It is recommended to switch to this mode in hard-to-reach places, so that the phone doesn't waste energy scanning for next-generation networks, saving battery power at the same time.
- How to change the network mode on your Samsung Galaxy
- What network modes there are
- Which network mode should I choose?
- Auto 2G/3G/4G
- Only 3 G
- Only 4 G
- WCDMA or GSM: what's the difference
- Which mode to choose
- What is the difference between WCDMA and GSM
- WCDMA and GSM Network Mode: Which to Choose
- What's the problem?
- Choice of network type via the engineering menu
- WCDMA
- WCDMA/GSM
- Other interesting articles:
- What is WCDMA
- What is the difference between WCDMA and other modes
- Switching on "2G only" or "3G only" modes on Android
- What's the problem?
- Selecting the type of network through the engineering menu
- What's the difference between WCDMA and other modes
- WiMax and Wi-Fi
- Conclusion
How to change the network mode on your Samsung Galaxy
There are three generations of network, the main difference is the speed of the Internet. The higher the generation, the faster the Internet:
- 2G (GSM, labeled G or E on the device) is the slowest internet and the lowest power consumption;
- 3G (WCDMA, indicated on the device as 3G, H or H+) – average Internet speed and average power consumption;
- 4G (LTE, referred to on the device as 4G) – the fastest Internet speed and average power consumption.
What network modes there are
Network mode is a rule (algorithm) by which the mobile device will connect to the cellular network. By default, the device works in automatic mode:
If the device supports 4G and has such a signal, the device will connect to it;
If the device does not support 4G or there is no such signal – the device will connect to 3G;
If the device does not support 3G or there is no such signal – the device will connect to 2G.
The ability to connect to a particular network generation depends on the device: if the device only supports 2G, then it will not be possible to connect to 3G or 4G. To find out which network generations your device supports, contact the support service.
- 3G only – the device will only search for a 3G network. If the 3G signal is weak or nonexistent, the device will not pick up the network.
- 2G only – The device will only search for a 2G network. If the 2G signal is weak or not available – the device will not catch the network.
Some operators (Tele2) do not have a 2G network in certain regions (Moscow). Take this into account when buying a phone – for example, the Galaxy Star Advance only supports 2G and it simply won't work with Tele2.
Which network mode should I choose?
In the settings menu of the smartphone, the user is offered items with which it is proposed to configure the network. They can select such types of connections as "only 3G" or combinations: "Automatic 2G/3G/4G". The number of lines in the menu, depending on the model and year of manufacture, may vary. In different situations, one of the items is the most useful, so manufacturers offer to choose the user's preferred mode.
But to make an informed choice, you need to understand what the different modes offer, what the disadvantages and advantages of each solution are. And why automatic detection of network type is not always the best option.
The difference between generations of cellular communication is not only in protocols, frequency range, types of signal encryption and data transfer rate. They interact differently with voice calls.
If it were only necessary to get better quality of communication (high internet speeds), the old networks would have been shut down a long time ago. But their advantage is that with fewer towers they provide a significant coverage area. And if you turn off the old type of network, many subscribers in rural areas will be left without communication. There are other features of the old networks that are worth considering when setting up.
Auto 2G/3G/4G
In the factory settings of each phone is set to this mode, with automatic selection of the best and most "advanced" network. The same mode is offered to choose, if you decide to configure the network in the office of the company.
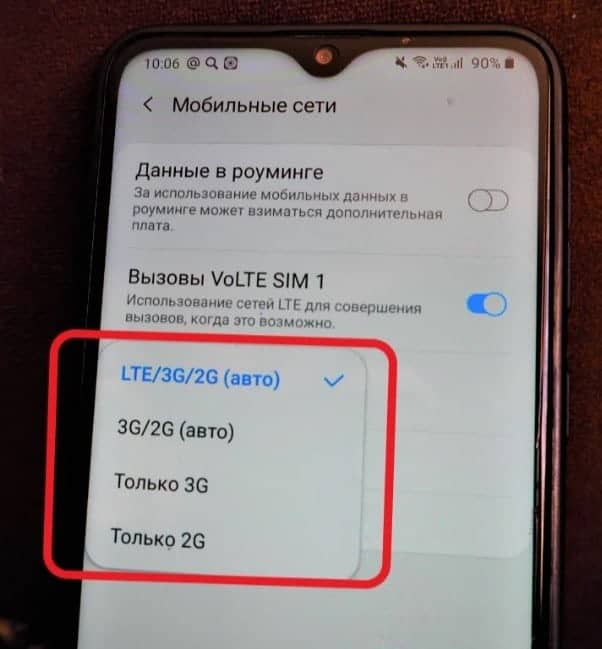
In this case, the smartphone itself determines which networks are available in the region, and which of them to connect to for calls and data transfer. It automatically evaluates the signal level, reception quality, priorities and other network settings. The owner does not need to keep track of whether he or she has left the network coverage area.
Only 3 G
The golden mean in terms of coverage and connection speed. As well as 2G, 3G also often catches in places where there is no LTE. But the speed of third-generation networks is already enough for YouTube, and for video calls with navigation. Disabling the search for the 4G range also gives the benefit of autonomy, but the problem is that many new smartphones setting "Only 3 G" now simply no.
When to use: If you want to stay connected away from civilization, and still use the Internet.

Only 4 G
This setting is available in a small number of devices, on many models, its inclusion is hidden in the settings deeper.
Here's whyOriginally 4G networks provided only Internet access, and it was not possible to make calls over them (for "regular" voice calls). Later, 4G technology was further developed, and the possibility to make calls appeared – it was called 4G VoLTE.
However, this function is still not available with all operators. And even if it is available, it can work with restrictions: for example, you can communicate via VoLTE only between numbers of the same operators, or in certain cities.
When to use In theory – if you need the fastest possible Internet, and you are in a city with good 4G coverage. In practice, it's better to choose the previous mode: if there is a 4G signal, your smartphone will connect to it automatically, and you will not be left without voice calls at the most inappropriate moment.
Subscribe to our Yandex.Zento not miss cool articles
Telegram Channel with the best discounts and instant news updates
Geekville on "Vkontakte"Our group with all the latest content
WCDMA or GSM: what's the difference
Both technologies have multiple access, which means that one tower can receive multiple calls. But the main difference between the two comes from exactly how data is converted into radio waves, which the device receives and broadcasts.
The main problem for telecommunications companies was the difference in frequency bands. This made it impossible for GSM-enabled phones to communicate with WCDMA networks, and vice versa. To solve this, most manufacturers had to use different frequency bands for 2G and 3G networks. This made it possible to use cells on almost any network and anywhere in the world.
Until the advent of 4G LTE technology, the main difference between GSM and WCDMA devices had to do with the SIM card. GSM-enabled phones were made with a SIM card slot, while CDMA devices were not.
In other words, WCDMA is a technology based on using a phone with a subscriber number that is linked to a specific 3G-enabled device. If you want to switch phones, you have to contact your provider, deactivate the old device and connect the new one.
In GSM devices, the number is linked to the SIM card, so to switch to another, all you will have to do is install the SIM card in the new gadget.
Which mode to choose
WCDMA is a next-generation (3G) cell phone mode. You can transmit voice and data through it, and it happens much faster. The quality of communication is practically the same in these modes. But WCDMA coverage is most often not available outside of the city.
Therefore, if you often go out of the city and communication is important to you, choose GSM. And if you often go to the city and want to use high-speed Internet, WCDMA is more suitable. The advantage of this network mode is that it saves battery power, and the connection will not glitch while moving around the city.

You can also select automatic mode (switching between networks depending on the quality of coverage). It will provide Internet and voice communication at any point of radio wave range. But its disadvantage is the increased power consumption, because two radio modules work simultaneously.
And since the radio module uses more power where the signal is poorly reachable, the battery will run out very quickly out of town. Therefore, when leaving the city, switch to GSM.
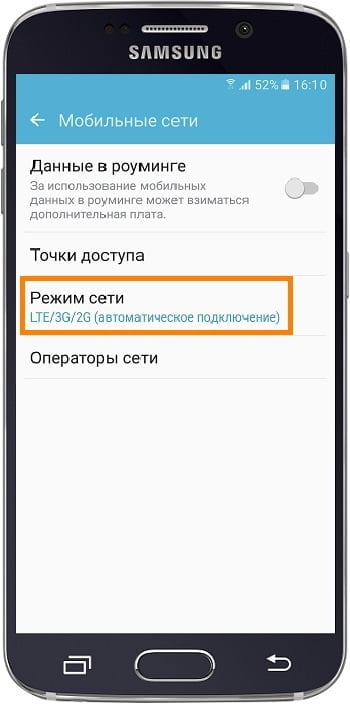
To turn on the Android smartphones (Meizu, Xiaomi, Lenovo, Prestigio, etc.) the required network mode, go to Settings > Mobile networks > Network mode > enable WCDMA / GSM / UMTS / HSDPA+.
That's all, friends! I hope this article was useful for you. Share it with your friends, and don't forget to give us likes and follow us on Facebook Twitter and VKontakte! See you soon!
What is the difference between WCDMA and GSM
GSM is a cellular communications standard that dates back to the late 1980s. It uses frequencies in the 800 to 1900 MHz range and provides basic cellular services.
In addition, GSM can provide a number of additional services, including: caller ID, call forwarding, call hold and call waiting, conference calls, voice mail.
As you can see, GSM provides basic mobile communication services, while WCDMA is a standard of cellular communication, which was created as a supplement to GSM. The WCDMA standard operates in a frequency range from 1900 to 2100 MHz and is used to provide access to third generation (3G) mobile communication services.
WCDMA and GSM also handle frequencies and channels differently. GSM uses time and frequency division of channels (TDMA and FDMA), while WCDMA uses code division (CDMA). Using CDMA has several advantages of TDMA and FDMA:
- Efficient use of resources. Code division does not limit the number of possible channels as much.
- High level of protection. The use of code division makes it much more difficult to allocate an individual channel, because the entire frequency band is almost uniformly filled with signal.
- Saving battery power. Phones that work with CDMA have less radiated power, which saves battery power.
WCDMA and GSM Network Mode: Which to Choose
Many phones have a choice of network modes. There are usually three options available, these are:
The choice between these three options depends on where you are. If you are constantly within a city where there is a stable signal and good coverage, it is quite possible to choose "WCDMA Only" network mode. In this case, the phone will only work with the WCDMA network. This will reduce the battery consumption slightly and eliminate the switching between GSM and WCDMA, during which there can be interruptions in communication.
If you live in the country or often travel outside of it, it is better to choose the automatic network mode. In this mode, the phone will automatically switch between WCDMA and GSM networks, depending on what coverage is available at the moment.
The network mode "Only GSM" should be chosen only in those cases, if you for some reasons do not want to use 3G services.
What's the problem?
On some Android devices to switch the network mode is enough to open the settings,
In my case (protected Chinese smartphone Iman X5 (Android 5.1)) when selecting the network type 2G, the phone worked only in this range, but when you select 3G the device worked in both 2G and 3G. On other Android devices (some Samsung smartphones for sure) the modes are called "only 2G(GSM)" and "only 3G". It's enough just to select the desired mode and enjoy the work of the device. I, on the other hand, had to find another way of forcing 3G.
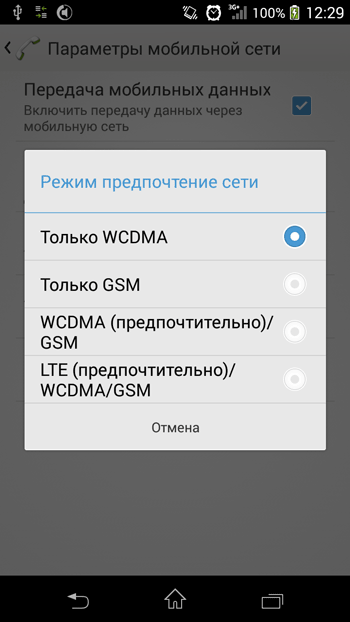
Choice of network type via the engineering menu
Despite the apparent complexity of this method it is simple – just dial *#*#4636#*#* on the phone (sometimes it may be necessary to press the call button)
Select "Phone Info", scroll to "Setup Preferred Network Type",
Select "WCDMA only" (only 3g) or "GSM only" (only 2g). The default setting is "WCDMA preferred".
WCDMA
WCDMA refers to third generation cellular communication (3G). WCDMA is a radio interface technology that uses code division multiple access broadband. It is WCDMA that has been chosen by many cellular carriers to provide broadband radio access to support 3G services.
What WCDMA does better is data transfer, as it can reach speeds of up to 3.6 Mbps. This is quite enough not only to download pictures on the network or go to sites, but even to watch online video.
This mode is worth using if you use both the Internet and communication at the same time. For example, for the city – this is the most optimal mode. However, the charge consumption will be slightly higher in comparison with GSM.
WCDMA/GSM
A universal mode of cellular communication, set by default. In general, it can be called optimal, since it provides both high-quality voice communication and data transfer at maximum speed. The only disadvantage is that the rate of battery discharge will be slightly higher than if you use only one mode.
- Leave a comment on the article.
- Subscribe to our YouTube Channel.
- Subscribe to our Telegram.
- Subscribe to our VKontakte group.
- Subscribe to our our channel in Zen.
Other interesting articles:
What is WCDMA
WCDMA network mode is set to get access to high-speed Internet connection (3G and above), in which you can go live on different platforms, watch videos in good quality and talk on video calls.
This technology is currently supported by all leading mobile operators, including those in Russia. It operates on the frequencies 1.9 GHz – 2.1 GHz and develops the data transfer rate from 3.6 Mbit / s to 42.2 Mbit / s.

- HSDPA, a low-speed protocol within 3G, offers about 3.6 Mbps;
- HSUPA – high-speed packet protocol (about 5.7 Mbit/s);
- HSPA – allows you to receive data from the network at 14.4 Mbit/s, while uploading information to the user at 5.76 Mbit/s;
- HSPA+ – the newest exchange method with a speed of 42.2 Mbps.
Now, when you see the WCDMA parameter, you will understand that this designation indicates the possibility to change the settings in the phone and connect to a high-speed network along with the standard one.
What is the difference between WCDMA and other modes
So what's better than WCDMA or GSM and what's the difference between the two in general:
- GSM came much earlier, long before the mass use of high-speed Internet. It is able to provide standard calls through the mobile operator, sending SMS and MMS messages and access to the World Wide Web to read something there or view photos.
- GSM frequencies range from 0.8 to 1.9 GHz.
- WCDMA uses your phone's resources more intelligently, uses less battery power, and provides a more secure connection.
There is also UMTS (aka 3GSM), which is an intermediate stage between the two described above. It appeared when GSM has ceased to fully meet the needs of subscribers, and has a better quality of connection, the establishment of a secure protocol and the speed of the Internet in the range of 0.4 – 2 Mbit / s.
Switching on "2G only" or "3G only" modes on Android
Modern smartphones and tablets operate in several cellular bands: 2G (GSM), 3G, 4G. The phone automatically scans the radio frequencies and switches to the preferred network. It would seem that everything already works perfectly and there is no need to change the settings. For most users – yes. But in some situations, activating the "2G only" or "3G only" mode can improve the performance of the device. For example, if your phone is out of 3G coverage, turning on the "2G only" mode will save battery power, because your smartphone won't scan for 3G frequencies and try to connect to them. Or another example: You need to connect to the Internet via 3G, but due to a weak signal the device automatically switches to 2G. In this case, activating "3G only" mode even with a weak but stable signal will provide stable Internet access at a relatively high speed.
What's the problem?
On some Android devices to switch the network mode is enough to open the settings,
In my case (protected Chinese smartphone Iman X5 (Android 5.1)) when selecting the network type 2G, the phone worked only in that range, but when you select 3G the device worked in both 2G and 3G. On other Android devices (some Samsung smartphones for sure) the modes are called "only 2G(GSM)" and "only 3G". It is enough just to select the desired mode and enjoy the work of the device. I, on the other hand, had to find another way to forcibly turn on 3G.
Selecting the type of network through the engineering menu
Despite the apparent complexity of this method is simple – just dial the combination *#*#4636#*#* (sometimes it may be necessary to press the call button)
Select "Phone Info", scroll to "Setup Preferred Network Type",
Select "WCDMA only" (only 3g) or "GSM only" (only 2g). The default setting there is usually "WCDMA preferred" (3g preferred).
What's the difference between WCDMA and other modes

So what's better than WCDMA or GSM and what's the difference between the two in general:
- GSM came much earlier, long before the mass use of high-speed Internet. It can provide standard calls through the mobile operator, send SMS and MMS messages and access to the World Wide Web to read something there or view photos.
- GSM uses frequencies from 0.8 to 1.9 GHz.
- WCDMA uses your phone's resources more wisely, uses less battery power, and provides a more secure connection.
There is also UMTS (aka 3GSM), which is an intermediate stage between the two described above. It appeared when GSM ceased to fully meet the needs of subscribers, and is characterized by a better quality of connection, the establishment of a secure protocol and the speed of the Internet in the range of 0.4 – 2 Mbit / s.
WiMax and Wi-Fi
Almost everyone is familiar with Wi-Fi, almost everyone has a router at home, and in many public places there are free access points. WiMax allows you to cover those areas where it is difficult to provide cable connections in every house. This is applicable in the private sector or in cottage communities. Base stations are used to provide coverage within a radius of several kilometers.
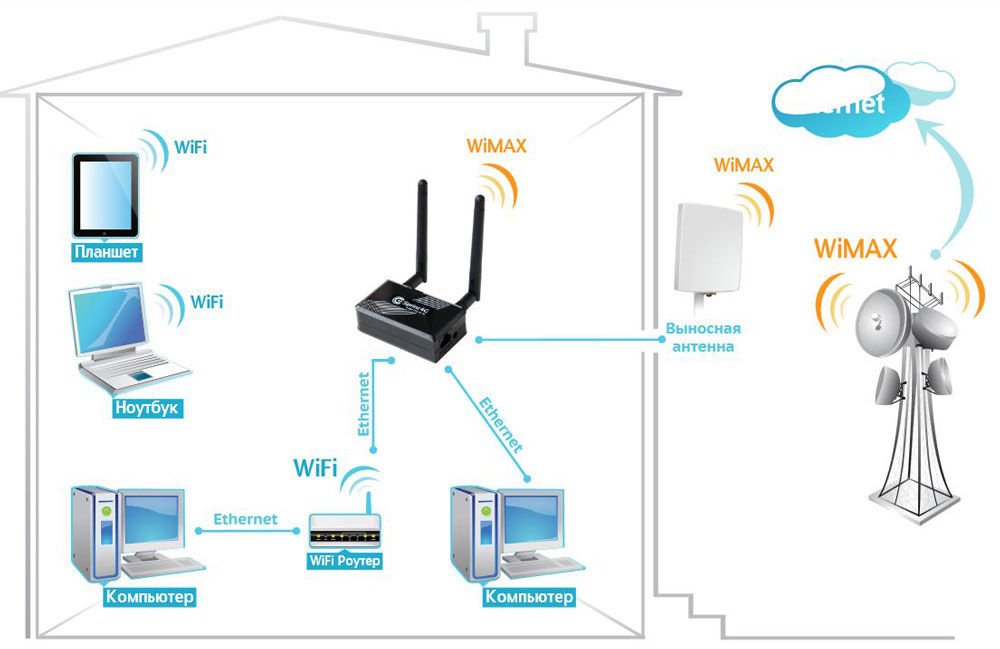
You need a special receiver for connection and an amplifying antenna when moving away from the station. This technology is not widely used, as it still requires a cable connection to the village. Much more expedient to use mobile Internet.
Conclusion
We have listed all the possible types of connection to the Internet. If you live in a city, your provider will most likely connect you via cable. This is the cheapest type of connection in high-rise buildings. Setting up the equipment will be different for different types of connection, you can read more about this issue in our article How to connect the Internet on a laptop. Also, never hesitate to contact your service provider's technical support to find out your network access parameters.
What type of connection do you use? Are you satisfied with the quality of connection? Write us in comments.
Read More: