Two frequency bands, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, are used for information exchange via radio waves.

- Wi-Fi how it works and what it is
- What is Wi-Fi and why do we need it?
- A brief history of wi fi technology
- The origins of Wi-Fi
- What does it take to create Wi-Fi?
- How to improve home network security
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a wireless router
- How Devices Connect to Wi-Fi Networks
- What is a Wireless Access Point
- What is a mobile access point
- Wi-Fi physical layer standards
- Signal representation
- Channels in the 2.4 GHz band
- Speed adaptation
- Wi-Fi security algorithms
- What is a Wi-Fi router and what does it do?
- Pros and cons of accessing the Internet via Wi-Fi
- 2 comments
- Leave a comment
- How does Wi-fi work?
- How do I connect wi-fi at home?
Wi-Fi how it works and what it is
Over the last ten years, the mobile device market has undergone a number of significant changes. Devices which used to have a status of elite, today are available for the average citizen. They started to have a wider range of possibilities. Cell phones, tablets and laptops nowadays turned into not only common work tool, but also became popular means of entertainment.
The number of users of mobile gadgets is growing rapidly, which requires the creation of technologies for communication between devices. For this reason, we are constantly working on the development of wireless technologies for data exchange.
What is Wi-Fi and why do we need it?
Wi-Fi is a technology for transmitting data wirelessly within a local area network, performed by devices based on IEEE 802.11 standards.
To put it simply, for people who are not familiar with the subject matter, Wi-Fi is a data transmission technology that uses invisible radio waves instead of wires. Similar technologies include infrared transmission, radio and Bluetooth.
Wi-Fi is not the Internet, as many ordinary users mistakenly believe. It is a technology that creates a local network where data is exchanged between different devices (printers, cell phones, laptops) without going to the World Wide Web. Connection to the provider via modem, router or access point allows the devices in the network to access the Internet.
The number of devices that can be connected simultaneously depends on the technical capabilities of the router.
Wi-Fi technology is necessary for devices that cannot be connected by cable. These include laptops, cell phones and tablets.
The technical characteristics of Wi-Fi make it possible to use it even at the scale of an industrial enterprise. The technology is convenient to use at dangerous and remote sites, as well as at the sites of secret production.
Thanks to wifi simple user becomes more mobile and does not depend on the length of the cable.
A brief history of wi fi technology
There is a widespread view that the history of Wi-Fi goes back to the early 90s of the last century. That's when the first wireless technology in the world was created in the Netherlands. It is a kind of precursor of the modern Wi-Fi. But such a statement is a bit at odds with the reality.
In fact, the history of Wi-Fi dates back to 1985. At that time, the Federal Communications Agency of the United States approved the unlicensed use of radio frequencies by all users.
The origins of Wi-Fi
The new wireless communication technology was created by Dr. John O'Sullivan, known as the "father of Wi-Fi", who worked in the 1990s at CSIRO (Commonwealth Scientific and Applied Research Organisation, Australia). The Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (now called the Wi-Fi Alliance) asked CSIRO to make the technology free to the public, but that didn't happen – now every manufacturer of Wi-Fi devices such as laptops, cell phones, smart home devices, etc. pays CSIRO to use the patent.
"Wi-Fi" is just a trademark registered by the Wi-Fi Alliance in 1999.
In fact, "Wi-Fi" means nothing and is not an acronym for "wireless fidelity", as was confirmed by Phil Belanger, co-founder of the Wi-Fi Alliance. Recently, "Wi-Fi" has increasingly been referred to as "WiFi." [2] .
What does it take to create Wi-Fi?
You need 3 components: bandwidth, a gateway and a router. Today, Wi-Fi can also be created on your phone with a hotspot function.
A wireless connection is essentially two-way communication between a router and a client device. Both devices are equipped with a radio transmitter and receiver to communicate with each other by sending signals over the radio band (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz).
Usually a Wi-Fi router is physically connected to an Ethernet jack or DSL/cable/satellite modem over a network cable to access the Internet. It then broadcasts its Wi-Fi name (SSID) to surrounding devices. When you intend to connect to a wireless network, the device sends a corresponding request signal to the router, and once received and accepted, the connection is established.
How to improve home network security
Attackers can intercept unencrypted signals sent over a public Wi-Fi network or, infiltrate your home network if you haven't secured it enough.
Public Wi-Fi networks are a separate story because many of them are not secure. Experts recommend taking precautions when using public Wi-Fi.
These include using a virtual private network (VPN) and not sharing sensitive personal information like credit card numbers. In some parts of the world, governments restrict what you can view on the Internet with a firewall, though a VPN can help you get around those restrictions.
How to increase security when using a Wi-Fi network:
- Use a VPN. A VPN can be useful for both your home network and a public Wi-Fi network. It creates an encrypted tunnel so that outsiders, including your ISP, can't monitor your online activities or collect data that may be shared with advertisers or governments.
- Use strong passwords. Your router probably comes with a default password, so it's important to change it to your own, secure one. A password manager can help you avoid the hassle of remembering complex combinations. Not doing so is like leaving your keys under the doormat.
- Use antivirus software. Antivirus software is another important element of Wi-Fi network security. This software scans incoming traffic and blocks malware, intrusions, or other attempts to steal your data.
- Update your device's software regularly. Always install the latest software for all your gadgets, and don't forget about your routers. There are firmware updates for them too, which improve functionality and security. If there is an automatic update option, do it, most people forget about it.
- Keep an eye on your settings. Pay attention to your Wi-Fi network settings. If your devices allow it, use the most secure encryption standard, WPA3, which has the latest security updates and is the hardest to crack. You can also take simple steps like disabling remote access, or the network when you're not using it, and keeping guest access to some devices.
- Change the name of your network. You should know the name of your network, but you don't need to tell intruders about it. You can change it to promiscuous or unidentifiable, or make your network "hidden" so that it can't be seen nearby.
- Be vigilant. Know who is using your network. If possible, enable notifications of new users on your gateway and disable anyone you can't identify. Create a guest network that cannot be used to access or change your settings or data, and people who are not your family members. Also for other devices like light bulbs or garage door opener modules.
Frequently Asked Questions
We've tried to briefly answer the most frequently asked questions related to Wi-Fi and wireless networks, devices and systems of this type.
What is a wireless router
A wireless router is hardware that serves as an Internet access point and connects other devices like a laptop, phone, or tablet.
You can connect any device to a router via Wi-Fi or, with an Ethernet cable.
How Devices Connect to Wi-Fi Networks
Your computer and other devices connect to a Wi-Fi network using radio waves.
Each device has a wireless module (adapter) that converts the data into radio signals, and these are decoded by the router.
What is a Wireless Access Point
A wireless access point is usually a component of your router, but it can also be a standalone device that provides a wireless network.
The access point then connects to the broader Internet network, usually over a wireless or Ethernet connection.
What is a mobile access point
Read More:If you don't have access to a public Wi-Fi network, you can use your phone or standalone device as a portable access point.
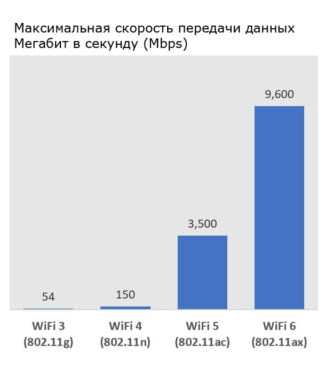
Wi-Fi physical layer standards
There are several different implementations of wifi, and they are described in 6 standards. The very first 802.11 standard was adopted in 1997 and had a speed of 1 or 2 Mbps, Ethernet at that time could transmit information at 10 Mbps. The current standard wifi 802.11as was adopted in 2014, the maximum transmission speed, more than 6 Gb/s.
Now wifi is used to transmit data – electromagnetic radiation or radio ether, but the first version of wifi used infrared radiation, now this method is used in TV remotes.
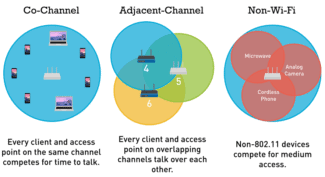
But since the second generation of 802.11b only electromagnetic radiation is used. Two frequencies are used, 2.4 and 5 GHz. Frequencies in this range can be used without licensing. However, other devices operate in the same range, such as a microwave oven and this interferes with the wifi signal.
Signal representation
Modern wi-fi standards use orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFMD) to transmit data. Data is transmitted in parallel on different frequencies. Although the frequencies overlap in the picture, the OFMD method allows the signals to be recognized reliably.
Channels in the 2.4 GHz band
The channels in the 2.4 GHz band uses 14 channels for data transmission, the picture lists their frequencies. The channels are slightly shifted in relation to each other, but still partially overlap.
Therefore the number of Wi-Fi networks which are in the same place is limited by the number of channels there cannot be more than 14. If more than 14 networks are operating in the same area, they will not have enough channels. This is known as a "wi-fi jungle" and is quite common, e.g. in apartment buildings with a wi-fi router for internet access in every apartment.
Speed adaptation
With Ethernet, the speed of the equipment is fixed, it will be the same for all devices on the network. Wi-Fi allows you to change the speed depending on the quality of the signal. If the signal quality is high, the speed increases, and if the signal quality is low, the speed decreases. In order to increase or decrease the speed, the wifi varies several parameters:
- You can use different channel widths from 20 MHz to 160 MHz.
- Supports a variety of modulations that allow you to transmit data at different speeds and reliability
- It is possible to change the data interval between the characters that are transmitted via wifi.
A table that shows the different speed options for the same wi-fi stream. The slowest speed of 6.5 Mbps is obtained when using a binary phase modulation BPSK channel 20 MHz and the interval between the characters 800 ns. The highest speed of 866 Mb/s is obtained by using quadrature amplitude modulation which has 256 states, the channel width of 160 MHz and the interval between the symbols of 400 ns.
Data presented for one spatial stream, if your access point and your station have multiple antennas, then you can use multiple spatial streams and at the expense of this even further increase the transmission speed.
Wi-Fi security algorithms
It's easier to intercept data in a wireless network than in a wired one, so the Wi-Fi Alliance has paid a lot of attention to security mechanisms and information integrity. The protocols are WEP, CCMP and TKIP.
WEP – is a weak cryptographic algorithm that uses a single key for encryption and decryption. Its use is not desirable.
TKIP – is an improved WEP that generates keys during the authentication phase. Because it uses the same encryption algorithm as its predecessor, it is not as secure.
CCMP – mandatory for modern devices and is based on one of the modes of the AES protocol. It ensures the integrity of received information and its confidentiality. For each session generates a new key.
Nowadays the main algorithm uses the WPA2 protection mechanism, which uses the cryptographic CCMP protocol and protects control frames (not only data frames).
What is a Wi-Fi router and what does it do?
Router or router is a device for organizing a network, connecting the various segments of the existing infrastructure. At the address of the recipient specified in the header of the packet (a formalized block of data transmitted over the network), it determines the best route to it and sends the data. If there is no route, the packet is dropped. In everyday life it is used as a wireless access point – it organizes general access to the Internet and local networks for quick data exchange between clients (computer, phone, tablet, laptop).
The most popular models, routers from D-Link, are equipped with 1-8 LAN-interfaces for connecting local networks and 1-2 WAN-ports for connecting local networks (enterprises, organizations, home) to provider networks.
Classic Wi-Fi router comes with a 4-port switch, WAN-interface and access point. Through it, customers exchange information and connect to a distribution system – mainly wired Internet, which is supplied by the provider via Ethernet. There are also USB models for connecting a network printer or wireless modem.
Routers work in one (2.4 and 5 GHz) or two bands. Some models are capable of operating in multiple bands simultaneously, creating two or more access points. The difference between a router and an access point:
- Routers are able to connect clients from different networks, access points switch devices within the same network;
- transmission of packets by routers is based on IP analysis, access points work with MAC-addresses;
- routers support address translation – multiple devices have a single IP address to access the Internet;
- routers can be equipped with firewall functions and dynamic IP-addressing.
Pros and cons of accessing the Internet via Wi-Fi
Of course, like many things, Wi-Fi has a number of advantages and disadvantages when compared to wire connections and mobile networks. I'll highlight the main ones.
- No wires. The less of them, the more convenient, nothing gets in the way.
- Mobility. With Wi-Fi you can work at any convenient point (within the network coverage area).
- One access point (router) allows you to connect several devices (in modern equipment – dozens).
- If the Internet is connected by a provider, the speed will be higher than via a cellular operator (except in cases of bad location of the point).
- Compared to a wired connection, relevant for desktop PCs and laptops, Wi-Fi speeds will be slower if you don't sit directly under the router. Every obstacle in the way will cancel out the signal.
- Stability. Carrier networks and wired connections are actually more stable. On Wi-Fi, there are more frequent failures, outages, including due to the overload of the communication channel on which the equipment operates.
- Security. For the old protocols (especially WEP) – very relevant. With the advent of WPA2 encryption security has significantly improved.
So, I've tried to tell you as much as possible about what is Wi-Fi. To summarize:
- Wi-Fi is not the Internet itself, but just a way to connect to it! And in the first place – a method of communication, which allows you to transfer data between devices without using wires.
- It can be used to access the global network, even with the help of mobile operators.
- All you need to know to connect is a WiFi network name (SSID) and password.
- Modern routers provide 5 GHz frequencies and devices supporting the same frequency can provide speeds commensurate with the capabilities of wired connections.
Even because of some of the disadvantages mentioned above, it is unlikely that anyone will refuse to use Wi-Fi. This is the present and the standards will only continue to improve.
2 comments
Artem, nothing, the generation of our parents and grandparents are far from the digital technology and, of course, it is normal that so called) But young people now do not understand at least the network basics, including Wi-Fi – not cool. We need to educate ourselves.
Leave a comment
Social Media Sharing interesting information not only on the blog, but also on social media! YouTube Vkontakte Classmates
Sign up for New Articles so I won't miss a thing!
All the interesting stuff ahead!
How does Wi-fi work?
Now to the interesting and very important, understanding how wi-fi networks work, you will be able to intelligently formulate your thoughts about Internet connections. So, in order for you to have a Wi-fi network at home, you must first install the Internet at home.
After, the Internet cable must be connected to special equipment – a router.
Router – a device which receives signals from the Internet, converts them into a so-called wi-fi network and transmits them to specific devices (phone, computer, TV).
How do I connect wi-fi at home?
As I said earlier, the first thing you need to do is to install the Internet in the house, apartment, office, the process is not complicated, you need to know what providers are working with your home, call them or visit the office, where they will accept the application for the laying of the Internet cable in your apartment.
You can find the right Internet provider through the service Inetme – just select the city, house and street to find out all the current offers for connections. All tariffs are up to date, you only have to compare them and make a choice.
As a rule, you will be given several dates to choose from, you choose the most convenient for you, when you can be at home, at the appointed time will come and install the internet cable in the place you need.
By the way, for laying cable no money are not taken, the company you choose does it at its own expense, you pay only selected rate internet connections, usually from 300 to 1000 rubles per month.
The monthly fee (tariff) will depend on the connection speed you choose.
For comfortable access choose the speed of 30 Mb/s, about 400-500 rubles/month.After the cable is installed you can connect it to your computer and use the Internet, but our goal is to create a wi-fi network, so let's move on. You need to buy a router (some companies provide their routers), it is to him you then connect the Internet cable, then the router will create an active wi-fi network, and already to it you can connect without any wires though from a laptop, though from a phone and here it is comfortable access to the Internet from anywhere in the apartment or house.
Tip 1: When you discuss the terms of connection to the Internet cable, you should ask what kind of router you should buy, because the choice in our stores is quite large. The right advice on buying the right router will save you time and money.
Tip 2: Router when you connect will need to configure (once), if you do not have the slightest idea how to do it, I recommend to ask the master, who will come to lay the Internet cable. Let him set everything for you at once (may require an additional fee for setup, about 500 rubles).