The physical properties and behavior of radio waves in the surrounding world are quite complex. You can't take just one parameter and use it to calculate the range of a wireless signal. In each case, the range will be influenced by different environmental factors:

How to correctly place a router in terms of physics

Bookmark

Do you often find that your Wi-Fi signal is lost or poorly received in any part of your apartment? The experts at Mashable tell you what you should focus on when installing your gadget.
It's all about wave propagation
We can accurately predict the interaction of intense electromagnetic waves because the underlying physical processes are governed by Maxwell's equations.
Armed with the knowledge of Maxwell's equations and how to solve them, the author of the article turned his attention to a simpler question – how to improve Wi-Fi reception in the apartment.
By matching the wall locations in the apartment, the author was able to create a map of the Wi-Fi signal strength, which varied as the virtual router moved.

The electromagnetic radiation emitted by the antenna in your wireless router is caused by a small current oscillating at 2.4 GHz (2.4 billion times per second).
Pick the right place for your router

Fact from Captain Hindsight – If you have a five-room apartment and your router is by the front door, don't be surprised that the signal to the fifth room will be weak.
Try to place the Wi-Fi router in the center of the living area in an open space. So that there is about the same distance to any room. Don't forget that the higher the router stands, the better. Radio waves propagate better down and sideways.
Turn your router's antennas up.

Most routers have physical antennas whose location can be adjusted. Many users place the router on cabinets and tilt the antennas horizontally, thereby degrading the signal.
For maximum signal strength, position the antenna vertically, pointing straight up.
If you have two antennas on your router, you should point them in the same direction, otherwise you won't get the best performance.
Properties of the WiFi signal
Absorption.
The main condition for creating a wireless link over a distance of more than a hundred meters is direct line of sight between the points where the equipment is installed. To put it simply, if we are standing next to a WiFi hotspot, we must not face a wall, a forest, a high-rise building, a hill, etc. when we look at the other hotspot. (That's not all, you should also take into account the interference in the Fresnel zone, but about that in another article.)
Such objects simply reflect and absorb the WiFi signal, if not all of it, then the lion's share.
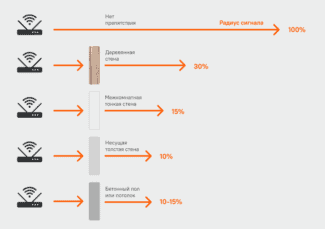
The same thing happens indoors, where the signal from a WiFi router or access point passes through walls to other rooms/floors. Each wall or floor "takes away" some efficiency from the signal.
At a short distance, for example from a room router to a laptop, the radio signal still has a chance to overcome the wall and still get to the target. But over a long distance of several kilometers, any such weakening has a significant impact on the quality and range of the WiFi connection.
The percentage of WiFi signal degradation when passing through obstacles depends on several factors:
- Wavelength . In theory, the longer the wavelength (and lower the WiFi frequency), the greater the signal penetration. Accordingly, WiFi in the 2.4 GHz band has a bоhigher wavelength than in the 5 GHz band. In real life, the implementation of this rule depends very closely on the obstacle through which structure and composition of the signal passes.
- The material of the obstacle or more precisely, its dielectric properties.
Non-toned window (no metallized coating)
* The percentage of effective distance – This value means what percentage of the originally calculated range (in open terrain) can pass the signal after overcoming an obstacle.
WiFi ranges and frequencies
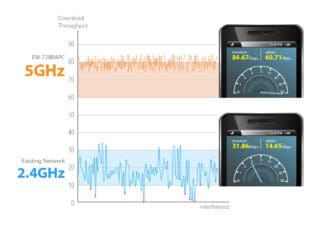
As we have already said, there are several different frequency bands allocated for WiFi communication: 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, 3.65 GHz, 5 GHz, 10 GHz, 24 GHz.
In Ukraine at the moment most often used WiFi access points and antennas WiFi 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
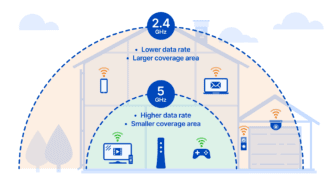
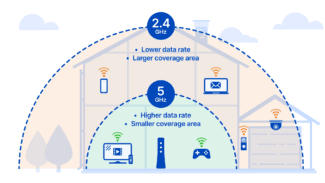
2.4 GHz. Wavelength of 12.5 cm. Refers to decimeter waves of ultrahigh frequency (UHF).
- In real conditions – less signal range due to a wider Fresnel zone, which is often not compensated by the fact that the signal at this frequency is less subject to natural attenuation.
- Better overcoming of small obstacles, such as dense forests, due to good penetration and circumvention of obstacles.
- Fewer relatively non-overlapping channels (only 3), which means "traffic jams" – cramped airwaves, and as a result, poor communications.
- Additional noise on the air by other devices operating on the same frequency, including cell phones, microwaves, etc.
5 GHz. . 6 cm wavelength. Refers to centimeter waves of ultra-high frequency (UHF).
- A greater number of relatively non-overlapping channels (19).
- Б о Higher data capacity.
- Greater signal range, due to the fact that the Fresnel Zone is smaller.
- Obstacles such as tree foliage, walls, 5GHz waves overcome much worse than 2.4.
Bands 900 MHz, 3.6 GHz, 10 GHz, 24 GHz are rather exotic to us, but can be used:
- To work in environments where the standard bands are densely occupied.
- If you need to create a wireless connection between two points in the absence of direct line of sight (forest and other obstacles). This applies to a frequency such as 900 MHz (in our country, it must be used with caution, since cellular operators operate on it).
- If you do not need to obtain a license from the regulatory authorities to use the frequency. This advantage is often found in presentations of foreign manufacturers, but it is not quite relevant for Ukraine, because licensing conditions in our country are different.