If the wires stretched through the apartment are annoying and there is no place to hide them, you can try PowerLine adapters, which transmit the network signal through the in-house wiring. But you should keep in mind that PowerLine is an unpredictable thing and sometimes flatly refuses to be friends with local cables. So it's better to buy PowerLine adapters with a return policy, just in case they don't work for you.
- A tinfoil cap and other tin foil. Trying "folk" ways to improve your home Wi-Fi signal
- How to "improve" Wi-Fi
- How to improve WiFi coverage
- Development of antenna-nozzle for the router (WiFi Ladder)
- About the benefit of moderation in all things
- Radio traffic load
- Asymmetric connection
- When higher power is required
- Interference from other types of radio devices and other electronics
- Long distances between Wi-Fi devices
- Obstacles to signal path
- Tuning channels
- Moving to 5 GHz
- Additional antenna, repeater, or point to point transmission?
- Supplemental Antenna
- Use of repeaters
- To summarize
- Control your applications' access to the Internet
- advertisement
- advertisement
- Repeater (signal amplification and expansion of the network radius)
- Test of Wi-Fi adapters: external adapter wins by leaps and bounds
- Redirect the signal
- Update the software
A tinfoil cap and other tin foil. Trying "folk" ways to improve your home Wi-Fi signal
What would we do without Wi-Fi? Wrapped in wires, probably. If you take a peek into that "wireless ether" today, you might be scared of the life going on there. The situation turned out to be even tenser after Belarusians began to actively switch to new telephony and data transmission technologies – modems with Wi-Fi activated by default began to appear everywhere, even when there was no need for it.
Most Internet subscribers use inexpensive routers and modems operating at 2.4 GHz. Their obvious advantage is the price, both for the consumer and for the operator, which provides devices by the tens, hundreds and thousands. The downside is that the airwaves are already crowded, and the technical capabilities of cheap devices are limited. In particular, we are talking about the power and quality of communication in general.
How to "improve" Wi-Fi
There are various ways to improve the performance of devices – both "scientific" and "popular". We decided to pay attention to the latter, but only those that are available to everyone, not only to those who can hold a soldering iron and screwdriver, can tell from memory what components are included in a homemade signal amplifier, and then blindfolded to assemble it even without the use of blue duct tape.
The choice fell on a few of the most common and accessible materials – foil and tin in the form of soda cans. They are the most frequently mentioned by the authors of "smart tricks" and by inventors of different heights. For the tests we also armed ourselves with a set of several popular and cheap routers, as well as those that are more expensive – with Wi-Fi support in the 5 GHz range.
They were wired to a 50-megabit Internet connection and then measured signal strength and data speeds – something that is important for people who use Wi-Fi primarily to connect to IPTV and "heavy" Internet surfing. The router was located both in the immediate vicinity of the computer and behind various obstacles in the form of a door and a reinforced concrete wall.
As "antennas" were used: two tin cans cut so as to create a directional (in theory) signal; a foil-covered shoebox lid with "ears"; and finally, a "kettle" made of several layers of foil, as well as the desire to make the world a better place.
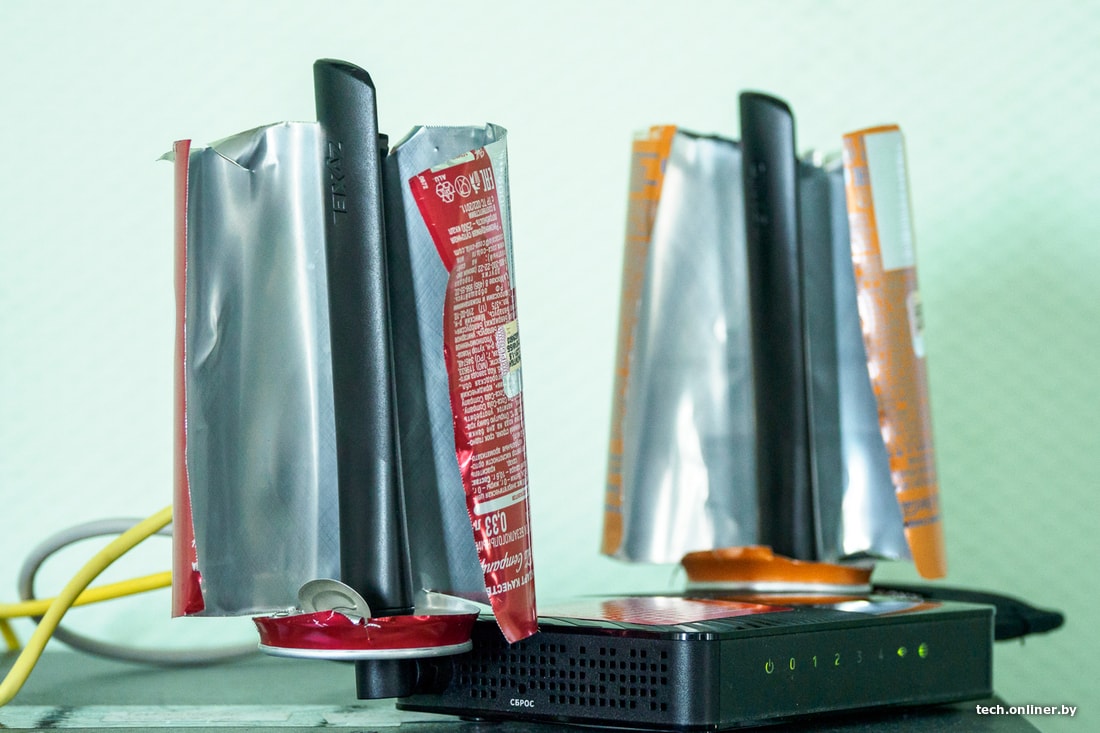

The experts of "Business Network", who helped us to conduct measurements, looked at all these crispy and sparkling "improveers" with interest. Probably the same way one looks at a raft made of shriveled planks when lowered on the water: what if it floats. But we didn't give up hope, remembering the TV antennas made of copper wires and pipes – they worked!
How to improve WiFi coverage
The first thing that comes to mind is to replace your router with a different one. Buy one with a stronger external antenna, or one with multiple antennas. If you have an older router model, it's worth a try. Be prepared that it will require additional costs, and a positive result is not guaranteed at all. Most likely the picture will improve, but the problem will not be eliminated (Fig. 4-5).

Figure 4. Router with two external antennas.

Figure 5. Router with three external antennas.
The next method is to use an active WiFi repeater, also called a WiFi repeater. This device is designed to extend the range of your WiFi network. This is a great method that can often solve the problem at the root. But it does have its disadvantages:
– prices from 1.5 thousand rubles and higher;
– the need for configuration;
– limited zone of use.
And that's not all: the repeater will again receive the signal from all sides and radiate around. That is, if we have an "uncovered" corner of the apartment far away, we will need two or even three repeaters. It would be great to concentrate the signal in a given direction, but you can not – built-in antennas repeaters have a circular pattern. We have not met any repeaters with a jack for an external antenna.
Another feature of WiFi repeaters is worth mentioning – the presence of 220V AC power. Not all people are willing to leave any device plugged in when leaving home. And turning it on and off every time is an occupation for the amateur. In addition, for a house or cottage solution is complicated by the fact that between the house and, say, a barbecue area, most often there is no mains power, and repeaters are often not designed for outdoor use.

Development of antenna-nozzle for the router (WiFi Ladder)
So, we have a router with an external antenna (important: routers with built-in antenna we do not consider). The question arises: how to use this own antenna as an active element (vibrator) of the antenna system? Our goal is to give directional properties to the external antenna of the router, which will result in an increase in the range of transmission and reception of WiFi signals in a given direction. The first thing that comes to mind is the "wave channel" antenna, also known as "UDA-YAGI" (named after its inventors from Japan). It is a simple and at the same time effective antenna design, which has proven itself all over the world.
So the idea appeared and it was necessary to put it into design. The developers faced the task of calculating a multi-element wave channel for the range of 2.4-2.5 GHz, in which it would be possible to "embed" the regular antenna of the router. During the simulation it was decided that the best option would be a 7-element "wave channel". With quite compact size of the design we got an antenna system, the gain of which allows us to solve the tasks. The size of the directors and the distances between them were optimized in the physical model, we believe they are the best for the task (Figure 12).

Figure 12. "Stuffing" of the BAS-2002 WiFi Ladder antenna
The next stage was the development of the antenna mount design. After monitoring the router market, we decided to place the "wave channel" on the external antenna of the router, using it as a carrier element (Fig. 13). We came across the fact that routers have different diameter antennas, and sometimes their shape is far from cylindrical or cone-shaped. For example, a "flattened" external antenna is quite popular. For this reason, the designers developed a universal clip that allows you to attach the product to almost any external antenna of the router. In some cases, it will not be the most rigid mount, but we want to note that the antenna is usually installed indoors and only once, so outside physical effects on it will be minimal.
About the benefit of moderation in all things
As mentioned above, reducing power is not always a bad thing. Not only that, but if you increase the power, the quality of reception may deteriorate considerably and it is not about the "weakness" of the access point at all. Below we will consider in which cases it can be useful.
Radio traffic load
The effect of congestion can be seen firsthand, at the time of selecting a device to connect. If the list of selected Wi-Fi networks contains more than three or four items, we can already talk about overloading the radio air. At the same time, each network is a source of interference for its neighbors. And interference affects the performance of the network, because it dramatically increases the noise level and this leads to the need to constantly resend packets. In this case, the main recommendation is to reduce the transmitter power in the access point, ideally – to convince all the neighbors to do the same, so as not to interfere with each other.
The situation resembles a school class, when the teacher is away. Each student starts talking to his or her roommate and other classmates. In the general noise, they can't hear each other very well and start talking louder, then even louder, and finally they start shouting. The teacher quickly rushes to the classroom, takes some disciplinary measures and the normal situation is restored. If we think of the teacher as a network administrator and the students as an access point owner, we get an almost direct analogy.
Asymmetric connection
As mentioned before, the transmitter power of the access point is usually 2-3 times stronger than the client mobile devices: tablets, smartphones, laptops, and so on. Therefore, it is very likely that there will be "gray areas" where the client will receive a good stable signal from the access point, but the transmission from the client to the point will work "not very". Such a connection is called asymmetric.
To maintain a stable connection with good quality is highly desirable that between the client device and the access point was a symmetrical connection, when the reception and transmission in both directions work effectively enough.
When higher power is required
The factors listed below require increased power in order to maintain a stable connection.
Interference from other types of radio devices and other electronics
Bluetooth devices such as headphones, wireless keyboards and mice operating in the 2.4 GHz frequency band can cause interference to the access point and other Wi-Fi devices.
The devices listed below can also have a negative impact on signal quality:
- microwave ovens;
- baby monitors;
- CRT monitors, wireless speakers, cordless phones, and other wireless devices;
- external sources of electrical voltage, such as power lines and power substations,
- electric motors;
- Cables with insufficient shielding, and coaxial cable and connectors used with some types of satellite dishes.
Long distances between Wi-Fi devices
All radio devices have a limited range. In addition to the design features of the wireless device, the maximum range can be reduced by external factors such as obstacles, radio interference, and so on.
All this leads to the formation of local "out-of-reach zones" where the signal from the access point "doesn't reach" the client device.
Obstacles to signal path
Various obstacles (walls, ceilings, furniture, metal doors, etc.) located between Wi-Fi devices can reflect or absorb radio signals, leading to a deterioration or complete loss of communication.
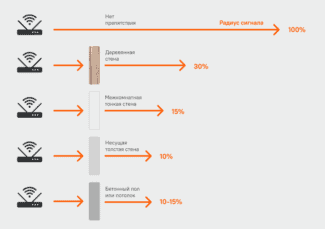
Things as simple and straightforward as reinforced concrete walls, sheet metal coverings, steel framing, and even mirrors and tinted glass noticeably reduce signal intensity.
Interesting factThe human body attenuates the signal by about 3 dB.
Below is a table showing the loss of Wi-Fi signal efficiency when passing through different environments for the 2.4 GHz network.
Tuning channels
Wi-Fi networks use narrow bands of the radio spectrum to transmit data – these are called channels. The number of channels available is small – as opposed to the number of people who want to use them. Therefore, in the most popular 2.4 GHz band, they can be blocked by noise from neighboring networks and other devices.
Each time you reboot – or at some scheduled interval – the router chooses the most interference-free channel. This can be compared to the way a GPS-navigator chooses the path along the highway where there is the least amount of traffic.
Usually the router does a pretty good job of this on its own, but if there are problems, you can try to intervene. For example, you can set the router settings to automatically search for the least clogged channels more often, or to determine them manually at all. However, you have to be careful with the latter: the spectrum load can change quickly – not only your router can automatically switch channels, but also the neighbor's.
Also, some routers allow changing the Wi-Fi signal strength in the settings – check if the maximum value is set there. If not, then feel free to turn it up to maximum.
Moving to 5 GHz
You're moving virtually, of course. The 5 GHz band is a more respectable area of the radio spectrum: there are more channels, and they are wider. Older models and very cheap routers usually do not work there. This is largely why there is less noise in the 5 GHz band, and transmission speeds can be much higher.
If your router doesn't support 5GHz operation, you can try upgrading to something more modern with 802.11ac (aka Wi-Fi 5) support – it's no longer a luxury, with inexpensive models starting at $50.
You don't have to chase the more advanced 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6). It's still expensive, and you'll probably only feel the difference if you really have a lot of voracious Wi-Fi devices at home.
Just keep in mind that moving to 5 GHz is not a panacea. The higher frequency has a disadvantage: the 5 GHz signal fades faster with distance, and the range in multi-room areas is poor.
So it all depends on what the problem is with your Wi-Fi network. If your home's 2.4 GHz spectrum is clogged with other people's networks, but the 5 GHz spectrum is free, an upgrade will really help. But if the point is that your 2.4 GHz network simply can't reach the desired location in your home due to the distance and the abundance of reinforced concrete walls, then most likely the 5 GHz won't save you either.
Additional antenna, repeater, or point to point transmission?
There are several ways to improve network performance. Accordingly, there are several varieties of equipment to help do this.
Supplemental Antenna
Additional external antennas are used to boost the signal of access points. Sometimes an amplifier is included in addition to the antenna itself. Such devices are often externally powered, such as from a wall outlet.
The main merit of the antenna is that it simply increases the signal strength.
This approach is good when there is a large space with a small number of customers. For example, an industrial warehouse. By placing an antenna from a single point under the ceiling in the center of the room, you can make the entire area available to several storekeepers and visitors in the warehouse.
If you put two such powerful radiators side by side, instead of helping each other, they will interfere with each other.
Keep in mind that no matter how powerful the antenna is, the number of clients that can be connected will be limited by the internal resources of a single access point.
For a busy office "anthill" where most customers are close to each other, building a network based on a single access point with even the most powerful antenna is not a good idea. The high power here is not so much in demand, much more useful will be load balancing between several points, the ability to accept a greater number of simultaneous requests from clients or to block unwanted access.
So we leave the access point with the external antenna in its place – proudly alone under the roof of the warehouse and move on to another point in our description.
Use of repeaters
A repeater is a device that receives the signal from an access point and forwards it to the client, or vice versa.
This allows you to extend your wireless network coverage. Clients can easily connect to a repeater in rooms where the signal begins to weaken.
To summarize
There is no "one-size-fits-all" methodology, however following some recommendations allows you to avoid many problems when designing, deploying and maintaining a Wi-Fi network.
Do not place transmitting devices too close together.
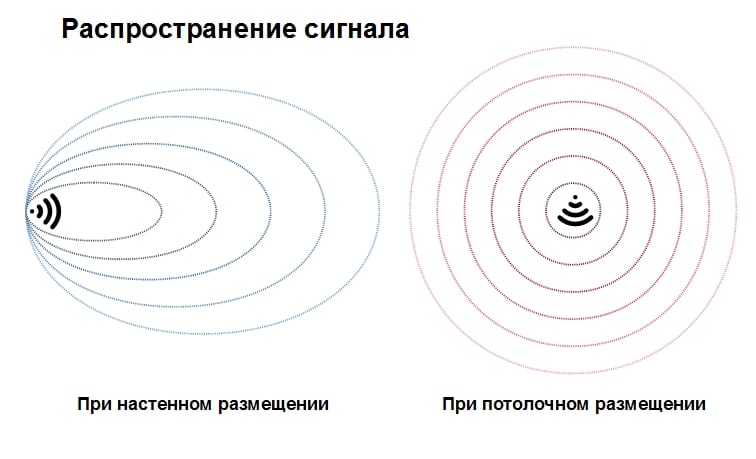
In some cases it is better to use access points for placement on the ceiling, in others on the wall. Consideration should be given to the directivity diagram for each option. There are universal access points with the ability to switch the mode of use.
In the next article in this series we will talk in more detail about wireless equipment placement issues.
Questions about equipment selection, setup and configuration advice, and sharing your opinions? We invite you to our telegram.
Control your applications' access to the Internet
If someone in your house is constantly watching streaming video, playing online games, downloading large files, it can significantly slow down the network. Pay special attention to torrent clients. Some of them are configured to start automatically at system startup and continue downloading and distributing data in the background. A separate pain is computer games, which quietly download multi-gigabyte updates and add-ons.
By default, the manufacturer sets the same well-known logins and passwords on all its routers. Each user has to change them himself to protect his network from unauthorized access. But unfortunately not everyone does it.
If you do not want your neighbors to use your wireless network, thus preventing you from doing so, you need to perform a detailed configuration of your router. How to do this, you can read our guide "How to protect your Wi-Fi network and router.
advertisement

As a result, instead of being in his two-room house, his mother-in-law sat under his nose in the evenings, explaining everything by the fact that she needed the Internet. I assume she was sitting there during the day as well, but since my acquaintance was at work at that time, this problem did not bother him much. To make a long story short: fighting with his wife, resentment, and yelling, to name a few of the problems that came down on his head. He needed urgent help. Getting wireless Internet into his mother-in-law's annex didn't work, because no carrier was working consistently outside the city. The signal is weak or there is just no signal. It is worth noting that about 5 years ago my friend's house had high speed internet with constant speed of 80MB. It was not much for the city but compared to 4 Mb which he had it was a real breakthrough.
By the time I got there my friend (let's call him Peter) had tried everything he knew. All this time he had a router that his operator sold him: the P-LINK TL-WR841N. It is quite a normal unit, which is sufficient for the needs of three people. As you guessed, Pete has a wife and a child who also has his own laptop. The wife has enough of a tablet, which is connected to the router. I can't say that my mother-in-law has put a lot of strain on the network, but it was extremely difficult to tolerate her presence all the time. So, let's list what my acquaintance had already done by the time I arrived:
Moved the router as close to the door as possible, hoping it would make it to my mother-in-law's house. It did not lead to anything good, because after such self-dealing revolted son Peter, who claimed that the signal on the 2nd floor, where his room was located, has become worse. Alas, the signal did not reach his mother-in-law. Next we will not count the useful recommendations from the Internet, which were used by my acquaintance, noting that there were 5 in total.
advertisement

The next step was to buy a more powerful antenna. Peter went to the router manufacturer's website and bought this thing: TL-ANT2409CL. It is an omnidirectional amplified antenna with 9 dBi power. Since the P-LINK TL-WR841N router has two antennas, I had to spend twice as much. Alas, despite the fact that in some cases it can increase the radius of the router, in this situation the router is equipped with non-removable antennas, which means that I had to send the purchase back. Fortunately, the money for it was returned.

The next desperate step was to make a parabolic mirror. You have not heard of it? Neither had I heard of it, but it exists! It is a simple device made of foil glued to heavy paper. The simple device is mounted on the antenna, focusing the signal, which can theoretically increase the range of the router. Peter spent the whole evening on this, giving up his beloved Tanks. My mother-in-law did not get Internet access, and everyone else could not use it at all, because now the network was perfectly catchable outside and in the summer kitchen, but disappeared on the second floor. Another fiasco. I do not know how effective the method is, but in this case it did not work.
Repeater (signal amplification and expansion of the network radius)
In addition to buying an antenna, you can also think about buying repeater . It is very useful in large houses and apartments.
For your information
Repeater is a special device designed to increase the range and improve the signal of the Wi-Fi network. The meaning of the device is that it receives the Wi-Fi signal from the router and distributes it. Thus, thanks to this device, it is possible to extend the Wi-Fi zone over the whole big house (apartment).
? By the wayif you have another router, it can be used as a repeater (if it has such a function).
*
The layout below shows a large two-storey house with a repeater by the stairs: to increase the signal on the second floor and in the room around the corner.
By the way, the repeater is a small box (something like a power supply), connected to an ordinary outlet (example below). It has the simplest settings, so I do not even dwell on them in this article.
The price of an average repeater in Russia ranges from 800 to 1500 rubles (relatively inexpensive if compared to the cost of a new router or drilling the walls and laying the cable).
Test of Wi-Fi adapters: external adapter wins by leaps and bounds
Built-in laptop Wi-Fi adapter (with which it receives the signal) is not very powerful (usually). And the results of a small test using the standard Windows tools fully confirm this (take a look at the screenshot below 👇 – it shows the results):
A normal laptop and an Alfa AWUS036NHR Wi-Fi adapter (not an advertisement, given as an example!)
The logical conclusion follows by itself: if you want to improve Wi-Fi reception on your laptop or PC (TV) – perhaps you should think about a normal external Wi-Fi adapter?!
Well, the choice is yours. All the options suggested in the article give real results and directly affect the quality and speed of your Wi-Fi network.
Redirect the signal
This method may seem the strangest and craziest but it works quite well. Its essence is to construct a home-made product. The basic material is suitable foil or tin. Of these materials is a kind of sail, which is placed behind the antennas router.
As a result, the signal is repulsed and sent in a certain direction, which is suitable for those who can not put the router in the center of the apartment or house, because hamper walls and other obstacles. Only this whole construction looks far from aesthetically pleasing.
Update the software
Finally, we recommend updating the software, because just like any other device, utilities and so on, routers also receive regular updates. And this advice applies not only to model nuances, but also to software. Any software should be updated regularly, and in the case of routers, it is especially important because it can greatly optimize the operation of the device.
In an extreme case, you can buy a new router, because they, like any other type of equipment, become obsolete after a certain amount of time. Although before a radical solution, it is still recommended to try each method, because many of them really solve the problem with poor connection.
Read More: