I don't have a dedicated line at home, and I want to buy a Beeline SIM with "unlimited for any device," including a router and a modem. What's the name of the device I need at home to distribute internet? What do I roughly ask in the store – a router or a modem, and which one? Does it have to be a Beeline device?

- How to Connect a Router via a Modem: Personal Experience Instructions
- Background
- Go to the Web-interface of the Internet center
- Table of settings
- Modems
- Dial-Up Modems
- ADSL modems
- 3G/4G modems
- Routers
- What is a modem?
- What is an access point?
- Configuring the Internet connection
- Table: Data for setting up the Internet (APN, login, password, etc.)
- Is there any difference in configuring 3G and 4G modem
- Step by step configuration of the Internet on the router via USB modem
- What does the modem do
- 3G/4G modem
- What a router does
- The main characteristics of a router
- Do You Need a Modem and a Router?
- What Does a Modem Look Like?
- Modem and Router Combo Devices
How to Connect a Router via a Modem: Personal Experience Instructions

Hello! This article I will devote to how to connect a router to a modem. The simplest situation – we have the Internet connected via ADSL modem, but want to distribute it further to the router and its Wi-Fi for further wireless coverage. It's an interesting and non-standard task to configure two devices. And most importantly, it's not that difficult.
In this article we will break down the basic principles. They are suitable for almost all models of routers and modems. But it is impossible to predict everything for every device. Therefore, I recommend that if you have any problems write your questions in the comments.
Background
This article is specifically about connecting a Wi-Fi router via a modem, that is:
The tasks of reverse connection and building bridges we also have already described on the site, but for such it is better to refer to the comments, so as not to create unnecessary garbage here.
In this article I already consider that the ADSL router itself you were able to configure, since you are interested in a more complex task. Otherwise – I recommend that you find your router and modem models on our website and read the detailed instructions on basic setup.
Go to the Web-interface of the Internet center
You do not need to install any programs or additional software – just connect to the router's network. This can be done in two ways: via Wi-Fi or by wire. To connect via WiFi, you need to connect to the network from a phone, tablet, laptop, using the password from it. If you are connecting for the first time and the router is new, the network password will be under the housing on the label. The line with the value may have this name or "PIN".

When connecting to the network by wire, you need to plug one end of the network cable into the network card of your laptop or PC, and the other end into the LAN port of the router.

WARNING! Do not mix up with WAN port, which is usually the only one for the cable from your ISP. It may be blue in color. It is usually different from other similar ports.
Once you have connected to the router's network, start any available browser and type the IP or DNS address of the device into the address bar. This information is also on that piece of paper under the box. The most commonly used addresses are 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1.
Here you are in the gut of the Internet center, but you must be asked for a login and password from the admin panel. The default on older models is admin-admin. On new ones, you will be greeted by a quick setup wizard or asked for a username and password the first time you connect.
Next, the instructions will vary slightly from router manufacturer to router manufacturer. Look up the name of the company that made your router and see the corresponding chapter later in the article. You'll also need more information on how to set it up:
All of this should have been given to you along with the SIM card. You can also find this information in the contract or in the box under the modem. You cannot set up the Internet without it.
Table of settings
The sign "-" means that this information is not necessary. Also the table below is only for information purposes. The provider could change the login data at any time, so it is better to use the settings that are provided with the SIM card. If any data in the table is incorrect – write about it in comments.
WARNING! In addition to the data provided below, you may also need the PIN code from the SIM card.
| Operator name | APN | Phone number | Login | Password |
| Beeline KZ | internet.beeline.kz | *99# | beeline | beeline |
| Kcell-Activ | internet | – | – | |
| Megafon | internet | *99# or *99***1# | gdata | gdata |
| Beeline RF | internet.beeline.ru or home.beeline.ru | beeline | beeline | |
| MTS RF | nternet.mts.ru | *99# or *99***1# | mts | mts |
| Tele2 | internet.tele2.ru | – | – | |
| U-Tel | internet.usi.ru | *99***1# | – | – |
| Yota | yota.ru | *99# | – | – |
| SkyLink | – | #777 | mobile | internet |
| SmartS | internet.smarts.ru | *99# or *99***1# | internet | |
| Kievstar | www.ab.kyivstar.net |
Modems
As I said above, these are modulators-demodulators. The very thing that converts the data into the desired form and gives you the output of the Internet. Its job is to convert the signals.
Dial-Up Modems
In everyday life the word "modem" probably comes from the old DIAL-UP modems, which used to work over the telephone networks. So they did wonders with the conversion on the phone line that they got the first very slow Internet out.
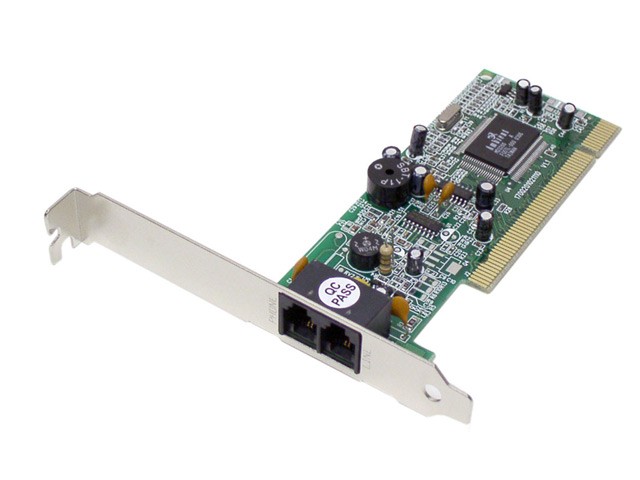
There were both external and internal. I had one like the one in the picture above.
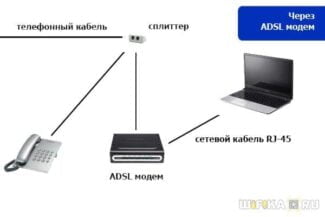
ADSL modems
But times went, new technology came to the telephone lines – ADSL, which made it possible to increase the speed, and to talk on the phone at the same time thanks to the splitter.
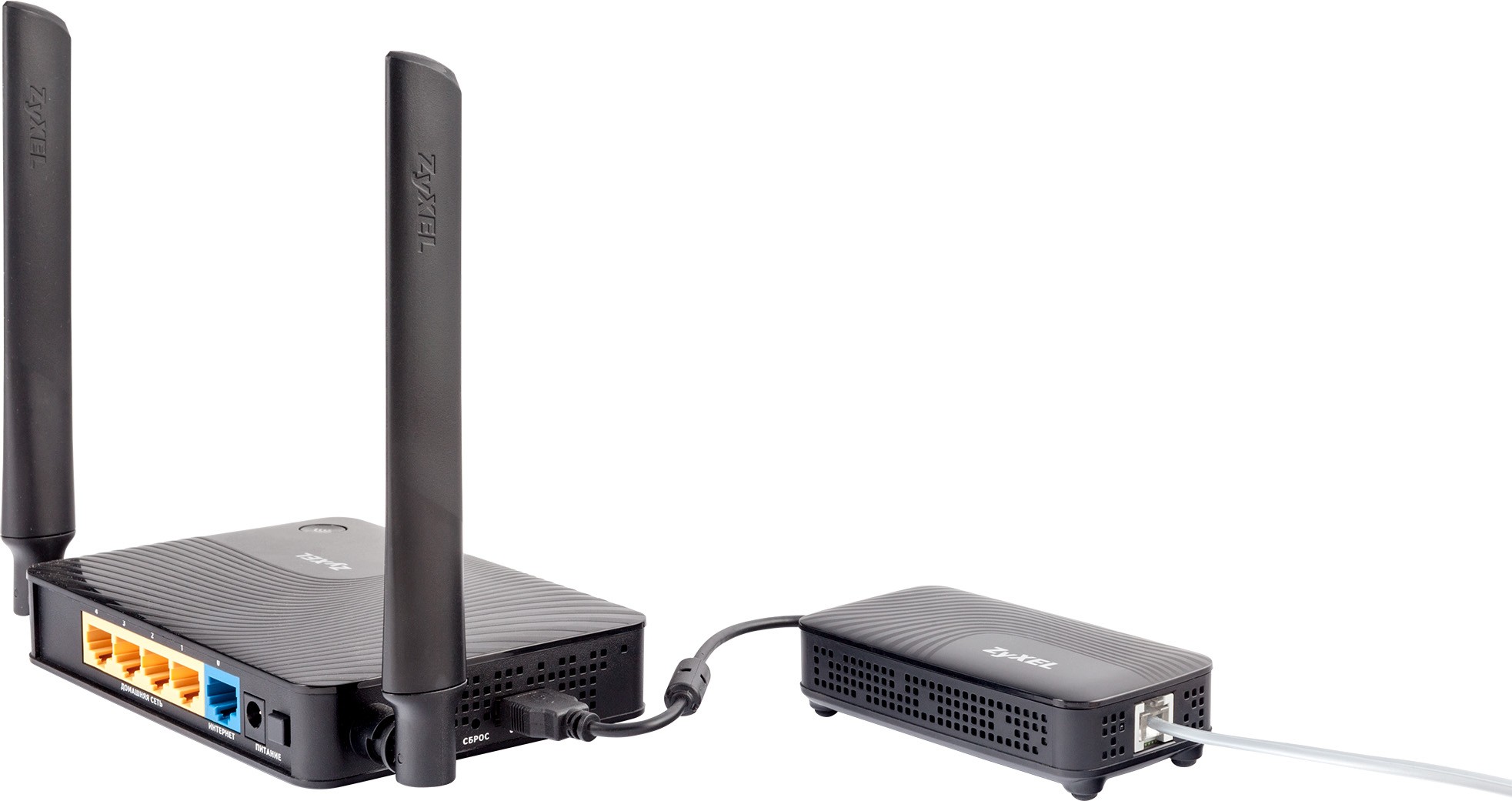

Some of these ADSL-modems were already quite a router and all could understand, but the name stuck with them tightly – and so they said, modem da modem. But their functionality was much higher-they were already connecting themselves and distributing traffic in your network and distributing Wi-Fi. Only the connection was through a telephone line. So with these devices, the word game was already on the verge.
3G/4G modems
And these are the representatives of a new era, but they were justifiably named. Their first task was to organize a connection to the global network via SIM-card channel and distribute it by USB to the computer or by Wi-Fi to everyone else. In other words, the functionality is minimal – only the connection, it is not a router.
For me, these days in the names for the household division is simple: "flash drive" 3G – these are modems, and the other "boxes" (even with 3G) – these are routers.

Routers
The task of a router is to distribute traffic between several devices. It usually also can successfully connect to the Internet – via its own modem, via an external 3G modem, or just to distribute traffic from the provider's wire.
The trick here is that the Internet is already there in the wire, and it only remains to redirect it to other devices. Initially, routers worked on the local network in offices, and no one was bothered. And now this technology has made its way into every home.
Sometimes people look for a difference between a router and a router… Actually Router can be translated from English as "router". It is the same device, only in different languages)
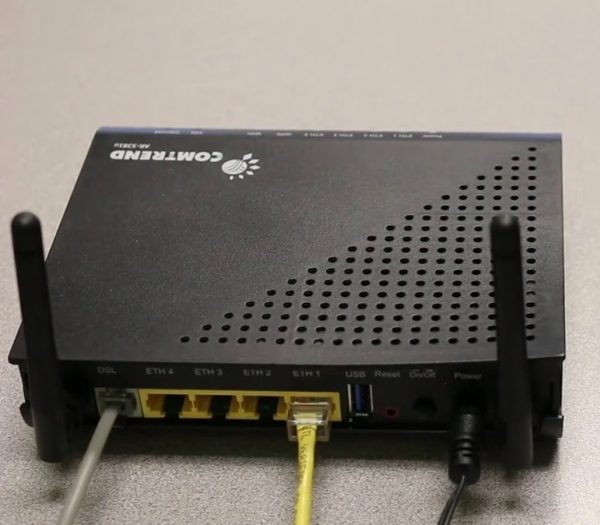

Note, the main feature of any router is a lot of outputs on the LAN ports. But this may not be the case. For example, if our router distributes traffic via Wi-Fi.
What is a modem?
A modem is a device that converts a signal and adapts it to the propagation environment. When a signal is received, it is modulated. When sending a signal, it is demodulated. This is why a modem is also called a modulator/demodulator. A modem is always responsible for the Internet connection for a single gadget, because it is technically the simplest device.
There are two main types of modems: 3G/4G and ADSL. A 3G/4G connection is made with a SIM card. Here is a typical 4G (or LTE) modem.

Another popular name for a router is a router. Many users think that these are different things, but in fact they are one and the same. The confusion arose when Wi-Fi routers were introduced that included an access point in addition to a modem.
What is an access point?

In essence, it is a simple hub that provides wireless access to an existing network or the creation of a new wireless network. When several connections are made to the same access point, the bandwidth is divided by the number of connected users. You could say that an access point is a stripped down version of a router. Yes, it can work in bridge or repeater mode, but most modern routers support these modes. Again, a router is the most complicated technical device of all described, which includes all the functionality of all its brethren.
Obviously, the most common and practical option is a router. Connected to the network with a cable from the provider and distributed Wi-Fi to multiple devices, what more do you need for home use?
A modem is fine if for some reason you do not have a fiber optic connection. This is often the case in private sectors, where providers do not lay cables. So if you can only access the World Wide Web with a telephone line, choose a modem that can convert the signal.
The access point For home use is rarely suitable. As mentioned above, its functionality is limited. But if you would like to set up a seamless Wi-Fi network in your office or to set up a HotSpot in a cafe, you will need a very good access point.
Configuring the Internet connection
We have made sure that the router and the modem will "get along" with each other. Now it is time to move on to the configuration. First we will present a table with the parameters which must be entered when debugging the connection. It shows popular cellular operators – most likely, you use one of them.
Table: Data for setting up the Internet (APN, login, password, etc.)
| Operator name | APN | Number | Login | Password |
| Beeline RF | internet.beeline.ru or home.beeline.ru | *99# or *99***1# | beeline | beeline |
| MTS | internet.mts.ru | *99# or *99***1# | mts | mts |
| Megafon | internet | *99# or *99***1# | gdata | gdata |
| Tele2 | internet.tele2.ru | *99# or *99***1# | leave blank | |
| Yota | yota.ru | *99# | leave it empty | |
Is there any difference in configuring 3G and 4G modem
There is absolutely no difference: while configuring you will enter the same parameters from the table above. After debugging and successful connection the modem will switch between 3G and 4G modes (if the modem supports both networks) depending on signal quality: what standard will be better in the area, that will be used.
Step by step configuration of the Internet on the router via USB modem
Let's take a detailed look at setting up mobile Internet on a Wi-Fi router:
-
First, let's connect the computer to the router. This can be done by "Wi-Fai" (the router's factory network is available immediately after the first power-on) – the network password will be indicated on the label at the bottom. But it is recommended to take a wired connection. Take the Ethernet cable from the router kit: one end plugged into the LAN on the router (yellow), and the other into the output of the network card on the PC.
- price: the cheapest options – from 1 thousand rubles, the most expensive – over 10-20 thousand rubles;
- The list of supported modems: the list of models with which the router can work;
- 3G/4G technology support: all modern routers can work with 3G network, but not all support 4G connection; if you try to distribute 4G Internet from a router that does not support this technology, it will automatically switch to the 3G protocol, the router will continue to work, but you will not get high speed;
- range: it depends on the radius to which the Wi-Fi signal will spread; manufacturers usually indicate a range in ideal conditions (no rain, with excellent quality of connection with the satellite, without concrete and other barriers), but in reality the router will be hampered by walls and other obstacles, and possibly low Internet signal (its quality depends on the modem), so feel free to cut the declared range by 5-10 m; the average range of routers – 100 meters in normal conditions and 300 meters on open ground, with the connection speed
What does the modem do
A modem is a device that looks like a USB flash drive. It provides a connection between one device (usually a desktop or laptop) and the Internet. When the user activates the modem, the following happens: The modem detects which internet service provider it is to work with, connects to it, starts transmitting user data and downloads information from the network to the computer. The modem is only responsible for maintaining the Internet connection for one device.
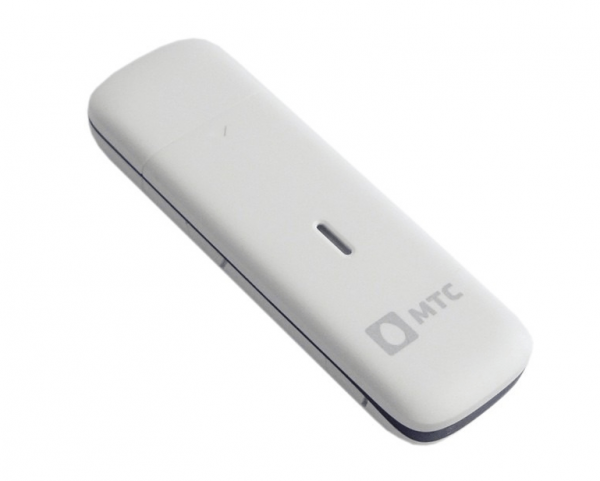

A modem looks like a USB flash drive and is also plugged into a computer's USB connector
There are two types of modems: 3G/4G and ADSL. Today the first type is mostly used, because it provides a more stable, fast, cheap and accessible connection to the network.
3G/4G modem
Modems of this type connect to the Internet using a SIM card. Almost all popular mobile operators (MTS, Beeline, Megafon, Yota, Tele2, and others) offer their services and special rates for modems. Most modems are ready to work with SIM cards connected not to a special tariff for computers, but only to the tariff with a package of mobile traffic.

Modems with 4G support provide a faster connection than 3G modems
Connecting to the Internet via a 3G/4G modem is as follows: a SIM card with a pre-selected and paid tariff is inserted into the modem, the modem is connected to a computer and, using a special program that comes with the modem, establishes a connection to the network.
The price of a modem can vary from one to several thousand rubles. An important factor affecting the price is 4G support: modems that support this standard are more expensive.
What a router does
A router is connected to the Internet via a modem or an Internet cable and connects to the "world wide web" via a Wi-Fi network several devices: computers, tablets or smartphones. Often you can also hear the word "router" applied to a router – it means that the router distributes the traffic coming from different devices.
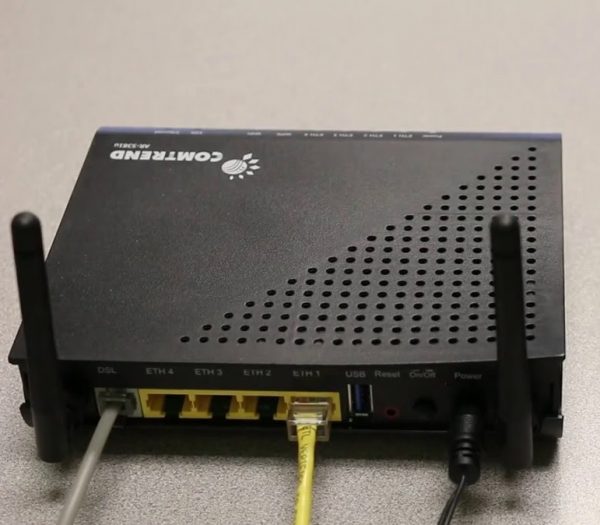

A router has inputs for a modem, an Ethernet cable, and a WLAN cable
Let's say you have two computers and one phone connected to a Wi-Fi network. On each device, the user does something on the network, sends some data to the Internet and receives information from the Internet. All these data flows through the router, which must independently determine which part of the information to send to a certain computer and which to send to the cell phone, without mixing anything up.
The main characteristics of a router
Getting ready to buy a router, pay attention to the following characteristics:
Do You Need a Modem and a Router?
You need a modem and a router to set up a home network. If you're connecting a single computer to the internet with a wire, you can use only a modem. There's no case where you can use just a router. You'll always need a modem to decode the signal from your ISP.
When you want to speed up your network, the router is usually what you want to focus on. It has bandwidth limits, and it distributes the signal to all your devices. Your router creates and manages your Wi-Fi.
The modem usually doesn't cause a slow connection. Generally, you'll get one from your ISP, and they'll give you one suitable for your subscription. If you plug in your computer directly to your modem and run a speed test, you can tell whether you're getting your advertised internet speed. If not, contact your ISP. There may be a connection issue, or your modem may be outdated. In this case, they may swap it out for a newer model.
What Does a Modem Look Like?
Modems typically look like small black, skinny, square boxes. Frequently, they have between two and four antennae but not every modem includes an external antenna. The images at the top of this article give you a good idea of what a modem looks like but every manufacturer uses a different style and shape.
Modems will also include between two and four ethernet ports, one or two USB ports, and range between six and nine inches wide to six to eleven inches long and about two to three inches high.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Modemexamples-735f453dd7bb44dca08a5bd7fd0c60c4.jpg)
Modem and Router Combo Devices
There are also modems with integrated routers that perform both functions. These modems can be rented from your ISP or purchased directly. These combo devices might include a VoIP function if you have a cable, internet, and phone package.
Combination devices are not usually the best option. If one part breaks, the whole thing is useless, and you can't upgrade one device at a time. Still, if you don't need the latest and greatest tech, buying a combo modem and router is convenient.
If one must make a comparison, the modem wins. A modem is always your main gateway to the internet, whether it's a modem connected via a coax or fiber optic cable or a modem in your smartphone. A router's function is to distribute (or route) that internet connection to other wired or wireless devices in your Local Area Network (LAN). Essentially, you can plug one device into your modem and have internet access. However, you can't connect a device to a router and have internet access—unless you've connected the router to a modem.
You need a modem to access the internet. Then, you'll need a router to distribute that internet access to your devices (computer, smartphone, smart TV, etc.). Routers can also connect devices within your network; for example, a router enables you to connect your printer to your PC. An internet connection is not required to connect devices within your network.