But this transmitter conceals many secrets and mysteries, about which I will tell you today. After reading the article you will not only know what this gizmo is, but you will understand – what good routers differ from bad ones, and you will have no problem choosing the ideal variant for yourself.

- What is the difference between a modem and a router, is there a difference and which one is better?
- Briefly .
- Modem
- How it works
- Router
- Routing
- Wi-Fi
- What is a modem?
- What is an access point?
- What is a modem
- 3G/4G modem
- ADSL model
- What to choose a modem or a router
- What a router does
- The main characteristics of a router
- What to choose: a router or a modem
- Table: Differences between a router and a modem
- What is a modem?
- What is a router?
- What is better?
- Quick comparison table
What is the difference between a modem and a router, is there a difference and which one is better?

Hi guys! Router or modem? This is the question I was asked the other day. In everyday life, okay, these words are often called the same thing – and the essence is not, because for the average user it's the same – all you need to access the Internet. But the difference between them all the same there is. So let's look at the difference between a modem and a router.
Briefly .
There are both modems and routers. Both take part in the distribution of Internet at home. Both are sometimes called the same thing – I don't see anything wrong with that in the home. But in essence they are two different devices.
- A modem is a modulator-demodulator – it does its own conversions.
- A router (or router in Russian) builds its own routes and directs network and Internet traffic to the right device.
In a home network it is common to combine all modern functionality into one device. Modems can build routes and routers can modulate. This leaves only some typical representatives, which the classics make it so. And these we would like to talk about below.
Modem

Modem is an acronym made up of the words "modulator-demodulator". It means that the device modulates signals for receiving and transmitting data. It is a kind of "door" to the Internet that receives and sends data between cables/telephone lines and all the devices in the house. The main function of the device is to convert one type of signal into another. Unlike a router, which we'll talk about later, a modem transmits the signal to only one device, such as a PC or laptop.
A modem is essentially an outlet to the World Wide Web. It is a small device, which is usually installed by the ISP, through which it connects the user to the Internet. The connection is established via cable (coaxial or fiber optic) or via a telephone line (DSL). The computer itself or a router is connected to the Internet via an Ethernet cable.
How it works
Usually, modems have LEDs/lights on the front so that the user can see what is happening at any given moment. One light indicates that the device is receiving power, a second indicates that it is receiving data from the Internet service provider, and a third indicates that the modem is sending data successfully. With these lights you can immediately see if there is something wrong: If the send and/or receive lights are blinking, it means that your ISP is having some kind of problem, or something has happened to the connection itself. Another LED indicates that only wired devices have access to the Internet.
Read More:Before we go any further, note that modems are not just for coaxial cable connections. Broadband access can also be served through a digital subscriber line (DSL). This type of Internet is accessed through telephone lines. DSL is usually slower than cable broadband and is useful in rural areas where telephone lines already exist, but lack the infrastructure to support cable television and full Internet services.
Router
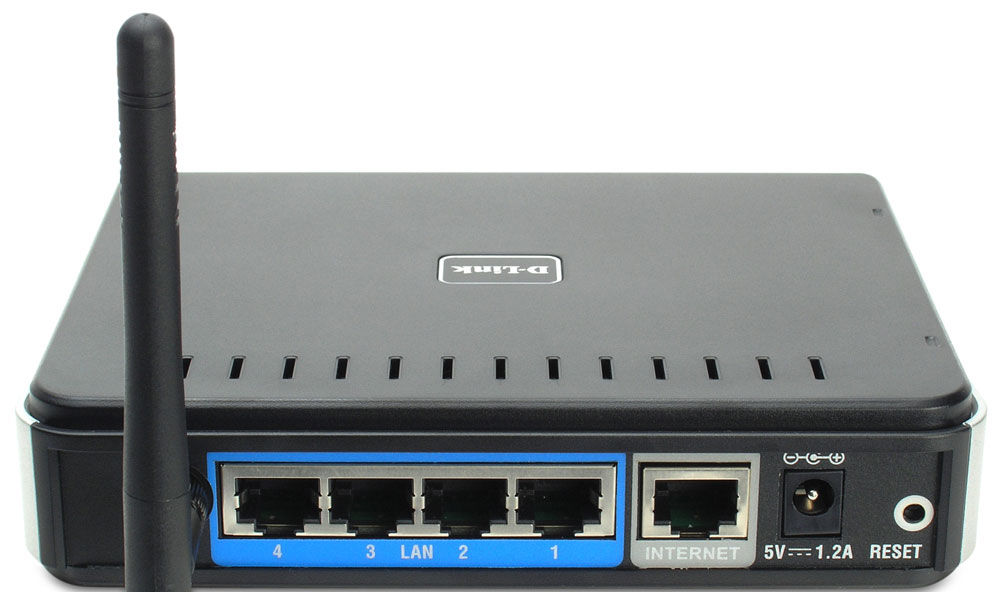
A router, often called a "router," is a standalone device that plugs into the Ethernet port on a modem and "routes" network/internet traffic to devices connected to it. Routers usually have a dedicated color-coded Ethernet port that the device uses to physically connect to the modem (WAN or WAN), and four additional Ethernet ports for wired devices (LAN or LAN).
Thus, the router sends and receives network traffic from the modem with a single connection and routes all that data through the four Ethernet ports as well as through the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. Despite these figures, a wired connection is still faster than a wireless one, and we still recommend using Ethernet if you want maximum speed. However, it is obvious that in the case of smartphones this is impossible to do, and stretching Ethernet cables along every wall is just pointless and stupid.
Routers come in different sizes, price ranges, and mostly promise a lot (but unfortunately do not deliver, especially in terms of maximum speed). As for wireless, these types of devices can include two or more external antennas, depending on the model. The more antennas, the better the Wi-Fi coverage – at least in theory. The speed of your connection will still depend on the proximity to the router and the technology that provides that connection.
Most modern routers use the 802.11.ac standard (Wi-Fi 5), while newer ones may support Wi-Fi 6. Wi-Fi 5 provides three outgoing streams and three incoming streams (3 × 3) in the 5 GHz band at up to 433 Mbps each. They are accompanied by three incoming and three outgoing 802.11n (3×3) streams in the 2.4 GHz band at 200 Mbps each. The latest Wi-Fi 5 technology update, also known as Wave-2, adds a fourth stream for additional bandwidth.
Routing
The question immediately arises: how does the router know exactly where to send the data? In this case, it uses a routing table as well as the IP addresses of the local network – all the computers and devices connected to the router at home. Local network addresses often start with the numbers "192.168". So if you see this combination of addresses, it's the address of some device inside the house or apartment.
As we've already figured out, the wire that goes into the router from the ISP connects us to the global Internet. This is where the router has a second address, an external address. This is given by the ISP, so that packets of information reach the right addressee.
As a result, Internet packets go over the wire to the WAN port using the external IP address. The router then calculates where to send the packet next and looks at the internal routing table, which mostly uses local IPs.
It looks at the table and sends the data to the father's computer if he was the one who sent the request. If several people use the Internet at once, the router masterfully distributes packets of data to each recipient. The principle is similar to email.
Wi-Fi
Many people associate the internet and a router with wi-fi technology. Wi-Fi is a technology for transmitting information via radio waves. Many people might now argue, "But isn't Bluetooth, cellular communications, and even the banal microwave oven using radio waves, too?" – And yes – you would be right! But Wi-Fi uses a certain standard – IEEE 802.11. This standard is used to build a local area network and to connect devices connected to a router.
Often some users confuse wifi and the Internet, thinking that they are the same thing. But in fact they are two different things. Since Wi-Fi is just a technology for building an airborne local area network. That is, if you turn off the internet or pull the cord from your ISP, the wi-fi won't go anywhere, just the local radio network will be without the internet.
The IEEE 802.11 standard has many kinds. They work on two frequencies:
As you can see, 5 GHz has a significant speed increase due to the increased frequency. Now 2.4 GHz models are more popular because they are cheaper, and not everyone needs as much speed on a LAN as a 5.
One more note – many people, seeing such figures, think about Internet speed, but, as we wrote earlier, Wi-Fi and Internet are different things. This means that this standard should only apply to the internal home network.
Each frequency has its pros and cons. 2.4 GHz is the most common, and all your neighbors (if you have them) are likely to sit on it. In order to be able to use one frequency in an apartment building and not interfere with your neighbors, channels were invented. There are 14 channels in the 2.4 GHz frequency. But if all your neighbors, for example, will sit on channel 1, where you sit too, there could be loss of connection, interruption and loss of speed.
What is a modem?
A modem is a device which converts the signal and adapts it to the propagation environment. When a signal is received, it is modulated. When sending a signal, it is demodulated. This is why a modem is also called a modulator/demodulator. A modem is always responsible for the Internet connection for a single gadget, because it is technically the simplest device.
There are two main types of modems: 3G/4G and ADSL. Connecting via 3G/4G is done with a SIM card. Here is a typical 4G (or LTE) modem.
Another popular name for a router is a router. Many users think these are different things, but they are actually the same thing. The confusion arose when Wi-Fi routers appeared, which began to include an access point in addition to a modem.
What is an access point?
In essence, it is a simple hub that provides wireless access to an existing network or the creation of a new wireless network. When several connections are made to the same access point, the bandwidth is divided by the number of connected users. You could say that an access point is a stripped down version of a router. Yes, it can work in bridge or repeater mode, but most modern routers support these modes. Again, a router is the most complex technical device of all described, which includes all the functionality of all its brethren.
Obviously, the most common and practical option is a router. Connected to the network with a cable from the provider and distributed Wi-Fi to several devices, what more do you need for home use?
A modem is fine If for some reason you don't have a fiber optic connection. This is often the case in private sectors, where providers do not lay cables. So if you can only access the World Wide Web with a telephone line, choose a modem that can convert the signal.
The access point For home use is rarely suitable. As mentioned above, its functionality is limited. But in order to create a seamless Wi-Fi network in the office or to arrange a HotSpot in a cafe, you will need a modem.
What is a modem
Modem is equipment for receiving and transmitting Internet traffic. However, before considering: what is the difference between a router and a modem, it is necessary to understand the types of these devices for transmitting communication.
The main distinguishing feature of modems is the ability to work with only one connected gadget.
Modems of different kinds differ in many characteristics:
The devices are also in different price categories. Therefore, you should consider the differences between a modem and a router from the point of view of each type of equipment separately.
3G/4G modem
Models that work with 3G or 4G connectivity are a popular solution for users who are far away from fiber-optic connections. Devices of this type use mobile SIM cards to connect to the network.
On 3G/4G models, the difference between a modem and a router is more significant. For example, the appearance of the device stands out: the equipment looks like a small flash drive, while the USB port is used for connection.
Also, due to the fact that the SIM card is chosen as the source of connection to the Internet, 3G/4G modems do not have high speed and quality of connection. However, this disadvantage is compensated by the mobility of the equipment.
The price of such devices varies from 1000 to 5000 rubles. More expensive options are devices supporting 4G.
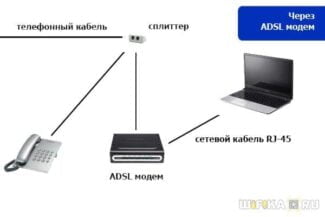
ADSL model
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) modems are used to connect to the World Wide Web via the telephone line. If the user uses the same cable for both the home phone and the Internet, then the use of this device is a must. Let's consider what is a modem of ADSL format in more detail.
What to choose a modem or a router
The difference between a router and a modem is due to the different type of Internet connection with which these types of equipment work. Moreover, you should keep in mind the different functionality of the devices. Some users use these two types of equipment to transmit the Internet signal together, because there are wifi routers that support modems of different models.
Speaking in simple words about what is better: router or modem, the answer will depend on the needs of the user. Therefore, when comparing the modem and router, before you understand what the difference is, you need to determine the purpose of the purchase of equipment.
If you need to create a Wi-Fi network via Ethernet cable for several devices, it is better to choose a router. However, for everyday use of the Internet you do not always need a perfect connection or excessive speed. A well-functioning modem is indispensable for trivial Internet surfing on a particular device without being tied to a specific location.
The connection speed does not always match the quality of the modem or router you bought. Sometimes this value depends on the computer or other device connected to the network.
What a router does
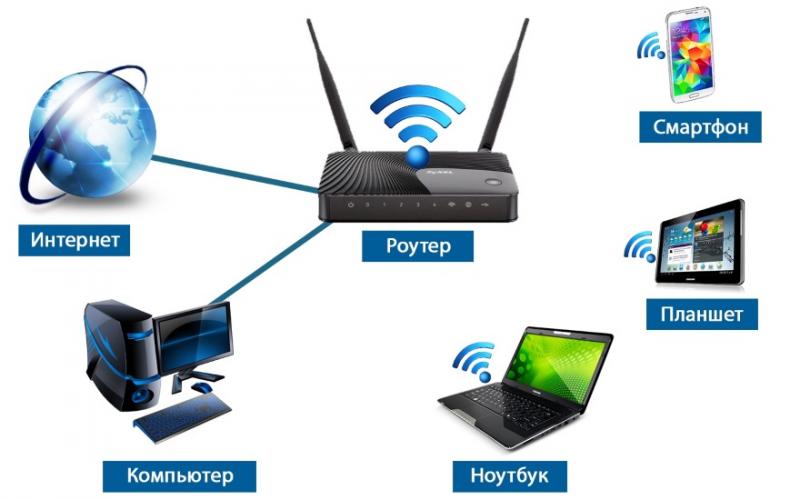
Router is connected to the Internet via a modem or an Internet cable and connects to the "World Wide Web" via Wi-Fi network several devices: computers, tablets or smartphones. Often you can also hear the word "router" applied to a router – it means that the router distributes the traffic coming from different devices.
A router has inputs for a modem, an Ethernet cable, and a WLAN cable
Let's say you have two computers and one phone connected to a Wi-Fi network. On each device, the user does something on the network, sends some data to the Internet and receives information from the Internet. All these data flows through the router, which must independently determine which part of the information to send to a particular computer and which to a cell phone, without mixing anything up.
The main characteristics of a router
Getting ready to buy a router, pay attention to the following characteristics:
- price: the cheapest options – from 1 thousand rubles, the most expensive – over 10-20 thousand rubles;
- list of supported modems: the list of models that the router can work with;
- 3G/4G technology support: all modern routers can work with 3G network, but not all of them support 4G connection; if you try to distribute 4G-internet from a router that does not support this technology, there will be an automatic switch to the 3G protocol, the router will continue to work, but the high speed will not work;
- range: it determines the range to which the Wi-Fi signal will spread; manufacturers usually specify a range in ideal conditions (no rain, with excellent quality of connection to the satellite, no concrete and other barriers), but in reality the router will be hampered by walls and other obstacles, and possibly low Internet signal (its quality depends on the modem), so safely, cut the stated range by 5-10 m; average range of routers – 100 meters in normal conditions and 300 meters in open areas, with the connection speed
What to choose: a router or a modem
You can not choose only a router for the reasons described in the paragraph "Does the router replace the modem? When choosing a particular connection configuration, it is advisable to proceed from the following considerations.
- If you need Internet for one device, but not tied to a single point, buy a modem. You'll be able to plug it into your laptop and use it anywhere in your region (and outside its borders, too, but outside the home region usually start to operate special conditions provided by the tariff).
- If you need Internet throughout the house for two or more devices at the same time – buy a modem and connect it to the router. You can remove the modem from the router at any time and start using it outside the home. Plus, today's routers are so small and lightweight that you can always take them with you if you need to.
- If you need to provide Internet access to a large number of devices, for example, in an organization or club, you need to install a router and connect either a powerful modem that can provide enough speed to work on all the computers simultaneously, or an Internet cable.
- If you are going to travel with a device that has a USB port or supports a SIM card (you can take the SIM card out of the modem and put it in your phone or tablet), it is better to buy a modem and choose the right rate for travel.
Table: Differences between a router and a modem
Characteristics Modem Router Connects to the Internet Yes No Distributes Internet to multiple devices via Wi-Fi or WLAN cable No Yes What it takes to work SIM card Modem or Internet cable Footprint Approximately 20 cm2 Approximately 300 cm2 Main task Installing an Internet connection To distribute an Internet connection to multiple devices What is a modem?
A modem is a device that is responsible for modulating or demodulating the Internet signal it receives. In other words, it is the one that converts the data coming from the global network so that the end device (computer, laptop, mobile gadget) can understand it as well as utilize it to exchange data packets. A modem is able to provide connectivity to a single device, receiving information from the Internet and sending it back.
They are divided into several kinds depending on how they are connected, the method of receiving data. Stationary modems most often receive them with a cable connection and transmit the decoded data to the end device also through the cable.
The mobile type of these devices differs from the stationary type in that, although it receives the signal without wires from the cellular operator, it still requires a direct connection to the end device. Most often for this purpose, the USB connector in laptops or tablets of certain configurations is used.
Thus, the modem is suitable for the first situation we described above. To connect just one device and give it access to the Internet.
What is a router?
A router (or sometimes called a router) is designed to distribute network traffic between several participants in the same network. In other words, this device is not capable of decoding data by itself. It is designed to create a small network and regulate its operation by distributing the signal from one Internet connection to several devices.
The modem is still responsible for receiving and processing the signal when disposing of this type of network device. Fortunately, most ultra-modern models are already equipped with the appropriate built-in module. The user does not have to buy two separate devices. When you buy even the most inexpensive model, you get a decoder for a wired or wireless Internet connection (depending on the operator you choose and the connection method), as well as a router that can intelligently, quickly and discreetly distribute data packets between several devices.
Several devices can be connected to the same local network in different ways, depending on the model, as well as on the characteristics of the devices themselves. Stationary models receive the signal via cable and are usually equipped with several RJ-45 connectors for wired connection of user computers, laptops and other equipment. Also, almost any stationary model is able to create a wireless network around itself, converting the signal received by cable into radio waves on the fly. This signal is broadcast via Wi-Fi protocol to connect smartphones, tablets and other gadgets that do not have the possibility of wired connection to the Internet.
Thus, for the second situation described above, a fixed router with a built-in modem and the ability to create a wireless network is ideal.
What is better?
The standard router is considered the best option for creating a home access point. It helps provide Internet access to several gadgets at the same time. Although a computer with a connected modem can be used as a router, it is better to choose a standalone device. Such a router requires minimum power.
4G modem is suitable for laptops. The capabilities of a compact Internet stick will be enough to work fully outside the office or home. The lack of multiple access is compensated by the hub mode of the device. If necessary the Internet can be distributed from a laptop. The modem is also suitable for travel. The router will need an additional power supply.
Quick comparison table
Parameter Modem Router Modem Router Availability of radio module Yes No Ethernet support No Yes Number of devices to connect 1 Up to 8, depending on model Self-contained battery Yes No Additional features No Firewall, hub-mode Modem and router are popular devices that are used to access the Internet. However, they differ in technical features and functionality.