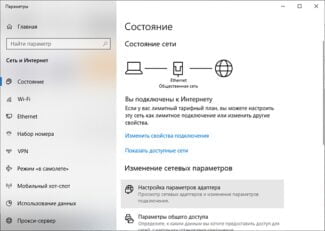
On the right side are the IP, mask and DNS address settings. In theory, the router should receive these settings from the ISP. Then just set the mode to "Automatic". If you have a static IP with mask, then put "Static" and enter the data from the sheet. Under "Local Network" goes configuring the IP address of the gateway or our microtic and range of local addresses.
- Russian Blogs
- AP (Access Point) Mode
- Access Point
- Definition of a "router"
- WISP on other routers
- "AP client router" on ASUS.
- TP-Link
- Zyxel Keenetic
- Selecting WiFi Mode
- Switching between wired and wifi Internet
- How to enable or disable wifi hotspot isolation in the router settings?
- ASUS
- TP-Link
- More info
- What is a wireless access point?
- Wireless AP vs. Router: what are the differences?
- Function
- Connecting
- Coverage
- Router and Access Point
- Conclusions
- What is router mode?
- What is AP mode?
- Changing the WiFi Mode
- AP (Access Point) mode
- TP-Link router as a wifi wireless signal adapter (WISP)
- How to connect a router in WISP client mode by Netis example?
Russian Blogs
As a rule, on TP-Link wireless routers there is AP (access point) mode, Router mode (wireless router), Repeater mode (repeater), Bridge mode and Client mode; but many users do not understand the difference between these modes, these modes will be described in detail below.
Note. Some TP-Link wireless mini-routers have only three modes: AP (Access Point) mode, Router (Wireless Router) mode and Repeater mode.
AP (Access Point) Mode
In AP (Access Point) mode, you only need to connect a network cable that can access the Internet to the router 192.168.1.253 and you can access the Internet without any configuration; but you should note that the wireless network on 192.168 .1.253 router is not currently encrypted. It is recommended that you set a wireless password.
Applicable location.: For example, hotels, hotels, or other places that have a network cable for Internet access.
Access Point
The router and access point are from the same manufacturer. They look identical:


First, let's get acquainted with the concept of an Access Point, or AP. Many of us can make an AP out of our smartphone or laptop. But that's not what we're talking about here. Well, the point is the same (Internet distribution), but we are talking about a classic access point.
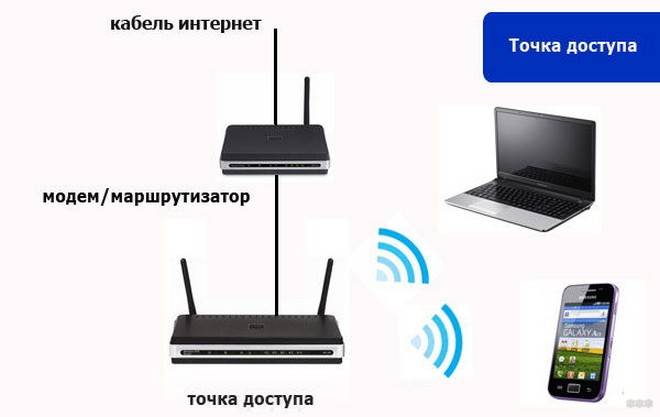
The Access Point is a stand-alone device, not a router. Its task is to connect to the existing network. It is a kind of "extender" of the cable network to connect to the Internet via Wi-Fi.
Modern APs can function in several modes:
- Wireless client – allows you to become a wireless client to another access point, in other words, acts as a wireless adapter.
- Bridge – allows you to connect two wired networks or two network segments that are independent of each other. Not all Access Points have this mode.
- Repeater – is useful for two wireless APs when a direct connection cannot be established between them. In this mode, the device retransmits the signal between the APs.
- Access Point – A classic access point. It allows laptops, smartphones and other devices to access the Internet via Wi-Fi. An AP has an SSID name that wireless adapters see and use to connect.
Another important difference between an AP and a router is that there is no WAN port. I'm not sure, maybe some models have an ISP cable connector. But most Access Points only have one LAN port, for connecting to the local network already created by the router.
Definition of a "router"
A router is a specialized computer that creates a local network based on routing rules and tables. It receives packets from the Internet service provider and passes them on, to network devices, via cable or Wi-Fi.
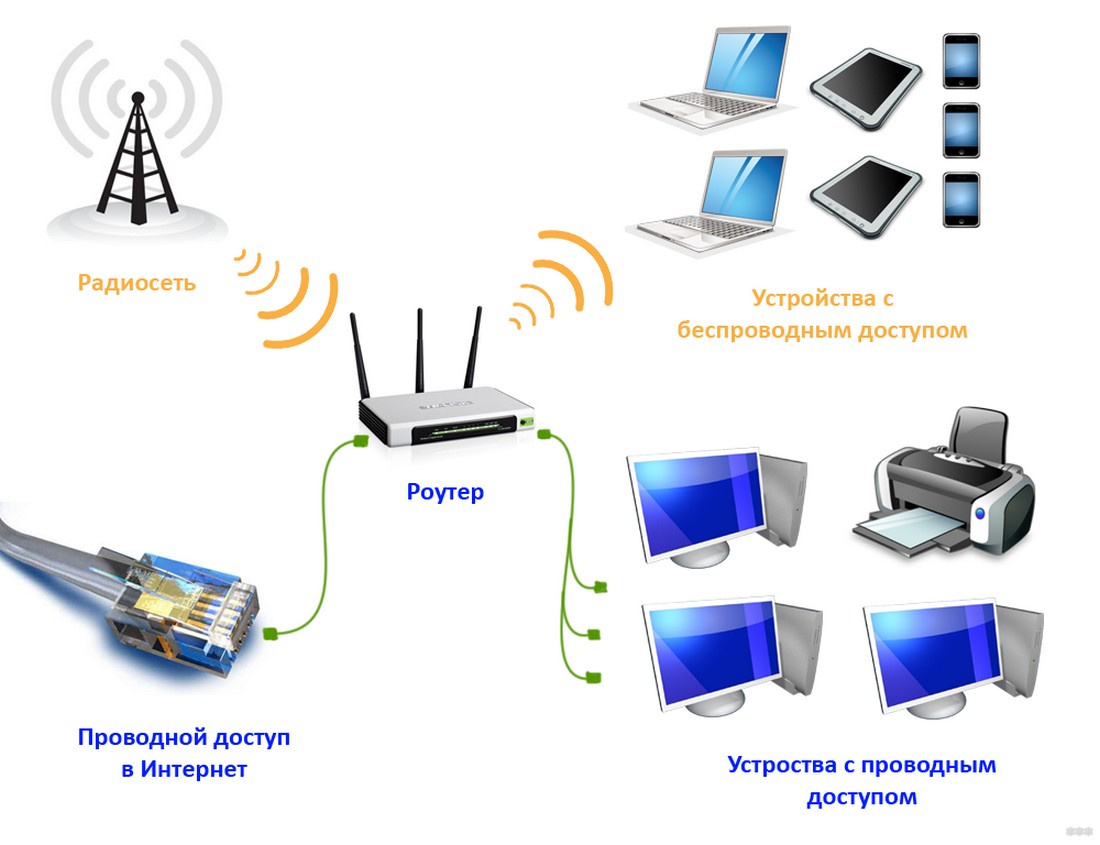
These are the basic tasks. But that's not all. So what is the difference between a router and an access point? Let me list it point by point:
- Distributes traffic between networks and assigns IP addresses to devices connected to it.
- It can swap the local IPs of computers, laptops, mobile gadgets for its external IP. As a result, the home devices access the network using the same IP address of the home ISP.
- The router has its own firewall (Firewall). It protects network communications from unauthorized access from outside and inside the local network. A firewall is a "barrier" that does the following:
- All communication passes through it;
- Allows only authorized traffic;
- Resists hacker attacks.
- The router can limit speed for specific home devices and can also protect the network from intruders by filtering MAC and IP addresses.
- Performs encryption of transmitted data on networks.
- With a router, you can limit children's access to certain sites or the time they spend on the Internet.
The classic router has 4 LAN ports, that is, you can connect up to 4 devices via a network cable. The WAN port is the input for data packets. Simply put, this is where the ISP cable connects.

WISP on other routers
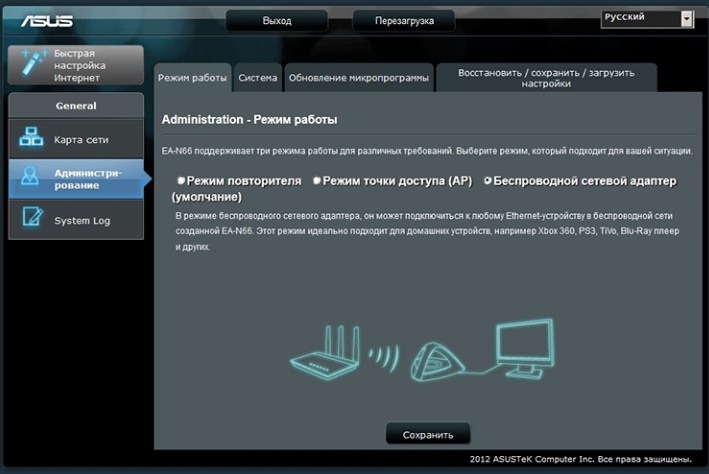
"AP client router" on ASUS.
On ASUS devices unfortunately the name is not adaptive and not clear. Maybe it has to do with the translation. But the Russian version of the mod is called "Wireless Network Adapter". To configure it, you can use the "Quick Setup" – just click on the magic wand in the left corner of the window. Or click on "Operation Mode" at the very top of the home page.
TP-Link
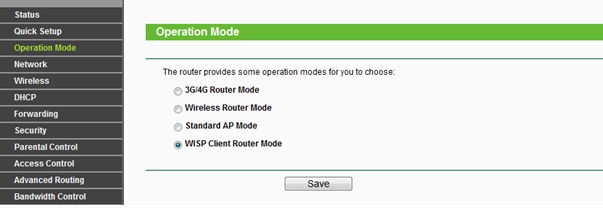
On TP-Link, there are two ways to enable it. Go to "Operation Mode," or "Operational Mode" in Russian. Then select our mod. Then go to "Network" – "WAN" and set the dynamic IP.
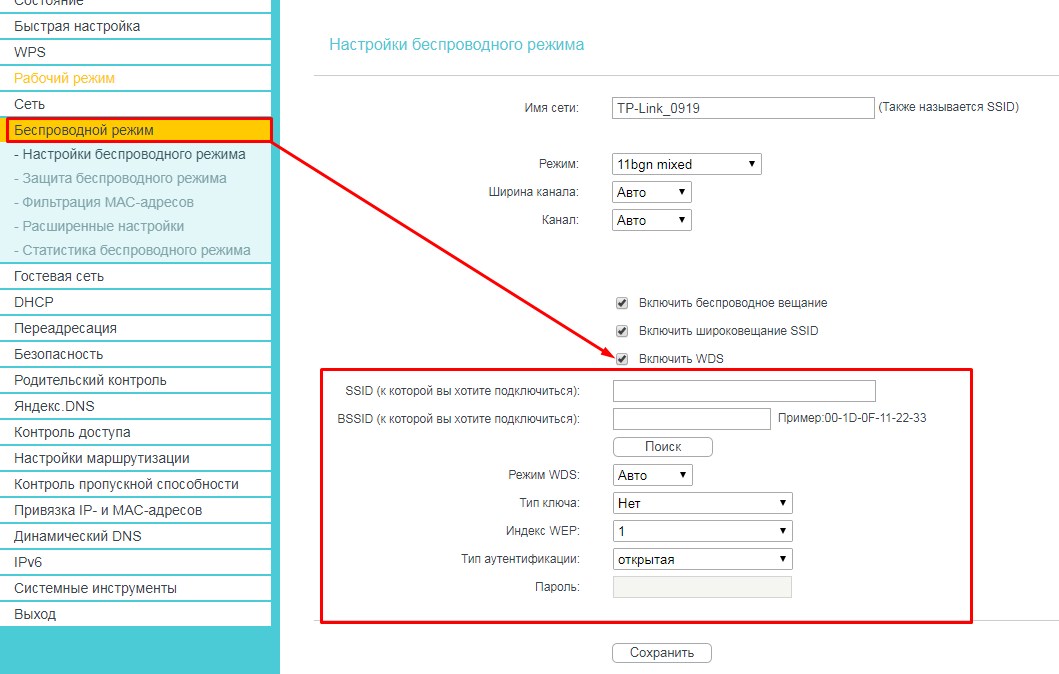
The second way is to go into "Wireless Mode". Now click on "Enable WDS". Then everything is simple, you just need to connect to the wireless network of the provider. To do this, enter the data wi-fi.
Zyxel Keenetic
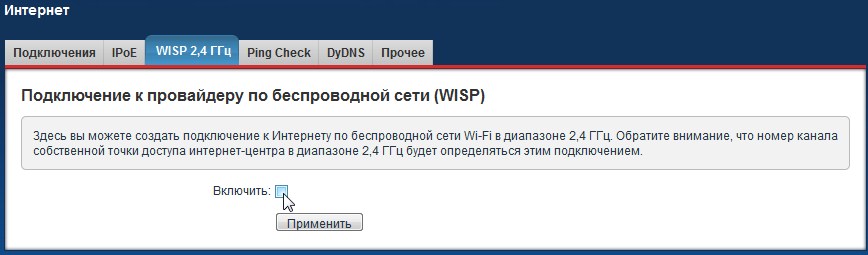
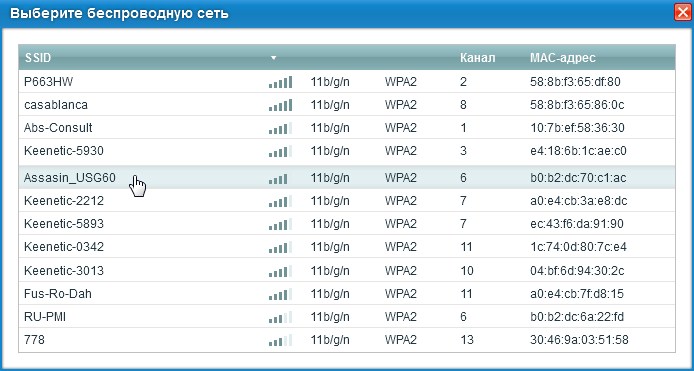
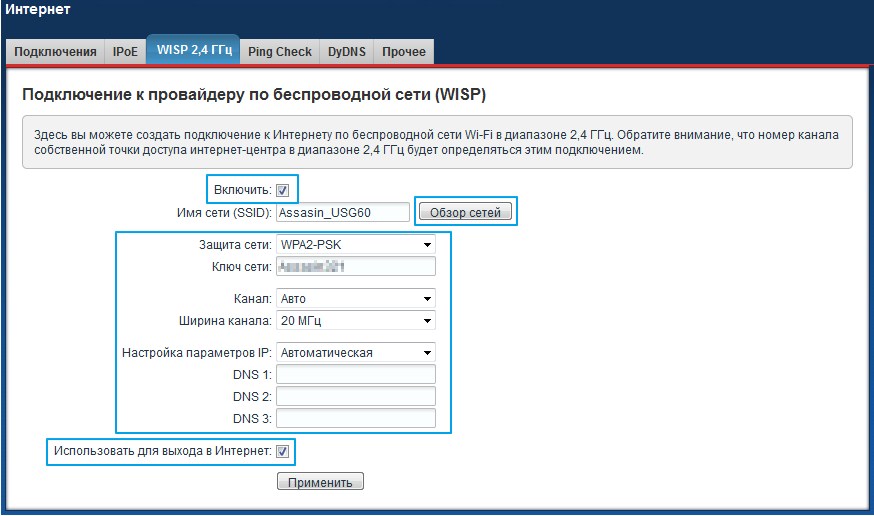
- Next, enter the password in the "Network Key" field.
- The IP and DNS settings are off-line, but you can always configure these parameters manually. You can use the following parameters from Google as the DNS: 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4.
Selecting WiFi Mode

Go to the Wirless – Basic Settings page. There are several access point modes (Wireless Mode):
- AP – access point mode, you can create several networks (probably in this mode)
- Client – client mode, when the router can connect to other networks, but you can not create your own wifi networks
- Client bridge – the same, but it goes from the router mode to the mode of the receiving access point (i.e. does not distribute the Internet by itself)
- Adhoc: Connect to a computer as a signal source (point-to-point mode).
- Repeater is the same as client, but you can create your own networks
- Repeater bridge – is the same as Client bridge, but judging by its name it amplifies the signal of the received AP
It is necessary to set the Repeater mode in Wireless Mode. In this case we will configure Wireless Physical Interface wl0 to receive the internet from the neighbor's access point, and by adding Virtual Interfaces wl0.1 at the bottom we will create our own home wifi network.
We also need to set the Wireless Network Name (SSID) at the top which is the name of the wifi network we connect to. And for the wl0.1 interface, set the name of the home network.
The settings of the channels (frequencies) for the home network will copy the settings of the network to which you are connecting, so nothing more can be changed here.

Go to the Wireless – Wireless Security tab.
At the top of the wl0 interface you define the settings of the network you are connecting to. It is important to select the Security Mode, WPA Algorithms (in my case, it does not connect in any mode except AES), WPA Shared Key (the password of the access point you connect to).
At the bottom we are given more freedom, regardless of the settings at the top we can choose any security settings for the home network.
Switching between wired and wifi Internet
In order to receive the Internet from your home provider again on the page Wirless – Basic Settings it is necessary to select AP mode in Wireless Mode. Also it is necessary to change SSID name for this network (at least adding "1" at the end) to your router will not let the clients of the neighbor access point to your Internet.
This way once configured router we can quickly switch to wifi internet when wired internet is not available without reconfiguring all home devices.
How to enable or disable wifi hotspot isolation in the router settings?
If your router settings are in English, it will most likely be "AP Isolation", or "Enable AP Isolation". If in Russian, it will be "AP Isolation" or "Client Isolation". These settings are usually located in the section with Wi-Fi network advanced settings (Wireless – Wireless Advanced).
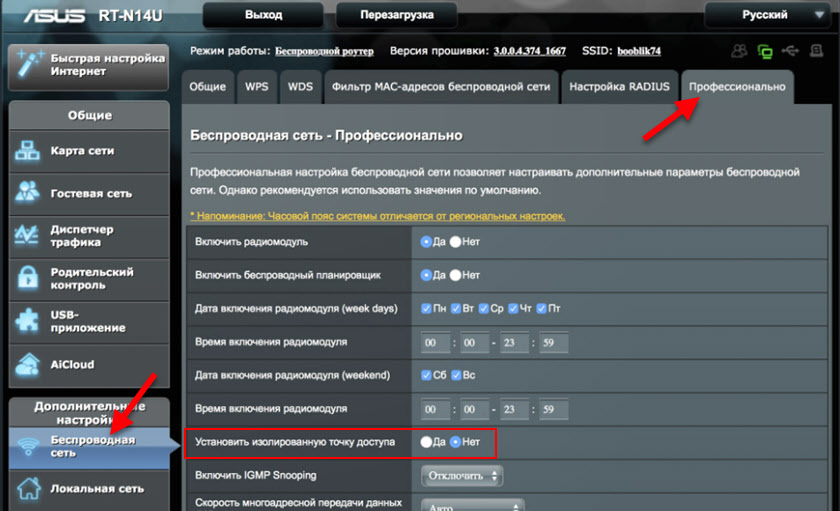
ASUS
You need to go into the settings of your ASUS router, go to the "Wireless Network" section and open the "Professional" tab. There will be an item called "Set Isolated Access Point". Set the switch next to "Yes" or "No" and save the settings.
TP-Link
Log in to your TP-Link router settings. The rest depends on what web interface is installed on your router. If the old (green), then in it this setting is located in the "Wireless – Wireless Advanced" (Wireless mode – Advanced settings). You need to check the box next to "Activate AP Isolation" and save the settings.

If you have the now popular blue web interface, go to "Advanced Settings" and open the "Wireless Advanced" tab on the left. There you need to check or uncheck the box next to "Access Point Isolation" and save your router settings.
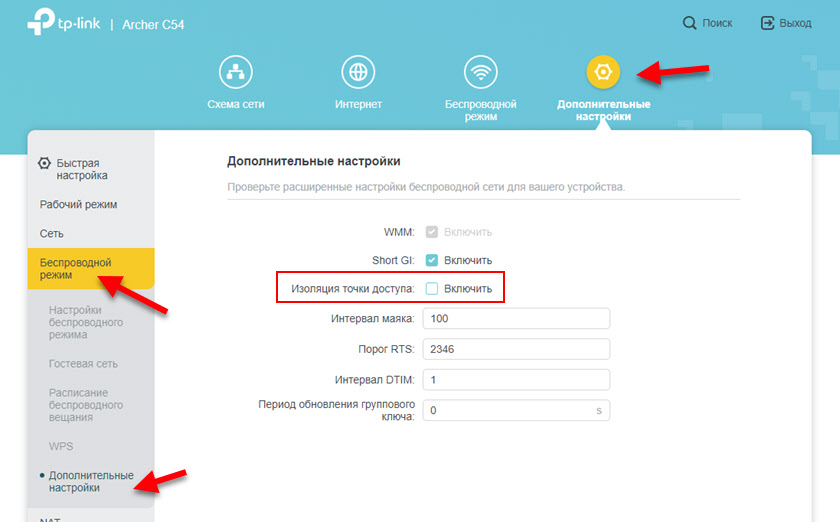
TP-Link has another kind of web interface (see screenshot below) . I show you how to activate or deactivate Wi-Fi access point isolation, if you have such web interface installed. That's where these settings are hidden quite far away. Go to Advanced Settings – System Tools – System Settings and there at the top of the page will be this item.
More info
If you're worried about the security of your home wireless network, I recommend the first thing you do is set up a modern type of security and a strong password. I covered this in more detail in this article: type of wireless network security and encryption. We also have a separate article in which I gave you recommendations on how to best secure your Wi-Fi network.
Aside from that, don't forget to use a guest Wi-Fi network (with wireless client isolation turned on) when you connect other devices to your router.
![]()
5

24654
![]()
Sergey
![]()
Tips for configuring routers (general)
Hello, how to disable WI-FI access point isolation on the subscriber terminal bdcom gp1704-2f-e ? terminal installed from Ukrtelecom, in the settings of the terminal did not find anything like this or similar, no guest mode, too, AP mode is not possible to switch , how to solve this problem ?
What is a wireless access point?
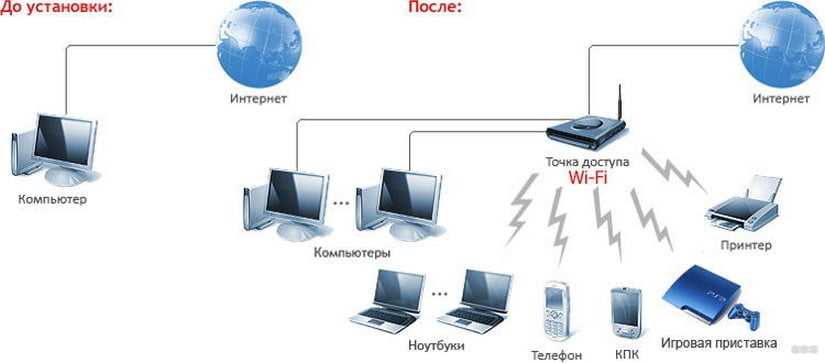
A wireless access point (also called a wireless AP or WAP) is a networking hardware device that adds Wi-Fi capabilities to an existing wired network, connecting traffic from a wireless station to a wired LAN. A wireless AP can act as an independent device or as a component of a router.
Generally speaking, a wireless AP allows devices without a built-in Wi-Fi connection to access a wireless network over an Ethernet cable. In other words, the signal from the router to the access point is converted from wired to wireless. In addition, if future access requirements increase, WAP can also be used to extend the coverage of existing networks.

Figure 2: Wireless Access Point Connection Scenario
Wireless AP vs. Router: what are the differences?
Both wireless access points and wireless routers support Wi-Fi network connections and play a similar role. So there's been some confusion. In fact, the two networking devices are more like cousins than twins. The differences between them will be explained below.

Function
Typically, most wireless routers combine the functions of a wireless access point, an Ethernet router, a basic firewall, and a small Ethernet switch. Wireless access points
are usually built-in components of devices such as routers or Wi-Fi extenders. In short, wireless routers can act as access points, but not all access points can act as routers.
There is no doubt that a wireless router, acting as an Ethernet hub, helps to create a local network by linking and controlling all the devices connected to it. However, the access point is an auxiliary device in the local network and only provides access to the network set up by the router. Therefore, if you are a network administrator, you can use a wireless router to change network settings, but a wireless access point does not have this function.
Connecting
Router mode vs AP mode, the way you connect is different. The wireless AP cannot connect to the modem. Usually the switch or router will be used as an intermediary. The wireless router has a broadband dial-up function and can be directly connected to a modem for Internet access.
Coverage
Wireless routers are the most common networking equipment today. But if a router can't cover a Wi-Fi signal, it will have weak or no signal. Conversely, wireless access points can be added in places with poor network conditions, eliminating dead spots and extending the wireless network.
Router and Access Point
The router itself, also acts as an access point, it allows you to connect to a Wi-Fi network. In addition, almost every router can operate in AP mode. Some manufacturers, like ASUS, ZyXEL, for example, simply enable this mode in the router's settings. Later, I will write detailed instructions on configuring this mode on routers from different manufacturers.

In Access Point mode, the router necessarily disables IP Address Distribution (DHSP), the firewall, and IP Address Translation (NAT). It simply disables several features of the router and turns it into an Access Point.
On some routers, there is no AP mode per se. You just need to manually disable the DHSP server there and make a few more adjustments.
Conclusions
If you do not know what device you need, a router or an access point, it is better to ask a knowledgeable person, or buy an ordinary router. Only buy an access point if you know exactly what you need.
Almost any router can work in Access Point mode. But the access point itself can't act as a router. It lacks many of the features that an ordinary router has.
By the way, an ordinary laptop or computer with a Wi-Fi adapter can also be turned into a wireless access point. I've already written about how to start a hotspot in Windows 10. And if you have Windows 7, see this article.
That's pretty much it. If you still have any questions, you can leave them in the comments. Have a nice day!
![]()
139

213587
![]()
Sergey
![]()
Useful and interesting
Hello Sergei.
Router Kinetik main to it is connected to the Internet wire, in one room.
Router Asus, in the other room, connected from the Kinetic LAN-WAN. The settings are set to AP mode. When configuring the router, the network name and password were changed automatically, became like the Kinetic. I cannot see which router the phone is connected to via Wifi.
Do I have to change the network name on my Asus?
Do both routers give out Wi-fi?
You can check this very easily. Look at the signal strength in the room near the ASUS router or behind it (the farther away from the Keenetic), then turn off the ASUS and look again at the signal strength on the devices.
In the apartment is the main router Zyxel Keenetic Viva it distributes wifi from it by cable goes to another router DIR-300, which cable distributes to the computer and the console. The dir-300 has its own wifi. How do I make one wifi?
What is router mode?

Your average home router will default to router mode. Devices are part of a local network and are assigned a unique identifying address, whether wireless or cable. Often what we call a router is actually a combination of an Internet modem, a Wi-Fi access point, a routing table, and an Ethernet switch for wired devices. This combination allows the router to examine incoming and outgoing data packets to decide where to send them.
If you use the router for Wi-Fi devices, the signal will fade as it is removed, leading to unstable performance and eventually to outages. Finding the right spot in your home for a router can help improve Wi-Fi conditions, but can be limited by cable length. Even the most reliable Wi-Fi antennas eventually fail when encountering thick walls or electrical interference from microwave ovens and other appliances.
What is AP mode?
An AP is a device used to connect devices to an existing local area network. Typically, offices and businesses can have many access points in one building providing Internet access. Routers can be set in access point mode and used in the same way, with the primary router still handling device addresses and Internet traffic.
Not all routers have dedicated access point mode, but that doesn't mean they can't act as one. Disabling routing services and assigning a unique IP address will have the same results. Normally the home router has an address of 192.168.1.1, so the AP cannot use it. Changing the address to any address that is not already in use will prevent conflicting traffic and allow devices to exchange data.
If APs are configured with the same name and password as the router, devices will be able to connect to either AP without having to re-authenticate their credentials. The closest AP or router with the strongest signal will be automatically selected when moving around large areas. Moving freely without losing your Internet connection is paramount to a successful business and a comfortable home.
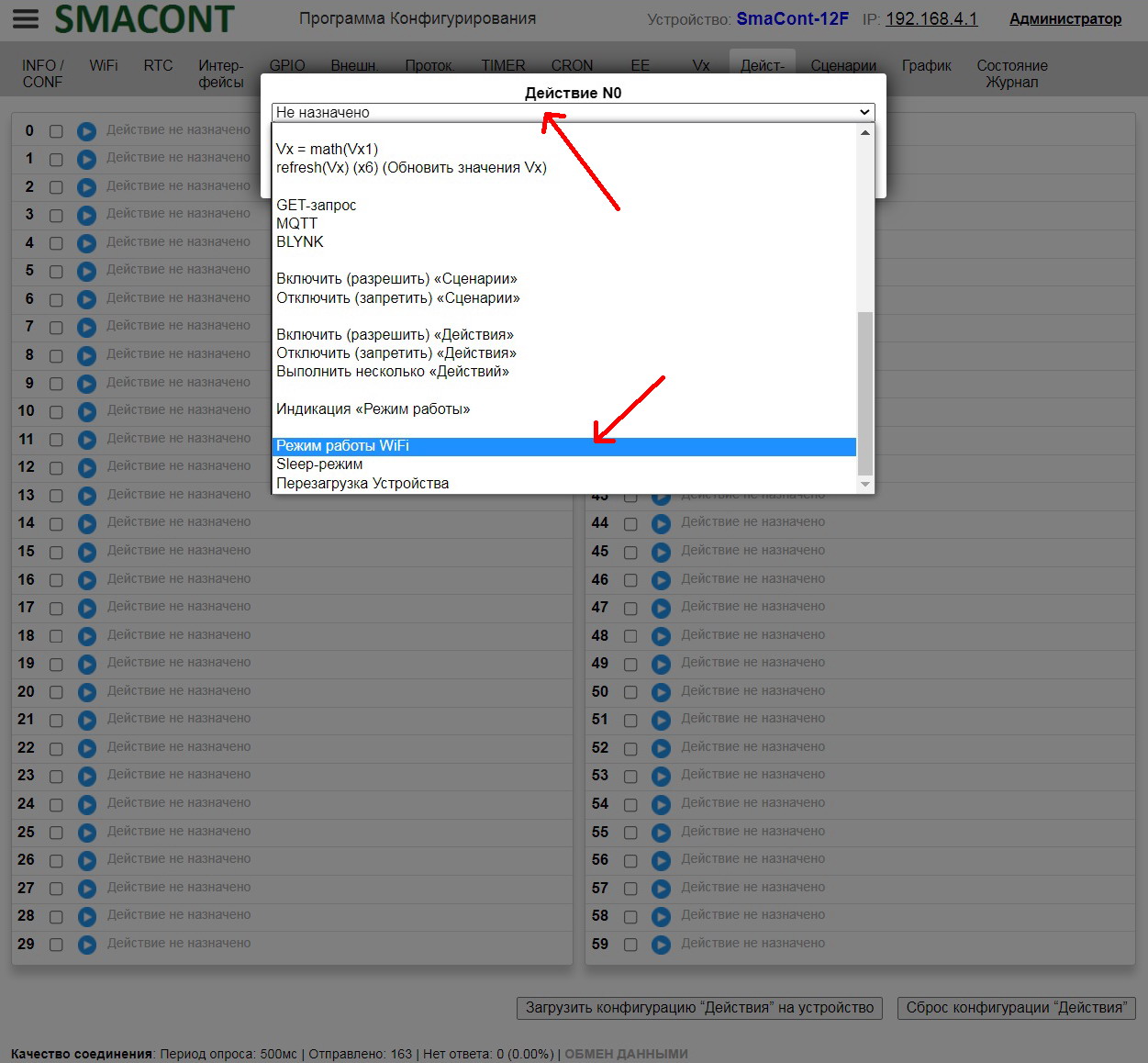
Changing the WiFi Mode
WiFi mode can be changed using the "Configuration Utility" under the "WiFi" tab.
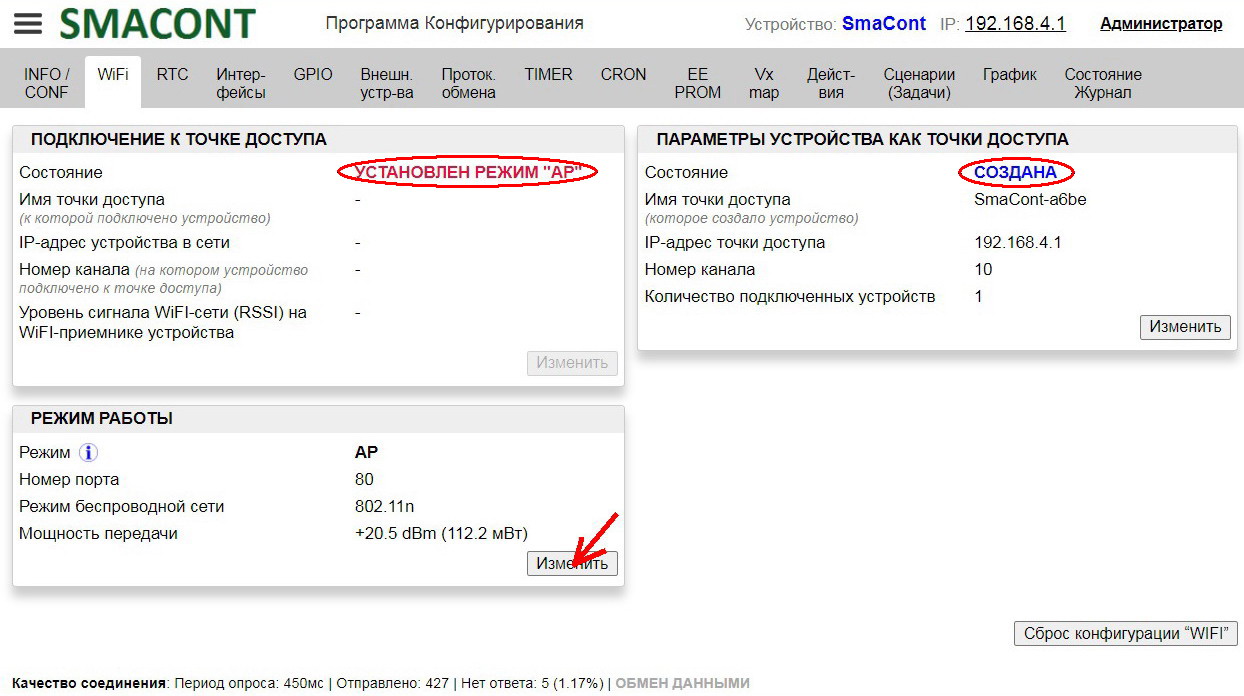
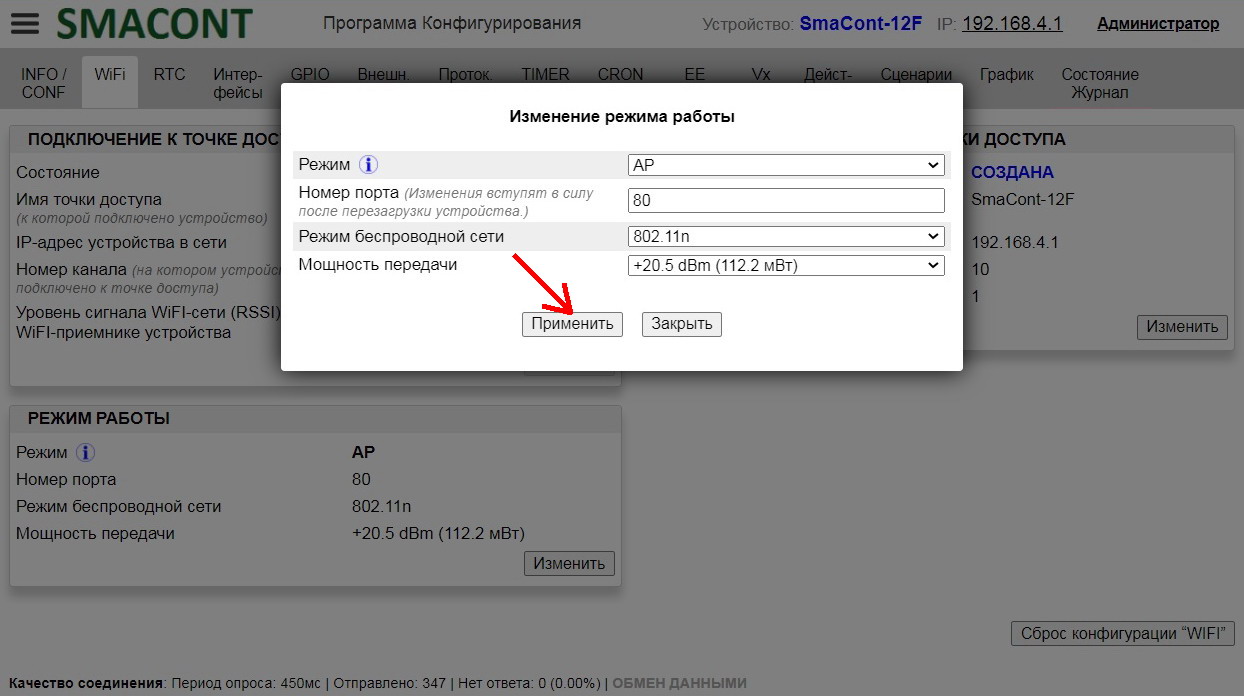
Clicking on the "Change" button in the "OPERATION MODE" field will open the "Change Operation Mode" window.
In this window you can set the following parameters:
• "Mode". – mode of the module's WiFi network ("AP", "STA", "AP+STA");
• "Port number". – port number is specified after the IP-address of the device, for example: 192.168.1.250:8080.
If the value of "Port number" is "80", the port number can be omitted, for example: 192.168.1.250.;
• "Wireless Network Mode". –
802.11b – Tx Power: +20 dBm; Rx Sensitivity: -91 dbm (11 Mbps);
802.11g – Tx Power: +17 dBm; Rx Sensitivity: -75 dbm (54 Mbps);
802.11n – Tx Power: +14 dBm; Rx Sensitivity: -72 dbm (MCS7);
• "Transmission Power" – determines the "visibility" range of the device.
Range: max +20.5dBm; min 0dBm.
After changing the required parameters, it is necessary to click on the "Apply" button, after which the device will reboot. During the application of the parameters, the device will be temporarily (1. 5 sec.) unavailable for connection.
Changing the WiFi mode is also available when running scenarios.
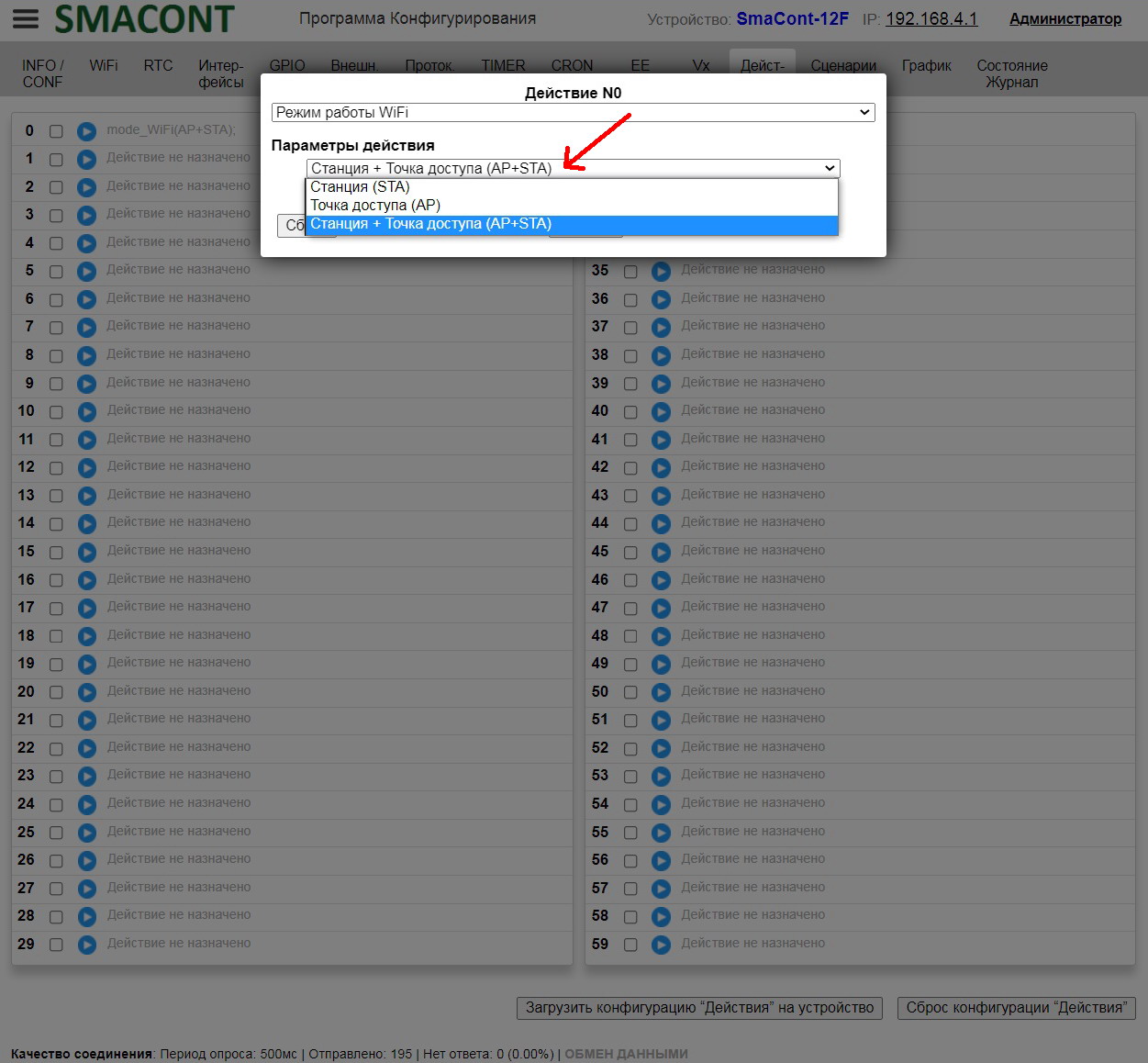
Changing the WiFi mode when running scenarios
AP (Access Point) mode
A diagram of connecting to a device in AP (Access Point) mode is shown in the figure below.
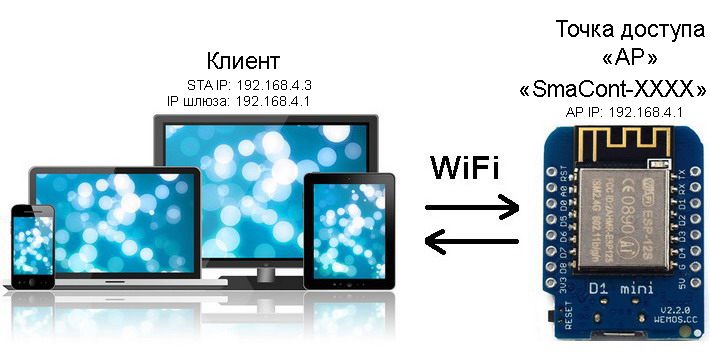
Connecting to a device in Access Point mode
In this mode, connection from a computer (laptop, smartphone or tablet) is possible ONLY TO THE MODULE as a client. The device WILL ONLY CREATE ITS OWN ACCESS POINT.
Smacont-ESP" firmware allows you to organize the operation of an autonomous network, where one device is configured to work as an "AP" (router), and other devices connect to it as clients. The number of clients can range from 1 to 8.
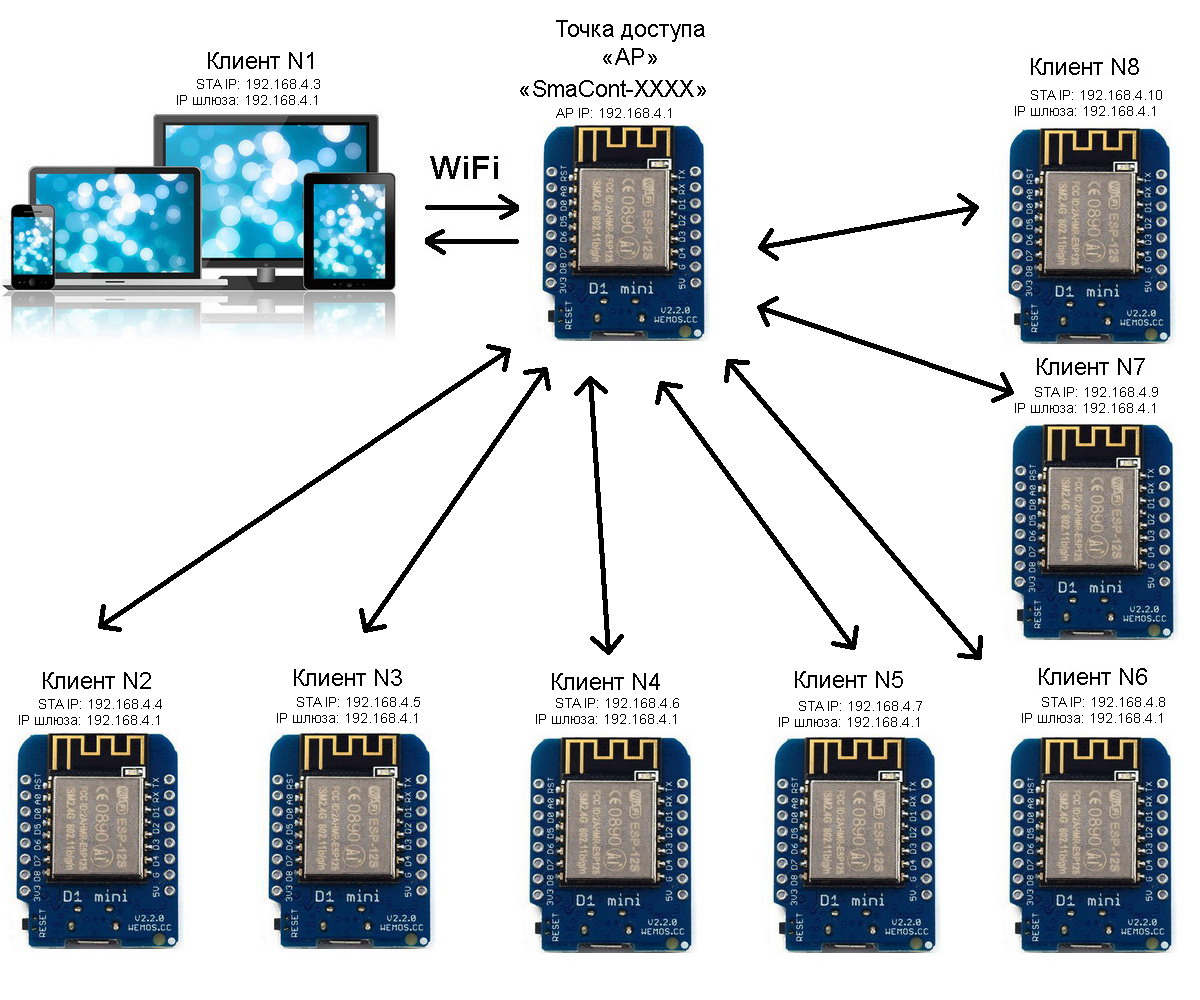
Connecting up to 8 devices to the module in AP mode
In this configuration, a computer (laptop, tablet or smartphone) can be connected as a client, through which any device on the network can be accessed.
The name, password of the module access point, as well as the allowed number of connected clients can be changed using the "Configuration software".
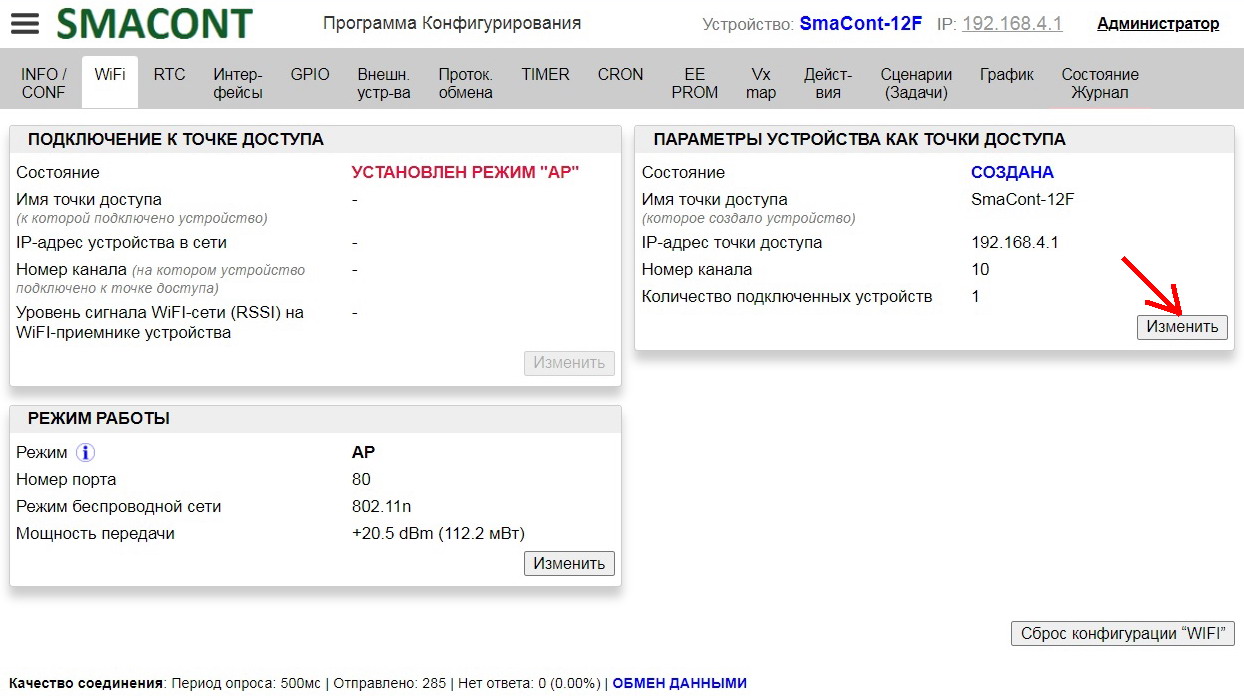
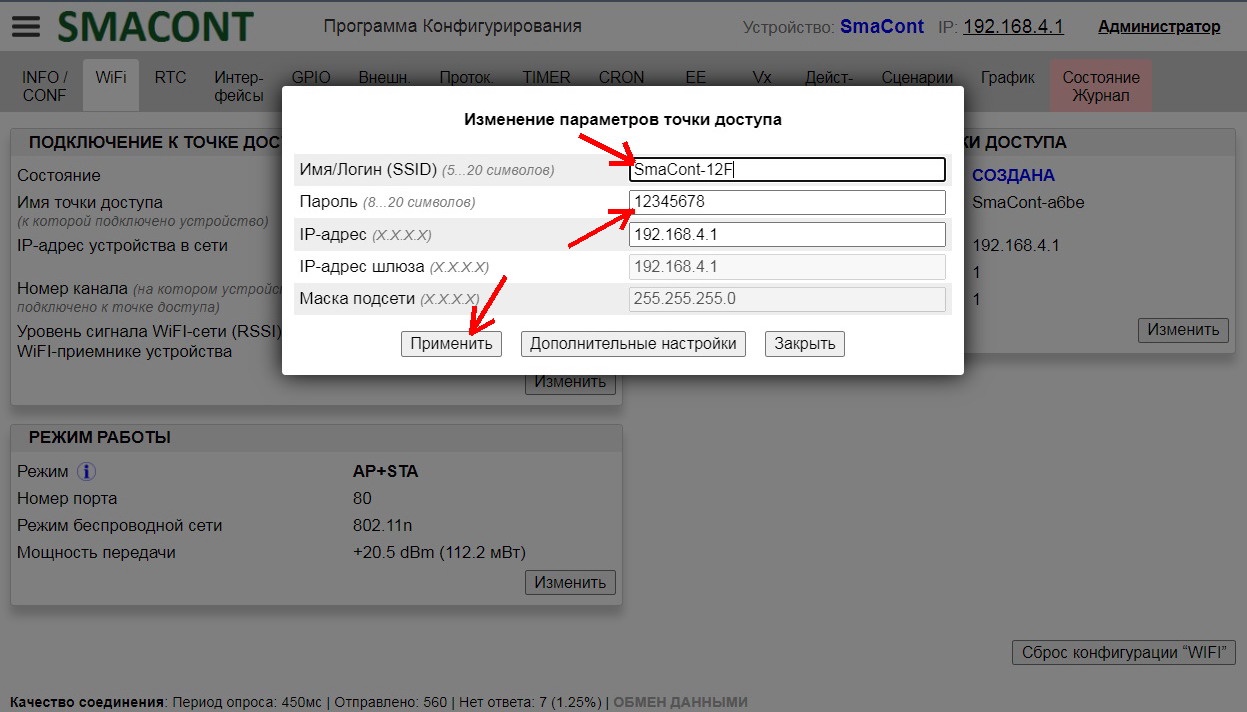
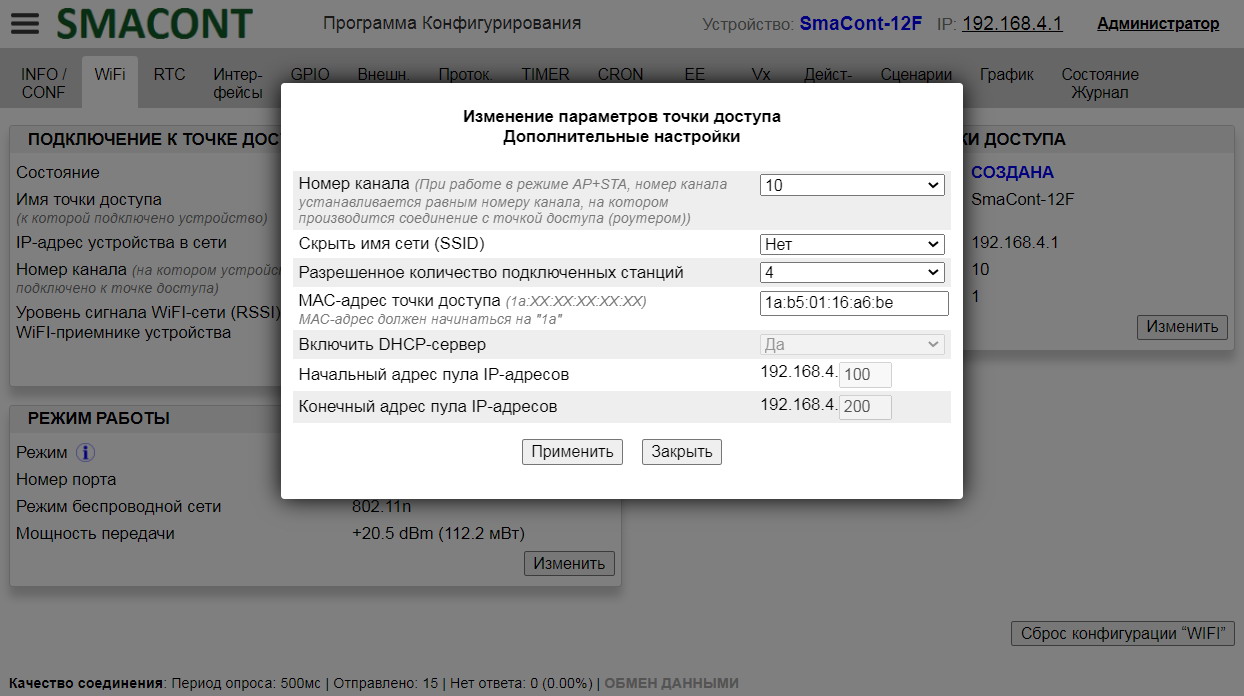
Advantages of this option (access point mode "AP"):
– there is no need for additional equipment (WiFi router);
– increased protection against unauthorized access. Two levels of access are realized:
1 level – login and password for the access point;
2 level – password of "Administrator" or "Operator".
TP-Link router as a wifi wireless signal adapter (WISP)
In the range of TP-Link routers, the client mode of the WISP adapter for receiving wifi signal is called "WDS Bridge". I took the TL-WR1043ND model as an example. Its administrator panel is located at 192.168.0.1 – go here to the menu "Wireless mode – Settings" and activate the checkbox "Enable WDS bridge" – additional fields for settings will open.

Here we do the same as with other routers – prescribe SSID, password and other data from the main network wifi, and then save the settings.
The video on configuring TP Link's client mode as a wireless network receiver shows it more clearly
How to connect a router in WISP client mode by Netis example?
Setting up a Netis router in client mode is also very simple – you need to configure all the basic Wi-Fi settings in exactly the same way as on the main access point.
- First, connect the router with a patch cord to your computer, go to the admin panel and activate client mode. Let me remind you, to get into the settings panel, you need to have the IP of the computer from the same subnet as the router (you can find it out from the manual or a sticker on the case)
- After that, go to the admin panel of the router, which will run in client mode, and activate the bridge mode, wireless adapter, client, or whatever else it is called.
- Then assign the router-client IP-address from the range that is specified in the access point settings. The easiest way to do this is to set the DHCP mode, so you don't have to add the settings manually.
 If you want to configure all settings yourself, specify the IP of the main router as the Gateway and the Primary DNS, and in the IP – the address of our router from the same subnet as the main one. That is, if the gateway (the main router's IP-access point) is 192.168.1.1, then our router in the client mode we give 192.168.1.2.
If you want to configure all settings yourself, specify the IP of the main router as the Gateway and the Primary DNS, and in the IP – the address of our router from the same subnet as the main one. That is, if the gateway (the main router's IP-access point) is 192.168.1.1, then our router in the client mode we give 192.168.1.2.  If you want to configure all settings yourself, specify the IP of the main router as the Gateway and the Primary DNS, and in the IP – the address of our router from the same subnet as the main one. That is, if the gateway (the main router's IP-access point) is 192.168.1.1, then our router in the client mode we give 192.168.1.2.
If you want to configure all settings yourself, specify the IP of the main router as the Gateway and the Primary DNS, and in the IP – the address of our router from the same subnet as the main one. That is, if the gateway (the main router's IP-access point) is 192.168.1.1, then our router in the client mode we give 192.168.1.2. - Save the settings, wait for reboot and connect it to the PC with the cable. To return to the control panel, enter the new IP of the router into the address bar of the browser.
- Now go to the section "Wireless mode" and set everything exactly as on the main router, from which we will receive the signal: Wireless mode, channel width, network name (SSID), security settings (encryption type, password for wifi) – everything is done the same with the main WiFi point.