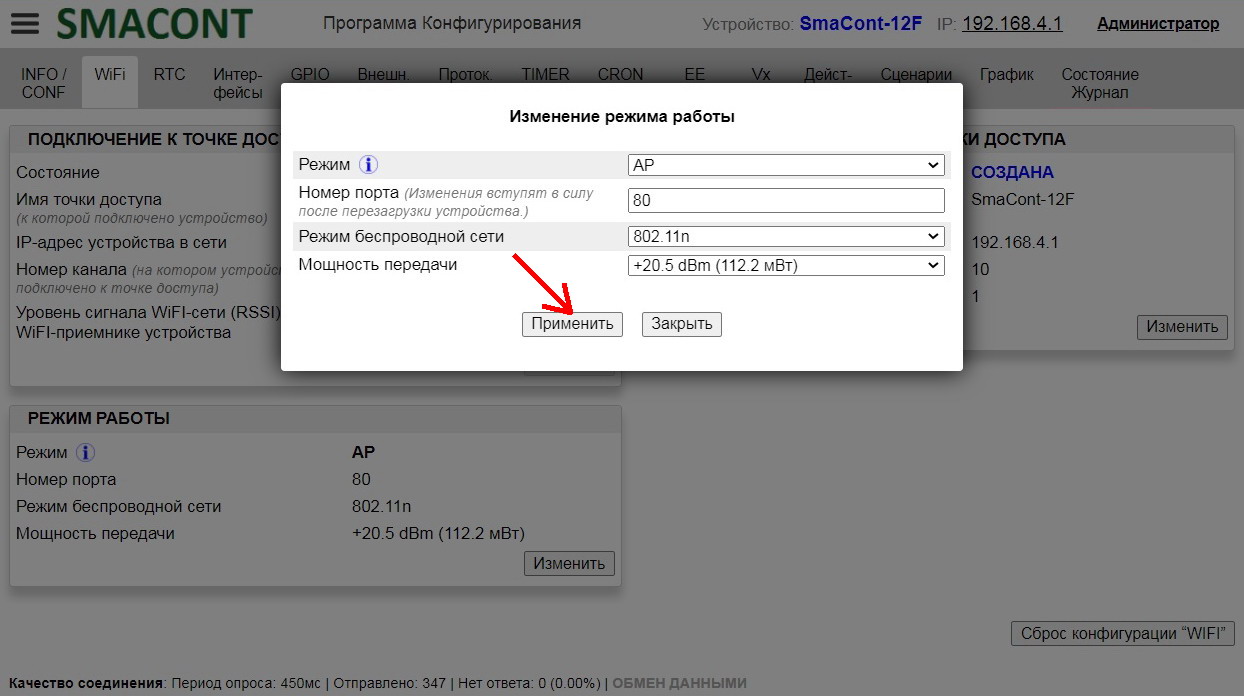
Clicking on the "Change" button in the "OPERATION MODE" field will open the "Change Operation Mode" window.
In this window you can set the following parameters:
• "Mode". – WiFi network operation mode ("AP", "STA", "AP+STA");
• "Port number". – port number is specified after the IP-address of the device, for example: 192.168.1.250:8080.
If the value of "Port number" is "80", the port number can be omitted, for example: 192.168.1.250.;
• "Wireless Network Mode". –
802.11b – Tx Power: +20 dBm; Rx Sensitivity: -91 dbm (11 Mbps);
802.11g – Tx Power: +17 dBm; Rx Sensitivity: -75 dbm (54 Mbps);
802.11n – Tx Power: +14 dBm; Rx Sensitivity: -72 dbm (MCS7);
• "Transmission Power" – determines the "visibility" range of the device.
Range: max +20.5dBm; min 0dBm.
After changing the required parameters, it is necessary to press the "Apply" button, after which the device will reboot. During the application of the parameters, the device will be temporarily (1. 5 sec.) unavailable for connection.
Changing the WiFi mode is also available in scenarios.
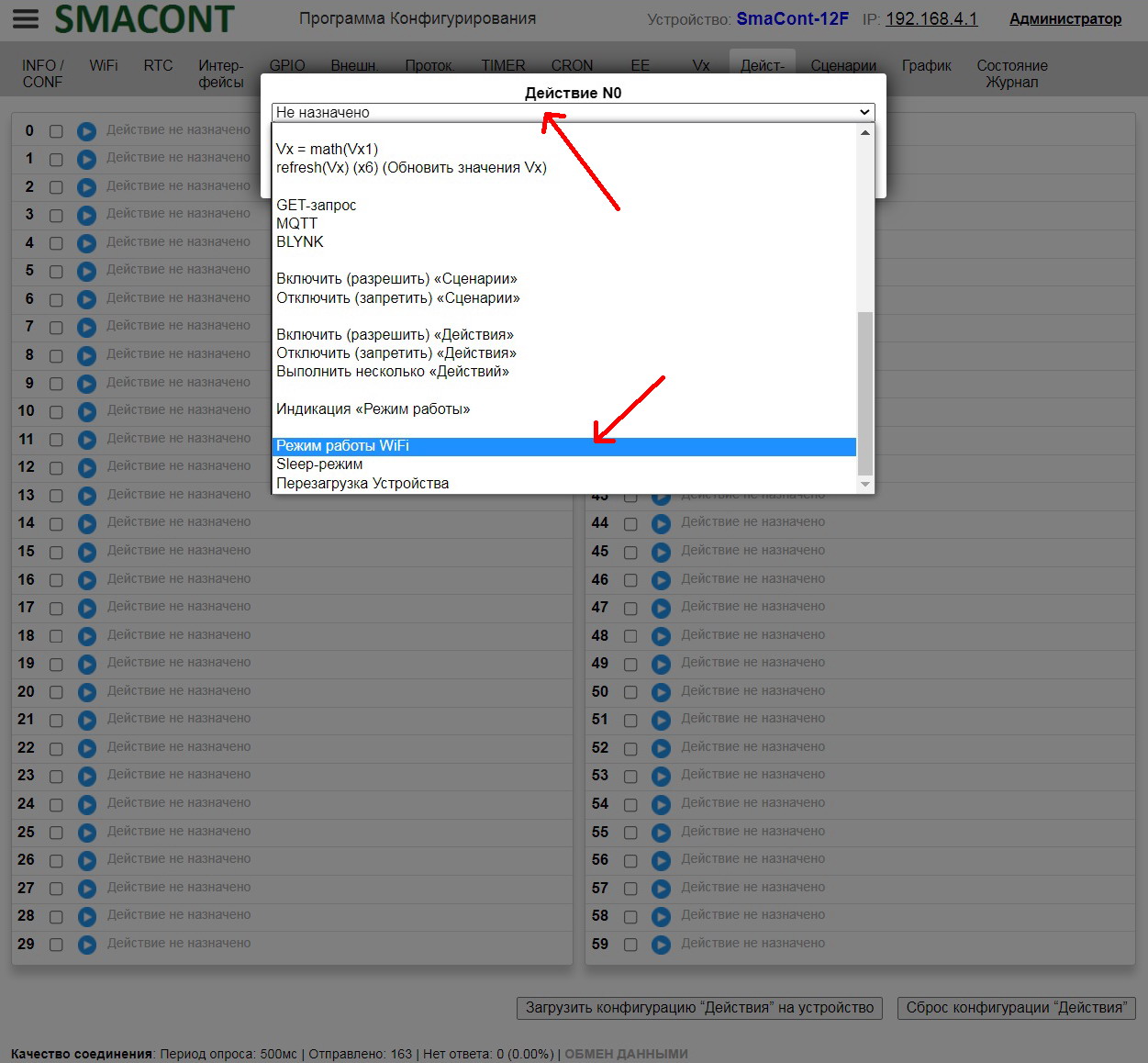
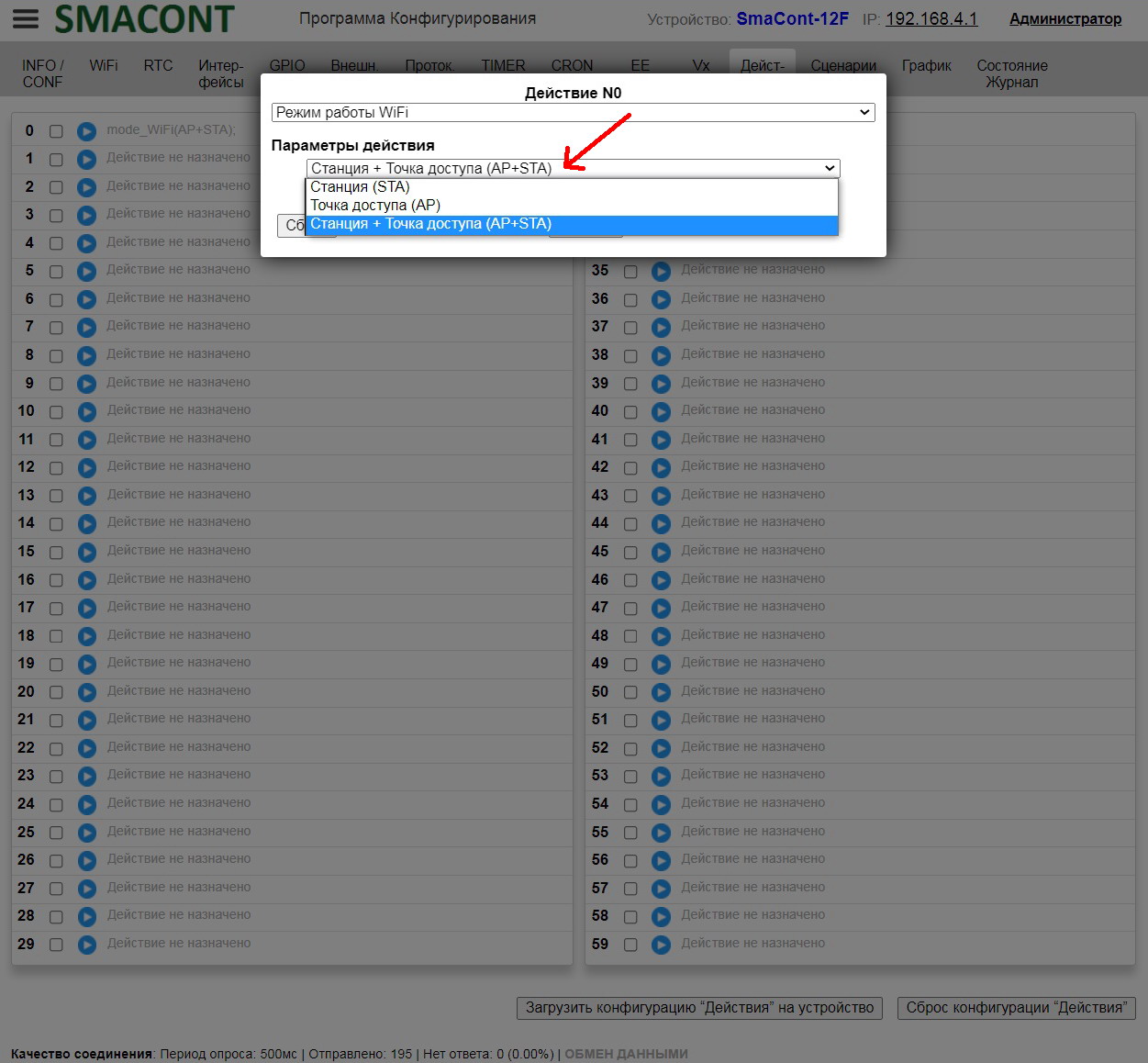
Changing the WiFi Mode in Scenarios
AP (Access Point) mode
A diagram of connecting to a device in AP (Access Point) mode is shown in the figure below.
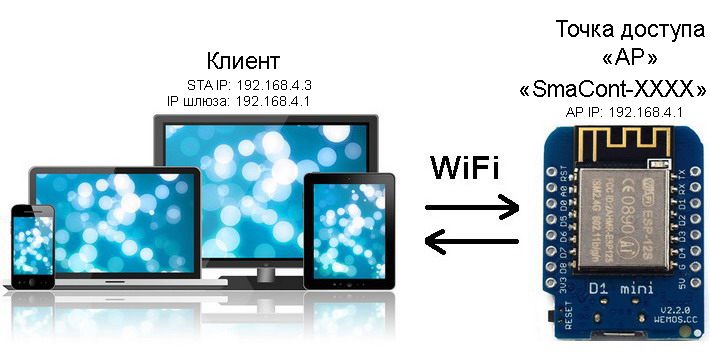
Connecting to a device in Access Point mode
In this mode, connection from a computer (laptop, smartphone or tablet) is possible ONLY TO THE MODULE as a client. The device WILL ONLY CREATE ITS OWN ACCESS POINT.
The "Smacont-ESP" firmware allows you to organize the operation of an autonomous network, where one device is configured to work as an "AP" (router), and the other devices are connected to it as clients. The number of clients can range from 1 to 8.
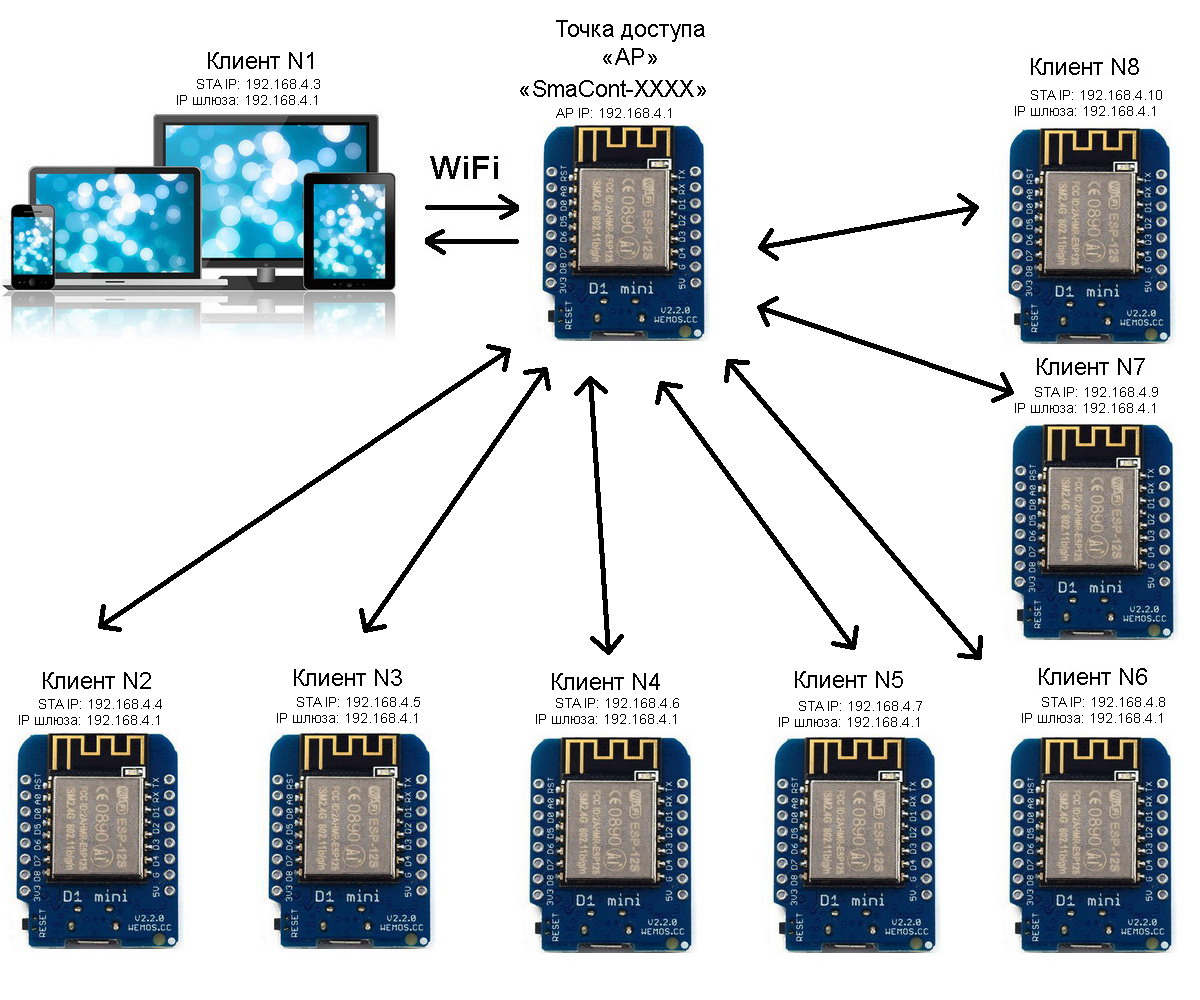
Connecting up to 8 devices to the module in AP mode
In this configuration, a computer (laptop, tablet or smartphone) can be connected as a client, which provides access to any device in the network.
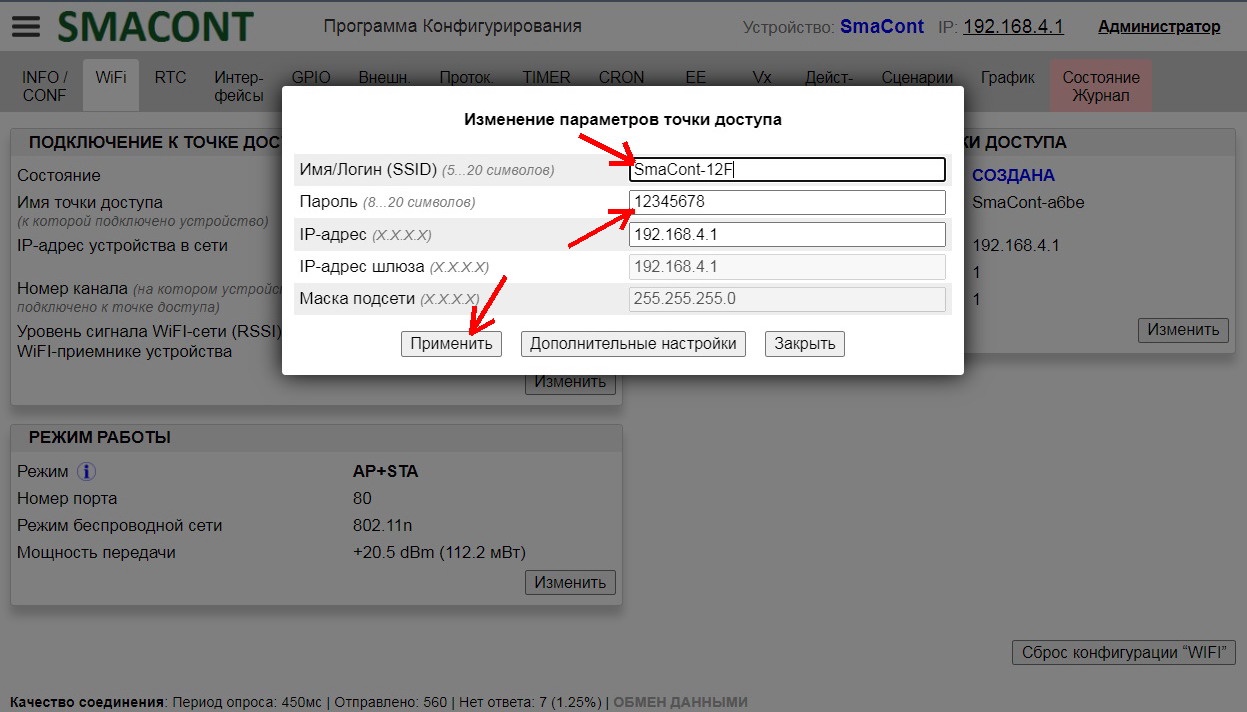
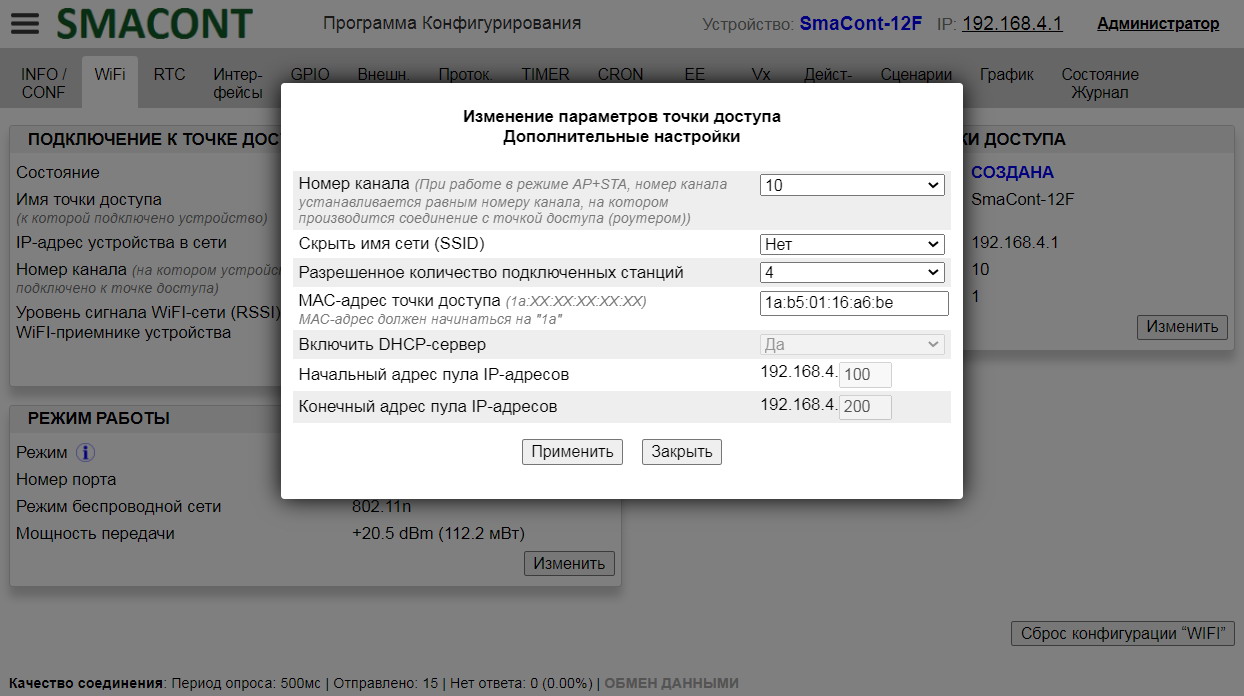
Name, password of the access point of the module, as well as the allowed number of connected clients can be changed using the "Configuration software".
Advantages of this option (access point mode "AP"):
– there is no need for additional equipment (WiFi router);
– increased protection against unauthorized access. Two levels of access are realized:
1 level – login and password for the access point;
2 level – Administrator" or "Operator" password.
Features of Access Point Mode and Router Mode

When a router supports multiple modes of operation, you may wonder what the difference between them is. This article gives a brief overview of the two most common and most popular modes and points out the peculiarities of each of them.
The final result of the device configuration is a stable working Internet everywhere. Unfortunately circumstances do not always allow to achieve this. Let's look at each mode in turn.
Comparing access point mode to router mode
A wireless access point allows all devices to connect to a wired network, it serves as a kind of adapter for those devices that physically can not do it. Of course, you can find several adapters to connect your phone to a wired network, but it's much more convenient to use a wireless connection. An access point can be compared to just such a set of adapters, only it works for more devices. Router mode offers more features than access point mode, it is more versatile, but may require more effort to set up.
Depends on your ISP's requirements
You may need to configure your connection to access the Internet. In access point mode, these settings have to be done on each device, such as entering a login or password. You only don't have to do this if the connection to the Internet is established immediately when you connect the cable. If, however, the Internet works immediately when you connect the cable, the provider may limit the number of devices that can be connected. In this case, the Internet will only work on one device and will either be tied to a specific device, or the first connected computer or phone will get access.
In router mode, things are much easier, because all the settings are done just once on the router. All other devices have to do is connect to the wireless connection.
Working with traffic
In access point mode, the device has no protection against network attacks, unless this is provided, and there is also no possibility to limit traffic. On the one hand this may not be very convenient, but on the other hand – everything works "as is", you do not need to configure anything additionally.
In router mode each connected device has its own "internal" IP address. Network attacks from the Internet will be directed at the router itself, the probability that they will detect a particular computer or smartphone is extremely low. In addition, some routers have a built-in firewall, and this is an additional protection, which is undoubtedly a big plus.
Read More: