If the router's task is limited to connecting to the Internet for a few devices, this is enough. It is not uncommon for weak signal and the appearance of "dead zones" even in such conditions. The reason for this is the same interference.
- A powerful wifi router
- Powerful Wi-Fi router
- The most effective way
- Antenna rotation
- How does an expensive one differ from a cheap one?
- TP-Link AC5400 – gaming router
- How to increase the speed by simple methods
- Expanding the signal coverage area by technical means
- Improving network coverage with the right installation
- Let's summarize .
- Author: Daria Tilnaya
- WiFi coverage
- What can be the range
- Proper router setup
- How to correctly position the router antennas to achieve maximum Wi-Fi signal range
- Complain to comment
- Method of calculating the effective distance
- Effective distance without obstacles
- Results of practical observations
- Maximum distance, confident reception
- What not to do
A powerful wifi router
The range of a wifi router depends on the type of router or access point used. Factors that determine the range of the router (access point) are:
- total transmitter power;
- The type of 802.11 protocol used;
- The length and attenuation of the cables connected to the antenna;
- Obstacles and interference in the signal path in a given room;
- the gain of the router's antennas.
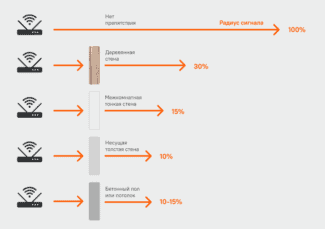
Range wifi router standard 802.11g, with the regular antenna (gain about 2dBi) is approximately 150m in the open and indoors – 50 m. But brick walls and metal structures can reduce this range by 25% or more. 802.11a uses higher frequencies than 802.11b/g, so it is more sensitive to various obstacles. In addition, the range of 802.11b or 802.11g Wi-Fi networks is greatly affected by interference from microwave ovens. Tree foliage is also a strong obstacle because it contains water, which absorbs the microwave radiation of the band in use. For example, heavy rain weakens the signal in the 2.4GHz band to 0.05 dB/km, thick fog – 0.02 dB/km, and the forest (dense foliage, branches) – up to 0.5 dB/meter.
Choosing a Wi-Fi router, the range can be roughly calculated using a special calculator, which is slightly below, it is designed for D-Link equipment, but the formulas and methodology used there will be suitable for any other.
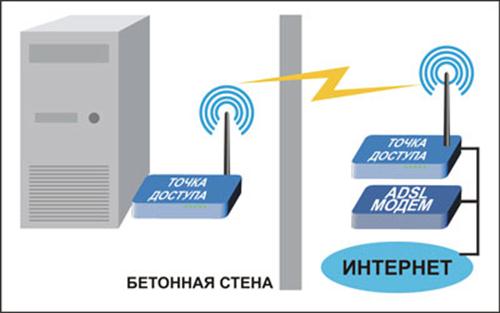
If creating a radio bridge between two networks, it must be taken into account that the space around the straight line drawn from the receiver to the transmitter must be free of
absorbing and reflecting obstacles in a radius equal to 0.6 of the radius of the first Fresnel zone. The size of this zone can be calculated by the following formula:
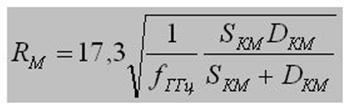
Powerful Wi-Fi router
If you choose a powerful router, its range and reception quality should satisfy your requirements.
The power of a wifi router is largely determined by the power of the signal boosters in it.
A powerful router on the Realtek 8187L chipset has not only a high power of 1 watt, but also large-scale support. Drivers for this chipset are supported by all operating systems. If you use an external optional antenna, the distance can reach up to 5 km.

Rasprostranenye brands Alfa, NEtsys, Senao EnGenius EUB Ext High-Power, Wifly city 8G , 20G , AIRLIVE, G-Sky GS-27USB-50, KASENS.

Amped Wireless has released its most powerful router, the R20000G High Power Wireless-N, which features 600 mW of 2.4 GHz signal amplification.
The R20000G is capable of two networks: 5000 MHz and 2400 MHz. Router provides indoor coverage up to 930 square meters. Two powerful antennas with 5 dB/inch of gain are connected to the router, but they can be replaced with more powerful ones.
The most effective way
A significant impact on the signal strength and speed of the Internet will only be able to buy a router more powerful. In practice inventing all sorts of amplifiers with your own hands from the Internet will not give any significant result.
Most devices on the market are limited to 100 mW. For more serious devices you need a license, but they can be found on the market.
The most popular among the devices with a large range of action, which you can install in your apartment, are:
- MikroTik routers, such as hAP AC, with an external antenna, the transmitting Wi-Fi module power is limited to 1W;
- ASUS with support for AiRadar technology, such as RT-AC3200, where the quality of communication is achieved by creating a directional signal for each client.
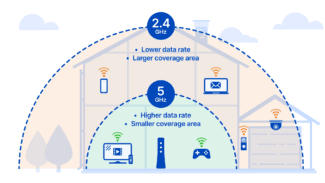
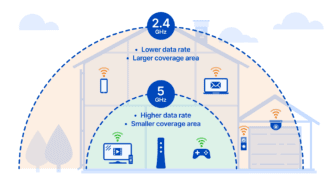
If you decide to buy a new device, consider buying one that supports the 5 GHz band. This channel is much freer than the 2.4 GHz band, and therefore the signal will be jammed less. Especially if you live in an apartment building where there are a couple more of these in the neighborhood, and almost every apartment has a wireless network.
Now let's look at some less effective but working methods for increasing the Wi-Fi range.
Antenna rotation
The coverage area is shaped like a torus – a bagel, not a sphere. Waves do not propagate in all directions, but rather in concentric circles on water. To change the plane of wave propagation, the antenna rotation function is provided. It is best if it is in a vertical horizontal plane position and the device stands in such a part of the apartment that all consumers receive this signal.

With the antenna pointing upwards, the toroidal field spreads horizontally throughout the apartment. The neighbors above and below will not get much. Below them, dead spots are likely to form – areas with negligibly weak signal.
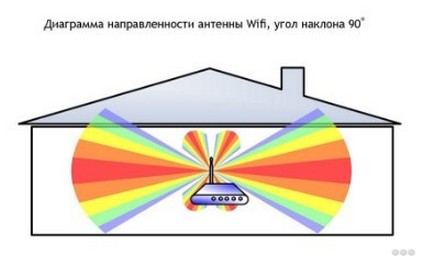
Placing the router at a height where most customers are, and pointing the antenna upward is the best way to improve Internet speeds.
How does an expensive one differ from a cheap one?
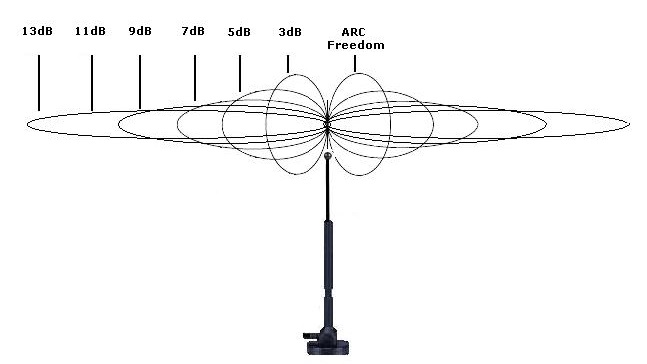
First, the expensive ones are more likely to have good antennas with high gain, which in itself increases the coverage area of the Wi-Fi network. Also they are usually on expensive models from 3 pieces. On expensive models, put a few powerful antennas. The thing is that when you increase the antenna gain, the coverage beam decreases. That is why you need to install a lot more antennas.
Also on such devices, there is powerful hardware, which allows you to simultaneously work with network resources – a large number of devices. If you have a large family, it is necessary to connect several computers, PCs, laptops, surveillance cameras – then a cheap model in a couple of months will simply fail. Now I will present my top best and longest range routers.
TP-Link AC5400 – gaming router
Powerful 4-core processor with a clock frequency of 1.8 GHz + in addition comes 3 co-processor. Supports 3 bands: 1 – 2.4 GHz and 2 – 5 GHz. All ports are 1 Gigabit, plus there are two built-in USB 3.0 ports. MU-MIMO support allows a large number of users to use network resources simultaneously.
There is 1 Gigabit of RAM built in. Rumor has it that it even penetrates 3 walls. Perfect for gamers – if ping in the game is important. Increased speed in two bands. Even at 2.4 GHz, the maximum speed in a local connection is 1 Gbit per second. It is the "RangeBoost" technology that allows you to use the network at a great distance from the station. It uses VPN data encryption to connect, without reducing the speed of the Internet. Costs, however, very expensive – from 27000 rubles.

How to increase the speed by simple methods
- Check the status of the router. Make sure that the antennas are turned in the working direction (looking vertically upwards).
- If necessary, move the router to an open space, for example, hang it on the wall 20-40 cm below the ceiling.
- Turn off torrents and other "rocking" sites, which can severely degrade the quality of your router's connectivity.
- Make sure that the router is connected to operate in the 5 GHz band. Manually disable the 2.4 GHz band. Make sure beforehand that there are no devices operating exclusively on this frequency.
If all these measures do not help, you may want to consider buying a more powerful device that gives more coverage.
Expanding the signal coverage area by technical means
Method #1 – to increase the signal range use a wi-fi far-end router. A router with a capacity of about 1 W with the possible connection of antennas is able to provide wi-fi coverage for kilometers. Recall that officially it is forbidden to use routers with a power of more than 100 mW without a license. However, you can find them on sale.

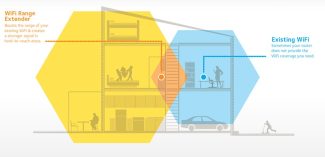
Method #2 – organize a system of several routers or using repeaters. You won't have to look for banned devices or install antennas. But it is not always possible to install an additional access point, even wireless, on the desired path.
There is another disadvantage is the quality of the repeatable signal. First, if you use additional router points, it will be twice as bad. Secondly, regardless of the device, the child networks will only work properly when the air is free.

Method #3 is to increase the range of the router by installing an effective antenna. This is an option to increase signal strength without buying a forbidden router. It is worth looking at the specifications of the antenna. The market offers options with a gain of up to 13 dB.

This will increase the coverage area, but there will be "dead zones". The plus side is that the router is also good at picking up signals from devices. This will be needed wherever a wi-fi camera is connected, the range of which is also enhanced. Not only can a more powerful antenna improve the connection, but multiple antennas on the same router can also improve the connection.
Another type of router that covers a larger area is the 5 GHz dual-band. It benefits from operating on a free frequency. But in addition to being expensive, it doesn't fit all gadgets, cameras, and other devices.
Improving network coverage with the right installation
Sometimes you can achieve the coverage you need without the expense of long-range wi-fi transmitters, antennas, and repeaters.
- Vertical Antenna Positioning. In a tilted position, the signal is spent spreading into the floor and ceiling. This is more of an installation optimization, but will work for a small expansion of coverage;
- optimal location of the access point. The latter should be located as close as possible to the receiver or equidistant to several;
- minimum amount of interference between the router and the devices. Either remove serious obstacles, or arrange the devices so that there is no interference between them. This is difficult to arrange;
- Changing the router mode. The new 802.11n mode has better propagation and signal quality. The inconvenience is the inability to connect to equipment with 802.11 B/G;
- changing the channel of the router. This is done in the settings. In fact, this method is a special case of the third point. It will only help against interference of neighboring networks;
- amplify the power. It is again a question of settings. Often only 75% of the possible power is set. But by changing the setting to the maximum, there is a risk of signal quality degradation;
- blocking the signal from propagating in the wrong direction. This is where metal-containing materials that do not allow the signal to pass through can help.

Some of these ways are difficult to do in practice. If you can still re-hang a mirror, you can not do anything with a reinforced concrete wall. Finding a suitable location for an access point is easy, but not the fact that there will be an outlet. In addition, these means are not very effective, but not too expensive and solve some problems. In any case, the method must be chosen according to the purpose. Next, consider the configuration of the network at the organization of video surveillance.
Let's summarize .
✅ When choosing a router, pay attention to the frequency. It is best if you have two frequencies at once – 2.4 and 5 GHz. This option is suitable for both a small apartment and a large house.
✅ Wi-Fi 4 is outdated.You need Wi-Fi 5 or Wi-Fi 6.
✅ To increase the coverage area, you need to choose the right place to install router: in the center of the room or near a computer, or if there is a load-bearing wall, near it, in a larger part of the room. It is also important to configure the antennas.
✅ Router options for small apartments: MikroTik hAP ac2 or TP-LINK ARCHER A8. For larger ones: Keenetic Air (KN-1611), Xiaomi Mi Router 4A.
✅ Router options for private homes: D-Link AC 1900 DIR-879, TP-Link AC5400, Xiaomi Mi Router HD Pro, Asus Rog Rapture GT-AX 11000.
✅ Office router options: Keenetic Ultra (KN-1810), Tenda AC18, Netis AC1200, TP-Link Archer C20, Asus RT-AC51U.
Author: Daria Tilnaya
When I write about technology, I am meticulous in my attention to detail. Not a fan of "quality quality", I look at the really important functions and features. Fan of visual storytelling: if you can explain complicated things with a picture, I draw and explain. I like to watch reviews, write reviews, and buy new appliances for the house.
WiFi coverage
As practice shows, such a parameter as the range of a wifi router plays an important role when choosing a router. After all, the further operation of your wireless network will depend on it.
Imagine, it is not very pleasant if the WiFi signal will not reach any point of your home, or the signal will be, but the speeds will be weak. So let's take a look at what the maximum range of your WiFi network can be and how you can increase it.
Usually, for an ordinary city apartment, the most common router is enough, its signal is distributed to all corners of the dwelling. But if you want to make a unified network with your neighbor, this is where problems can arise.
It happens that a person lives in a private house and wants to have Internet in the garage and the summer kitchen. Here we will have to think about the distance your router will cover and how it can be increased.
What can be the range
To make an analogy, the work of a wireless router can be compared to that of a mobile operator's tower, the only difference is that the router has a much smaller coverage area and the connection it makes via WiFi. The range of a standard router is around 100-200 meters and that is if there are no obstacles, but if it has reinforced concrete walls or steel constructions on its path, the coverage area can fall down to 50 meters.
Factors that affect the range of the network:
There are a variety of ways to increase the range of your wireless network. This parameter is affected by both the location of the router itself and its settings. Let's see what you can do to increase your network coverage.
Proper router setup
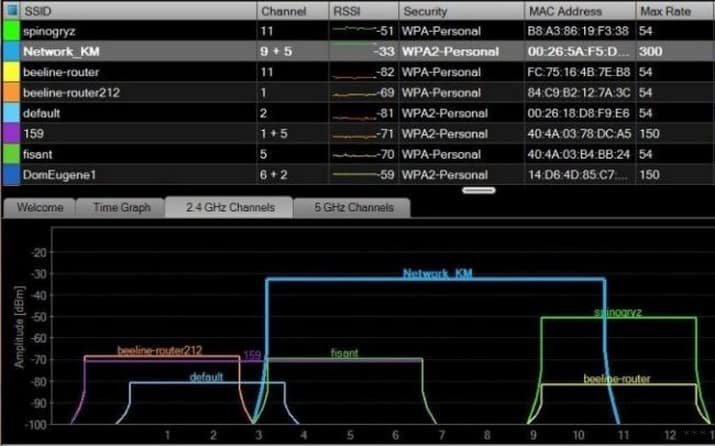
Your wireless coverage area can be severely limited by interference from your neighbor's WiFi devices, microwave oven, or even a regular baby monitor.
To avoid this, pay attention to which channel your router is operating on. If the channels are the same as a nearby router, you may have network problems and a significant reduction in range. So go into your router's settings and see what channel it is operating on.
How to correctly position the router antennas to achieve maximum Wi-Fi signal range
Quite often, visiting friends and relatives, I see that on their wi-fi routers antennas are located as you like, but not as necessary. And this happens because people simply do not know how the signal from wi-fi antennas spreads. But in fact it's very simple. And even the manufacturers themselves show exactly how the antennas should be located. Look at the box from your router (if you haven't already thrown it away), there will be a hint. Below I will tell you exactly how to position the antennas for better signal reception and transmission.
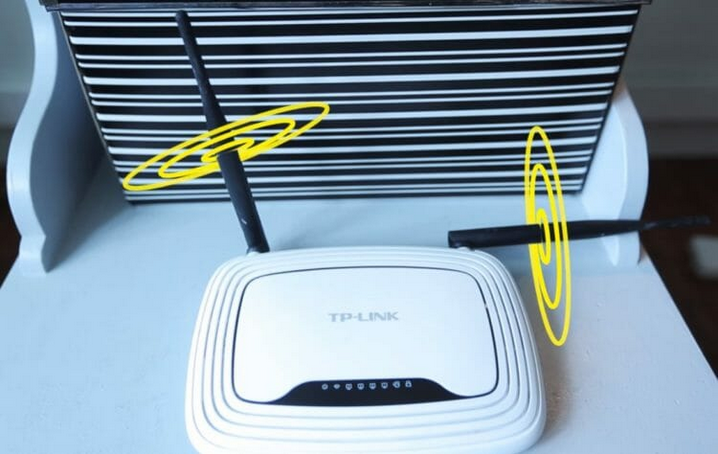

In order to understand how to place the antennas on the wi-fi router, it is necessary to understand how the signal from these very antennas is dispersed. And here, of course, not everything is so simple. And there are many different types of antennas. But we are interested specifically in the antennas in household routers, which are usually a spring, with the right number of coils, hidden in a plastic pin. The classic antenna on a router looks like this:


This is the type of antenna installed in most home routers. Although there are models with built-in antennas and omni-directional antennas. But we will not consider them, because in this case the manufacturer himself took care that the antennas were installed in the right direction.
Now let's see how the Wi-Fi signal diverges from this type of antennas. Googling will help us for this, where you can find a bunch of different studies and measurements. If we take a simplified diagram, it looks like this:
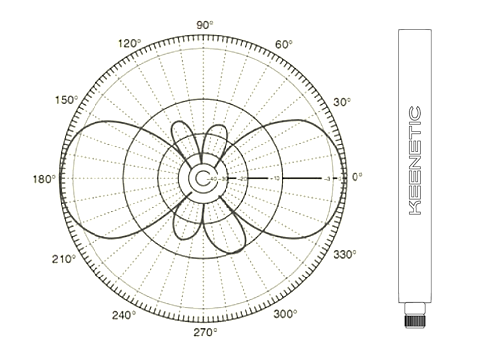
Complain to comment
Then you have to wrap your head in tinfoil. Because apart from the router, the apartment is full of other radiations: microwave, cellular, neighbor's routers, 5G towers, reptiloid transmitters, radio waves from radios and repeaters, radio and TV signals.
Oh, my gosh, I'm so scared myself.
If you ever stood next to a spectroanalyzer, your confidence would shake to some extent.
What's the point? You need a grounded screen with a grounding resistance of less than 0.01 Ohmm, which is at least 2,000 pins of 15 meters in the ground at a distance of 20 meters from each other. Then your screen will help, otherwise hide in a bunker with walls of one meter of armor:)
Knock on the door and introduce yourself as an employee of an Internet company, say preventive maintenance, and then do with the antennas what you need!
Here for example in my apartment catches 3 router from the sasedej all with a password of course. And what is free? Without knowing the password, I can not use the Internet, then.
It also happens that the router is lying somewhere on the floor behind the desk in a pile of wires and of course there are complaints about the poor connection. So it was with friends in St. Petersburg's old stock, where thanks to the wooden slabs WiFi worked more for communal neighbors from downstairs and was not the full coverage is not such a big three-bedroom-settlement. As soon as you put the router up on the cabinet, there is a stable connection in the far room.
And my router doesn't have any antennas outside.
What am I supposed to do, put it on its side or upright?
What are you smoking out there that's got you so worked up?
What difference does it make which side you put the oil on, it'll fall down anyway!
Well, lamers don't get it.
And who at least the user – they get.
//Ps
How strange, my router is 15 years old.
The incoming channel is 250 Mbps, by youfly 220-230 Mbps load holds steady…
And what are the numbers stated?
For example claimed gigabit per second.
And you have to understand that firstly this gigabit is possible only in ideal conditions – the air is clear, the signal is good, and the subscriber's device supports it.
Secondly, gigabit is the speed of the link – the radio channel through which the data will be transmitted. Data can be service and user data. In wi-fi, the share of service data is about 55%.
Accordingly, the transmission speed of user data will be about 450 megabits.
Method of calculating the effective distance
Let's assume that the wireless connection works when the distance between the access point and the smartphone is N meters with no obstacles in the path of the signal. A table from which you can find out how many times the intensity decreases when passing this or that obstacle, there are several sites (such as ZyXEL). At the same time, it is known that reducing the intensity by 2 times (by 3 decibels) is equivalent to reducing the effective distance N by the root of two times. It's simple – the square of the distance is inversely proportional to the intensity.
When a signal passes through a glass window, the intensity is reduced by exactly 3 dB, so the effective distance is reduced by a root of two times. Using this technique, you can calculate at what distance the Wi-Fi connection will still work in a given situation:
- Glass window – reduces intensity by 3 dB (2 times)
- Tinted window – 6 dB (4 times)
- Wood wall – 9 dB (8 times)
- Interior panel wall, concrete floor – 15-20 dB (32 times or more).
The coefficient by which you divide the distance value is equal to the square root of the intensity reduction factor. Consider an example.
Let us assume that N is 400 m. Now we "put" one panel wall and one wall of wood between the router and the smartphone. Adding up the decibels (15+9 dB), we get 24 decibels. On a logarithmic scale it is 24, and on a linear scale it is equivalent to a 251-fold decrease in intensity. Now, calculate what the root of 251 is (it's 15.84). Divide 400 meters by 16, and you get 25 meters. As you can see, it is simple and similar to the truth.
Effective distance without obstacles
The reader is probably wondering what is the value of N with no obstacles at all, depending on the choice of Wi-Fi range. If the transmitter power of the router is 40 mW, and its antenna "amplifies" the signal in the horizontal plane by 3 dB (it is multilink), then, according to ZyXEL, the value of N is 400 meters. See: the router has a less powerful transmitter than the smartphone, but it uses a multilink antenna. Bottom line: the connection between two Wi-Fi devices with a transmitter power of 100 mW and an ordinary pin antenna is confidently maintained at a distance of up to 400 m. Here we were talking about the 2.4 GHz band.
Results of practical observations
Let's evaluate the "breakthrough capability" of Wi-Fi in practice. For this purpose we will take a set of access points supporting communication in the range of 2.4 GHz: this is TEW-411BRP+ from TRENDnet, DWL-2100AP from D-Link, and USR 805450 from US Robotics. As the subscriber device we will use a smartphone, the transmitter power of which is 100 mW. At the access points we will install regular antennas, and they themselves will be located on the fifth floor of a panel building.
Maximum distance, confident reception
Already on the third floor of the building where our equipment is installed, there is no Wi-Fi network. The wave overcame 2 reinforced concrete slabs, so we lost 30 dB and that's it, no connection. In fact, consider that 35 decibels are lost when going through two slabs. You have to add the attenuation depending on the length of the distance, then we get about 36-38 dB. So, this is the attenuation for 100 milliwatts that is critical.
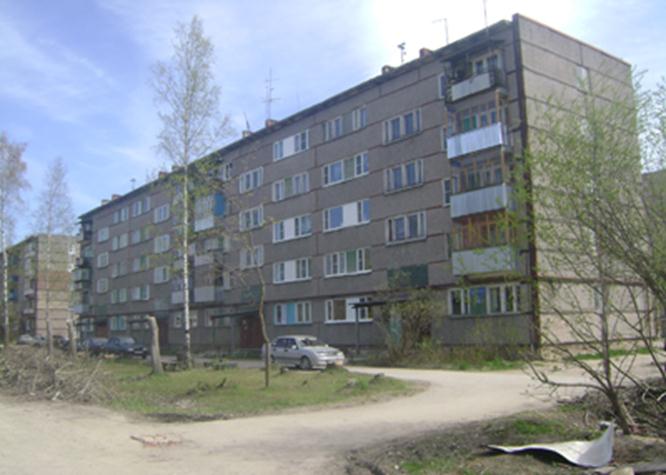

Let's try to catch the signal on the street. At a distance of 150-180 meters you can notice the presence of the network, but this is true if you are in front of the window of the room where the equipment is installed. A stable connection remains at a distance of 100 meters. As you can see, the theory corresponds to the practice with a sufficient level of reliability. For reliability, the theoretical result (one window -> 200 meters) is better to divide by 2.
What not to do
It is clear to everyone that it is hardly worth increasing the power of one of the transmitters when the second, i.e. "subscriber", remains unchanged. The same can be said of the use of antennas which allow increasing the intensity of the wave, but narrowing the diagram. However, the use of sectorial and multi-link antennas will still be effective, and here's why. Routers and other radio wave emitters may not only be in your apartment, but also the neighbors, etc. And by narrowing the capture sector, you can rid your router of extraneous RF noise.
Read More: