For Google Chrome, you need to install the add-on "Save traffic" from the app store. It will be active all the time.
- Does the Internet speed depend on the router
- The power and the location of the router
- Selecting a free Wi-Fi channel
- WPA encryption specification
- Adapter
- 802.11n mode of operation
- High band load
- Software and hardware limitations of the Wi-Fi router
- What does Wi-Fi network speed depend on, and how to get the maximum speed?
- How to organize a Wi-Fi network, so that the speed loss would be minimal?
- Use WPA2 and/or WPA3
- Don't hide the SSID
- Change the channel width
- Find the least busy Wi-Fi channel
- Check up speed
- Ways to speed up
- Checking the load
- Troubleshooter
- How to speed up WiFi Internet
- Security
- What you can do to increase Wi-Fi speed
- STEP 2: in which mode does the router work, can you use 5G
- Poor reception – low speed!
- Router setup and low Wi-Fi speeds
Does the Internet speed depend on the router
The task of the network team is to act as an intermediary between the provider and the recipient of the service. In other words, the cable enters the WAN connector, and the next step is to distribute the global network to the PC, laptop and other equipment by wired and wireless. The question arises whether the router affects the speed of the Internet. In theory, this parameter does not depend on the router, because it just distributes the global network. But in practice, it is the network equipment that affects the speed of the Internet.
- The WiFi standard of the router. For example, if your router only supports 802.11g, reduce the speed setting to 15-20 Mbps, even if your ISP broadcasts much more. So think about whether it's worth saving money.


- The area and organization of the apartment, the thickness of the walls and the material. The quality of the Network depends on the square footage, the number and composition of the sections. So, to cover an area of more than 50 square meters will require more powerful equipment. To solve this problem, you may need to buy a repeater or other router configured in bridge mode. But before you do so, make sure you can cover the entire area.
- Location. Many people wonder if the location of the router can affect the speed of the Internet. As in the previous cases, the answer is yes. This parameter directly depends on where the network equipment is located. For example, if you put a router in a metal panel or a cabinet, the quality of WiFi connection will noticeably deteriorate.
- Interference with the Wi-Fi network. Another point – whether the speed of the Internet can depend on another router. Also in this case the answer is positive, since many interferences in the network cause deterioration of communication and, as a consequence, deterioration of speed characteristics.
- Type of connection. It is no secret that when using a dynamic or static IP, the speed will be higher than in the case of PPTP, L2TP or PPPoE.
The power and the location of the router
In addition to the latest drivers, optimizing wireless network efficiency can be achieved by properly positioning the router in the room. Due to the fact that the signal from the device spreads around the apartment in circles, it is better to install the router in the central part of the apartment, away from the corners. In ideal conditions, the equipment is installed under the roof. With this tip you can achieve the most efficient distribution of Wi-Fi waves around the room. It is also worth taking into account the number of devices connected to the computer, and in what area the Wi-Fi access point should be. For example, if you live in a two-story private house or a five-room apartment, you can provide a comfortable Wi-Fi access point in all the rooms by buying a second router.
There are a number of factors that affect in a certain way the speed that a router emits. Let's consider the main ones.
Selecting a free Wi-Fi channel
To improve data quality, you can try to find a Wi-Fi channel that isn't busy with other connections. If your device detects a large number of points, you should know that all of them can act as a kind of interference to the transmission of a quality signal. Try to find the channel with the lowest load and change your router settings.
WPA encryption specification
The next possible reason for the slowdown is the outdated WPA encryption specification, so you may need to replace it with WPA2-PSK.
Adapter
Internet speed can be slow regardless of the power of the router. This happens when the receiving device has an outdated adapter that is not compatible with the 802.11n standard. Please try updating the software of this device and measure the speed again.
802.11n mode of operation
If the problem persists after updating the driver, check if 802.11n mode is set. This has been the standard for most Wi-Fi networks since 2009. If you have a different mode set, you will need to change it.
High band load
In large cities, the number of available 2.4 GHz networks can be so high that changing your WiFi channel does not produce the desired results. Data rates drop even after selecting the freest segment of the frequency range. The optimal solution to this problem is to switch to the 5 GHz band, which is not yet widely used.
Its use is possible in dual-band routers. Such routers create two networks at once, which have different names, encryption and authorization parameters. Client devices whose radio module supports 5 GHz will be able to connect to WiFi in this range. Outdated models will connect to a second network. With this scheme of operation, you need to consider a number of disadvantages, the main ones being:
- Less coverage in the presence of obstacles, due to the physical properties of radio waves of this length.
- Lack of compatibility with older devices.
- High cost of dual-band equipment.
Software and hardware limitations of the Wi-Fi router
The problem with the fact that the router lags most often occurs to owners of the most common routers – D-Link, ASUS, TP-Link and other cheap ones. By cheap I mean those, the price of which is within the range of 1000-1500 rubles.
Just because it says 150 Mbps on the box doesn't mean you'll get that speed over Wi-Fi. You can approach it using a static IP connection, over an unencrypted wireless network, and preferably the intermediate and end equipment should be from the same manufacturer, such as Asus. These ideal conditions do not exist for most ISPs.
As a result of using cheaper and less efficient components we can get the following result when using a router:
- Slower speed with WPA network encryption (because signal encryption takes time)
- Significantly slower speed when using PPTP and L2TP (as mentioned above)
- Speed drop when using the network intensively, many simultaneous connections; for example, when downloading files via torrent, not only the speed can drop, but also the router can hang up, the inability to connect from other devices. (Here's a tip: Don't leave the torrent client on when you don't need it).
- Hardware limitations may also include low signal strength for some models
If we talk about the software part, everyone has probably heard about the router firmware: after all, a firmware change can often solve speed problems. New firmware fixes bugs made in the old ones, optimizes the work of the same hardware components for different conditions, so if you have problems with Wi-Fi connection, you should try to update the router with the latest firmware from the developer on the official website (you can read how to do this in the "Router settings" section on this website). In some cases, the use of alternative firmware shows good results.
What does Wi-Fi network speed depend on, and how to get the maximum speed?
As promised, I will write more details about how to increase the speed in a separate manual. For now, I'm going to list the main reasons that affect the speed of a Wi-Fi network:
- Wi-Fi router. The network standards (802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11as) that it supports, what technologies it uses, and the power of the hardware. As a general rule, the more expensive the router, the faster the wireless speed.
- The software on the router and the Wi-Fi receiver on your computer. Very often, with the update of the router firmware, or the adapter drivers on your computer, the speed becomes faster.
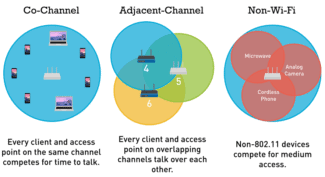
- Interference. Interference can come from other neighboring Wi-Fi networks (mostly) as well as from household appliances.
- Power of Wi-Fi network. It's no news that near the router, where the signal is maximal, the speed will be higher than in the other room, where the network signal is not so stable.
- The number of devices connected to your network. If one device is connected to your router, it will get all the speed that the router can give. If we connect another device, and start downloading something on it, the speed will already be divided by 2, and so on. In addition, all connected devices put a load on the iron router, which leads to a drop in speed.
- The type of Internet connection used by your ISP. The fact is that if your ISP uses a connection type Dynamic IP, or Static IP, the router will cut the speed less than with PPPoE, L2TP and PPTP connections.
- Router settings. Proper configuration of network protection, selection of network mode and channel width, as well as changing the channel can slightly increase the speed.
How to organize a Wi-Fi network, so that the speed loss would be minimal?
As for the Internet provider: If you have not yet connected the Internet, and if possible, choose a provider who uses Dynamic IP connection technology, or Static IP. This will make it easier for the router, and it's much easier to set up such a connection.
Choosing a router: If you want minimal speed loss, you'll have to splurge on a router. My recommendation is to buy a router which can run at 5GHz (GHz), and support the new 802.11ac standard. The 5GHz frequency is practically free now, which means there won't be much interference there. After all, for now, mostly all Wi-Fi networks operate at 2.4GHz. And the new 802.11ac standard, even compared to the currently most popular 802.11n, allows you to transmit information at as much as 6.77 Gbps. This is of course in theory, with special equipment.
The devices that you will connect to the network: As I wrote above, the speed also depends on the network clients. Preferably, your devices should be new, supporting the current 802.11ac standard, or at least 802.11n. If it is a computer, update the driver on your Wi-Fi adapter. I wrote about this in a separate article.
Check your internet speed, share your results in the comments, and tell me if your router is slowing down too much. All the best!
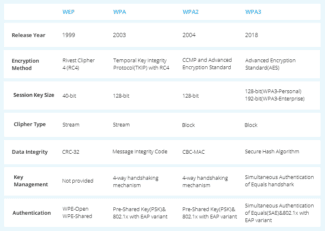
Use WPA2 and/or WPA3
It's no secret that WEP security is not as secure, although almost all access points still support it. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is more secure, but it depends on the version you use. Keep in mind that when using the first version of WPA, you are limited to 54 Mbps, which is the maximum speed of the old 802.11a and 802.11g standards. To ensure that you can take advantage of the higher data rates offered by newer devices, only use WPA2 and/or WPA3 security.
If you have multiple SSIDs configured on your access points, keep in mind that each virtual wireless network must broadcast separate beacons and control packets. This takes airtime, so use SSID capabilities sparingly. One private SSID and one public SSID are certainly acceptable, but try not to use virtual SSIDs for things like splitting wireless access across company departments.
If network sharing is still required, consider using 802.1X authentication to dynamically assign VLAN users when connecting to an SSID. That way, you can have only one private SSID, but still virtually share wireless traffic.
Don't hide the SSID

You may have heard that hiding the network name by disabling the SSID in the beacon broadcast can help with security. However, it only hides the network name from casual users. Most devices will show that there is an unnamed network nearby. In addition, anyone with a Wi-Fi analyzer can usually detect the SSID because it will still be present in the control traffic.
Hiding the SSID also causes additional management traffic on the network, such as sample requests and responses. In addition, hidden SSIDs can be confusing and time-consuming for users because they have to manually enter the network name when connecting to Wi-Fi. Therefore, this approach to security can do more harm than good.
A better security method is to use WPA2 and/or WPA3 enterprise mode. If you find that not all devices on the network support enterprise mode or that it is too difficult to set up, be sure to use a long, strong passphrase with mixed-case and mixed-character characters. Also consider changing the password periodically and be sure to change it after any employee quits or loses a Wi-Fi device.
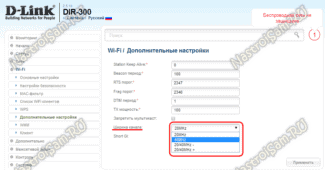
Change the channel width
The wider the channel, the higher its bandwidth. In the router settings, the default setting is "Auto". And some users, following the recommendations, choose the maximum width – 40 megahertz. This is correct, but only if you have high internet speeds and a minimum of neighboring networks with which you share the band. In apartment buildings, where you see a list of a dozen routers, you should, on the contrary, reduce the channel width.
In the wireless mode settings, set the channel width to 20 MHz.

Or leave it set to "Auto" if you have few neighbors. But I do not recommend choosing 40 MHz.
Find the least busy Wi-Fi channel
There are many articles on this topic, so I'll describe it briefly. There are 13 channels in the 2.4 MHz band. It's like lanes on the road. If you're in your lane alone, you can go as fast as your car allows. If you share it with other cars, however, they force you to slow down.
By default, the channel on your router is in "Auto" mode. This means that when you turn it on, the router analyzes the range and chooses the free or least busy channel. Everything seems to be fine. But then a neighbor came over, turned on his router and connected to the same channel. And then another one. A large number of devices on one channel has a negative impact on its bandwidth. Therefore, we will try to choose the channel with the lowest load.
To do this, use the Wi-Fi Analyzer program. It is easy to use and shows all wireless networks in your router's coverage area. Here you can also see how many devices share a particular channel. Then choose a free one and manually set it on your router.
You can do without any special software. Try to switch on all channels one by one and measure the speed. Where it is higher, leave that channel.

Open the drop-down list in front of "Channel". Select the desired channel number and save your changes.
Check up speed
First, check the actual speed of the Internet on your computer.
Before testing, close all programs that may be consuming traffic. Compare the test result with the advertised speed in your ISP's data plan. It is better to run several tests at different times of the day, because short-term internet performance degradation can be caused by excessive network load, glitches, weather conditions, and other factors. If the speed is consistently low (less than expected), then there is indeed a problem.
Measure at the same time from another device. Make sure that the problem occurs on the specific computer and not on the network.
Now you can move on to diagnosis and troubleshooting.
Ways to speed up
Checking the load
The first thing to do is to deal with programs that can "steal" traffic.
If you have closed all browser windows, disabled torrent and autoloading of updates, it does not mean that background applications on your computer do not use the Internet connection. Task Manager can help you identify "intruders" on your Windows computer.
Launch it by simultaneously pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc. Or right-click on the Start menu, select "Task Manager" and go to the "Processes" tab.

Note the numbers in the last column "Network". This displays how much traffic each application is currently consuming. Viewing this information allows you to understand the overall network load situation.

For detailed information, go to the "Performance" tab and at the bottom of the window click the "Open Resource Monitor" link. Here select the "Network" tab. This will show you the programs currently using your Internet connection. Deactivate the most voracious ones. To do this, right-click on the name of the application in the list and select "End process".

Check the internet speed again. If it is normal, then the problem has been found. Uninstall unnecessary applications or prevent them from connecting to the Internet on their own in the settings.
Troubleshooter
Use the built-in Windows utility to automatically find and solve connectivity problems.
- In the lower right corner, next to the clock, locate the network connection icon and right-click on it. Select Troubleshooting.

- The diagnostic tool will start. Wait for the process to complete and follow the prompts.

How to speed up WiFi Internet
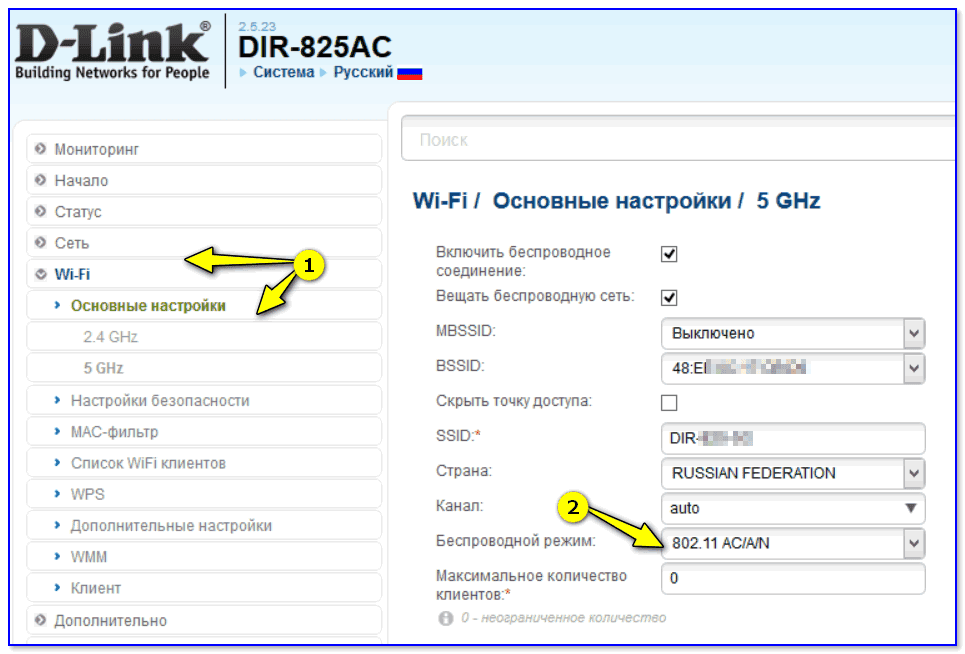
If there are a couple or three networks nearby and users start complaining about slow WiFi, the reason is usually due to improper settings. Very often it goes like this: they connected the Internet, set up a router and worked for a while until they realized that the router was cutting speed and that they had to do something about it. No, it's not bad and you don't need to change it. You just need to check and properly set some settings, which I'm about to tell you about. To get there you first need to access the web interface of your modem or router via its IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1). After that, locate the section responsible for wireless networking and follow these recommendations.
Unless you have very old laptops, tablets, or phones that use the outdated 802.11b or 802.11g standards, it is best to disable them in the basic WiFi settings, leaving only 802.11n.
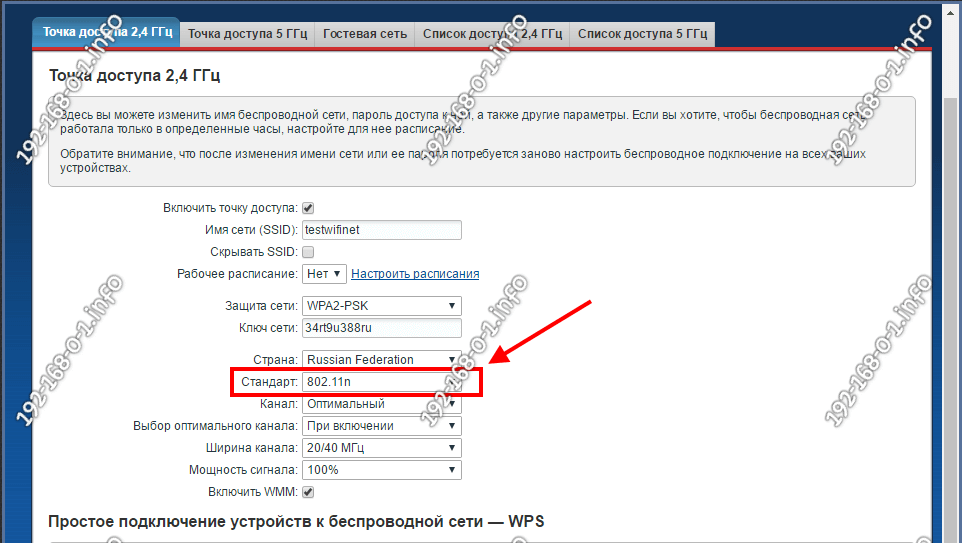
This only applies to the 2.4 GHz band, since there are simply no b or g standards in the 5 GHz band.
Security
Yes, even the wrong security standard can affect your WiFi speed. The only standard you need to use is WPA2-PSK Encrypted AES ENCRYPTION.
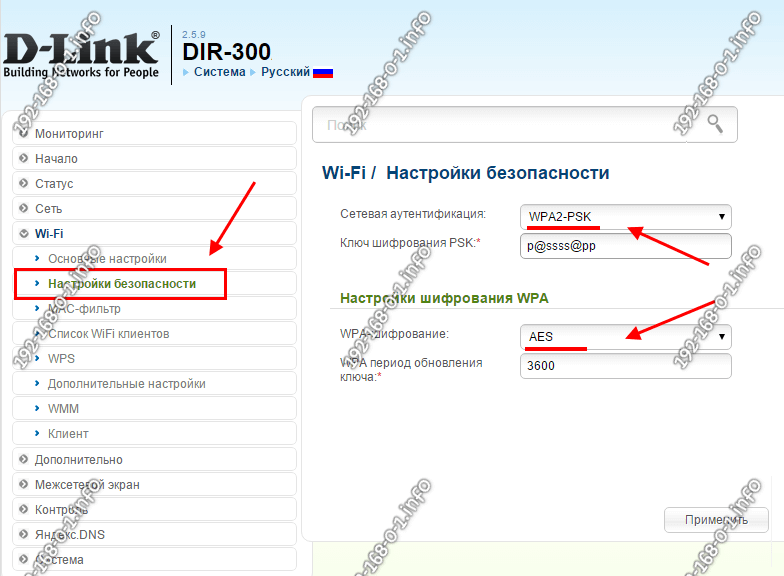
Other network authentication options will result in slower speeds. For example, with WPA-PSK you will never get more than 54 megabits per second, as this is a software limitation of the obsolete protocol.
What you can do to increase Wi-Fi speed
SoI recommend that you start by paying attention to the signal strength of the Wi-Fi network – in general, it is not even necessary to go into any settings of the router.
It is enough to look at the network icon: if the signal level is OK – you will see all the bars "flooded" (as in the example below). 👇
In general, Wi-Fi signal strength 👇 In general, the distance between the devices, e.g. the laptop and the router, has a big influence on the signal strength. The farther apart they are, the lower the speed of exchange.
In addition, if there is a wall (mirror, door, etc.) between the router and laptop – the quality of the signal (and the speed of transmitted information) can be significantly reduced. When diagnosing and searching for the reasons of slow Wi-Fi – try to put the laptop not further than 2-3 meters from the router.
Well, one more thing should be mentioned – most modern routers have a special option: adjustable signal strength. It is called "TX Power" (TX Power, Transmitter Power, Signal Level and other derivatives) .
To change the wireless power level – 📌 go to the router settings, go to the tab of additional Wi-Fi parameters and change the transmitter mode (below are screenshots of how it is done in devices from TP-Link and D-Link).
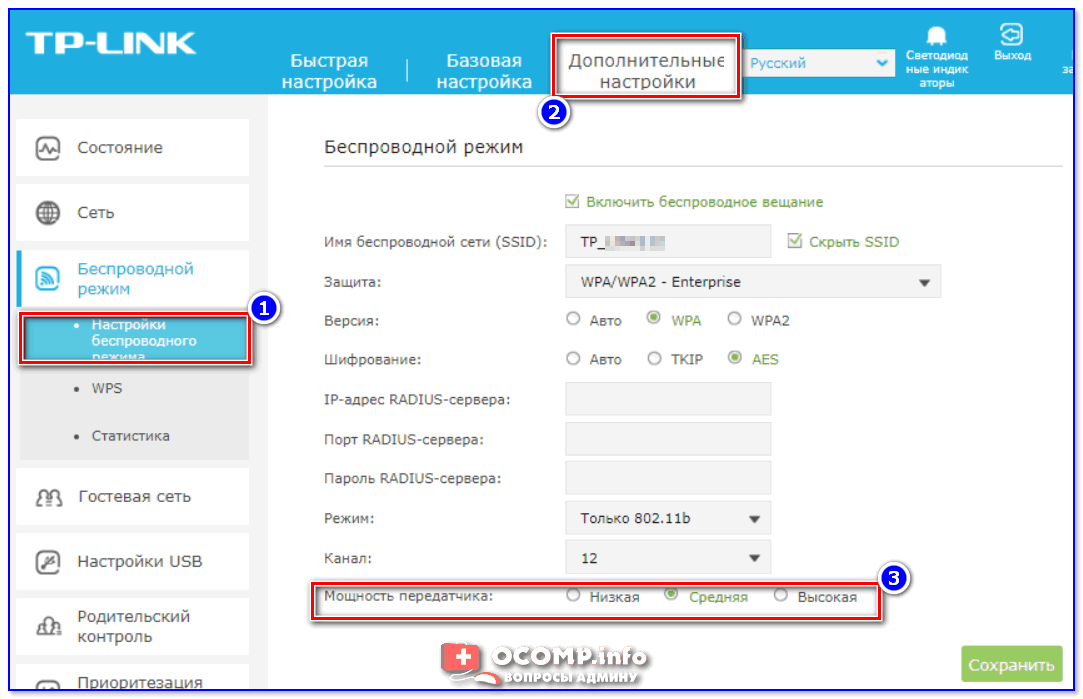
TP-Link – setting the wireless mode (signal strength)
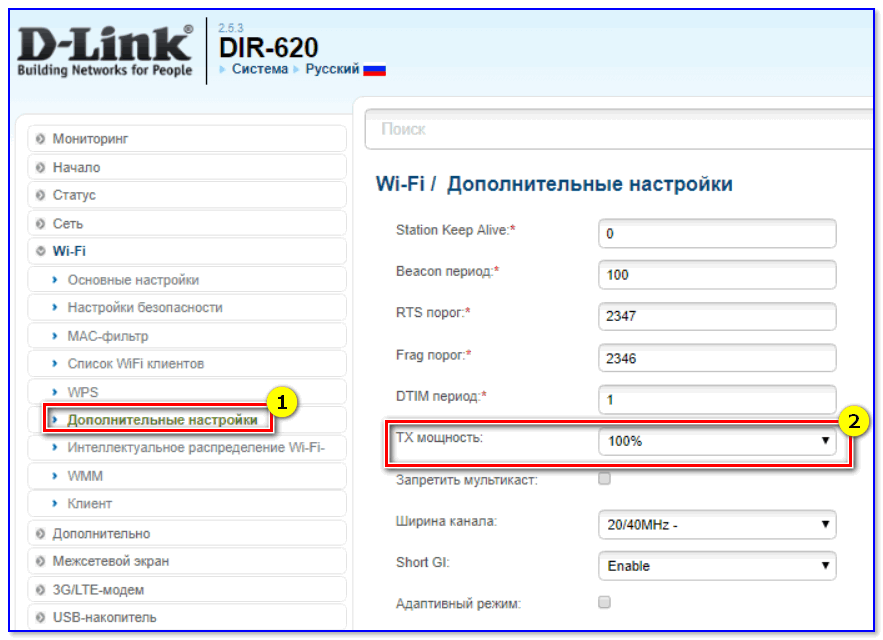
STEP 2: in which mode does the router work, can you use 5G
Each Wi-Fi network works in a certain mode (standard). Its bandwidth depends on it. Currently the most popular networks are based on the standards: 802.11ac, 802.11n, 802.11g (see table below).
| The standard | Year of development | Max. speed (theoretical) | Average speed (in practice) |
| 802.11a (2.4 GHz) | 2000 | up to 54 Mbps | ~20 Mbps |
| 802.11g (2.4 GHz) | 2003 | up to 54 Mbit/s | ~20 Mbps |
| 802.11n (2,4 GHz) | 2010 | Up to 600 Mbit/s (4 antennas) | ~60-150 Mbps |
| 802.11ac (5 GHz) | 2014 | Up to 6.77 Gbps | 1 Gbps |
| 802.11ax (5 GHz) | 2019 | up to 11 Gbit/s | ? (2-4 Gbps). |
So, ideally in the settings of the router you need to set the most advanced standard for today (802.11ac (5 GHz), if you have a router working only at 2.4 GHz – 802.11n).
Important point: If you have older devices that do not support 802.11n (such as devices using 802.11g) connected to your Wi-Fi network, your throughput may drop significantly! Therefore, it is highly desirable to manually upgrade your router to the latest standard and connect devices that support it.
Poor reception – low speed!
Don't even count on good WiFi speeds if your signal strength is low. Signal strength affects the number of packets lost in transmissions. The weaker the signal, the more packets will be lost and the lower the speed will be.

The range of a Wi-Fi access point depends on the power of the transmitter as well as the size and position of the antennas of the receiving devices. If we consider ordinary gadgets, for example, a laptop will always have better Wi-Fi coverage due to the fact that it has a much larger antenna than a tablet or smartphone, whose antenna size is limited by the size of its body.
What to do in this case? Get closer to the router in the zone of better reception. The better the signal quality, the faster the wireless speed will be. But you should not overdo it either. Some users come very close to the router, i.e. closer than half a meter from it. This, too, is wrong. The minimum distance between the receiver and the transmitter should be at least 1-1.5 meters.
Router setup and low Wi-Fi speeds
There are several things that greatly affect the speed of the wireless network. They must be taken into account if you want to have a fast WiFi network.
The fastest WiFi speed you can get is with WPA2+AES authentication. If you use WPA or even older versions, you will not get more than 54 megabits, even if your hardware supports several times the speed. You can check this point in the security settings of the Wi-Fi.
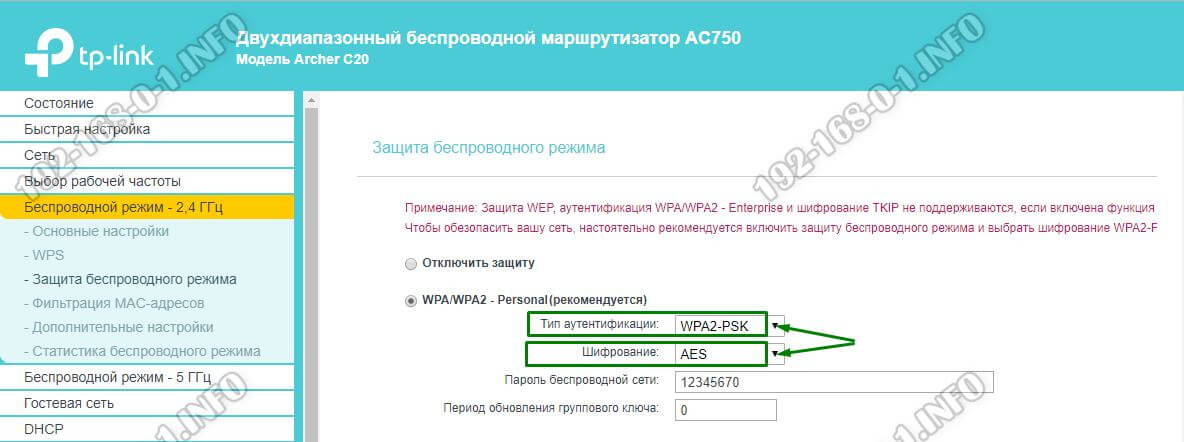
The next important thing to consider is the correct setting of the basic parameters of the radio module. First, choose the correct mode of operation. For the usual, classic range of 2.4 GHz, it is best to set the mode "802.11n only", if the device allows it.
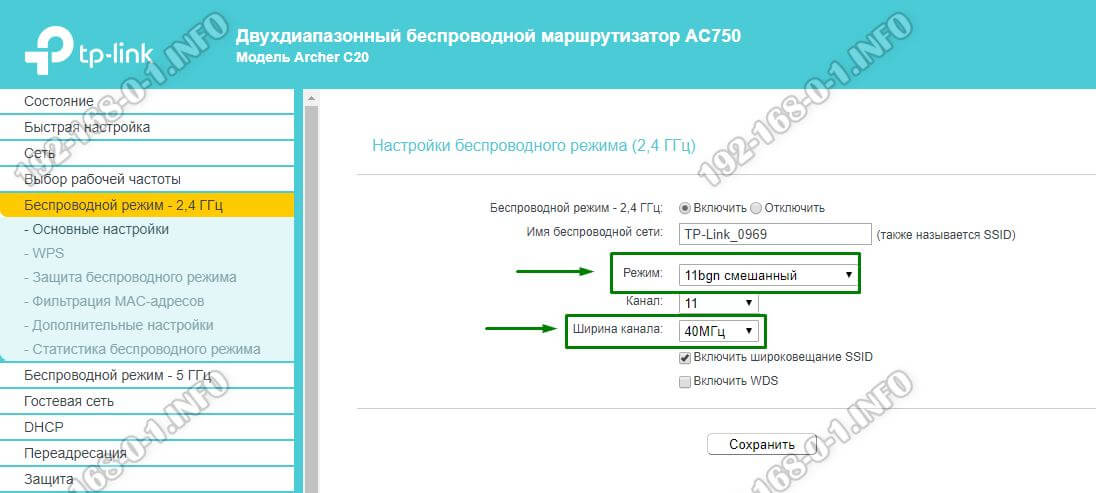
You should also pay special attention to such a parameter as Channel width. The correct setting will significantly increase the speed of Internet over WiFi. Sometimes even several times faster. You should take into account the following. If you are working on a wireless network within a few meters of the router, it is best to set the channel width to 40 MHz. If you are working at a greater distance, it is better to set the channel width to 20 MHz, otherwise there will be frequent disruptions in communication.
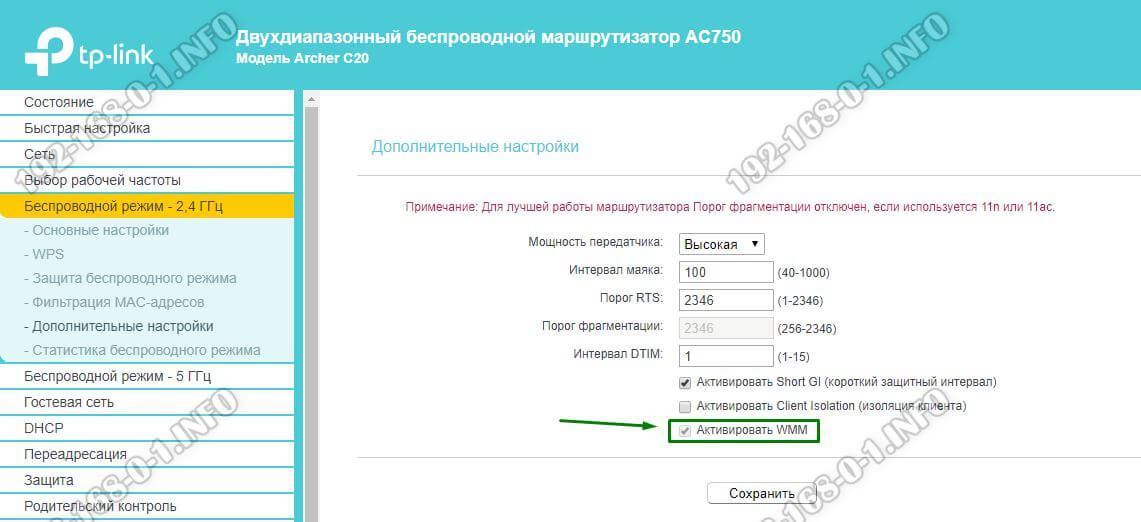
The WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia or Wireless Multimedia Extensions) protocol is based on the IEEE 802.11e standard and is used to provide basic Quality of Service (QoS) functions for wireless networks. You won't be able to boost your Wi-Fi speed if WMM is turned off. You can enable this option in the advanced radio module settings.