This is important to understand because overlapping Wi-Fi channels can interfere with one another. With 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi, there are four non-overlapping 20 MHz channels: 1, 6, 11, and 14. Note that due to varying regulations, not all channels are available for use in all locations. For example, only 11 channels are available in the United States.

- What's the best wi-fi channel width for your home Internet access, 20 or 40?
- What channel width to set
- Different channel widths and their features
- How to set the channel width on your router
- What is the best 2.4 GHz wifi channel for a router?
- Selecting the most powerful channel on the 5 GHz
- How to Choose a WiFi Channel Width (20, 40, 80 MHz) – What's the Best Bandwidth for 2.4GHz and 5GHz on a Router
- What does the width of the wifi channel affect?
- Recap: What are WiFi channels?
- What is WiFi channel width?
- Set 2.4 GHz WiFi channel width to 20 MHz
- Set 5 GHz WiFi channel width to 20, 40, or 80 MHz
- Что нужно установить?
- What is width?
- How to set the channel width on the router
- Answers to questions
- What's Dual-Band Wi-Fi?
- 4 Ghz WiFi: 20 MHz vs 40 MHz vs 80 MHz
- Limitations and Considerations
- Bottom Line
What's the best wi-fi channel width for your home Internet access, 20 or 40?
Wireless computer networks are well included in the life of modern man. The desire of an average user to independently establish a local network connection and properly configure it is natural and understandable, but each action in the setting must be conscious. It is necessary to understand what leads to a change in one or another component of the Wi-Fi signal, what it can improve or deteriorate. One of these parameters, which directly affects the reliability of Wi-Fi, is the subject of this review.
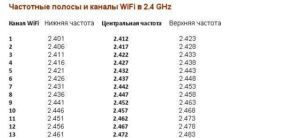
The channel width is the band from the lower boundary to the upper boundary. So, for the 2.4 GHz channel 5 standard with a center frequency of 2432 MHz (2.432 GHz), the lower bound of the band is set at 2421 MHz, and the upper bound is 2.443 MHz. Thus, the bandwidth is 21 (conventionally, 20) megahertz. The standard range provides several discrete bandwidths from 10 to 160 MHz. Household networks use 20 or 40 MHz bands. For a practical understanding of this value, an analogy to vehicular traffic is often given. If there is a highway with 20 lanes, half as many cars can drive on it at the same time as on a highway with 40 lanes. Consequently, with a 40 MHz frequency band, the channel can handle more devices than a narrower 20-MHz band.

Important! In most cases, the router sets the channel number automatically.
What channel width to set
It would seem that 40 MHz Wi-Fi bandwidth is clearly better, and you can forget about 20 MHz when setting up your router. In fact, it's not that simple:
- A wider frequency band is more susceptible to interference, reducing connection stability, especially if signal strength is low. For example, from wireless devices that have become part of our everyday lives. To use an analogy with the freeway: a wide road that takes up more space is easier for unauthorized vehicles that do not recognize the established rules;
- a wider signal in turn increases the likelihood of crosstalk from other devices;
- possible conflict situations with Wi-Fi, installed in the neighboring room. An analogy: neighbors have built their own highway, without coordinating with anyone the plan of its laying (choice of Wi-Fi channel), and it crosses other highways in random places. The wider the lane (width of the highway), the greater the probability of such a conflict.
Different channel widths and their features
Channel widths can vary, including 20, 40, 80 and 160 MHz. Often routers operate on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz bands typically use 20 and 40 MHz wide channels, and the 5 GHz bands use 40, 80, and 160 MHz wide channels.
Choosing the optimal channel width depends on a number of factors, such as the number of devices on the network, their location, types of applications, and possible sources of interference. In general:
- For 2.4 GHz, 20 MHz is recommended because it reduces the chance of overlap with other networks and provides good compatibility with various devices.
- For 5 GHz, you can use wide channels (80 or 160 MHz) for maximum speed if your home does not have many other networks that might cause interference.
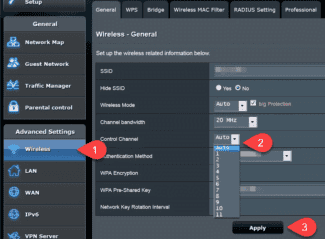
How to set the channel width on your router
You'll need to access your router's administrative interface to set the Wi-Fi channel width. The steps may vary slightly depending on the router manufacturer and model, but the process is usually as follows:
- Enter the IP address of the router in the address bar of your browser. This is usually 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1.
- Enter your username and password to access the router's settings. If you haven't changed them before, look for the information on the router label or in your documentation.
- In the router settings menu, find the section related to wireless settings (Wireless Settings).
- Select the desired channel width for each band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz).
- Save the changes and reboot the router if necessary.
- Solving problems with Wi-Fi channel width
Clear instruction, using a TP-Link router as an example:
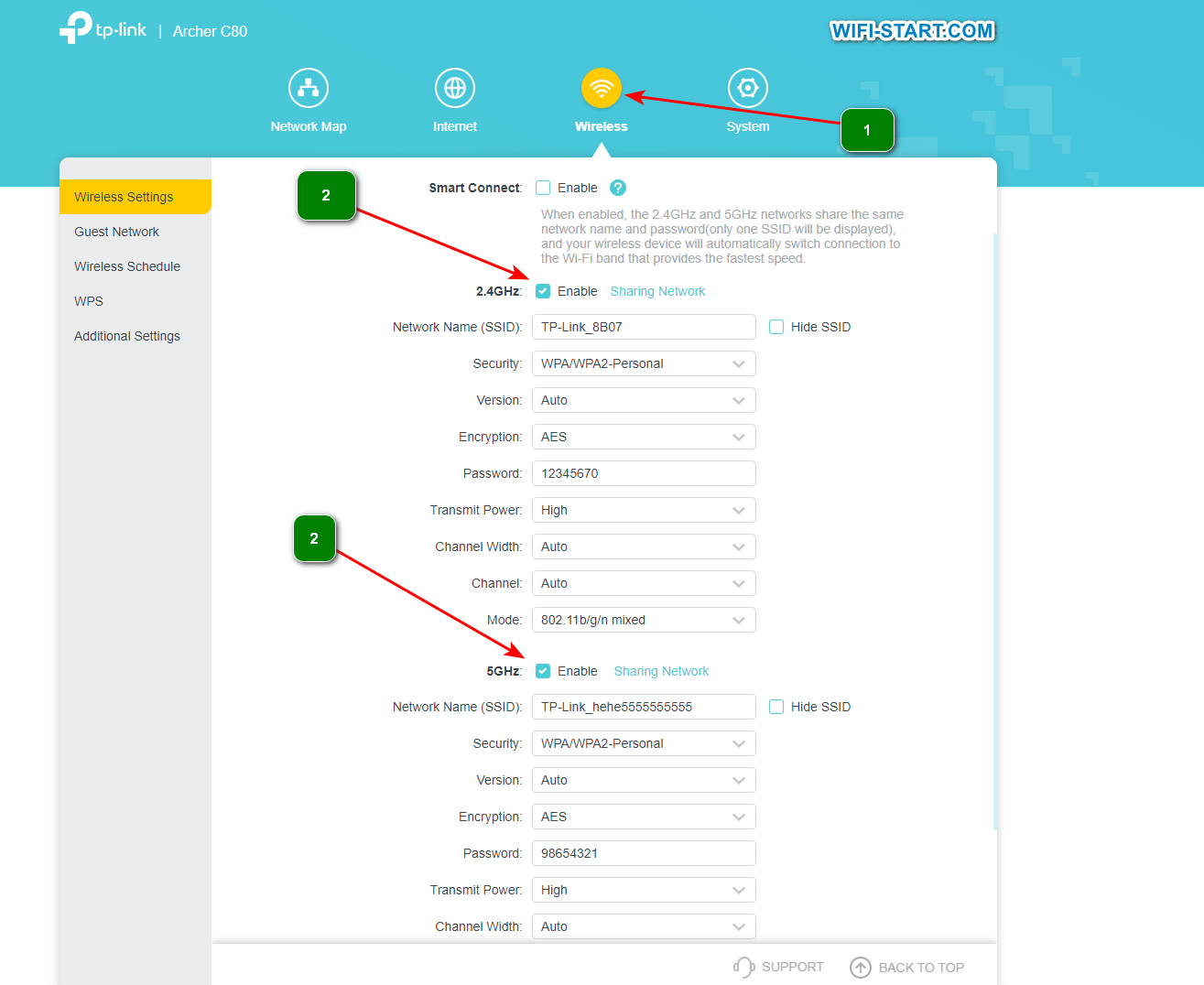
If you encounter problems such as slow speeds, signal loss, or device compatibility, try changing the channel width. Start with the smallest width and gradually increase it, observing signal quality and network performance. You may have to experiment with different channel widths to find the best option for your situation.
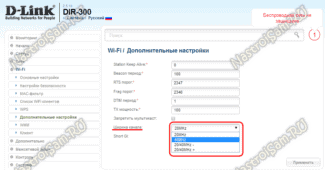
What is the best 2.4 GHz wifi channel for a router?
For the best connection quality, you need to reconfigure the channel and choose a frequency that is 5 units different from the most used. In our case from the first and the tenth (there are 14 in total, by the way).
Therefore, the fifth and sixth channels will suit me best, but since "6" is already there, let's choose "5".
There is also a similar program for the laptop – Inssider. You install it, run it, and it will start scanning the air and determine the parameters of each network in the access area. We will be interested in the parameter "Channel"

For convenience, here is a detailed list of non-intersecting channels:
Did you notice that I didn't specify 12, 13 and 14? Well, the thing is that different countries have different regulations regarding the number of allowed WiFi channels. For example, in Japan it is all 14, but in France it is only 4. In Russia and the CIS countries, 13 channels are supported. Well, if you have a router made in or for the States, it will only have 11 channels.
Once you have selected the most suitable free channel, you can move on to the settings on the router.
Selecting the most powerful channel on the 5 GHz
The 5 GHz band no longer uses 12-13 channels, but all 17. At the same time, the higher its number, the higher the frequency and therefore the lower the bandwidth. Therefore, if in addition to high speed and absence of interference it is important for you to maintain a wide signal coverage area, it is recommended to set the channel value from 36 to 64 in the settings.
To change the WiFi channel on your TP-Link router, you need to log in to the admin panel at http://192.168.0.1. I told you about how to find out the authorization data in another article. Usually the login and password are the same and look like "admin" by default.
Then you have to go to the settings section of the wireless mode for which you want to change the TP-Link WiFi channel. That is 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz if your router is dual band. In the "Main Settings" in the TP-Link admin of the selected frequency, look for the "Channel" drop-down list. Here we choose the one we want, to which we need to reconfigure the router. Then click on the "Save" button.

In the new version of the TP-Link router control panel, the menu for changing the WiFi channel is in the "Advanced Settings" tab. Here you need to go to the "Wireless Network" section and select the "Wireless Mode Settings" menu item
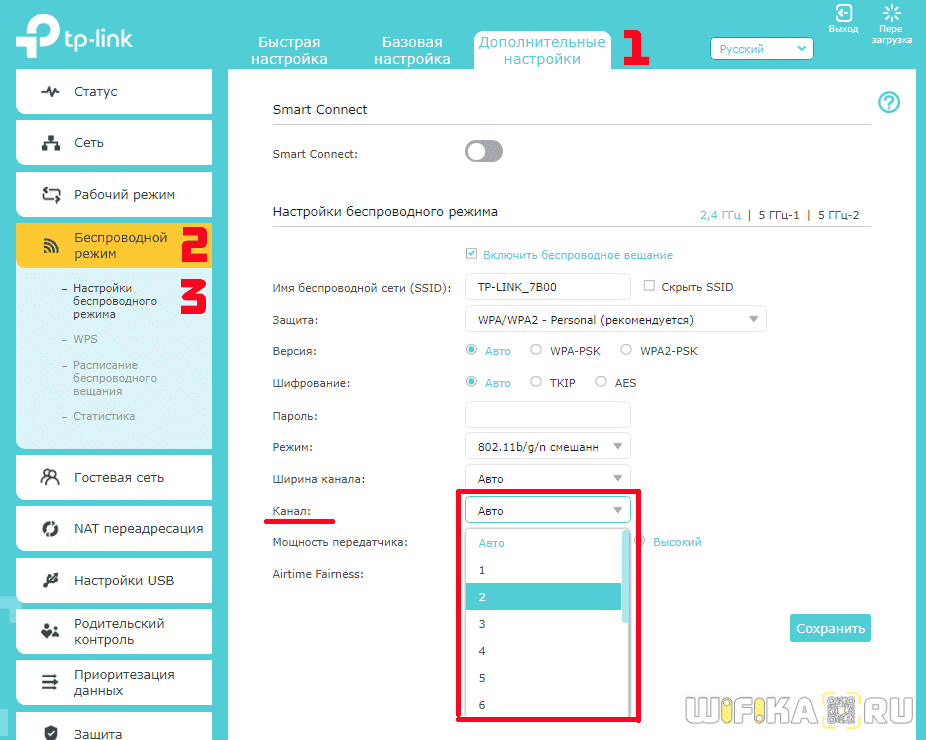
How to Choose a WiFi Channel Width (20, 40, 80 MHz) – What's the Best Bandwidth for 2.4GHz and 5GHz on a Router
When connecting a router, many users are confused by the "WiFi Bandwidth" option that comes up when setting up their wireless network. For each of the frequency bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), it has a choice of several values – 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz or auto. Which one is best to choose? Ideally, you could leave everything to automation, so that the router itself, based on its analysis of the current state of the network, would choose the best mode for work. However, as you know, the robot does not always work correctly. And to fine-tune your WiFi, it makes sense to figure out for yourself what the channel bandwidth affects, and which one to choose and how to change it later if necessary.
In simple words, wifi channel width (Bandwidth, Channel Width) is its bandwidth.
I have already talked at length about what a wifi network channel is. To make a long story short, it is a separate segment within a single frequency band on which wireless devices are operating. In the picture below, they are marked as arcs.

So that all these gadgets don't interfere with each other, they are separated into different segments by manually selecting the freest channel. In the 2.4 GHz band there are only 13 channels, in the 5 GHz band there are 33. And the length of these arcs is exactly the width of the channel. By default it is 22 MHz, but in the router settings for simplicity they specify "20 MHz".

In order to make it wider, you can increase the value by 2 times, so that it becomes 40 MHz. And here we come to the next question.
What does the width of the wifi channel affect?
The width of the wireless channel directly affects the speed. The wider the channel, the more devices can communicate with each other at the same time. It's the same as comparing a single track railroad to a two-, three-, or even four-lane railroad, which can pass many more trains and carry more passengers at the same time. Only the passengers in our case are the data exchanged between laptops, computers, smartphones and TV set-top boxes via a wifi router. Therefore, you can manually assign a certain value to it.
It would seem, put the highest number – and there will be happiness? But it's not so simple. The fact is that outdated devices may not support more modern standards. And if, for example, you set the channel width of 40 MHz, they will not be able to connect to such a wifi signal. In addition, the wider the channel, the less distance the signal "shoots", and thus the reception area is reduced.
Therefore, there is a general rule, which channel width is optimal to choose in this or that case
- 20/40/80 MHz (Auto) is the default value, which is suitable for most users. It is recommended to leave it for universality and in the absence of problems with the network
- 20 MHz – can be set in the presence of interference from other people's routers and unstable wireless signal. It provides three non-intersecting 2.4GHz channels, which means that if you connect three devices to the router at the same time, they will not interfere with each other in any way. Suitable for apartment buildings with many surrounding networks that cause interference
- 40 MHz – cuts off the ability of some gadgets to work with the network. Also in 40 MHz there is only one channel that does not overlap with others, which means that only one device will work comfortably on wifi. Connecting each new one creates additional interference. Only use it if automatic mode does not work or if you live in a separate house and use a Mesh system.
Recap: What are WiFi channels?
Before we discuss WiFi channel width, let's recap what WiFi channels are. Essentially, WiFi channels are smaller bands within WiFi frequency bands that are used by your wireless network to send and receive data. Depending on which frequency band your router is using, you have a certain number of WiFi channels to choose from:
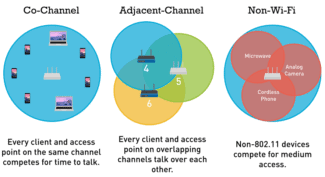
The key takeaway here is that some WiFi channels are better to use than others because of interference, specifically Co-Channel interference and Adjacent-Channel interference. In the former, devices are competing for time to talk on the same channel. In the latter, devices from overlapping channels are trying to talk over each other. You can avoid such interference by choosing to use a non-overlapping, uncrowded WiFi channel.
Additionally, there are reasons to use one frequency band over the other; learn more about these reasons here!
What is WiFi channel width?
WiFi channels are each allotted a 20 MHz segment in the frequency band they're in, and can also be bonded together to form wider segments. The width of a WiFi channel dictates how much data can pass through and at what speed, where the wider channels are usually associated with more data transferred at faster speeds— at least, when they aren't impacted by interference.
Interference is more common in certain frequency bands and on certain WiFi channels than others. Depending on the likelihood of interference, there are recommended WiFi channel width settings for routers and access points, as described by Apple for achieving optimal WiFi performance with iOS devices. However, the same recommendations apply to boosting WiFi performance with any connected device. Here's a summary:
Set 2.4 GHz WiFi channel width to 20 MHz
It is typically advised to use the narrower 20 MHz WiFi channel width when in the 2.4 GHz band. The main reason is because there are several overlapping channels in this band— in fact, 8 out of the 11 channels overlap. As we know, overlapping WiFi channels are one of the main causes of network interference. So, if you were to choose a wider channel width that bonds multiple overlapping channels in this band, it is more likely than not that you will experience a weaker wireless performance than the expected faster speeds.
Set 5 GHz WiFi channel width to 20, 40, or 80 MHz
Wider WiFi channel widths— including 40 MHz and 80 MHz— are best used in the 5 GHz frequency band. In this band, there are not only significantly more WiFi channels, but also less overlapping channels (24 out of 45 do not overlap). As such, the 5 GHz band is known for being less crowded and is more equipped to support wide WiFi channel widths, in addition to the narrow 20 MHz width.
When adjusting WiFi channel width settings for this band, the key is to enable support for all channel widths rather than for a single wide channel width. Doing so will ensure no client devices are prevented from connecting (e.g., a device may only support 40 MHz channels, and if you enable a 80 MHz-only mode, it won't be able to connect).
Что нужно установить?
Сначала хотелось бы разобраться с практическим вопросом, а вся теория уже будет ниже, дабы не напрягать читателей, ищущих лучший вариант пеленками текста. So, here are the basic values on 2.4 GHz routers:
- 20/40 MHz (Auto) – recommended to set if there are no problems.
- 20 MHz – recommended to try if you suspect general interference from neighbors and poor Wi-Fi performance.
- 40 MHz – a special case if the router is not listening. Better to try with Auto.
The newer 5 GHz routers have another mode: 20/40/80 MHz. The use is similar.
Pure modes like 40 MHz are not recommended by IEEE 802.11n standards because they can cause incompatibility between older devices. That's why routers sometimes have only 2 modes – 20 MHz and Auto.
What is width?
Very briefly, channel width is the bandwidth of a channel.
But there is nothing cooler than the word "width" itself. A little bit of theory. The entire frequency range around 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies used in Wi-Fi is divided into channels – small frequency bands, so that it was possible to accommodate a lot of devices within one frequency without a strong impact on each other. In the 2.4 GHz band, the standard allocates 13 of them:
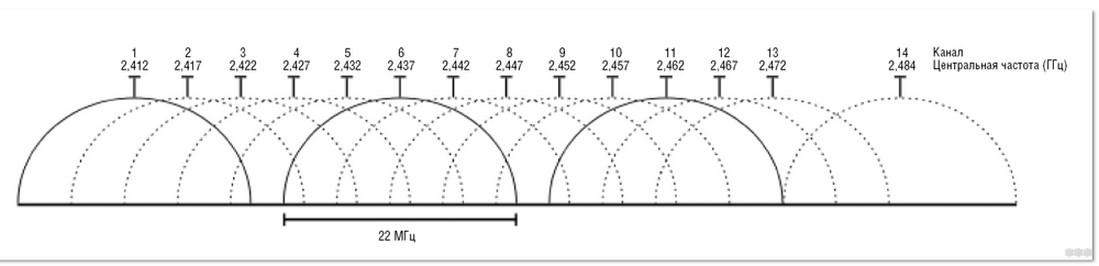
Do you see those 22 MHz wide arcs? That is the width of the channel. Notice how the channels overlap each other. It's the same in life, the neighbors' Wi-Fi in our house somehow affects our network as well, and in the worst case, there can be so much interference that the network speed will just fall through the cracks. That's why the topic of channel selection and moving to 5 GHz (where the overall width and number of channels is greater) has become more and more relevant lately.
But it turns out that you can set the width at 40 MHz. I.e. the difference would be – that the channel would take up more space. What will change from this? It will change its bandwidth. To put it in a nutshell – there is a country dirt road. A tractor drives on it, and everyone else is kind enough to fall into the ditch, because there is no room. And there is the Moscow Ring Road – there are more lanes, in general more cars pass through, but also sometimes it is worth it. And now imagine that on the Moscow Ring Road to demolish everything and lay there a dirt track…
How to set the channel width on the router
To configure the Wi-Fi channel width, you will need to access the administrative interface of your router. The steps may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer and model of the router, but the process usually goes like this:
- Enter the router IP address in the address bar of your browser. Usually this is 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1.
- Enter the username and password to access the router settings. If you have not changed them before, look for information on the label of the router or in the documentation.
- In the router settings menu, find the section related to wireless settings (Wireless Settings).
- Select the desired channel width for each of the frequency bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz).
- Save your changes and reboot your router if needed.
- Troubleshooting Wi-Fi Bandwidth Issues
Visual instruction, using the example of a TP-Link router:


If you encounter problems such as slowdown, loss of signal, or device compatibility, try changing the channel width. Start with the smallest width and gradually increase as you monitor signal quality and network performance. You may need to experiment with different channel widths to find the best fit for your situation.
Answers to questions
Wi-Fi channel width determines the frequency range on which your network operates. The wider the channel, the more data can be transferred per unit of time, which usually leads to an increase in the speed of the Internet connection.
Channel widths vary, including 20, 40, 80, and 160 MHz. Often routers operate on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
Choosing the optimal channel width depends on a number of factors, such as the number of devices on the network, their location, types of applications, and possible sources of interference. In general, 2.4 MHz is recommended for 20 GHz, and wide channels (5 or 80 MHz) can be used for 160 GHz to achieve maximum speed if your home does not have many other networks that can cause interference.
To set the width of the Wi-Fi channel, you will need to access the administrative interface of your router and change the settings in the corresponding section of the wireless settings.
If you run into problems, try changing the channel width. Start with the smallest width and gradually increase as you monitor signal quality and network performance. You may need to experiment with different channel widths to find the best fit for your situation.
What's Dual-Band Wi-Fi?
Dual band refers to Wi-Fi routers that support both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. Using a dual-band router allows you to get the "best of both worlds". Higher speeds and lower interference for 5 GHz devices, and wider range for 2.4 GHz devices. It is very common for modern Wi-Fi routers to support dual-band functionality.
With an understanding of Wi-Fi frequencies and channel bonding, we can now dive into the decision-making process. As we go, remember that a prerequisite for using any particular channel width is device support.
4 Ghz WiFi: 20 MHz vs 40 MHz vs 80 MHz
If you're using 2.4 GHz, the answer is simple. The best bandwidth for 2.4 Ghz is 20 MHz.
In the majority of cases, using wide widths on 2.4 GHz isn't worthwhile.
The performance tradeoffs from interference on overlapping channels will likely outweigh the throughput benefits. One possible exception to this rule is remote areas where there are not many other Wi-Fi networks or devices.
Additionally, 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi and 20 MHz channel widths offer the broadest range of client device support. If you need to support legacy devices and Wi-Fi standards like 802.11b or 802.11g, you'll need 2.4 GHz and 20 MHz.
Limitations and Considerations
Even if you live in a remote area with no neighbors, going to the widest channel possible is not always your best bet.
Most limitations, apart from interference, come from compatibility.
First, not all devices are 5 GHz compatible. And as discussed before, if you are using 2.4 GHz, it’s best to stick to regular 20 MHz channels.
Even if your devices are compatible with 5 GHz frequencies, they might not be compatible with wider channels. Some devices only support 20 MHz widths and simply won’t be able to connect to any other channel bandwidth.
You might find it difficult to widen channels without interference. If that’s the case, consider moving less important devices to the 2.4 GHz frequency. Clearing up space for wider channels in the 5 GHz frequency for your main devices can make a big difference.
Bottom Line
Increasing channel width based on your compatible devices and neighboring signals can offer big performance improvements.
However, there are a lot of things to consider, and you need to be mindful of interference.
Setting up wider channels without being careful can bring more drawbacks than benefits. You will most likely be better off letting your router decide (auto) or sticking to 20 Mhz channels. Especially for 2.4 GHz.
Increasing channel width is not the only thing you can do if you want faster speeds. If interference is too much of a problem, there are several other ways to boost your performance.
Read More: