The most economical modifications of network equipment may not contain this button either on the front or on the back panel. In this case the debugging is only possible via the web configurator. How to enter it is mentioned above and will be described below in detail.

- What connection type should I choose when setting up a Wi-Fi router?
- Consequences of incorrectly set connection type
- What is a DMZ in a router and how to configure the demilitarized zone
- How to enable and configure a DMZ on a Wi-Fi router/modem.
- NAT Terminology
- NAT Types
- Static NAT
- Dynamic (Dynamic) NAT
- PAT (Port Address Translation)
- WAN port: for the advanced and different from LAN
- WAN network.
- Connecting technology for gadgets and TV
- What is WPS on the router?
What connection type should I choose when setting up a Wi-Fi router?
Useful information for those who want to configure correctly Wi-Fi router and can not choose the type of connection. Let's see what type of connection to choose when setting up a router, the basic functions of the MAC-address and a few other nuances.
Before you start configuring the router, you need to clarify all the information in advance, without which you will not be able to access the Internet, no matter how correctly you set up the rest of the configuration parameters. This information includes the type of connection to the World Wide Web and the MAC-address binding used by your ISP.
For the router to be successful, all settings and options must be specified correctly, for example: if your ISP uses a connection type based on Dynamic IP, just select this type in the router setup, and the rest of the data will be applied automatically.
In addition, it is important to know whether the ISP uses binding by the physical address of the network device. Typically, when signing a contract with a subscriber, the Internet service provider registers one MAC-address, which will supply the Internet, so if you reconnect the network cable to a device with a different address (to the router), there will be no connection to the ISP and therefore the Internet, too.
The router's main job is essentially to connect the router to the Internet and distribute access to it to other devices, and to do that it needs to connect to an Internet service provider. However, this will not happen with the wrong network and router settings: connection technology, etc.
Consequences of incorrectly set connection type
Most problems are related to this error. When the user sets a connection type that does not match the one specified in the contract with the provider, there will be no access to the network. Wireless connection will be set up, but when trying to open some web-resource the device will give error "No access to the Internet". The same picture will occur when connecting via cable and PC. The reason is simple – no connection to the Internet provider due to errors in the network settings.
In the Russian Federation, Ukraine and other CIS countries, the most popular technologies are:

- First of all – Dynamic IP.. This technology is popular among Internet service providers, in addition, it simplifies the configuration of the router. It is enough to select this technology among the possible options and connect the network cable to the router. As a rule, dynamic type is used in routers by default, so no additional settings are needed.
- A less common technology is Static IP. With this type of connection, the Internet service provider assigns a specific IP address to the subscriber, which is entered into the network and device settings.
- PPPoE is widely used in the CIS. However, a high speed connection is important for it. Internet provider, which uses PPPoE, gives his client a static IP, as well as login and password to the network, which are specified only in the settings of the router. A representative of the Internet company, which works on this technology, creates the necessary settings on your computer.
- The last type PPTP and L2TP protocols. With this type of connection, the user specifies the login and password when configuring the network device. In addition, the subscriber prescribes the server address and static IP provided by the ISP.
What is a DMZ in a router and how to configure the demilitarized zone

The functionality of a Wi-Fi router is quite wide, but some options of this network device are quite unfamiliar to some users. Certainly certain functions in the interface of the device are unnecessary for ordinary users, but if you need to solve non-trivial tasks, then you just need to know about them. For instance, gamers, who have a game server at home or who have secured themselves with a video surveillance system, should know what a DMZ in a router is and how to set up a virtual zone in order to open access to a DVR recorder.
Many recommend doing port forwarding in such cases. This is really relevant, but in this case there is a risk of encountering some problems. Often the web interface of the DVR uses port 80, which can not be changed and at the same time on the router it is also busy, which means that port forwarding in this case is irrelevant. There are experienced guys who redirect the network stream with the firewall, but in my opinion it is better to use the built-in router option DMZ.
DMZ is an acronym for DeMilitarized Zone. Basically, it is a specialized local network segment which contains publicly available services with full open access for internal and external networks. At the same time, the home (private) network remains closed behind the network device and there is no change in its operation.
Once this feature is activated, the DMZ host will be accessible from the World Wide Web with full control over its security. That is, all open ports in this zone will be available from the Internet and the local network at a trusted IP address. Thus DMZ provides the necessary level of security in the local network and makes it possible to minimize the damage in case of an attack on a public (added to DMZ) IP. As you understand, the attacker only has access to the device that is added to the DMZ.
How to enable and configure a DMZ on a Wi-Fi router/modem.
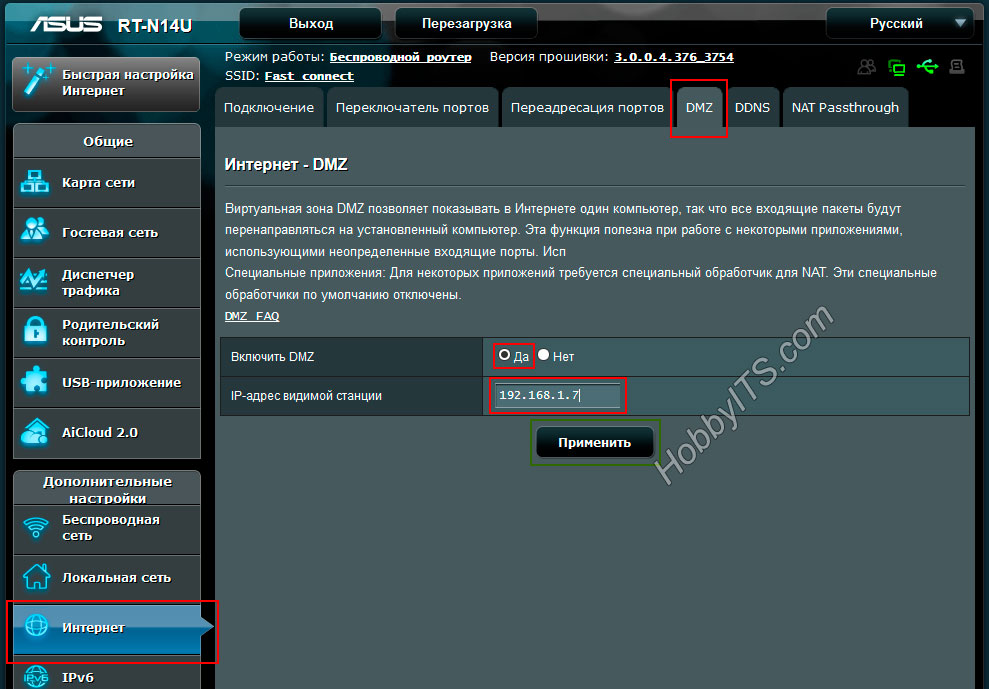
Budget models of these network devices do not have the ability to create a full-fledged zone for all participants in our network segment, but we do not need it. The main thing is that it is possible to add one IP address of the visible station to the demilitarized zone. With this action, we will make the DMZ host and open access from the external network to all its available ports.
Go to the interface of the router and in the administration panel, look for the tab called DMZ. For example, for network devices from the company ASUS, this tab is located in "Internet" -> "DMZ".
On your TP-Link router, you can enable DMZ under "Forwarding" -> "DMZ".
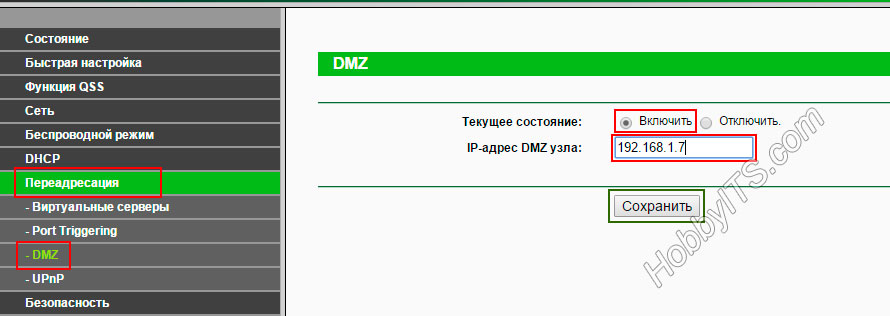
Unfortunately, from other manufacturers of network devices to create a screenshot is not currently at hand, but where to find this function in other models in words. D-Link has put it in the "Firewall", and Zyxel Keenetic can add this option in the NAT settings.
As you can see, it is pretty easy to enable DMZ on the router. I wish you all kinds of attacks will keep you safe.
If you find a mistake, please highlight text and press Ctrl+Enter.
NAT Terminology
There is different terminology in the NAT field which you can find in the router configuration or on the connection diagrams.
- Insidelocal – The internal local address that is stamped in the initial client request.
- Insideglobal – external IP address of the router.
- Outsidelocal – is the internal global address of the server on the Internet. It is internal because it appears in the initial request from the computer on the internal network.
- Outsideglobal – The external global. The IP of the request to the destination server which is written in the external request from the router.
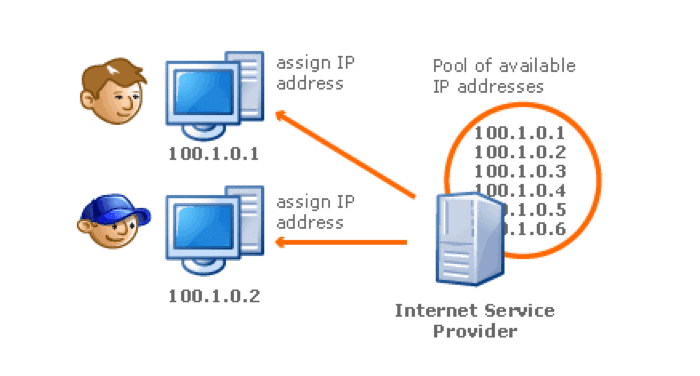
Nothing clear yet? I will try to show you an example. Let's look at a NAT addressing example. Take a look at the picture below.
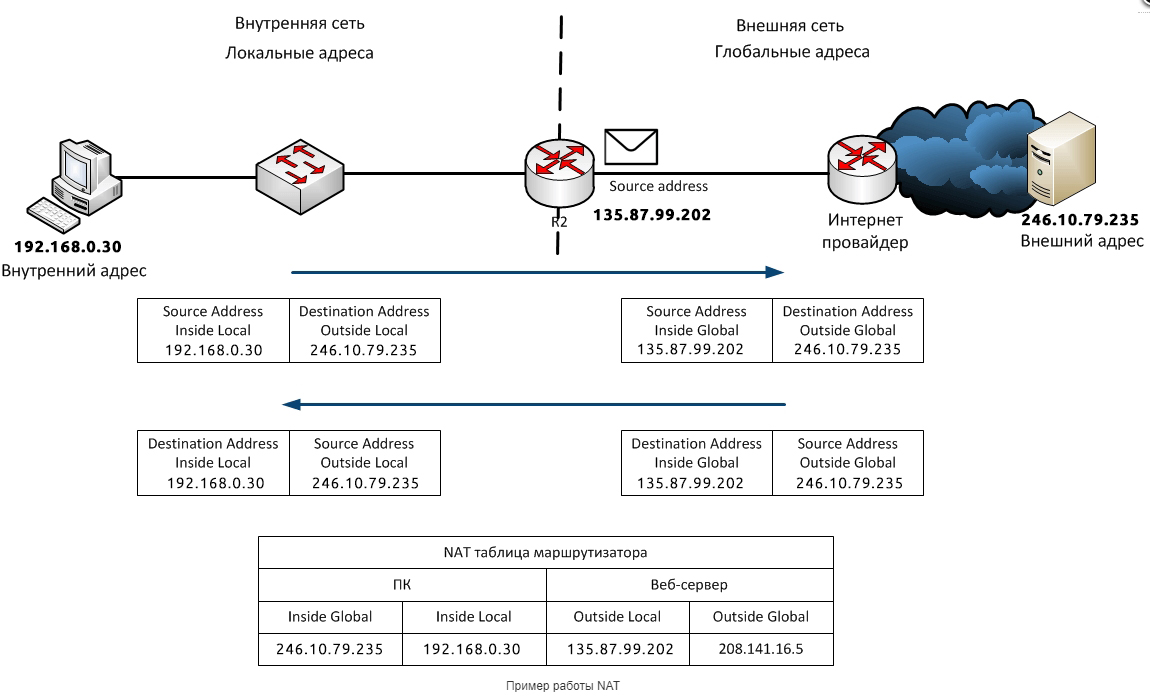
- We have a computer with an (Inside Local) address of 192.168.0.30 which is on the home network.
- It sends a request to the server with the (Outside Local) address 246.10.79.235.
- The router receives the response and translates the request:
(Inside Local) 192.168.0.30 -> (Outside Local) 246.10.79.235
(Inside Global) 135.87.99.202 -> (Outside Global) 246.10.79.235
- When the server receives the request, it sends a reply and all requests are redone in reverse order. For the router to understand who the response came from and who to send the request to, it writes all the data in its routing table.
NAT Types
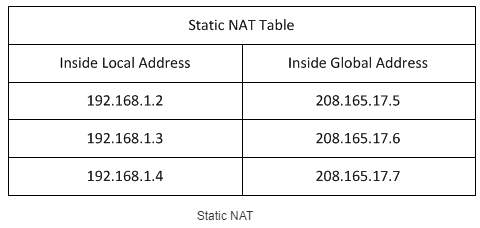
Static NAT
Static NAT is when each local internal address has its own global address. This is often used for Web servers. All traffic is routed like this through one node and each device has its own local and global IP.
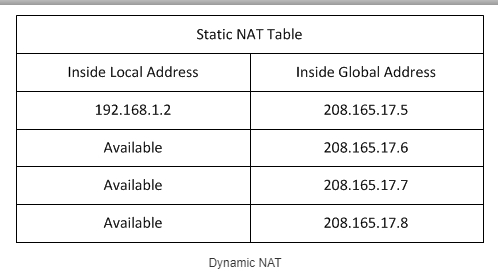
Dynamic (Dynamic) NAT
We have a pool of internal IPs which are constantly being assigned different global external addresses. External IPs are assigned according to what is free and what is assigned by the router. It is often used in urban networks by ISPs, which is why your global IPs are constantly changing. To expand on this subject a bit, read more about white and gray IPs.
PAT (Port Address Translation)
This is the most popular form of NAT. That's what I was talking about at the beginning. When several local addresses are assigned to one global address. That is, when the whole family, roughly speaking, uses a single external IP. For the router to understand to whom exactly to send a response from the server to which it has been previously requested, it uses the port number in its request. And it sends the response to the right local user.
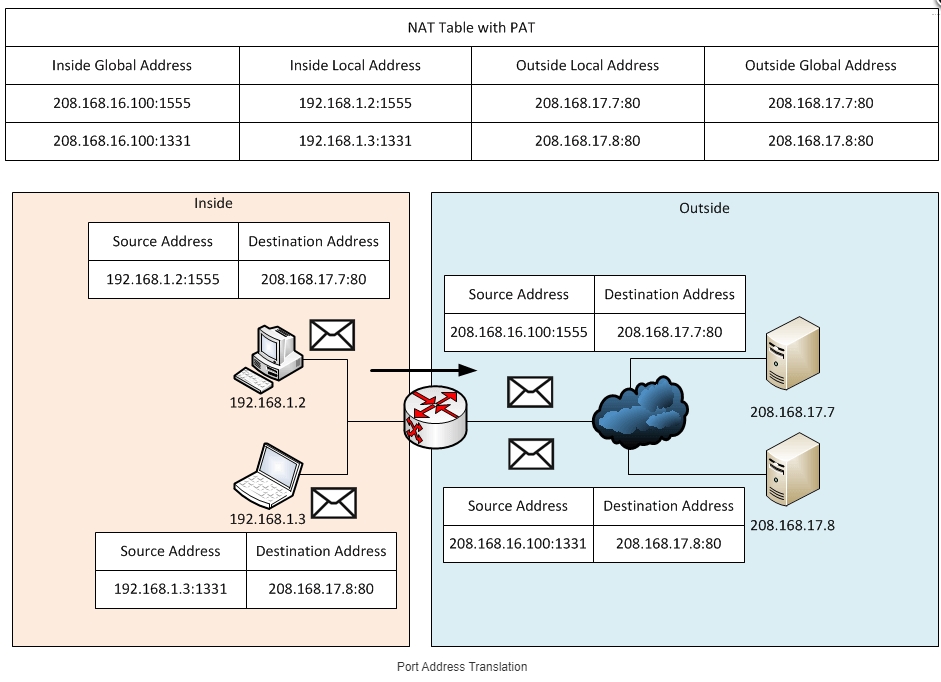
Take a look at the picture above. As you can see, when making a request to a dedicated server, in addition to the fact that the router translates addresses, it also adds the port number to the request. That is the response from the server also has this port, which is then used for the response received by the desired computer.
WAN port: for the advanced and different from LAN
The advanced user needs to understand a little more – the WAN connector is not just a place to stick the cable of his Internet provider, but it is the OUTPUT from the router. That is, there are inputs, there are outputs. Let me break it down "on my fingers".
The home router is the centerpiece of the home LAN. The key word is local. That is, your home is your little network with phones, laptops, computers, TVs, and other useful devices connected to each other.
WAN or LAN? All your home devices connect to your router either via Wi-Fi or a LAN port. IP addresses are usually distributed to them via the router's DHCP server.
That is, in this matter, the router allows any device to connect to itself – the INPUT connection. But the router can also perfectly connect itself – for example, to the global network via the ISP, and distribute to everyone in the local Internet. It makes its outgoing connections via the WAN port (but can also connect via Wi-Fi if necessary). That is why the ISP wire is usually connected to the WAN.
Sometimes there are tasks, such as combining several local networks into one with filtering. Then you can connect from one router via WAN to another router in the LAN. And then there will be some kind of output from the LAN to the WAN and then to the LAN. I.e. for the first router the second network will be as an external one, and it will do its distribution from there. So solve problems not often, but in my experience.
And finally as a summary in this section some differences between WAN and LAN in the context of ports:
- Through WAN interface you connect to the Internet, through LAN you connect to the router your local network devices.
- WAN ports are usually one and blue, LAN ports are usually several and yellow.
- The port connector is usually the same for Ethernet.
WAN network.
Another option for theorists. WAN – World Wide Area Network. A network that connects several other networks together. A bit of theory can be taken from the following video:
For a brief understanding. There are usually 2 types of networks, but sometimes they try to add a third one:
- WAN – read "WAN" – Wide Area Network – a global network – meaning that all-encompassing Internet. One World Wide Area Network.
- LAN – read "LAN" – Local Area Network. The key word here is closed. It can be a home network, it can be a huge enterprise network with tens of thousands of computers and distributed all over the world. But not everyone has access to it from the outside.
- MAN – read "MAN" – something in between and in between – the Metropolitan Area Network is an urban network. The concept of "metropolitan" is also blurred, I would think here more to understand the networks provider – when everyone completely can not see each other, but when downloading from local file sharing provider speed between members of this non-global network is still higher, because it is essentially the same large local network, but with built filters.
Sometimes, these networks are also classified by radius (like MAN – 5-50 km), but nowadays it is already outdated nonsense – there are different networks. Classify them to understand WHY they are created.
The differences between WAN and LAN are relevant for students in this segment as well. Under the record:
- The size of the network – the global one is not even limited by space, the local one is limited by its architect. In theory, it can also go into space, but it does not belong to the whole world and will always be smaller than the global one.
- The number of machines – everyone connected to the Internet is a member of the global network. Local networks are disparate, and there are always fewer in a single network.
- Services. On a local network, folders and printers fumble. On a wide area network everything is client/server architecture – global routing, WWW, etc.
Connecting technology for gadgets and TV
How to work with laptops and portable handheld receivers of wireless networks is clear from the above, but what to do if a problem arises in the synchronization of a smartphone, TV or tablet? For Android OS the following scheme is suitable: you need to go into the general settings and find the wireless network settings. Then you should go to the advanced options menu, where you will find the synchronization functions via WPS or PIN-protected technology. Further connection is made automatically.
Android TV works on the same principle, only there are not many TVs on this platform yet. Apple does not welcome such innovations: there is no support for Wi-Fi Protected Setup in the functionality of iPhones. Users are left to use standard password entry methods.
What is WPS on the router?
For 80% of users, this button is of no use. Home devices automatically connect to networks as soon as they come within range. Passwords are made up independently, which allows you to remember them by heart, and the entry does not take more time than the activation of technology. It will be useful if you are renting an apartment, but you are not told your Wi-Fi password or in other similar situations.
Experts recommend disabling the feature if you don't use it for a long time or if this is the first time you've heard of it at all. According to the developers of network software, a permanently active option can be useful for hackers who try to steal data from a personal computer or just surf the Internet at someone else's expense. Disabling it is done by the same algorithm as activating it.
Read More: