This, for example, is what it looks like on LG TVs (new and old) :
- Does your TV have Wi-Fi? How to find out, where to look?
- Solution #1: check if Wi-Fi is present in the technical specifications of the TV
- LG TV example.
- Other options
- What for and how to connect?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What Smart TV and WiFi are for
- Advantages and disadvantages of built-in Smart TV and Wi-Fi
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Peculiarities of SPWF01Sx integration
- Wi-Fi module control
Does your TV have Wi-Fi? How to find out, where to look?
In this article, I'll show you a few simple ways you can quickly find out if your TV has Wi-Fi. Today, there are hardly any TVs on sale anymore with Smart TVs and without a built-in Wi-Fi module.
Looked around and found only a few models. Which means that in a little while, every smart TV will have built-in Wi-Fi. And that's the right thing to do. Otherwise, they came up with these proprietary, external USB Wi-Fi adapters, which had to be bought for a lot of money, and it was difficult to buy them. And now they are so hard to find. And you do not buy a TV for a year or two. Many of today's Smart TVs do not have built-in Wi-Fi. And you can only connect them to the Internet with a cable.
To begin with, you need to understand that if the TV is without Smart TV, there is definitely no Wi-Fi in it. In this case, it is not needed there at all. I have already written a separate article on this topic: Smart TV function in your TV: is it there or not, how to check it? But if there is support for Smart TV, it is not certain that there is Wi-Fi. There can be a variant that the connection to the Internet is only by cable, or via an external Wi-Fi receiver (which often must be purchased separately).
If you are wondering if your TV has Wi-Fi, or not, you can find out in several ways:
Let's look at the first two ways in more detail. Solutions are universal, suitable for all TVs: Samsung, LG, Sony, Toshiba, Philips, Panasonic, Hisense, TCL, Kivi, Ergo, etc. As for Xiaomi TVs, all models of this manufacturer have built-in wi-fi.
Solution #1: check if Wi-Fi is present in the technical specifications of the TV
All we need is to know the manufacturer and model of the TV, and access to the Internet. I don't think there's any problem with the latter. Well, the model of the TV can be found on the box, in the documentation, and on the sticker on the back of the TV.

Then you simply enter the name of the manufacturer and the model in the Google search engine, or Yandex. For example, I have Philips 43PUS7150/12. It is desirable to go to the official site of the manufacturer.
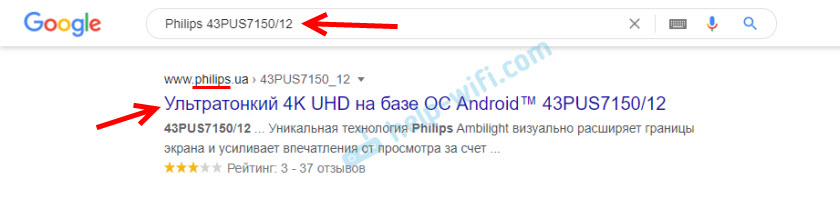
Or open some popular online stores and look at the specifications. There, as a rule, it is always specified the availability of Wi-Fi. I, on the other hand, recommend looking at the specifications on the official website. In my case, under "Connections", opposite "Wireless connection" it says support for built-in Wi-Fi 11n 2×2.

So there is wi-fi in my TV. I'm just not quite sure why it says "Dual Band". 5GHz Wi-Fi is not supported on this TV. Only 2.4 GHz. If it says 802.11ac support, it means your TV supports the 5 GHz band.
If the test shows that your TV does not support Wi-Fi connection, but you need to connect it to the Internet through a wireless network, read this article: How to connect a TV without Wi-Fi to the Internet via Wi-Fi.
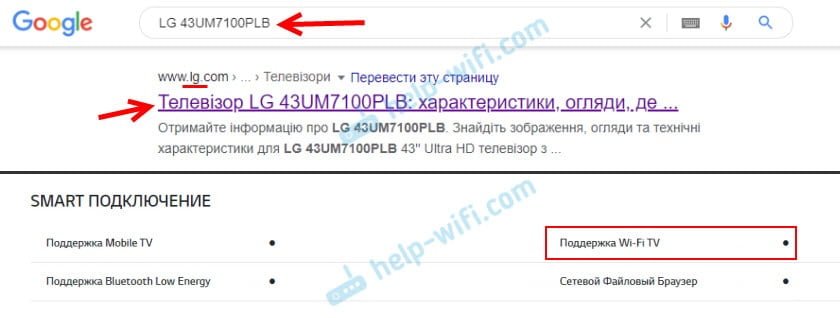
LG TV example.
Let's take the model LG 43UM7100PLB. Find this model on the official LG site and look at the technical specifications. If there is a dot next to "Wi-Fi support" it means that it is supported.
Other options
We have already found out that most TVs come already bundled with Wi-Fi, but there are other options:
- Connecting to the Internet by wire (Ethernet) – inconvenient, so very many have become concerned about the connection "over the air".
- External Wi-Fi adapter – bought, usually separately. It is connected to the USB port of the TV. And it has to be compatible with your model. And here with the compatibility is not always convenient. Therefore, built-in modules have earned popularity, the more technically it does not add much in price.
What for and how to connect?
Why do we need Wi-Fi on our television? For me this is a philosophical question, most of the time for nothing. Occasionally I watch Youtube or IVI movie on it, very rarely I use it to transmit a picture from my laptop or phone. Is it possible to do without it? Of course you can. But in any case, the presence of this feature is much better than the lack of it.
The methods for connecting the internet on your TV via wire and air are basically the same, and our site has pre-defined instructions for many manufacturers:
Frequently Asked Questions
To summarize why TVs need Wi-Fi, let's briefly answer popular questions on the subject.
This refers to the built-in Wi-Fi adapter for wireless connection to the network.
It is needed to connect wirelessly to the Internet, to access smart functions.
Smart TV is television, Internet, and pre-installed applications. Essentially, such devices work like tablets or smartphones, but with narrowly defined functions.
Needed if you need access to the Internet and online applications.
Bluetooth is most often used to connect Bluetooth headphones or speakers, and you can also use this module to transfer data from other devices that also have Bluetooth.
Leave your email and get the latest articles from our blog. Sign up to not miss anything
What Smart TV and WiFi are for

A TV with smart TV and WiFi allows you to watch regular analog TV as well as connect to a large number of digital TV channels, but its big advantage is the ability to connect to the World Wide Web. Media content is viewed through its own browser, if there is a built-in wi-fi you just need to enter the password after the first turn on.
To control the device using the remote control that comes with, with a separate button for your own browser.
Smart TV can work with all possible third-party devices – PCs, laptops, tablets and smart phones, which can be synchronized by downloading a special program. Synchronization is based on the principle of Plug and Play (plug and play).
Expensive models with a diagonal of more than 32 inches can respond to simple voice commands, such as "next channel", can even recognize gestures, have a gyroscope and some other interesting features, which ultimately increase the cost of the device.
Although the Internet in Smart-TV has less functionality than in the same PC or laptop, its capabilities are impressive. First and foremost, it is watching movies online on special sites, as well as listening to music and getting information about the weather.
So how to choose a TV with Internet and wifi? The answer to this question depends on the needs of the user. Will he watch movies and programs from external media? Smart devices read any external storage devices – from a flash drive to a DVD.
And if the possibility of reading is provided, then there is also the possibility of recording the program of interest, provided that the channel does not have protection against such scanning.
Advantages and disadvantages of built-in Smart TV and Wi-Fi

Before deciding how to choose a TV with smart TV and with the ability to connect to a Wi-Fi router, you need to familiarize yourself with its strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages
It is the convenience and ease of connection to a wireless home network and the absence of wires, which do not add to the aesthetic appearance of the home.
Disadvantages
The weaknesses of the built-in features include a lack of stability, with occasional glitches at high viewing speeds.
When comparing the speed of content transmission over a wireless and cable network, wired connection is faster.
Last but not least, the high price of Smart TV with built-in Wi-Fi scares away potential buyers of devices.
Peculiarities of SPWF01Sx integration
From the schematic point of view the connection of the module to the external microcontroller is not difficult. The pin assignment of the module is described in Table 2. The wiring diagram of SPWF01SA.11 in the minimum configuration is shown in Figure 5. The main control interface is a 5V level compatible full UART with RTS/CTS handshaking and a maximum rate of 921 kbps. If the exchange rate is limited to 115 kbps, you can limit only the lines RXD1 and TXD1 (without the connection CTS1_DN, RTS1_DP), but this connection is not recommended by the manufacturer. In future firmware is expected to support SPI with higher data transfer rate.
| Signal line name | Type | Number pin number | Main function | Alternate function1 | Note |
| GPIO general-purpose I/O lines | |||||
| GPIO[0] | I/O | 16 | General purpose I/O port; restore factory settings2 | SPI MISO | Input pulled to ground; output compatible with 5 V level |
| GPIO[1] | I/O | 17 | General purpose I/O port | SPI MOSI | Input pulled to ground; output compatible with 5 V level |
| GPIO[2] | I/O | 19 | General purpose I/O port | SPI Chip Select | Floating input; output compatible with 5 V level |
| GPIO[3] | I/O | 1 | General purpose I/O port | SPI Clock | Input pulled to ground; output compatible with 5 V level |
| GPIO[6] | I/O | 22 | General purpose I/O port; denies Wake Up/Sleep3 modes | ADC 0 | Input pulled to ground; output compatible with 5 V level |
| GPIO[4] | I/O | 18 | General purpose I/O port | UART34 data input | – |
| GPIO[5] | I/O | 20 | General purpose I/O port | UART34 data output | – |
| GPIO[7] | I/O | 13 | General purpose I/O port; STA/Mini AP5 mode switching | ADC 1 | – |
| GPIO[8] | I/O | 4 | General purpose I/O port | UART24 data output; ADC2 | – |
| GPIO[9] | I/O | 7 | General purpose I/O port | UART24 data input; ADC3 | – |
| GPIO[11] | I/O | 11 | – | I2C SCL | – |
| GPIO[12] | I/O | 12 | General purpose I/O port | I2C SDA | – |
| GPIO[15] | I/O | 21 | General purpose I/O port | DAC | – |
| Status monitoring without alternative functions | |||||
| GPIO[10] | I/O | 5 | LED | – | Flashing in RUN mode |
| GPIO[13] | I/O | 15 | LED | – | – |
| GPIO[14] | I/O | 14 | LED | – | Power status display |
| UART1 control interface outputs | |||||
| RXD1 | I | 8 | UART1 data input | – | Output is compatible with 5 V level |
| TXD1 | O | 6 | UART1 data output | – | Output is compatible with 5 V level |
| CTS1_DN | I | 9 | UART1 "Clear To Send" input | – | Active low level; output is compatible with 5 V level |
| RTS1_DP | O | 10 | UART1 "Request to send" output | – | Active low; output is compatible with 5 V |
| Reset | |||||
| RESETn | I | 3 | Reset input | – | Reset requires 5ms active low; output is internally pull-up to 2.5V and not compatible with 5V level |
| Power and ground lines | |||||
| 3.3 V | – | 24 | Power supply voltage | – | 10 uF decoupling capacitor |
| Ground | – | 23 | Ground | – | – |
| Ground Paddle | – | 25 | Ground Paddle | – | Sufficient vias must be provided to allow for heat dissipation to the PCB ground layer |
| Built in Boot loader | |||||
| BOOT0 | I | 2 | Boot loader6 | – | – |
Wi-Fi module control
All the module's features can be controlled with AT commands and are similar to the way of controlling a GSM-modem with a built-in TCP-stack. The list of AT commands is given in Table 3. The complete list of interface messages that are possible between the controlling microcontroller and the module consists of:
- AT commands;
- Configuration variables;
- Module status variables;
- asynchronous unsolicited responses (WINDS).
Figure 6 shows directions of various interface messages.
Asynchronous unsolicited messages can arrive at random moments of time and look as follows:
After power-up, the module generates several unsolicited messages that reflect different hardware and software initialization stages, for example:
+WIND:13:ST SPWF01SA IWM: Copyright (c) 2012-2014 STMicroelectronics, Inc. All rights Reserved.
The module is ready to receive AT commands only after the message +WIND:0:Console active
| Various commands | |
| AT | Attention |
| AT+S.HELP | Display hint page |
| AT+S.FWUPDATE | Firmware update |
| AT+S.WIFI | Allow/Disallow Wi-Fi |
| AT+CFUN | Change current mode (reset) |
| AT+S.MFGTEST | Test for manufacturing process |
| AT+S.PEMDATA | Configuration of the certificate storage |
| AT+S.ECHO | Return "ECHO" on a serial port |
| AT+S.HTTPDFSUPDATE | Update static HTTPD file system |
| Configure | |
| AT+S.GCFG | Read current configuration value |
| AT+S.SCFG | Set configuration variable |
| AT+S.SSIDTXT | Set text value of SSID |
| AT+S.STS | Get current states/statistics |
| AT&V | Display all configuration values |
| AT&F | Restore factory settings |
| AT&W | Save current settings |
| AT+S.NVW | Write production settings |
| File management | |
| AT+S.FSC | Create file |
| AT+S.FSA | Add to existing file |
| AT+S.FSD | Delete existing file |
| AT+S.FSL | Show list of file names |
| AT+S.FSP | Print file content |
| Network commands | |
| AT+S.PING | Send ping to a specific address |
| AT+S.SCAN | Scan channels |
| AT+S.HTTPGET | Send HTTP GET request |
| AT+S.ROAM | Reconnect to Wi-Fi |






