Access to the adjustment on the router is opened by the following data:

- How to find out a router's wi-fi frequency
- How to change and configure your router frequency
- What frequencies are allowed in Russia?
- What does 802.11ac have to do with it?
- 5 GHz Wi-Fi wireless network – Keenetic
- How to find a free channel on a router
- InSSIDer utility
- WifiInfoView .
- How to change the channel on a particular router: step-by-step instructions
- TP-Link
- ASUS
- Useful Tips
- How can I find out wi fi frequency?
- How do I know the frequency of my Wifi router? Adjusting the hardware and software
- Keenetic
- Increase or decrease WiFi range
- How to choose the right signal frequency?
- What does the signal frequency affect?
- How to see the Wi-Fi channel that we use
- See Wi-Fi Channel in the settings.
- Find out the Wi-Fi channel from the command line
- Which Wi-Fi channel the router is using
- How do we know what Wi-Fi band we're connected to
- See Wi-Fi range in the settings
- View the name of the Wi-Fi network
How to find out a router's wi-fi frequency
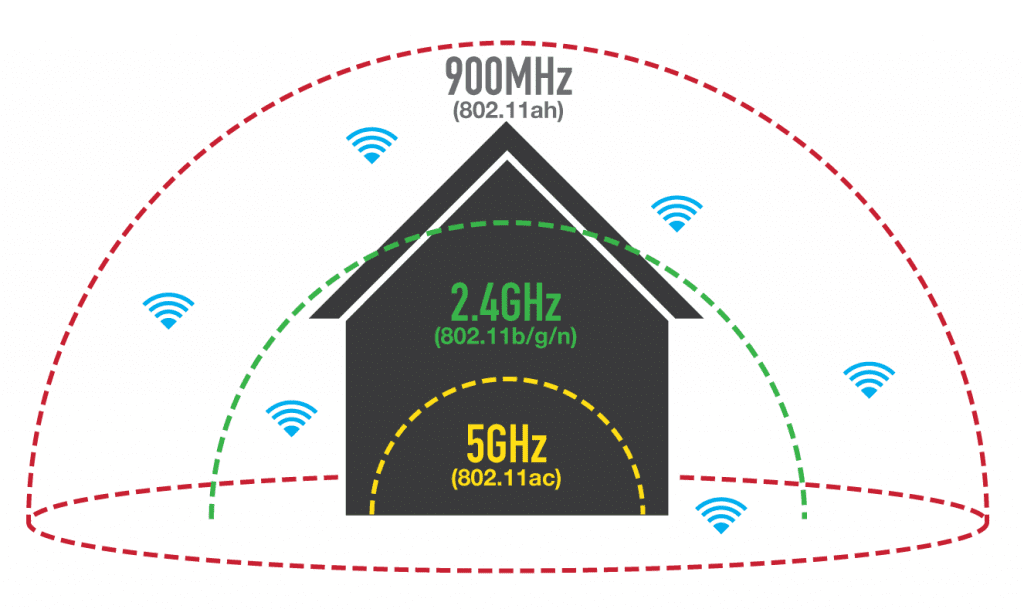
The choice in favor of wireless Internet, makes our life much more comfortable, but at the same time, creates some obstacles to signal transmission. Unlike the local data transfer via cable, where the Internet connection is made directly from the provider, the Wi-Fi signal is transmitted via specific channels in several frequency ranges.
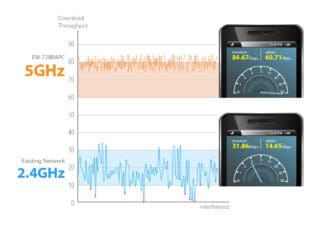
Currently, routers operate on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Moreover, 2.4 GHz appeared earlier, so the bulk of access points are working in this range. In turn, each Wi-Fi network on this frequency, works on channels from 1 to 13. Often, connection problems can arise if several neighboring routers work on the same channel and share the speed between them. Usually, routers automatically connect to a freer channel, so this problem can be solved by simply resetting the network equipment. Nevertheless, this does not relieve the 2.4 GHz band from the load of a large number of devices working on it, especially since it can be not only routers, but also some household appliances. Therefore, we recommend to use 5 GHz frequency additionally, as it is newer and free. Why additionally? The fact is that both frequencies work independently of each other and not all devices (especially obsolete ones) work in the 5 GHz band. Although, if you are absolutely sure that you will not need to connect devices supporting only 2.4 GHz, you can change the frequency of your Wi-Fi router to 5 GHz completely.
How to change and configure your router frequency
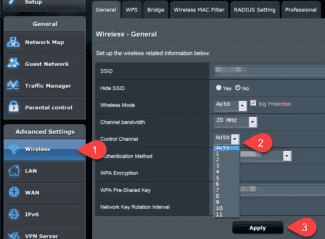
It's worth saying right away that in order to change the band from 2.4 GHz to 5 GHz, you need the router to technically support this frequency and the corresponding Wi-Fi certificate, as we wrote about in detail in the previous article. In other words, if you have an old router model, you will have to change the hardware. You can find out the frequency of the Wi-Fi router and change it, if the device is working in two bands, in the settings. You can enter the router settings either with the cable (which is usually supplied with the device when you buy it) or by entering the IP address in your browser address bar (for example, http://192.168.1.1 or http://192.168.0.1). The default login and password are set by the manufacturer and are specified in the manual or on the router itself. All necessary information can be found in the "Wireless Network" or "Wireless Mode" (the type of interface, of course, depends on the specific manufacturer). 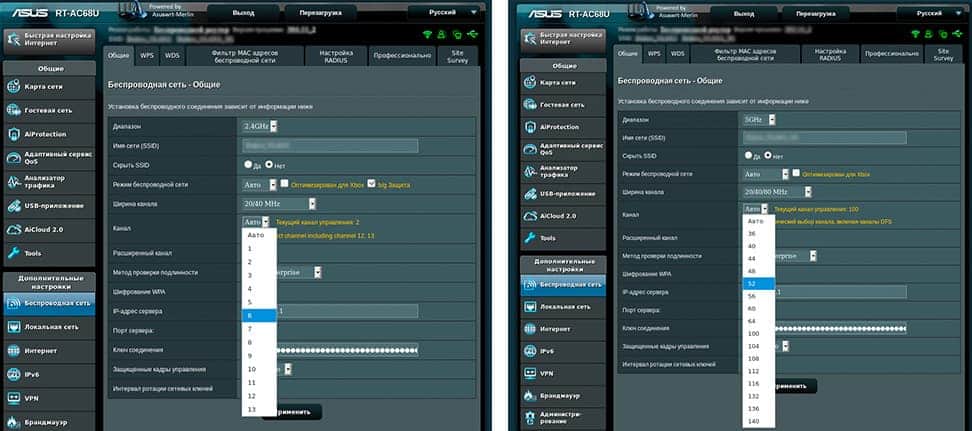 Either way, you can tune the channel even if there is no band change. At 2.4 GHz, it is best to choose bands 1, 6 or 11 because they are non-overlapping according to the standards for providing a minimum of 25 MHz.
Either way, you can tune the channel even if there is no band change. At 2.4 GHz, it is best to choose bands 1, 6 or 11 because they are non-overlapping according to the standards for providing a minimum of 25 MHz.  As for the 5 GHz frequency, there are four bands that form the channels. At a minimum, you will have channels 36, 40, 44 and 48 – this is the UNII-1 block, but depending on the device, there may be more, up to 161.
As for the 5 GHz frequency, there are four bands that form the channels. At a minimum, you will have channels 36, 40, 44 and 48 – this is the UNII-1 block, but depending on the device, there may be more, up to 161. 
Increasing the speed through your ISP by connecting other Internet rates makes no sense if you have old network equipment that does not support the new Wi-Fi standards and frequencies. With the increase in the number of users, the load on the wireless network has increased, with the same progression, the number of interference in the 2.4 GHz band has also increased. The 5 GHz frequency for Wi-Fi routers is now freer and more stable, with more non-intersecting channels, which means signals from neighboring devices are less likely to overlap and not share speeds. To increase your Wi-Fi signal and Internet speeds, you need to keep up with the times and buy modern routers that meet the new wireless network requirements. Source
What frequencies are allowed in Russia?
Each WiFi frequency has individual characteristics and uses. For example, low-frequency signals cope better with obstacles in the way, but have high levels of interference and noise. That's why it's important to be guided by your specific tasks and current situation when choosing.
There are many choices in total – 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, 5.0 GHz, 10 GHz, etc. At the same time permitted WiFi frequencies in Russia only two – 2.4 and 5.0 GHz. These are the frequencies that can be used without a license. Most routers support 2.4 GHz, but recently there have been routers that allow you to select this setting yourself.

There is one more thing to be aware of – the range of frequencies that are available in RF. So, the frequency spectrum of 2.4 GHz implies a conditional division into 13 channels. Each of them is characterized by a certain range of operation. For example, the 1st channel transmits between 2.401 and 2.423 GHz. As for the 13th channel, the range from 2.461 to 2.483 works here. The situation is similar for the other channels.
A slightly different approach to the Wi-Fi frequency range is used for the 5 GHz. Unlike the last variant, here the "higher" channels are used – from 34 to 180 (some of the channels drop out of the list). Each variant is characterized by its own range – from 5.17 to 5.905. In Russia, the indoor band used is from 5150 to 5350 MHz.
What does 802.11ac have to do with it?

This is a new wireless networking standard that replaces 802.11n. At full power it works exclusively in the 5 GHz band, it is backwards compatible with 802.11n, so it will also understand 2.4 GHz frequencies. But the speeds will also be the same as before.
802.11ac boasts a huge bandwidth (up to 160MHz!) and a theoretical speed of 6933 Mbps. It's nice, but in the real world you're unlikely to get more than a gigabit per second, which isn't bad either. Plus, this default standard includes two cool features:
- MU MIMO – up to 8 spatial streams that are shared between devices for a more stable connection. In other words, some torrent on your PC won't put your network to shame anymore, the other devices will work at the same speeds.
- Beamforming . – Beamforming. With this feature, the router is able to transmit antenna signals in a way that directs them to the device that is currently connected.
802.11ac is the future, that's obvious. We're still a long way from the speed limit, but manufacturers are improving devices every year. In many countries though 802.11ac hasn't even begun to spread. Many people think that this is true for Russia too. I hasten to dispel this myth:
5 GHz Wi-Fi wireless network – Keenetic
5 GHz Wi-Fi network setup is available on Keenetic models that support dual-band 802.11n/ac Wi-Fi (2.4 + 5 GHz frequency range).
NOTE: Important! Not all mobile devices can connect to a 5 GHz Wi-Fi network. Only devices (smartphone, tablet, laptop) that support this band will work. If your device does not support operation in the 5 GHz frequency band, it will be able to connect to a 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi network without any problems. For information on setting up this network, see "2.4 GHz Wi-Fi Networking".
The advantages and disadvantages of each band can be found in the article "Differences between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands".
When you first turn the internet center Keenetic deploys the most secure WPA2 dual band Wi-Fi network (2.4 + 5 GHz) for laptops, smartphones, tablets and other wireless devices. For guest devices there is a separate Wi-Fi network with Internet access only without access to the home network. Optimal working channel is selected automatically on the basis of periodic analysis of radio air. In most cases there is no need to make any additional settings of the main Wi-Fi access point. You only need to know the name and password to connect to the wireless network of the Internet Center (they are listed on the sticker on the bottom of the Keenetic).
If necessary, you can configure the wireless network settings yourself.
On the Home page in the 5 GHz Wi-Fi network section, you can change the wireless network name, password, and other settings. If you want your wireless network to work only during certain hours, set a schedule for it. The settings for a 5 GHz Wi-Fi network are almost identical to those for a 2.4 GHz network, except for some settings.
To change the preset network name and password, refer to the "How do I change my Wi-Fi network name and password?" instructions.
How to find a free channel on a router
When searching for the selected hardware or a "clean" slot, experts advise using special programs. Applications allow you to find out all available information concerning the device that provides a connection to the Internet.
InSSIDer utility
The program shows information about broadcast regulation, the effect of nearby equipment on the user's connection. It offers recommendations to improve router security and speed.
- download and install the application from the official site of the developer;
- launch it and in the appeared window select "NETWORKS" block;
- among those displayed on the device choose the actual one, study the features of the connection – they are given in the column "CHANNEL".
After the check, you can look for the freed band and rebuild the device to it.

InSSIDer utility
WifiInfoView .
The application is similar to the previous one, but has less functionality. To view important information you need:
Important! WifiInfoView shows information about all available connections. You can see the available bandwidth and move your hardware to an unoccupied Wi-Fi channel.

WifiInfoView app






![]()
![]()
How to change the channel on a particular router: step-by-step instructions
Regardless of the type of hardware used, debugging the free bandwidth is performed according to a conventionally uniform algorithm. At the same time, the user must know the IP address of the device and its password in advance.
TP-Link
The devices are widespread in the country, but their interface for the inexperienced user looks complicated and confusing. Which channel on this router is better to choose for Wi-Fi:
- After going into the settings of the device, open the tab "additional adjustment", located at the top of the display.
- Among the information find the block "wireless mode", open the subsection "debugging".
- In the window that appears on the screen look for the "Wi-Fi channel" parameter and choose one of the suggested slots.
- Complete the adjustment by pressing the "save" button – after that the changes made will take effect.
Old routers require a slightly different approach. The algorithm of actions includes:
Important! Any changes made to the hardware interface must be saved. Otherwise, the user will have to go through all the steps again.

ASUS
Adjustment of the specified type of devices practically does not differ from the work with the equipment having standard debugging design. There are no problems with changing the working slot, even for beginners.
- After going to the adjustment subsection, find the inscription "additional debugging" on the left side of the screen.
- Open the sub-item "wireless connections".
- In the opened properties search for "channels" and select an unoccupied slot.
Confirm the changes made by pressing the "apply" button. The system will automatically save the settings entered by the user.

Useful Tips
Most of the problems users have are caused by inability to enter the hardware interface. Standard data for all devices (login and password) is "admin". If the owner has changed the factory settings and forgotten the values, the issue is resolved by a hardware restart of the router. After that, it will return to the original values.
Trying to study the hardware leads to questions: short gi Wi-Fi what is it and what is it for. The short security interval refers to the interval between data packet transmission (from the device and back to it). So it is sgi Wi-Fi: routers function at the standard values of 800 ns. When the functionality is activated, the interval between Wi-Fi signals is halved and information is transmitted faster. So it sounds in theory, but in practice the speed figures fall due to possible failures and interference on the line.
Important! Interference and signal attenuation occur under the influence of other radio frequency sources, including neighboring routers.
To regulate the operation of the equipment (search for non-intersecting broadcast bands) you need to do some experiments, turn on the specified function and look at the indicators of Internet speed. If they will be extremely low, then the problem lies in the devices working nearby and the signal clogged them.
The router automatically looks for the fastest options, but does not cope in all situations. Problems arise:
- When the Internet connection speed drops drastically.
- If there are a large number of devices registered on the line. They use randomly matched bands, interfering with each other to function stably.
- When using powerful equipment, but not being able to connect at a distance.
Any of the above options requires manual reconnection of the channel connection. You can use any of the computer utilities or use the analyzer on your mobile device.
How can I find out wi fi frequency?
You can find out the frequency of the Wi-Fi router and change it, if the device operates in two bands, in the settings. You can access the router's settings either by using a cable (usually supplied with the device when purchased) or by entering the IP address in the address bar of your browser (for example, http://192.168.1.1 or http://192.168.0.1).
- Click the network icon in the lower right corner on the PC that is connected to your Wi-Fi network.
- Click [Network and Internet Settings] in the window that appears.
- Click WIFI on the navigation menu.
- Click [Settings] under [WIFI].
- Then you will see the connection settings, which will tell you what network you are connected to.

Clicking on it will give you access to the network name, password, transmitter power, channel and bandwidth settings, network mode, etc. If you can't figure out the problem, email me!
How do I know the frequency of my Wifi router? Adjusting the hardware and software
- Go to the router settings
- If you have the green interface from TP-Link, select the Operating Frequency Selection setting and specify which Wi-Fi bands you want to use: 2.4 GHz only, 5 GHz only, or both simultaneously.
As you can see, 2.4 GHz has a number of drawbacks. Its advantages are its ability to bypass obstacles when operating over short distances and the lower cost of devices operating on that band. Its advantages are the ability to bypass obstacles when operating over short distances and the lower cost of devices operating in this range. Simply put, Wi Fi frequency is the number of waves that pass through a particular point in space in one second.
Keenetic
The 5 GHz Wi-Fi settings on Keenetic routers can be found under "My Networks and Wi-Fi" – "Home Network". You may find the instructions on how to enter the Keenetic router settings helpful.
Band Steering is enabled by default. It synchronizes the Wi-Fi settings in the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands and the devices see the same network. Band selection is done automatically. If you want to set different Wi-Fi settings for the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz network, Band Steering must be disabled.

You can disable and enable the 5 GHz band with a separate switch.
There is also a link to a page with additional 5 GHz band settings. By clicking on it we get access to the settings of the network name, password, transmitter power, channel and channel width settings, network mode, etc.
You can even configure the schedule of the Wi-Fi network in a particular band. Don't forget to save the settings after you change the settings.
I will gradually add information on 5GHz band settings on other routers. If you do not find the instructions for your router, or if you have any questions, then write in the comments. I will definitely answer and try to help you.
Increase or decrease WiFi range
There are a lot of ways to increase range. That's why my colleague wrote about it in this article. It clearly explains how to improve the signal and make it wider at home. But sometimes in a small apartment the connection can be worse because the device is too powerful. That's why you need to reduce the power. Why this should be done – you will learn in this article.
The range of an 802.11n Wi-Fi router with a regular antenna (gain of about 5 dBi) is about a hundred and fifty meters in an area without obstacles and indoors – 50 m. But obstacles such as brick walls and metal elements can reduce the range by more than 25%. 802.11a/ac uses higher frequencies than 802.11b/g, so it is more sensitive to various obstacles. In addition, the range of 802.11b or 802.11g Wi-Fi networks is strongly affected by interference from microwave ovens. Even tree foliage is a strong obstacle, as it contains water, which absorbs microwave radiation of this range. For example, heavy rain weakens the signal in the 2.4 GHz band to 0.05 dB/km, thick fog – 0.02 dB/km, and the forest (thick leaves, branches) – up to 0.5 dB / meter.
Choosing a Wi-Fi router (on how to do it correctly, we wrote here), the range can be roughly calculated with a special calculator designed for D-Link equipment, but the formulas and methodology used there will be suitable for any other.
If creating a radio bridge between two networks, it is necessary to take into account that the space around the straight line drawn from the receiver to the transmitter must be free from absorbing and reflecting obstacles in a radius equal to 0.6 of the radius of the first Fresnel zone.
In real conditions, the signal level at different distances from the transmitting device can be measured with a special device (Wi-Fi detector).
How to choose the right signal frequency?
With this in mind, the question arises – what frequency works best for WiFi, and what parameter to set on your router. Here you need to be guided by the current situation. Most often 5 GHz is chosen for transmitting WiFi over long distances and reducing noise levels. If you need to distribute the network in normal conditions (apartment, house), suitable 2.4 GHz. But against the backdrop of congestion of existing WiFi networks users are increasingly choosing 5 GHz.
Universal solution is to buy a router that can operate simultaneously on two frequencies. In this case, you can set two modes and connect to the network at 2.4 or 5 GHz, depending on the circumstances.
What does the signal frequency affect?
The frequency of the WiFi signal is a parameter that is involved in the formula for calculating the wavelength and affects its value. In addition, a number of signal properties depend on this parameter:
- Absorption. The higher the WiFi frequency, the higher its penetration capability. The greatest impediment to the wave has reinforced concrete pavement, concrete floors and ceilings, interior partitions, etc. In addition, in rainy weather there is a slight deterioration in signal quality, which is common.
- The ability to bypass obstacles. According to the laws of physics, the shorter the wave and the higher the frequency, the harder it is to overcome various obstacles in its path. That is why 2.4 GHz is more suitable for ordinary apartments and houses, and the most effective from this position is 0.9 GHz.
- Natural attenuation. Like any other parameter, WiFi signal tends to attenuate. The higher the frequency, the more active this process is.
- Reflection. WiFi signal tends to bounce off or pass through surfaces (all or only part of them). In either case, signal strength is reduced.
- Information density. The higher the frequency range of WiFi, the more data can be transmitted in a given time period.
Against the background of the information received, it is easier to make a decision. In normal mode, you can set it to 2.4 GHz. If you live in an apartment building, where all channels are heavily overloaded, you can switch to 5 GHz, but to do this you need to buy special equipment and know how to change the frequency of the router. Universal option, when the device supports two modes at once. In this case, you can configure both networks in parallel and work with the one that gives the best WiFi signal quality.
How to see the Wi-Fi channel that we use
We have several ways to know Which Wi-Fi channel we are connected to At any time in Windows 10. We are going to show three different fast methods. It will also help us to find improvements in case we notice that the wireless speed is not the best and it may be interesting to change the channel our router is broadcasting on to make it more free.
See Wi-Fi Channel in the settings.
In this case, we need to go to Start, open Settings and go to Network and Internet . Later, when we get here, we have to enter the Wi-Fi section. . There we will find everything related to the wireless network and we can analyze some aspects.
To find out which Wi-Fi channel we are connected to, click on Hardware Properties. . It will automatically open a new window where we will see different data related to the network. One of them, as we can see in the image below, is the network channel we are using. In our case, it is 108.
Find out the Wi-Fi channel from the command line
We also have another very simple option from Windows 10 that you need to know Which Wi-Fi channel we're connected to. Now we need to go to the Start menu again, but this time we will go to the command line. Here we have to run the command netsh wlan show networks mode = BsSid.
This time we are going to find information about all Wi-Fi networks that are available. We can see each Wi-Fi encryption type, name, signal strength, and network channel. We just need to see which one we are connected to and look at the corresponding channel.

Which Wi-Fi channel the router is using
The third option we can see Which Wi-Fi channel the router is using , whether it's in one band or the other, is to directly access the device. It is very easy to log into the router and there we will find all the parameters that we can change, see information about the device, analyze the usage, etc. Д.
How do we know what Wi-Fi band we're connected to
In addition to the Wi-Fi channel we connect to, another fundamental factor is group . Modern routers allow us to connect to both 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz. It is interesting to know which one we are connected to for maximum speed. Each has its own positives and negatives.
See Wi-Fi range in the settings
The best way to find out which Wi-Fi range we are connected to in Windows 10 is to configure it. To do that, go to Start, we go to settings. , we go to Network and Internet , we choose Wi-Fi and we go to Hardware Properties.

Here again we will find a number of data related to our Wi-Fi connection. For example, the transmission speed or the name of the network. We'll also see the network range in use. In this case, we are connected to 5 GHz.
View the name of the Wi-Fi network
Another way to find out which Wi-Fi band we are connected to is to see network name . We won't always be able to get this information this way, but usually the Wi-Fi name will give us this information.
In many cases we can find two networks with similar names, but with a slight difference. For example: RedWifi5G and RedWifi2.4G. If we are connected to a network that has "5G "Or" 5GHz "in its name means that we will be connected to the 5GHz band. Otherwise, or "2.4 GHz" appears, it means that we are connected to the 2.4 GHz band.
Hence, we also have these two options to know which Wi-Fi band we are connected to in Windows 10. As we can see, in both cases, we can follow simple steps to get this information.
Read More: