NPS fully supports the Remote Authentication User Service (RADIUS) protocol. The RADIUS protocol is the de facto standard for remote user authentication and is documented in RFC 2865 and RFC 2866.

- Configuring WiFi authentication through a RADIUS NPS server on a Mikrotik
- Setting up an NPS network policy server in Windows 2012.
- Configure the RADIUS client connection.
- Create a policy for WiFi authorization.
- What is a RADIUS server and what is it for?
- What is FreeRADIUS and why is it associated with RADIUS servers?
- RADIUS authentication and authorization
- RADIUS accounting
Configuring WiFi authentication through a RADIUS NPS server on a Mikrotik
Using domain accounts for WiFi authentication is a very convenient solution for any organization with a domain controller. It is very convenient in case you have more than one office as you can login to any office with your own username and password and it is very safe in case an employee leaves your company as his domain profile will be deleted or locked.
To configure WiFi authorization through a domain profile, you will need to make the following settings:
You can learn how to configure MikroTik from scratch or systematize your existing knowledge in an in-depth MikroTik administration course. The author of the course, certified MikroTik trainer Dmitry Skoromnov, personally checks the laboratory work and monitors the progress of each of his students. Three times as much information as the vendor's MTCNA program, more than 20 hours of practice, and access forever.
Setting up an NPS network policy server in Windows 2012.
Open "Server Manager" and proceed to install The "Network Policy Server" role via the "Add Roles and Components Wizard". I will not discuss the installation procedure in detail, there are no complications here. On my server, this role is already installed (see screenshot).
After installing the Role, a reboot is required. Reboot the server and configure NPS.
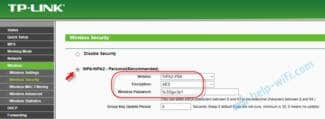
Configure the RADIUS client connection.
In the Server Manager we open /Items/Network Policy Server..
Go to /NPS/Radius clients and server/Radius clientsClick the right mouse button and select "New document".

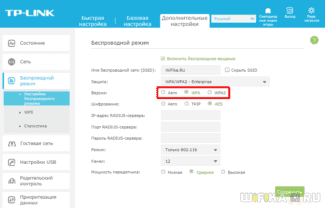
Specify the name (any name you like), the ip-address of the Mikrotik router and make up a more complicated general secret (you can use a generator).

Create a policy for WiFi authorization.
At this setup step, we will use the 802.1x setup wizard.
Left click on "NPS (Local)".Then in the right window expand the item "Standard Configuration"..
At the Configuration script item, we select "RADIUS Server for wireless or cable 802.1x connections and then click on the link "802.1x Configuration.".

Select "Secure Wireless Connections.

In the next step, add the RADIUS clients that were previously connected to the RADIUS server.

What is a RADIUS server and what is it for?
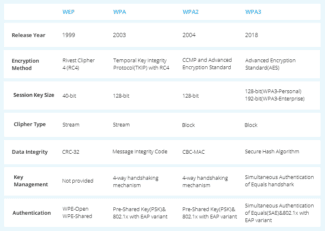
RADIUS ( Remote access service for users with a dial-up connection ) is a protocol that stands out because it offers a security mechanism, flexibility, extensibility and simplified credential management for accessing a network resource. It is authentication and authorization protocol For network access, this protocol uses a client-server scheme, that is, a user with credentials for accessing a resource connects to a server, which will be responsible for authenticating information and will be responsible for determining whether the user is accessing the shared resource. By using RADIUS servers, the network administrator can control the beginning and end of the client authentication and authorization period at any time, for example, we can easily exclude a user who has previously logged on for any reason.
RADIUS servers are widely used by Internet Service Providers (PPPoE), but they are also widely used in hotel Wi-Fi networks, universities or anywhere else where we want to provide extra security to the wireless network, it can also be used to authenticate clients who make use of 802.1X for Ethernet, and it could even be used to authenticate VPN clients that we want, this way we will have all centralized authentication in one point, without having to have several
RADIUS servers use the protocol in UDP transport layer on port 1812 to establish a connection between commands for authentication. When we configure the RADIUS server, we can determine whether we want it to use TCP or UDP, and we can also determine the port used, although the default is always UDP 1812. In terms of devices used, there are excellent Many routers can offer this service to authenticate WiFi clients to a local or remote RADIUS server. In addition, you can use servers, OLTs and even NAS servers, the possibilities are really wide, which not only allows you to install a RADIUS server, but it is not anything cumbersome for the user, and it is not difficult because the manufacturers of NAS servers already easily include an internal RADIUS server. configurable. RADIUS servers typically use authentication protocols such as PAP, CHAP, or EAP,
What is FreeRADIUS and why is it associated with RADIUS servers?
FreeRADIUS is always associated with a RADIUS server because it is the software primarily for installing a RADIUS server. If we need to install a RADIUS server on any computer (servers, routers, NAS, etc. E), We will always resort to FreeRADIUS software because it is multi-platform and all operating systems are compatible with this software. This software supports all common authentication protocols such as PAP, CHAP, EAP, EAP-TTLS, EAP-TLS and others. This software is fully modular, free and provides excellent performance for client authentication.
Some modules that we can include in FreeRADIUS should make it compatible with LDAP, MySQL, PostgreSQL and even Oracle and other databases, so we can have a database of thousands of clients without any problems. This software is configured using text configuration files, however, there are graphical user interfaces for quick and easy setup, as with pfSense, so it will make setting up a RADIUS server with FreeRADIUS much easier.
The FreeRADIUS software can be optionally installed in the pfSense operating system, a popular firewall and router that we can install on almost any hardware. In this operating system we can install it in the packages section, after installation we can enter its configuration in the " Services / FreeRADIUS " section. In this menu we can configure this RADIUS server in an advanced way, we will have different tabs to configure different sections, and in the View Configuration menu we can see the raw configuration file that is created as a result of the configurations that we made in the other tabs. Here we also see integration with SQL and even LDAP.
RADIUS authentication and authorization
The following diagram shows an authentication client ("User") connecting to the Network Access Server (NAS) through a point-to-point telephone connection. To authenticate the user, the NAS contacts the remote server with the NPS. The NAS and the NPS server communicate using the RADIUS protocol.
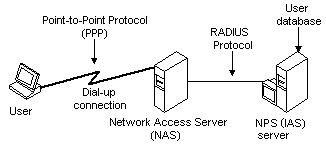
The NAS acts as a client to a server or servers that support the RADIUS protocol. Servers that support the RADIUS protocol are commonly referred to as RADIUS servers. The RADIUS client, that is, the NAS transmits user information to the designated RADIUS servers and then performs the response returned by the servers. The request sent by the NAS to the RADIUS server to authenticate the user is usually called an authentication request.
If the RADIUS server successfully authenticates the user, the RADIUS server returns configuration information to the NAS so that it can provide network service to the user. This configuration information consists of "authorization" and contains, among other things, the type of service the NAS can provide to the user (such as PPP or telnet).
Although the RADIUS server handles the authentication request, it can perform authorization functions such as verifying the user's phone number and verifying that the user has a session. The RADIUS server can determine whether the user already has a session by contacting the state server.
For more information on RADIUS authentication and authorization, see rfC 2865.
RADIUS accounting
The RADIUS server also collects various information sent by the NAS, which can be used for accounting and reporting of network activity. The RADIUS client sends information to the designated RADIUS servers when a user logs on and off. The RADIUS client can periodically send additional usage information during a session. Requests that the client sends to the server to record login or logout and usage information are commonly referred to as "accounting requests".
The RADIUS SERVER can act as a proxy client on other RADIUS servers. In such cases, the RADIUS server associated with the NAS forwards the authentication or accounting request to another RADIUS server, which actually performs the authentication or accounting task.
Read More: