With the available technology of Internet service providers, buying a network adapter with speeds above 100 megabits is hardly the best solution. Network cards for computers with Wi-Fi are more sensitive to such parameters as speed, the ability to work in several frequencies and supported protocols.

- Wi-Fi LAN adapter: why do I need it and how do I use it?
- Varieties of .
- Wired cards
- 4 ports
- Manufacturers continue to work on network card technology to improve speed and throughput
- Wireless Adapters
- Synopsis at
- Key Features
- A short review
- TP-Link TL-WN725N.
- D-Link DWA-137A1B.
- TP-Link Archer T1U.
- TP-Link Archer T2U.
- TP-Link Archer T9E
- Types of network adapters
- Classification based on network connections
- Classification based on bus interfaces
- Other factors not to ignore when deciding to buy a network adapter
- How to choose a network adapter?
- How to connect the network adapter?
- What does the WiFi adapter do?
- How to choose?
- Wireless module
- Antenna
- Connector
- How to Install a Network Interface Card in a Computer
- What to do if the computer does not see the network card
Wi-Fi LAN adapter: why do I need it and how do I use it?

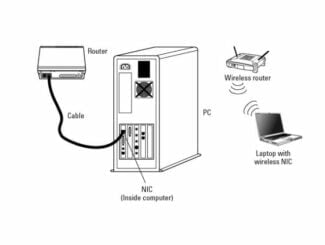
A Wi-Fi LAN adapter is a device that includes a wireless module and one or more LAN ports for a wired Ethernet connection. If there is one LAN port, it usually works both ways, if there are two, then one works as a WAN (Internet feed) and the other as a LAN (wired client connection).
Note that there are network adapter adapters in stores that connect via USB and have a LAN connector. Such a dongle will solve the problem when the PC network card failed or you need to connect an additional computer to the router with a cable, and all the LAN ports are already busy. There is no Wi-Fi module in such devices.
Varieties of .




The latter, of course, connect to a laptop, which has a Wi-Fi module (mostly taken for ultrabooks because they do not have LAN ports). The distribution of Internet in this way is done via laptop Wi-Fi, and through the LAN patch-cord from the modem is connected.
In each firm producing network equipment you can find models of Wi-Fi adapters with Ethernet, corresponding to the characteristics you are looking for:
- Strong 300 repeater (1 LAN, second universal LAN).
- Strong 750 repeater (1 LAN, second universal LAN).
- TP-LINK TL-WA850RE (1 LAN).
- Asus RP-AC53 (1 LAN, 1 socket).
- Edimax EW-7438RPN Mini (1 LAN).
- SILVERCREST M13-990013 (1 LAN).
Some support operation with 5th generation wireless networks (802.11ac standard).
Wired cards
Wired cards are more suitable for offices – they can be used not only to connect the Internet, but also to connect devices into a single local network. Wired cards have a different number of ports: if you only need to connect to the Internet, then one port is enough, for the LAN requires more ports.
Network cards with a single port are characterized by a greater variety of interfaces and connection speeds:
With interface PCI Express x4 and 10Gb/s connection speed – Intel X550T1BLK;
With PCI Express x8 and 10 Gb/sec speed: Intel X520-DA1 E10G41BTDAG1P5 (SFP+ connector) and Mellanox ConnectX-4 Lx EN MCX4111A-XCAT (SFP28 connector);
With interface PCI Express x8 interface50 Gbps and QSFP28 connector: Broadcom P150P BCM957414A4140C;
We would like to separately note the network cards that are connected via proprietary manufacturer's interface, support Fibre Channel at 16 Gb/s and have LC network connectors: Huawei OceanStor 22/26 V3 03057210 with four connectors and Huawei OceanStor 22 V3 03057701 with two connectors.
Via the interface PCI Express x1 motherboard is connected to the model Dell Broadcom 5720 540-BBGW. It has two RJ-45 connectors and supports 1 Gb/s connection speed.
Some network cards connect via PCI Express x4, support 1Gb/s connection speeds, and have two RJ-45 connectors. As an example: SILICOM Intel i350AM2 PE2G2I35, Supermicro I350 AM2 AOC-SGP-I2, Intel ET E1G42ETBLK и HP Enterprise 361T 652497-B21.
Via Interface PCI Express x8 interface The following models work via the PCI Express x8 interface. They all support 10 Gb/s and differ in their connectors:
4 ports
A fairly common standard for network cards 4 port connection.
Various vendors' cards listed below connect to your motherboard via PCI Express x4. They have RJ-45 type connectors and support 1 Gb/s speed:
Manufacturers continue to work on network card technology to improve speed and throughput
- All posts
- KVM equipment (equipment) (2)
- Powerline Adapters (2)
- Security (security) (4)
- Wireless adapters (4)
- Power Supplies (12)
- Video cards (videocards) (38)
- CCTV (6)
- HDD & SSD Drives (60)
- Disk Shelves (JBOD) (2)
- Sound cards (sound cards) (3)
- Instruments (instruments) (1)
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) (25)
- Cables & Patch Cords (5)
- Switches (switches) (12)
- Computer peripherals (41)
- PC (42)
- Controllers (RAID, HBA, Expander) (4)
- PC cases (13)
- PC Motherboards (24)
- Multifunctional Devices (MFP) (6)
- Memory Modules for PCs, Notebooks & Servers (16)
- Monitors (monitor) (35)
- All-in-one PC (8)
- Desktop Storage Systems (NAS) (2)
- Laptops (notebook, laptop) (34)
- General Information (46)
- Cooling (15)
- Tablets (3)
- Plotters (1)
- Printers (6)
- Software (software) (37)
- Consumer business software (12)
- projector (2)
- PC and server processors (41)
- Workstation (5)
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs) (1)
- Office Supplies (1)
- Wi-Fi extenders (repeaters, repeaters) (3)
- Routers (routers) (14)
- Servers and Server Equipment (42)
- Network Cards (4)
- Surge Protectors (2)
- Storage Systems (NAS) (1)
- scanners (scanner) (1)
- Telecommunications Cabinets & Racks (6)
- Telephony (phone) (4)
- thin client (2)
- transceivers (5)
- Smart watches (1)
Wireless Adapters
Wireless networks are developing rapidly, it seems that Wi-Fi 6 appeared quite recently, but there are already freely available access points with support for the newer speed standard Wi-Fi 6E, promising gigabit speeds over the air. Moreover, the newer Intel 12th generation chipsets have native support for this standard, but you can't always see the connectors for the antennas on your motherboards: it all depends on the engineering of its manufacturer.
So if you get a motherboard without built-in wireless support, and your computer just needs to be connected to Wi-Fi, you can separately buy a wireless board for your PC. There is enough space in your case, the main thing is to find a free PCI-E slot. But if everything is occupied – no problem, there are models for M.2. Such modules do not have their own antennas, they have connectors for connection, the same as in laptops. The main mistake is that very often the antennas are mounted by users inside the computer case, which is made of metal and can shield the Wi-Fi signal very well.
If a wireless network adapter for a computer is a bit exotic, then a laptop without Wi-Fi is comparable to a smartphone without a SIM card slot. Why then an additional wireless adapter might be useful at first glance may not be clear.
Often in many laptops to reduce its thickness minimized the number of connectors not only for peripherals, which are visible outside, but also internal slots, so the Wi-Fi module in most cases soldered to the main board of the laptop. And it can happen that the built-in wireless module, for example, supports only 2.4 GHz, and a new access point with 5 GHz was purchased.
Of course, a newer router has backward compatibility and will not leave your laptop without connection, but after comparing connection speeds you will immediately want to use faster Internet not only in your smartphone, but also in your laptop. Even if the Wi-Fi module is made in the form of a separate board, the chances to upgrade it tend to zero: the lists of supported adapters are artificially limited to single models, and the first found wireless module is not sure that it will fit in size, not to mention the fact that the laptop will correctly identify it. Therefore, the easiest way to solve this problem is to buy a Wi-Fi adapter that supports the new speed standard.
Synopsis at
The use of network cards and wireless adapters may be necessary in some cases. All possible variants of these devices will work for personal computers, but it is still better to pay attention to discrete boards. As for laptops – there are not as many options for them as for PCs, often they are USB devices the size of an ordinary flash drive.
- All posts
- KVM equipment (equipment) (2)
- Powerline Adapters (2)
- Security (security) (4)
- Wireless adapters (4)
- Power Supplies (12)
- Video cards (videocards) (38)
- CCTV (6)
- HDD & SSD Drives (60)
- Disk Shelves (JBOD) (2)
- Sound cards (sound cards) (3)
- Instruments (instruments) (1)
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) (25)
- Cables & Patch Cords (5)
- Switches (switches) (12)
- Computer peripherals (41)
- PC (42)
- Controllers (RAID, HBA, Expander) (4)
- PC cases (13)
- PC Motherboards (24)
- Multifunctional Devices (MFP) (6)
- Memory Modules for PCs, Notebooks & Servers (16)
- Monitors (monitor) (35)
- All-in-one PC (8)
- Desktop Storage Systems (NAS) (2)
- Notebooks (notebook, laptop) (34)
- General Information (46)
- Cooling (15)
- Tablets (3)
- Plotters (1)
- Printers (6)
- Software (software) (37)
- Consumer business software (12)
- projector (2)
- PC and server processors (41)
- Workstation (5)
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs) (1)
- Office Supplies (1)
- Wi-Fi extenders (repeaters, repeaters) (3)
- Routers (routers) (14)
- Servers and Server Equipment (42)
- Network Cards (4)
- Surge Protectors (2)
- Storage Systems (NAS) (1)
- scanners (scanner) (1)
- Telecommunications Cabinets & Racks (6)
- Telephony (phone) (4)
- thin client (2)
- transceivers (5)
- Smart watches (1)
Key Features
Wi-Fi adapter is a complicated technical device and it has its own characteristics. The data is usually listed on the equipment or in the user manual. What values I want to pay attention to (will come in handy when buying an external or PCI module):
- Connection interface – USB 2.0, 3.0.
- Wi-Fi protocols – 802.11a/b/g/n/ac.
- Range – 2.4 and/or 5 GHz.
- Transmitter power – measured in dBm (preferably at least 20).
- Antenna gain – defined in dBi (not always specified).
- Security type – most reliable WPA/WPA2-PSK.
- Compatibility with operating systems.
All of these characteristics should be considered when buying a Wi-Fi adapter. For example, if your home devices do not support the 802.11ac standard, you do not need to buy a module that supports 5 GHz.
A short review
Let's give examples of models, their characteristics and price.
TP-Link TL-WN725N.
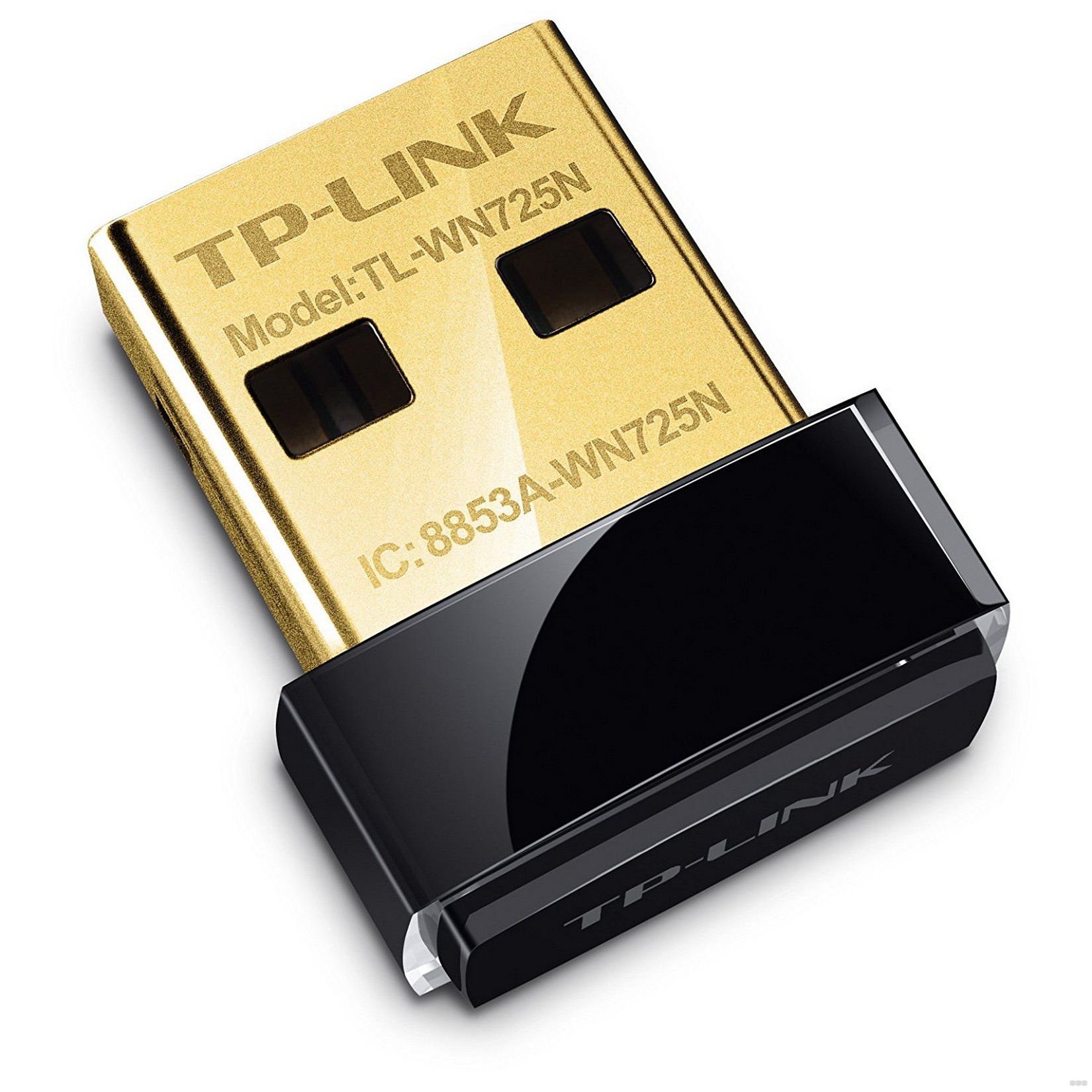

The simplest mini adapter for a computer or laptop for 500 rubles. It connects to the USB port (version 2.0). Works in the 2.4 GHz band with support for 802.11b/g/n protocols. Works with WPA/WPA2-PSK data encryption. The maximum data transfer rate is 150 Mbps.
D-Link DWA-137A1B.
USB receiver with external antenna. The antenna has a gain of 5 dBi, which is suitable for expanding the Wi-Fi signal access area. Range – 2.4 GHz, Wi-Fi standards – 802.11b/g/n, maximum speed – 300 Mbps. The price in electronics chain stores is about 1000 rubles.
TP-Link Archer T1U.
Compact USB module operates at a frequency of 5 GHz, provides speeds up to 400 Mbit / s. Supports 802.11a/n/ac. USB 2.0 connection interface. The price – up to 1000 rubles.
TP-Link Archer T2U.
Dual-band Wi-Fi adapter (2.4 and 5 GHz) for a price of 1200 rubles. It supports the latest 802.11ac standard. Fully compatible with Windows 7 and 8. According to reviews on the "ten" also works perfectly, the drivers are installed automatically.
TP-Link Archer T9E
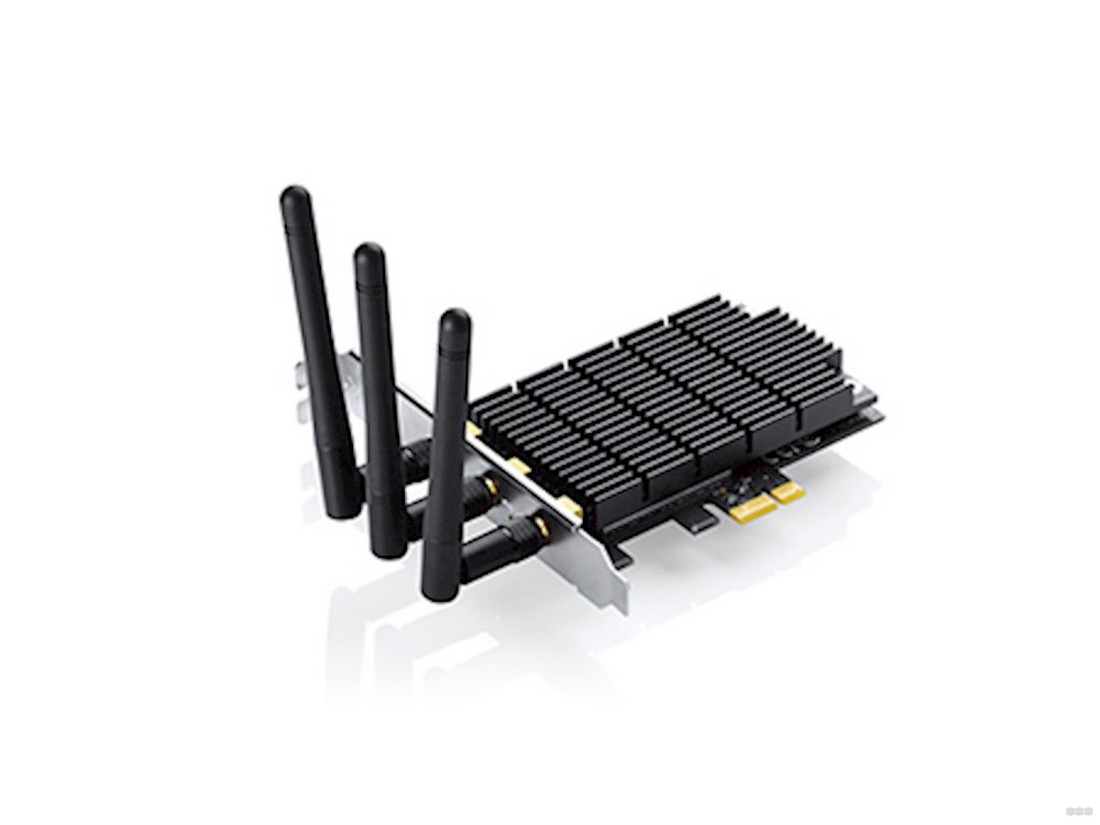

Powerful device, connects via PCI interface. Dual-band, with three antennas, high speed (up to 1900 Mbps) – an excellent option for torrent downloads and games. The board is equipped with a good radiator, which protects against overheating even during prolonged operation. The price is about 4000 rubles.
Which device is better – PCI or USB? Check out the details in the next video:
Types of network adapters
Network adapters can be classified into different types based on different functions, such as host interface, baud rate, and applications. The next part gives the details.
Classification based on network connections
Depending on how the network adapter accesses the network, there is a wired network adapter and a wireless network adapter. As the name implies, a wired network adapter usually needs to connect the host to the network using a cable, such as an Ethernet cable and an optical cable. A wireless network adapter often comes with a small antenna that uses radio waves to communicate with an access point to connect to a wireless network.
Classification based on bus interfaces
The ISA (Industry Standard Architecture: ISA bus was developed in 1981 and was the standard bus architecture for IBM-compatible devices. Because of the low card speed (9 Mbps), the ISA bus interface is no longer a recognized type and is difficult to find in today's stores.
The PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect: PCI bus was developed in 1990 to replace the previous ISA standard. It has a fixed width of 32 bits (133 MB/s of data transfer) and 64 bits (266 MB/s of data transfer). This type of network card was first used on servers and then gradually applied to PCs. Today, most PCs do not have expansion cards, but rather devices integrated into the motherboard. As a result, the PCI network card has been replaced by other bus interfaces such as PCI-X or USB.
The PCI-X (Peripheral Component Interconnect eXtended) network adapter: PCI-X is an advanced PCI bus technology. It operates at 64-bit speed and is capable of speeds up to 1064MB/s. In many cases, PCI-X is backwards compatible with PCI network cards.
The PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) network adapter: Is the latest standard and is now popular on computer and server motherboards. The PCIe network card is available in five versions, and each version supports five types of lines at different speeds. To learn more about PCIe Network Cards read: The PCIe Card Guide: everything you need to know about PCI Express cards.
Other factors not to ignore when deciding to buy a network adapter
Budget is always a significant factor when you are considering how to choose a NIC. The price of an NIC card varies greatly as it is designed by different models, speeds, features, and manufacturers. Also, make sure that you buy from vendors with a good reputation, because a vendor with a good reputation will usually provide a better service. Some suppliers may not offer comprehensive services to customers. Choosing a vendor that offers 24/7 customer service and technical support, covering pre-sales and after-sales support to solve all your problems, which can be a plus.
How to choose a network card? Based on the above, it is advisable to consider the bus type, baud rate, port numbers, connector type, operating system, features, brand and price factors of the NIC based on the actual network environment before buying.
How to choose a network adapter?
The existence of several varieties of these cards requires the user to have some knowledge of the technology used and how to solve the problem with Internet access. The purchase of an unproductive card leads to problems when connecting, and the functionality of outdated network equipment does not meet modern requirements. Let's look at the main issues to consider when buying this electronic device:
- The way the router connects to the computer – via Wi-Fi or cable.
- The claimed speed of the card must match the actual speed of the network.
- For servers, it is advisable to buy a card with several additional ports.
- There are several connector standards, your PC NIC must be compatible with your existing hardware.
- Your operating system must support this NIC (especially important for older models).
- The functionality of the device must be suitable for the task at hand.
- It is desirable to buy adapters from a proven manufacturer – Intel, Synology, ASUS, D-LINK, ZYXEL.
How to connect the network adapter?
The complexity of working with NICs depends on the specific type of product. It is easier to work with external devices. They are connected by simply attaching the plug to the corresponding jack on the PC. More difficult to cope with the task of how to install a network adapter of the internal type. To solve it, you will have to disassemble the computer case and perform a number of the following actions:
- Unscrew the left cover of the PC.
- Select the appropriate PCI slot.
- Try on the internal board in place.
- In most cases, you need to break out the strip in the back wall, which interferes with the installation of the power adapter.
- Lightly and gently press the board into the slot.
- Screw the metal plate of the adapter to the PC case.
- Screw the antenna to the appropriate connector of the network adapter.
What does the WiFi adapter do?

As mentioned above, the adapter is needed to connect the device to an existing Wi-Fi network, created with a router, access point or smartphone in the absence of a wired Internet connection. Thus, the adapter allows:
- detect available wireless networks,
- provide connection to them via an encrypted channel,
- organize data transfer via a local network (access to other devices, local file storage),
- provide high-speed access to the Internet without the need to buy patch cords (patch cords) or make them from twisted pair, lay them and connect them.
In fact, WiFi-adapter is a full-fledged additional network card, which takes full control of the network connection. Accordingly, it can be used not only in the strict need to provide a wireless connection, but also as a temporary or permanent replacement for a failed built-in network adapter.
How to choose?
What is WiFi-adapter, why they need and what it does, we have identified, then it is time to turn to the most important information for any consumer – questions of choice and the main parameters.
To determine which WiFi adapter to choose for your home, apartment or small office, you need to pay attention to the following aspects.
Wireless module

More specifically, the connection standard that it supports. Most modern adapters are dual-band, that is, they allow you to connect to a network broadcasting on frequencies 2.4 and 5 GHz. You can find out about their support from the technical specifications and the labeling of the supported Wi-Fi standard – 802.11n and 802.11ac, respectively. That said:
We recommend buying Wi-Fi adapters that support the 802.11ac standard, since it provides higher data transfer speeds and is still less common, so home and office networks operating at 5GHz frequency are less noisy with "neighboring" devices. But it is worth remembering that the router must also have support for the appropriate standard.
Antenna
The Wi-Fi adapter necessarily has an antenna, but in most cases it looks like a twisted track on the board. Nevertheless, for most cases (for work within 1-3 room apartment, small office, store) it is more than enough.
If the computer or other device is expected to be at a considerable distance from the router, and there will be some thick, solid walls between them, it makes sense to choose an adapter with an external antenna. It looks just like a router and works to boost the signal and improve connection quality.
Connector

How to Install a Network Interface Card in a Computer
Installing a USB adapter in the computer is very simple – plug it in and it's done. So let's consider installing an internal adapter. Before you connect the network card to the computer, you need to remove the plug on the back of the system unit opposite the corresponding PCI or PCI-E connector. Then you just need to carefully insert the device into the slot and tighten the fixing bar with the screw. That's it. Naturally, you have to perform the whole operation with the computer turned off.
You have to configure the adapter according to your needs. So, in most cases, once the cable is installed and connected, it should work out of the box. Quite often you have to change the settings for getting an IP address. There are two types: obtaining the address automatically and specifying it manually. In most cases, the automatic option is enough. You can check what mode is set or change it by going to the control panel of the Start menu. The main thing is to find the item "Local Area Connection" Here you need to find "Network and Sharing Center" and click on "Local Area Connection". The current connection status window appears in the status window, in which we are interested in the "Properties" button. In the new window that opens, select "Internet Protocol version 4" and click again on the "Properties" button. Among the protocols you need TCP/IP version 4 or 6. The next window will prompt you to select the option to obtain the IP address by setting the switch to the desired mode. In most cases, an IP address is assigned automatically, so you're unlikely to have to configure
What to do if the computer does not see the network card
This is a fairly common problem. It can be solved in different ways, depending on the situation. Consider solutions for integrated and internal cards. The situation when the computer doesn't see the card can occur for several reasons:
In all other situations, the card should appear in the Device Manager at least as an unidentified device, which will allow you to install drivers. For disabling the network card in BIOS the item Onboard H/W LAN is responsible. It must be in Enabled mode. It is interesting that here, in BIOS, sometimes disabling the Green LAN item helps to detect the card. This is not a universal approach, as different models of motherboards may not have these items at all. Standard BIOS for most motherboards As such, the lack of drivers usually still allows the network adapter to be detected in the Device Manager. If the card is built-in, you will need to install motherboard drivers to detect it.
In laptops it is very easy to find the required driver package by device model, whereas in desktop systems you have to determine the exact model of the motherboard and download the drivers from the official site.
ATTENTION! Always download drivers only from official sites of developers. This will allow you to avoid viruses and harmful programs to penetrate into your system and use the freshest version of software. As for the physical malfunction, there is nothing you can do. Especially if the card is built-in. The only thing left is to buy a new external or internal one. If you have your own experience with installing and operating or configuring network cards, feel free to share it in the comments.
Read More: