The price of this device is slightly higher than its cousin – 1190 rubles. But this does not negate the fact that TP-Link Archer T2UH – an excellent choice for any user.

Advantages of switching to a new frequency
Have you ever had an ISP that promised you one speed, but de facto it was many times lower? This problem is common to all 2.4GHz router owners. The whole reason is that this frequency has only three non-intersecting channels, so with a large number of signals the dip in the air is inevitable.
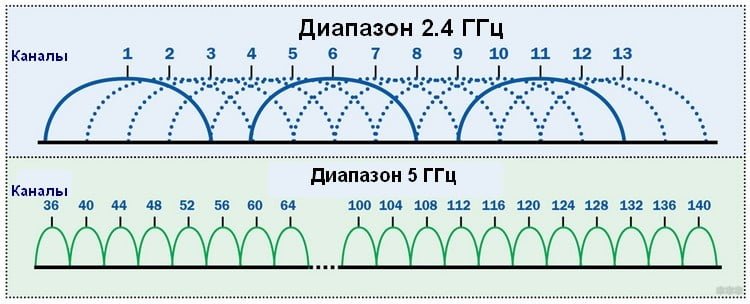
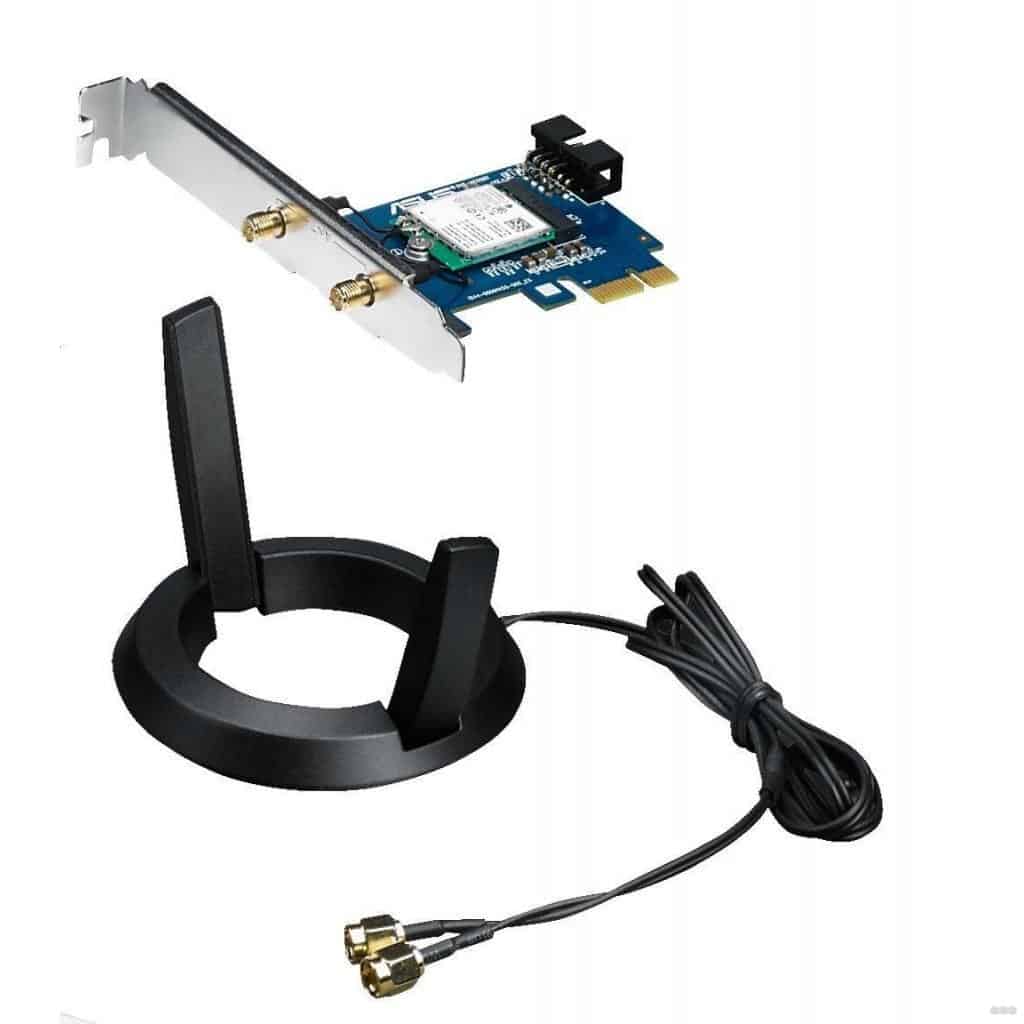
Don't rely on the usual router functions: a hat like "automatic channel selection" doesn't help in this situation in any way. That's why the only way out of the trap of low speeds is to switch to the 5 GHz frequency and the 802.11ac standard. To do this, you will need to buy a special 5 GHz Wi-Fi adapter.
An adapter is a device that can receive a signal from a router or other access point.
The secrets of channel and range selection are described in the following video:
What to look for?
To choose the best 5 GHz Wi-Fi adapter, you should consider several factors. The first is the availability of antennas. This factor greatly affects the price. 5 GHz USB Wi-Fi adapters without antennas are much cheaper than counterparts endowed with them.
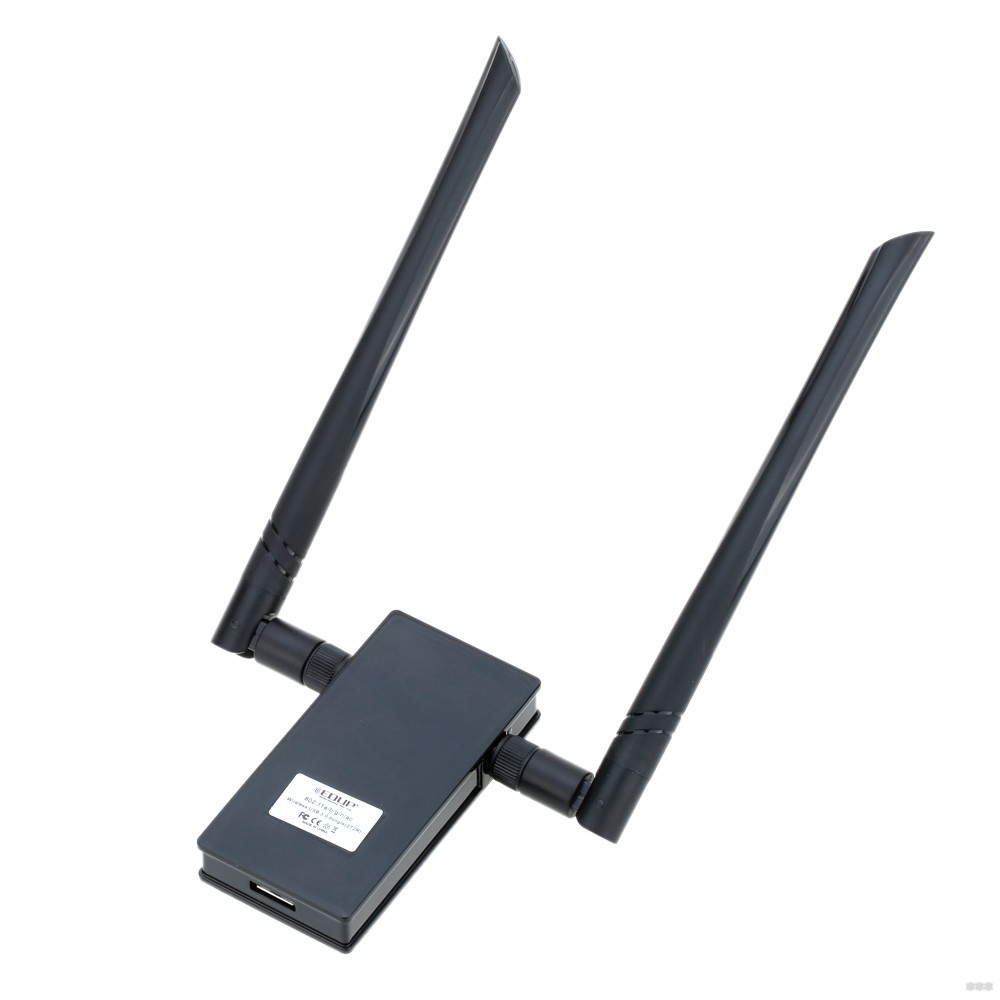

But why not buy them? Because the lack of antennas reduces the possible speed threshold. The technological lag of such devices makes them uncompetitive with the performance of antennas. That's why the price is lower.
But if you still choose an adapter with antennas, you should not forget about their number. For example, one adapter has a speed threshold of 300 Mbit/s and one antenna, and the second has 150 Mbit/s and 3 antennas. The second one will be faster, because the specified limit applies to each antenna. Roughly speaking, its ceiling would be 3*150 = 450 Mbit/s versus 300 Mbit/s.
All calculations are very simplistic, and it is unlikely that you will get the whole maximum, but it is still worth keeping this information in mind.
In addition, adapters come in a variety of sizes, from a 2-by-2-cm square to a brick-sized mechanism. As a rule, size is not a common convention. The logic is simple: more size, more functionality. Knowing these factors, you can choose the best Wi-Fi adapter for you.
Be careful with the bus type of the NIC card
NIC cards can be classified into PCI, PCI-X, PCIe, and USB network adapters based on different bus interfaces. Typically, the three types of PCI-based NICs are used to install the appropriate slots on the motherboard for devices such as hosts and servers, while the USB (Universal Serial Bus) NIC is the external bus standard.
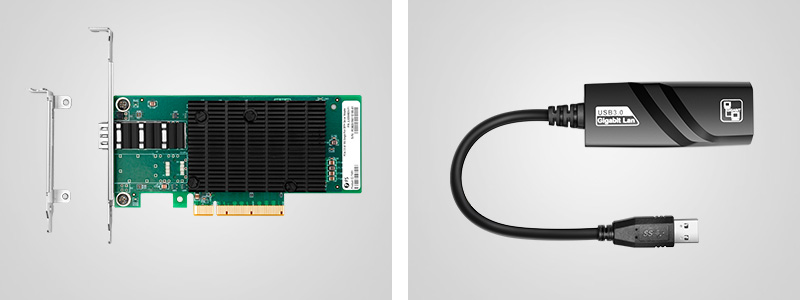
Figure 1. PCIe Network Card vs USB Network Adapter
The PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) network card was developed in 1990 and has a fixed width of 32 bits (133MB/s transfer) and 64 bits (266MB/s transfer). But later the PCI card was gradually replaced by the PCI-X card. The Peripheral Component Interconnect eXtended (PCI-X) network interface card was an improvement on the PCI bus technology and was backwards compatible with the PCI NIC. The PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) card is the latest interface standard that is only software compatible with other PCI bus specifications. Its hardware layout is different. The x1, x2, x4, x8, and x16 are the four physical sizes of PCIe Express network cards on the market (learn more about PCIe card types). Because the PCIe hardware mechanism is different than PCI and PCI-x, it is not possible to plug a PCIe card into a PCI or PCI-X slot and vice versa (check details on PCI vs. PCI-X vs. PCIe).
Note that PCIe network cards are the most popular type of network card on the market, while PCI and PCI-X cards are only used in older devices. Newly released servers, PCs, and other hosts usually have PCIe slots. Thus, PCIe network cards seem to be the best choice in the long run.
Find out the right speed for your network adapter
Definitely, if you are not sure how to choose a network card, this factor cannot be ignored. Make sure that the speed of your new network card matches the speed of your network. For example, if your ISP only offers 1Gb speeds, you can't expect to achieve 10Gb speeds with a 10Gb Ethernet card. Today, almost all network cards can run at least one gigabit speed, which will meet all of your home network requirements. But if you plan to use the new card on your servers, which require higher speeds to handle more traffic, you're better off choosing a 10GB and 25GB NIC or even a 40GB NIC.
Typically, a single-port NIC NIC card is fine, which will satisfy most transmission requirements. But NIC cards with multiple ports are a great choice for servers or workstations for a variety of tasks. For example, one port of a network interface card can be deployed to deliver basic data, and other ports can be used to transmit common signals. This can improve network security. In addition, multiport NIC cards can provide network redundancy. If one port cannot work, users can use another port to deliver data.
Network adapter function
The definition of a network adapter is very simple, but what does a network card do and what is its function? In the OSI systems model, the network card is responsible for the operation of the second, data link layer. In conjunction with the driver, it also ensures the operation of physical equipment. The task of allocating responsibilities between them, each manufacturer decides for itself. For the data link layer in addition is responsible module OS (operating system). Together, they perform two basic operations: sending and receiving data from the network to the PC and vice versa, and also take part in:
- monitoring incoming/outgoing traffic;
- remote configuration changes;
- improving performance and prioritizing the network;
- remote activation from the central workstation;
- encoding/decoding of sent/received data;
- packet formation (transmit/receive mode).
Network adapter components
Traditionally, a network adapter basically consists of a controller, a boot ROM slot, one or more network card ports, a motherboard connection interface, LED indicators, a profile bracket, and some other electronic components. Each component of the network card has its own unique function:
Controller: The controller is like a mini-processor, processing the data it receives. As the main part of the NIC, the controller directly determines the performance of the NIC.
Boot ROM connector: This connector on the board provides a bootable ROM. The boot ROM allows diskless workstations to connect to the network, which increases security and reduces the cost of the hardware.
Network adapter port for cable/module: Usually this port is connected directly to an Ethernet cable or a module that can generate and receive electronic signals that are superimposed on a network cable or an optical cable.
Bus interface: This interface is located on the side of the circuit board, which serves to connect between the network card and a computer or server through a connection to their expansion slot.
LED indicators: Indicators help users determine the operating status of the network adapter, whether the network is connected, and whether data is being transmitted.
Profile Bracket: There are two types of profile brackets on the market. One is called the full height bracket with a length of 12cm, and the other is the low profile bracket with a length of 8cm. This bracket can help users to fix the network card in the expansion slot of a computer or server.

How do I configure the NIC settings?
The settings are configured differently in each operating system. You can search for the "Change adapter parameters" function. Then you must select the corresponding connection with the cursor and call its submenu (right mouse button). Then select the item "Status – Information". In the window that opens you will be able to see the MAC-address, IP-address and netmask, DHCP-server address.
There is another option to view and change the settings of the network card – with the command ipconfig. It is performed directly at the Windows command prompt.
How does the network card affect the speed of the Internet?
Choosing the model of the card to create a network connection, you can notice that the speed is designated as one of the most important parameters. The cost of the device will also depend on it. It is obvious that the network adapter in some cases can affect the speed of data transmission and sending, and directly. However, the limit can also be set by the ISP itself. That is, with network cards, you can increase the speed to the maximum posted by the provider or reduce it, but not surpass it.
Choosing an adapter is a complicated task, and there is a great risk that the card will not function if it does not fit the device in terms of parameters. It is recommended that you consult with experienced IT engineers to make sure you don't get the wrong NIC model.
Read More: