Modes b and g give low data rates and shorter range, while n through a single antenna transmits up to 150 Mbps at a distance several times greater.
- Positioning the antennas correctly
- Proper placement of the router
- How is the signal transmitted?
- Where to place?
- How to configure? And is it worth changing anything in the default settings
- Turn off compatibility with older versions of the standard
- Access point power tuning and performance impact
- Conclusion
- Organizing your internal local network
- Let's start with the wires
- How to correctly position the router antennas in order to achieve maximum Wi-Fi signal range
- Complain to comment
- Higher is better
- Horns up!
- Where not to place the router
- Where is the best place to install a router?
- Connecting all devices to the network
- Troubleshooting the wireless network bottleneck
- How the Wi-Fi signal works
- Recommended locations for placement
- Where not to place
- Changing the settings
- Conclusion
Positioning the antennas correctly
Do you know how the Wi-Fi signal propagates from an omnidirectional antenna in space? You'd like to say that the access point is the center, and the signal from it is pointed in different directions and you get this kind of sphere that takes over the rooms on this floor and a couple of the neighboring ones that are below and above.
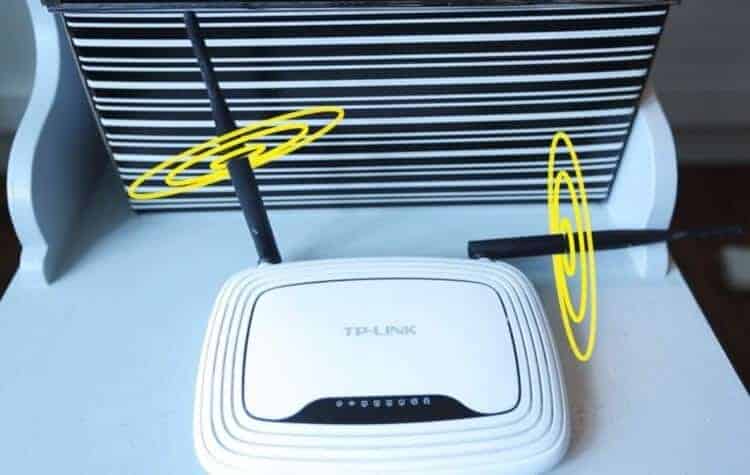

This answer is wrong. The Wi-Fi signal coverage area forms a toroidal field that is shaped like a donut. The omnidirectional antenna of the router acts as the axis of this doughnut, and its rotation determines the angle of Wi-Fi propagation.
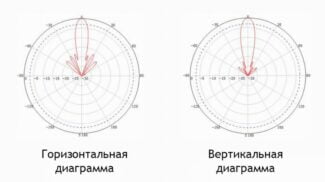
To select the best position of the antenna within one floor, place it perpendicular to the floor, at right angles. The radio waves will then travel parallel to the floor and cover the desired area.
Proper placement of the router
About the secrets of installing a router in an apartment, we have a whole article. You can read it here.
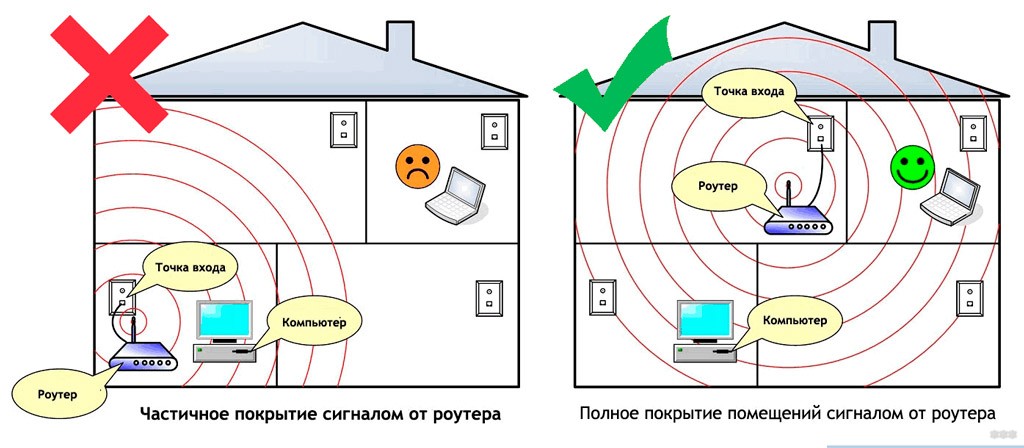
Improper location of the router is the main reason for poor coverage. The antenna emits radio waves in all directions away from itself. Near the router, the signal is strongest, and the farther away, the weaker it gets. At the edge of the zone, the signal becomes weak.
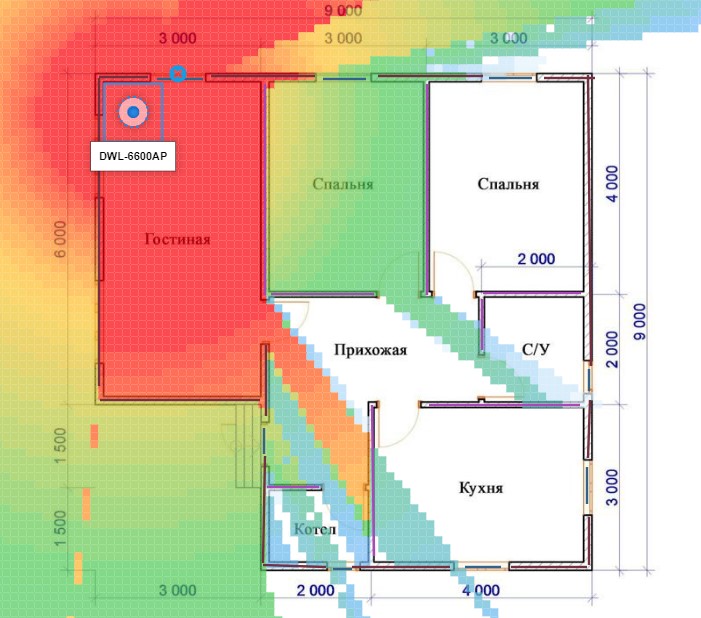
Placing the router will allow some of the radiation to go outside the building, and the remote corners of the living area remain virtually without coverage.
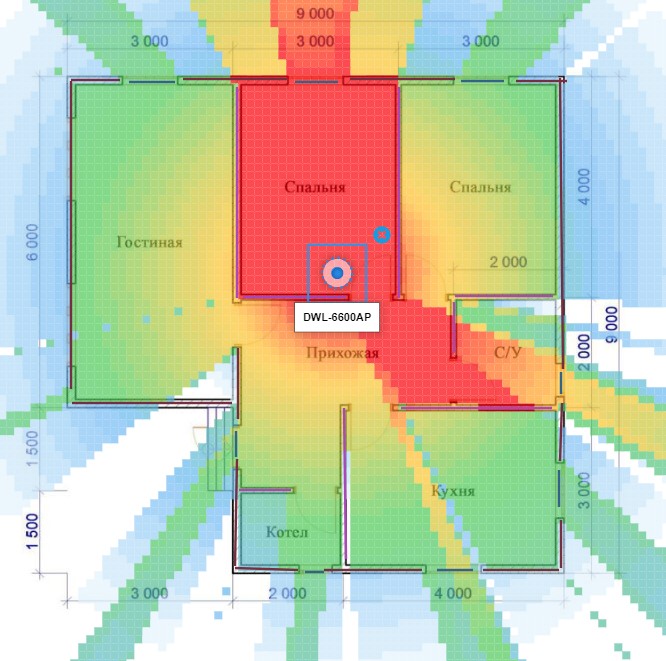
Placing the router in the center of the room will allow the electrical wave to disperse in all directions parallel to the floor, virtually eliminating dead zones.
Unfortunately, practically placing a router in the middle of the house or apartment is not always possible, due to the lack of outlets, problems with cabling, complicated layout or all together.
The following video explains how to boost the wireless signal in a very interesting way:
How is the signal transmitted?
Equipment with Wi-Fi wireless access provides Internet connectivity for laptops, phones, TVs with the Smart TV option, tablets, smart watches and other devices. The signal in the space is transmitted in the airwaves. Walls, furniture, and other structures prevent it from spreading in the apartment. They create a kind of barrier and reduce the quality of the connection. The more such obstacles, the weaker the signal. The signal strength is also affected by the distance from the access point.
When placing the router in the apartment, the degree of material absorption is taken into account:
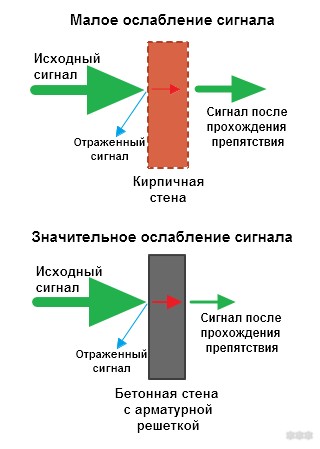
- Building materials with insignificant absorption – ordinary glass, plastic, fiberboard, wood, gypsum plasterboard.
- Tinted glass, brick, primer, plaster, water have medium absorption.
- Materials with a high degree of absorption significantly affect signal conductivity – ceramic, iron, aluminum, reinforcing bars.
Where to place?
See a video about finding a place for a router here:
Where should I put my router in my apartment? To ensure a quality signal, stick to the rule of thumb: "fewer obstacles between connection points – better connection." To achieve a clear connection, stay in the area with the fewest obstacles between the router and the receiving device. Before installing, consider whether the router will be used exclusively for wireless connectivity or whether a desktop computer will be connected to it.
A suitable place where it is best to install a router in an apartment with a standard layout, is the corridor. First, in this situation it is easier to connect the cable coming from the entrance hall. Secondly, the hallway in standard 2- and 3-room apartments opens up access to other rooms with less interference.
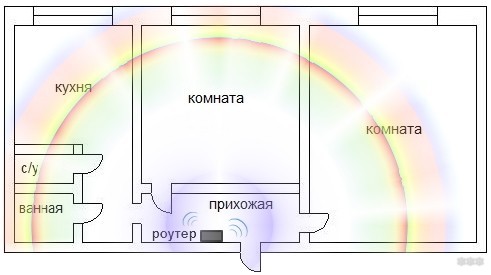
You can also place the device in the area where the person will most often use the wireless network. An alternative option is a central room.
Once the location is chosen, you need to determine the point of location. It is better to install the router on the wall or put it on a dresser or shelf. Many devices have holes for attaching to the wall. The location of the router in the apartment at a height gives the owner more advantages. In such cases, the waves are distributed evenly in the absence of obstacles.

How to configure? And is it worth changing anything in the default settings
Turn off compatibility with older versions of the standard
Wi-Fi hotspots provide backward compatibility with all available devices the router will see on the network. To get the maximum speed your Wi-Fi router can deliver, it is best to turn off compatibility with older Wi-Fi standards in its settings. The most common today are 802.11n and 802.11ac. If you don't have any devices running on earlier versions of Wi-Fi in the room, it makes sense to leave only 802.11ac in the router's settings.
After all, common with older devices, the access point will provide compatibility mode and spend more time and resources transferring data for that device than with other higher-performance devices.
It should be noted that newer models of wireless equipment have a new technology called Airtime Fairness. This technology limits a client session not by the number of packets transmitted but by the time they are transmitted. Thus, thanks to Airtime Fairness technology, only the adapter with the lowest performance will lose data transfer speed, because it will be able to transfer less data during the allocated period of time.
However, although Airtime Fairness has appeared, it will not become ubiquitous anytime soon. If you are looking to purchase a router in the near future, look for a device that supports Airtime, or switch off compatibility mode for older standards: 802.11a/b/g/n.
Access point power tuning and performance impact
As transmitter power increases, so will coverage, leading to potential connectivity bоmore customers will be potentially connected. This is of course a plus, but the bandwidth of the access point itself may not be enough for a large number of users, which will lead to a decrease in transfer rate and increase the network latency. Thus, you will get quite the opposite effect. The same is true for a router in an apartment building. Your device will be loaded with packets from other devices.
Conclusion
So, above we have considered the most important points, in our opinion, which should be taken into account when installing a router indoors. Let's briefly list the main recommendations:
- Choose a location in the room that is far enough away from supporting structures and far enough away from other sources of Wi-Fi signals.
- Place the Wi-Fi router so that its antenna radiates as effectively as possible.
- Use a device that supports Airtime Fairness, or turn off compatibility mode for older standards: 802.11a/b/g/n.
- It makes sense to increase the channel width to 80 or 160 MHz.
- It makes sense to reduce the power of the access point to equalize the power relative to users' wireless adapters (laptops, tablets, and smartphones).
After reading these recommendations, you may have already figured out what you can do with your home wireless device to make the Wi-Fi network quality a little better.
Organizing your internal local network
If people come to small country houses to escape from city life, work and abundance of information for a short time, then there are more serious requirements for communications in country cottages. People who live in such houses want to have reliable communication, for example, in order to keep up with current events, to work remotely, in general, to keep a hand on the pulse of life. That requires a more serious infrastructure than a single WiFi router.
Tip. To get rid of most of the problems associated with selecting and matching equipment with each other, use a comprehensive solution from one vendor.
Let's start with the wires
"Why is it with wires?" – asks the inquisitive reader. It would seem that everything could be done easier – put WiFi access points and go! But there are nuances everywhere.
Of course it is possible to build the whole network solely on wireless equipment. This kind of networking is called a Mesh. But then, first of all, part of the transmission and reception resources will be spent for the connection of access points and router with each other, and not only for data transfer, but also for exchange of service information.
For example, if an access point has two radios, then if there is a sufficiently high density of devices (consoles, tablets, smartphones, TVs, and so on)-if one of the radios is used for both Mesh and clients, then there will be a loss of performance in this range.
If you have two radio modules (2.4GHz and 5GHz), you can, for example, give the 5GHz radio module to the Mesh only and the 2.4GHz to the clients only. There would be no problem with 2.4GHz reception, but the 5GHz channel would be lost. Wouldn't it be easier to plug the access points and firewall into the switch?
Second, some devices are preferable to a wired LAN, such as a desktop computer, a network printer, and so on.
Third, there are also surveillance cameras. A wired connection is much better for transmitting a good steady picture.
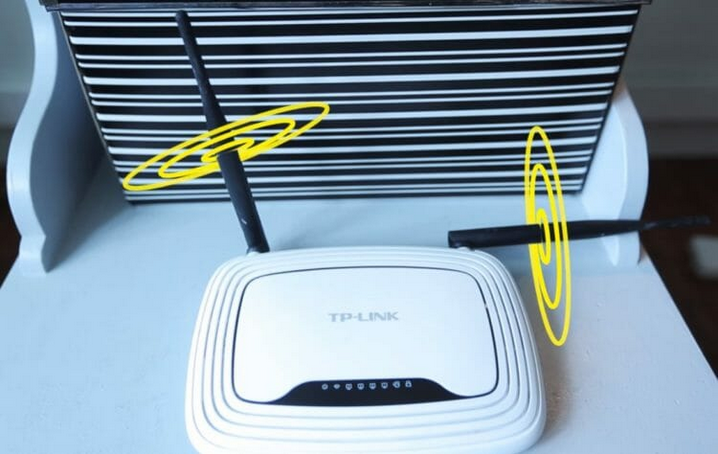
How to correctly position the router antennas in order to achieve maximum Wi-Fi signal range
Quite often when I visit friends and relatives I see that on their wi-fi routers antennas are placed in any way, but not as required. And the reason for this is that people simply don't know how the signal from wi-fi antennas spreads. But in fact it's very simple. And even the manufacturers themselves show exactly how the antennas should be located. Look at the box from your router (if you haven't already thrown it away), there will be a hint. Below I will tell you exactly how to position the antennas for better signal reception and transmission.

In order to understand how to place the antennas on the wi-fi router, it is necessary to understand how the signal from these very antennas is dispersed. And here, of course, not everything is so simple. And there are many different types of antennas. But we are interested specifically in the antennas in household routers, which are usually a spring, with the right number of coils, hidden in a plastic pin. The classic antenna on a router looks like this:
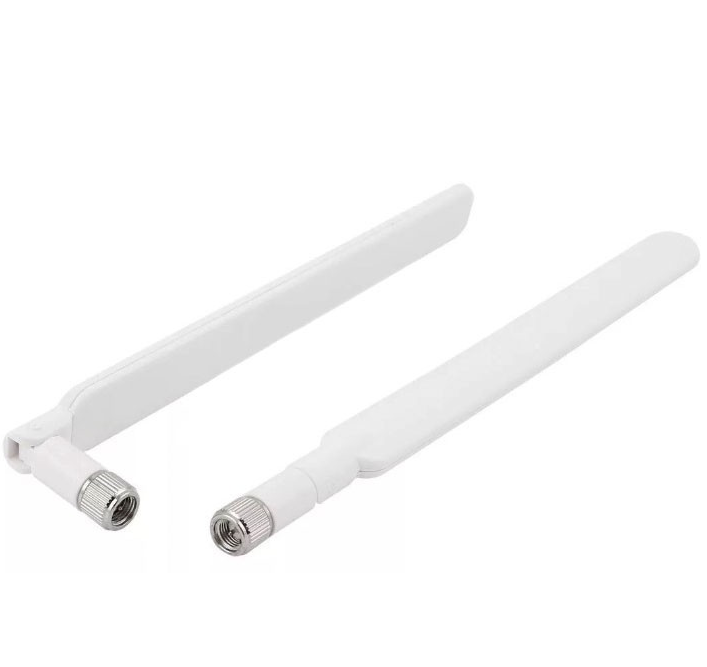


This is the type of antenna installed in most home routers. Although there are models with built-in antennas and omni-directional antennas. But we will not consider them, because in this case the manufacturer himself took care that the antennas were installed in the right direction.
Now let's see how the Wi-Fi signal diverges from this type of antennas. Googling will help us for this, where you can find a bunch of different studies and measurements. If we take a simplified diagram, it looks like this:
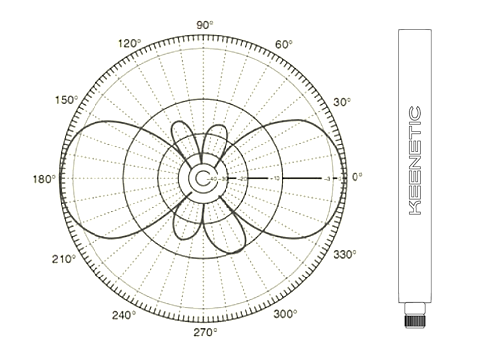
Complain to comment
Then you have to wrap your head in tinfoil. Because apart from the router, the apartment is full of other radiations: microwave, cellular, neighbor's routers, 5G towers, reptiloid transmitters, radio waves from radios and repeaters, radio and TV signals.
Oh, my gosh, I'm so scared myself.
If you ever stood next to a spectroanalyzer, your confidence would shake to some extent.
What's the point? You need a grounded screen with a grounding resistance of less than 0.01 Ohmm, which is a minimum of 2,000 15-meter metal pins driven into the ground at a distance of 20 meters from each other. Then your screen will help, otherwise hide in a bunker with walls of one meter of armor:)
Knock on the door and introduce yourself as an employee of an Internet company, say preventive maintenance, and then do with the antennas what you need!
Here for example in my apartment catches 3 router from the sasedej all with a password of course. And what's free? Without knowing the password, I can not use the Internet, then.
It also happens that the router is lying somewhere on the floor behind the desk in a pile of wires and of course there are complaints about the poor connection. So it was with friends in St. Petersburg's old stock, where thanks to the wooden slabs WiFi worked more for communal neighbors from downstairs and was not the full coverage is not such a big three-bedroom-settlement. As soon as you put the router up on the cabinet, there is a stable connection in the far room.
And my router doesn't have any antennas outside.
What am I supposed to do, put it on its side or upright?
What are you smoking out there that's got you so worked up?
What difference does it make which side you put the oil on, it'll fall down anyway!
Well, lamers don't get it.
And who at least the user – they get.
//Ps
How strange, my router is 15 years old.
The incoming channel is 250 Mbps, by youfly 220-230 Mbps load holds steady…
And what are the numbers claimed?
For example claimed gigabit per second.
And you have to understand that firstly this gigabit is possible only in ideal conditions – the air is clear, the signal is good, and the subscriber's device supports it.
Secondly, gigabit is the speed of the link – the radio channel through which the data will be transmitted. Data can be service and user data. In wi-fi, the share of service data is about 55%.
Accordingly, the speed of user data transmission will be about 450 megabits.
Higher is better
What do the router and the cat have in common? They both just love to look at the world from above. Just like a cat can lie for hours on the closet, a box with Internet works best when it's standing somewhere higher up. For example, on a shelf closer to the ceiling. The reasons for this are utilitarian – the signal travels better from top to bottom.
A number of routers even have special mounts to hang them on the wall without buying a separate shelf. Thus, it is sufficient to drill a couple of holes in the wall and screw in screws with dowels, and the router to hang on them. But here's an important point: it is better to choose plastic self-tapping screws. The router does not like the extra metal and reacts unpredictably to it.

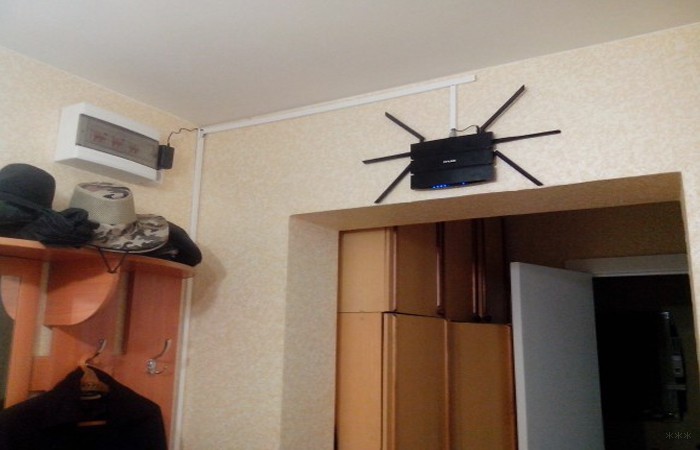
Horns up!
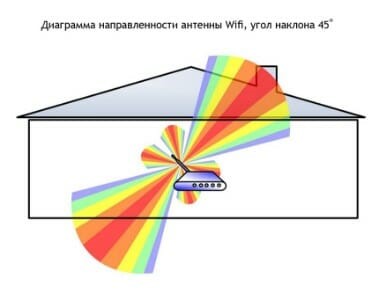
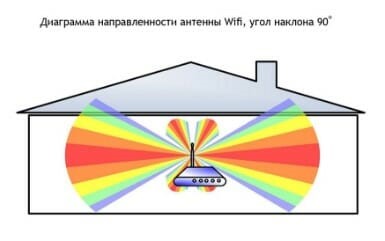
And one last tip: keep an eye on the position of the router's antennas. Regardless of their number, the "horns" of the router should point upwards if possible, not sideways. This is in the case if you have followed all the previous advice, and there are no obstacles between the router and Internet-hungry devices.
If there are (for example, you can not do anything bearing a wall or a mirror), it is better to buy a router with multiple antennas and change their direction so that the signal went around obstacles. Experimentally, by changing the position of the antenna, you can achieve good reception.

Read about other routing secrets in our materials:
Where not to place the router

- Do not place your router near your home electronics like TVs, microwave ovens, computers, etc. In general, all those devices that can interfere with radio waves.
- Do not place your router on metal structures. They perfectly block and weaken the Wi-Fi signal.
- Do not place it near a mirror. It reflects the signal and can severely interfere with its propagation if the mirror is placed on the wall between rooms.
- Do not install your router in a bathroom or other room with high humidity. Especially if your router does not have water protection, and by the way, it is not present in the vast majority of home routers.
Where is the best place to install a router?
The main rule of choosing where to install the router – between it and any extreme point in the apartment should be the least of the walls. And, that means the router definitely should not be installed in a side room. The ideal place for its installation we have shown in the diagram below.

As you can see, on one side the router is close to the front door, because of which you will not have to lay the ISP cable throughout the apartment, thereby disturbing the neatly made repairs. On the other hand, the router is separated from each room (except the bathroom) with only one wall, and this ensures maximum Wi-Fi coverage throughout the apartment.
Of course, even here there can be nuances like metal structures, reinforced interior partitions and other elements that we did not take into account. It's also worth considering where you use Wi-Fi most often. For example, if you prefer not to use the phone in the bathroom, it might be a better solution to install a router in Room 1. Especially if that's where you work with Wi-Fi most often. But you definitely shouldn't put it in room #2 and the kitchen.

In general, in reality, the ideal location for the router may be different, but we have only tried to clearly show the principles that must be followed when choosing it.
Connecting all devices to the network
The first step on the path to optimization is the same: everything that can be connected via cable must be connected via cable. In this uncomplicated way we eliminate the possibility of problems with speed and stability of the corresponding client devices. The bottleneck in the wireless network will be solved in the second stage.
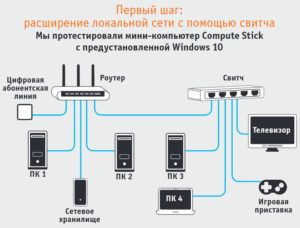
Almost all stationary devices – TV, game console, Blu-ray player and others – are equipped with an Ethernet port for a LAN cable. Just what they need is a broadband twisted-pair connection for stable video streams (media library, YouTube) and media data from other home network devices (PC, NAS) at high speeds.
Instead of pulling a twisted-pair cable from each client device to the router, you can connect all the devices in one room to a gigabit network switch (about 1000 rubles, see "Gigabit Switch"). right) – this option would make more sense, given that the cable from the switch to the router, which will provide Internet access and data exchange with the rest of your home network, can easily be hidden.
If that's not possible, go to the section on mesh extensible networking systems and Powerline Wi-Fi Extenders designed to extend wireless network coverage (see page XX) – these technologies also allow you to connect the switch to the router.
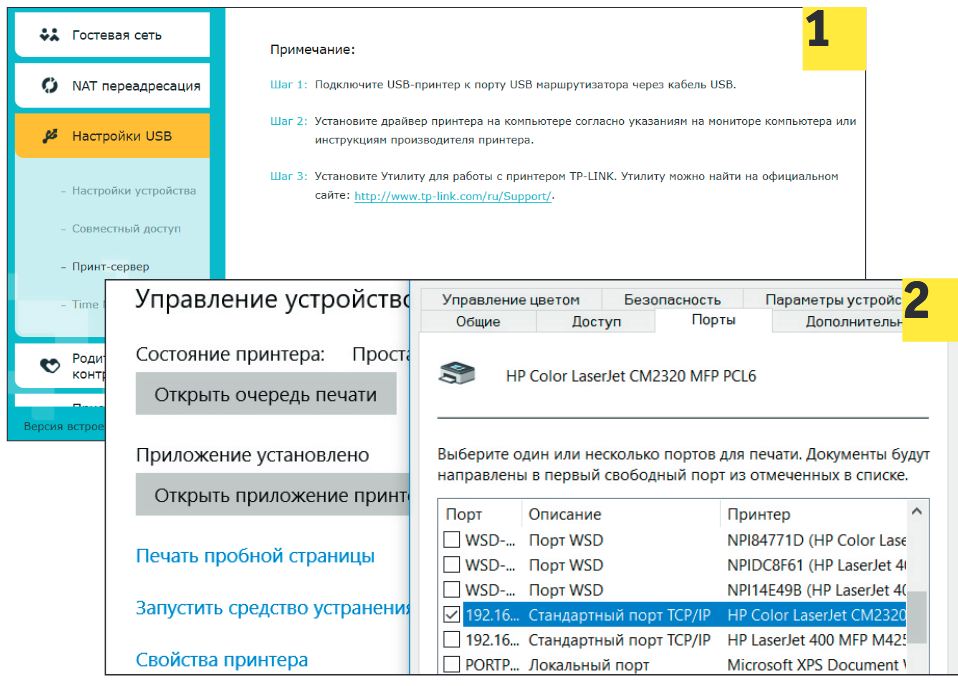
The more features that are available to you over your home network, the more convenient it is to use it. For example, if your printer still does not support networking and does not connect to the router over a twisted-pair or wireless network, you will have to take steps to be able to print files from any computer or mobile device.
Troubleshooting the wireless network bottleneck
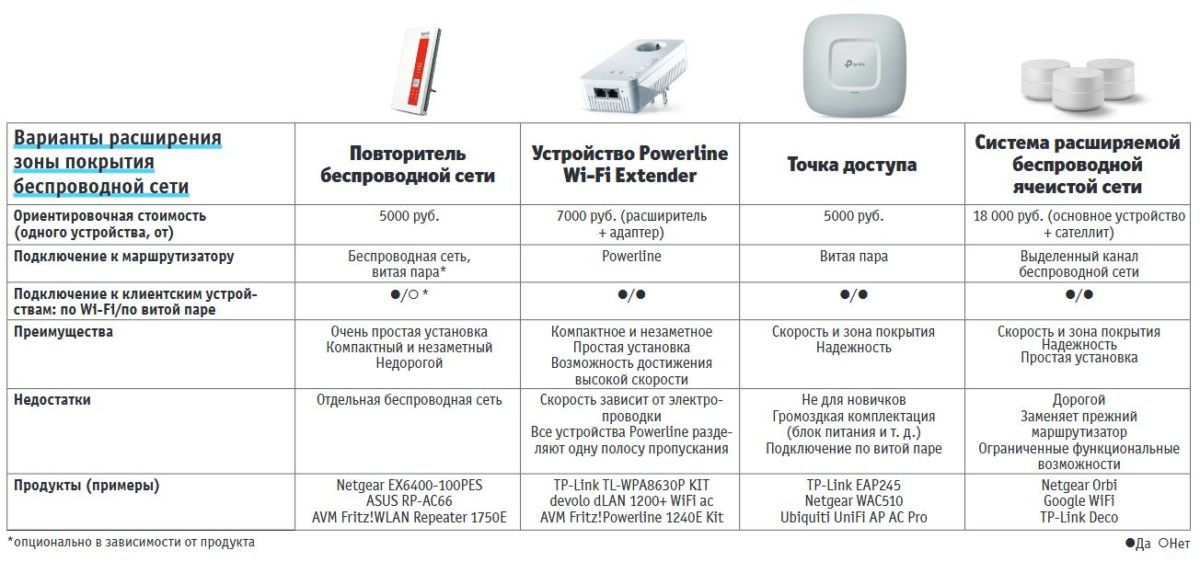
To meet today's wireless speed requirements, the router must support at least the 802.11ac standard with a nominal throughput of 1333 Mbps (802.11n can handle large amounts of data in most cases, too). Make sure the router is not covered by anything, and place it higher up.
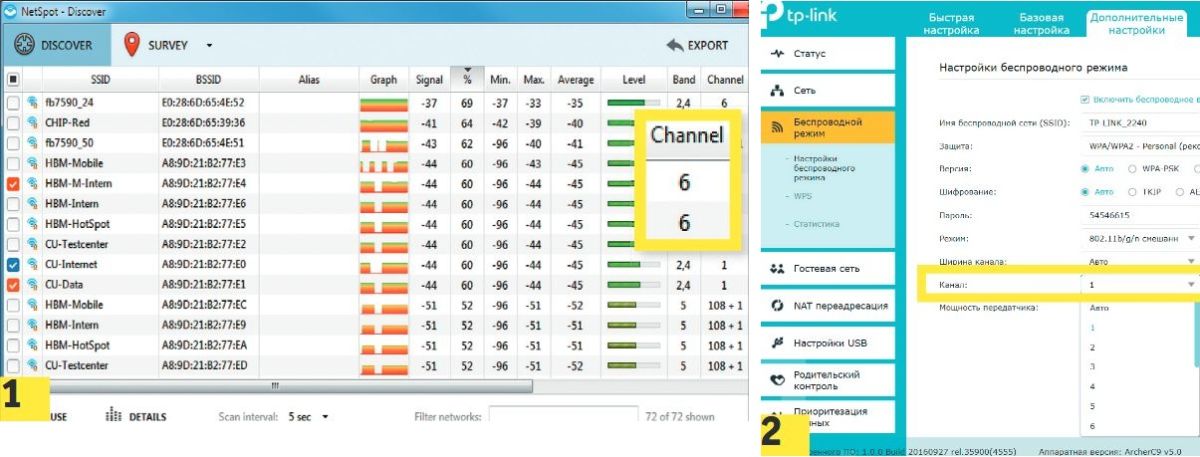
If some parts of the network are slow – find out where the dead spots are by using an Android app (like WiFi Analyzer) or a Windows tool (like NetSpot) from your laptop. If changing the channel (page 100) does not improve the connection, you can install signal boosters that are as close as possible to the client device: repeaters, access points, Powerline Extender devices, or mesh-based Wi-Fi-Network extensible systems.
The easiest option to increase network coverage is to install a Wi-Fi repeater. You need to place it, as well as the router, as high as possible (about midway between the router and the "dead zone") and make sure there are no obstacles for the signal to pass nearby. The setup process usually involves plugging in the power and pressing the WPS button on the router and extender.
Next, you connect the client devices that were previously in the "dead zone" to the wireless network deployed by the extender. Since the extender sends and receives packets of data simultaneously during its operation, in many scenarios (namely, when the hardware or location of the devices only allows you to use the 2.4 GHz band) the speed of the already slow data transfer through the wireless network is halved.
How the Wi-Fi signal works
And you should start with the basics, namely the principle of signal operation, because without this theory it is impossible to choose the best location for the selected router. Thanks to it it will be possible to take into account all the factors that are usually ignored. So, the signal is transmitted through the radio air, and consequently, its passability will interfere with the walls, furniture and so on. If you make a gradation on the absorption, it turns out about the following:
The access point, or rather the distance to it, also plays an important role. If you are far away, obviously the signal will be worse.
Recommended locations for placement
Now what about where to place the router in the apartment. The first rule that should be observed when choosing a place – there should be a minimum number of obstacles to the signal transmission. If you take the "standard" layout, it is best to put the router in the hallway. It is not necessary to install it near all the used zones. The signal is distributed equally and if you want to increase its strength, it is recommended to use special repeaters. This is where it is recommended to place the devices:

It is also worth considering the range of the signal. Yes, it can be increased, but it will be only after identifying all the "blind spots", which take time to detect. Router on the wall in this case will be the best option, if located in the center of the apartment. However, when the placement on the wall is made in some corner of the apartment, the distance from the access point increases. This negatively affects the signal transmission.
Where not to place
So, we have understood, where you can put the router. However, we also need to consider where and where it is better not to install the router. If we confine ourselves to a brief list, it is approximately as follows:
- isolated spaces: cupboards, furniture, niches – all these things "muffle" the signal, and therefore the router should not be placed there;
- on the floor: there are still many objects that will interfere with the normal signal path, and this location can only be chosen in an empty apartment;
- next to the TV: do not hang the router there, because this will interfere with the signal, and keep a distance of about one meter from such devices;
- metal constructions and any iron, which are characteristic for use in a private house: here there will be the maximum level of absorption, which will make it much more difficult to use the Internet;
- install near warm objects, which are heating: not only will the life of the device due to constant heating, but the signal will become worse.
Changing the settings
There is another option to improve the quality of the radio pulse – to change its settings. Let's consider why to do it.
Your signal may be clogged by transmissions from your neighbor's router behind the wall, which also gives out Wi-Fi, but to your apartment and, worst of all, on the same frequency. As a result – you will be missing the Internet from this.

This problem is solved by switching to another channel. Most routers do that. They can select the most congested channel and switch to it. To do this, you have to activate the "Auto" item in the list of Wi-Fi channels. Alas, not all devices have this feature.
You can try to increase the power of the radio signal. True, this option is limited to a range of 0 to 100%. But if your router has the ability to increase the power level above the standard values, it can save the situation.
Increasing the power violates the standards of the State Commission on Radio Frequencies. No one, of course, will control you, but still – keep it in mind.

Conclusion
Now you know for sure that Wi-Fi routers have antennas in any case, and they can be located in different ways. How many – one, two or more – depends only on the area of Wi-Fi coverage. And if your speed is up to 100 Mbit/sec, then it's not so critical for small rooms. But if you have high-speed Internet, which is used to watch streaming video in an improved quality or for online games, then you need a router with a large number of antennas.
Read More: