In 2009, a "modification" of the standard codenamed 802.11n appeared and new routers and network adapters began to support this standard along with the previous b and g. So, to turn the n standard to the maximum, the Wi-Fi WMM parameter should be obligatory turned on. And now in order.

What is WMM and WME on Router – How to Enable and Configure Wi-Fi Mode for QoS
Consumption of video and audio content on the Internet is growing every year. And it means that more and more load is put on the router. In order to optimize it the developers come up with new technologies that allow evenly distribute the load on the network and provide continuous and trouble-free operation of WiFi network standard QoS (Quality of Service). One of these is WMM (WiFi Multimedia), which can also be referred to as WME (Wireless Multimedia Extensions). What is this setting on your router and how do I enable and use it?
WMM, or Wi-Fi Multimedia, is a router setting that allows you to prioritize the type of traffic that needs maximum WiFi bandwidth at the moment. For more technical specifications, see WikiPedia
In practice this means that when "Wireless Multimedia" is turned on, the router first of all makes the network with one or several SSIDs free for broadcasting the "heavy" content. So that it plays on your computer, TV or set-top box without delay. And only then to transmit text documents.
This is the so-called QoS (Quality of Service) environment, or "quality of service" in Russian. When several users connect to WiFi and consume different content, each of them, depending on the type of data being downloaded, has its own bandwidth "corridor". So that neither of them is uncomfortable while working within the network. With simultaneous connection to the router, the person who makes an online call via WhatsApp or watches high definition video in an online cinema will get higher speed than another client who is sitting in a social network or downloading files via FTP or Torrent.
Types of WMM (WME) traffic
WMM technology on a router handles four types of content transmitted over the network:
- Voice traffic (AC_VO or Voice) – by default has the highest priority and allows multiple simultaneous voice calls over VoIP
- Video (AC_Vi or Video) – prioritizes online video from movie theaters (Kinopoisk, IVI, Megago, KEON, OKKO, etc.) or such services as YouTube or Vimeo
- Ordinary traffic, or the so-called "WMM priority of non-guaranteed delivery (AC_BE or Best Effort) is the work with devices that do not support QoS mechanisms. It is used for normal Internet surfing – accessing sites and services through an application or browser
- Background traffic (AC_BK or Background) is auxiliary and has the lowest WMM priority because it is not too picky about latency
Features of the standard
What is WMM in router settings? WMM or Wi-Fi Multimedia is a specification that supports four classes of traffic: voice (higher priority), video (multicast and unicast), standard and background (lower priority).
When WMM is enabled in the adapter settings on a computer or router, traffic is processed according to stated priorities, i.e. video and voice go first without additional delays.
In addition, WMM mode affects speed. If the router works with WMM turned off, which is implemented in 802.11n for 2.4 GHz networking and 802.11ac for 5 GHz networking, you won't get speeds higher than 54 Mbps.
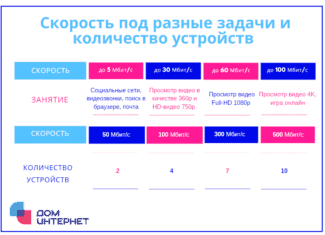
Here's what else your Internet speeds depend on, as seen in the following video:
Settings
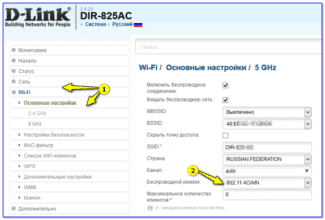
How to enable Wi-Fi Multimedia mode? If it is a router, the WMM settings are in the personal cabinet. If the adapter connected to the computer – then in its properties, which can be viewed in the Windows operating system.
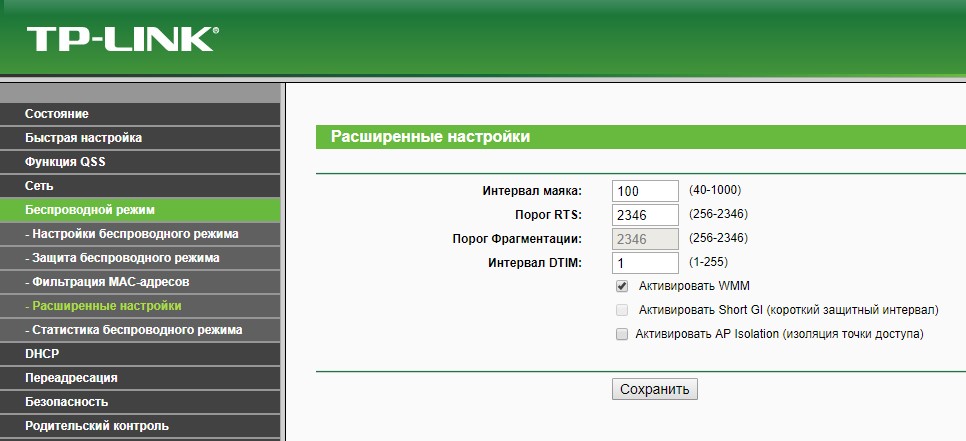
- Using the address bar of your browser, log into the router's personal cabinet at 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 through the admin/admin username and password. If you are using more modern devices, see the admin login addresses in the instruction manual.
- Go to the Wi-Fi or wireless networks section.
- Move to "Advanced Settings".
- Check the "Activate WMM" box.
- Click OK.
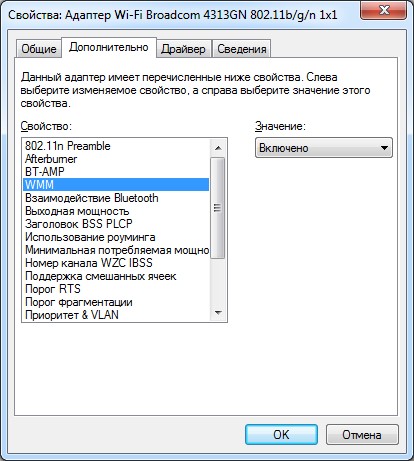
- Click the Start button and select "Device Manager".
- Expand the "Network Adapters" branch and select wireless (not to be confused with the network card).
- Select the properties and click on the "Advanced" tab.
- Find the WMM section and activate it.
Basic settings.
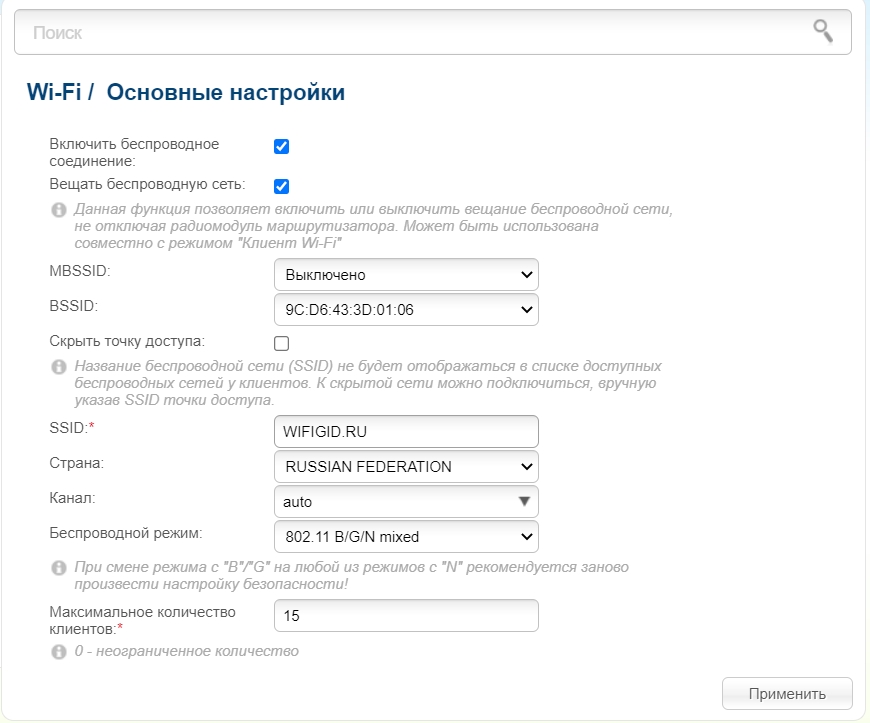
- Enable wireless network – If you uncheck it, the wi-fi will stop working at all.
- Broadcast wireless network – If you uncheck this box, there will be no internet when you connect via wi-fi. It will be only when connecting by wire.
- BSSID – MAC address of the wireless network. An ordinary user does not really need this item.
- Hide Access Point – if unchecked, it will exist, but will be invisible, and you will only be able to connect to it if you enter the name manually.
- SSID – Wi-Fi network name.
- Country – In different regions and countries, there is a limit to the signal strength. This restriction is regulated by the law of the country. Therefore, it is better to choose your region. They say Japan has the lowest limit, so you can try this country.
- Channel – The 2.4 and 5 GHz frequencies have their own channels on which the dedicated router works. This is to ensure that the neighbor routers do not interfere with you. You can choose a channel by load, but it is better to set the mode "Auto", in this case the device will choose the most unloaded channel automatically when you turn on the router.
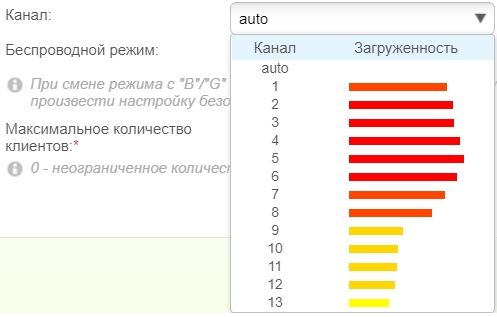
- Wireless mode – This setting is needed in order to choose what standards of wi-fi will be used. For 2.4 GHz it is B, G, N, and for 5 GHz it is usually N, AC and in rare cases AX. If you don't have older devices manufactured before 2009, you can choose N at 2.4 GHz. You can read about the standards here.
- The minimum number of clients – everything is quite clear here. This parameter shows the limit for connections to wi-fi. You can reduce or increase this figure depending on the load of the router.
Configure security
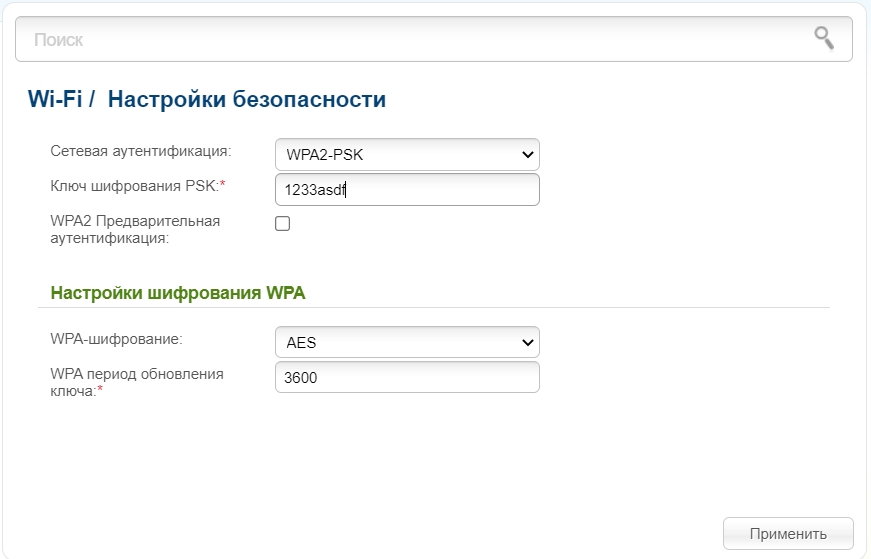
- Network authentication – is an encryption option that is used when connecting over wi-fi. Normally, when you connect to a password-protected network, all packets coming and going are encrypted. The most secure at the moment is still WPA2-PSK. WPA has a lot of faults and is easily hacked. There is also the newer WPA3, but it is only supported on Wi-Fi 6.
- WPA2 Preauthentication – This feature allows you to connect faster between access points if you have more than one. It does this by caching connection data that is stored on the device. This is only useful if you have another AP connected in repeater mode. Also, security may suffer a bit in this case.
- WPA – is also used for encryption. It is better to use "AES".
- WPA key renewal period – How long it takes for the key to change. It is written in seconds. 3600 seconds = 60 minutes.
Disabling 40 MHz channel usage
The 802.11n standard provides for the use of 40 MHz wideband channels, which provides an increase in throughput. But the reality is that if the channel width is changed from 20 MHz to 40 MHz, you might even end up with a noticeable reduction in speed performance instead of the expected increase.

Using a 40 MHz channel width can give you a potential 10 to 20 Mbps increase in throughput, but in the vast majority of cases you will only see such an increase if you have a strong enough signal. If the signal strength decreases, this bandwidth ultimately becomes much less efficient and does not allow for any increase in throughput. Thus, if 40 MHz will be used in the presence of a weak signal level, it can reduce the bandwidth by 80%.
If you decide to use such a channel, but notice a significant drop in speed, simply reconfigure your device to use the 20 MHz channel. In this way, you can achieve a noticeable increase in connection bandwidth.
Use only the latest drivers

In order to configure your Zyxel router for normal connection speeds, you should only use the latest wireless adapter drivers. It is not uncommon for situations where a significant increase in connection speed has been achieved after a newer version of the manufacturer's driver has been installed.
So, we've only looked at the most affordable and effective ways of how you can configure your Zyxel devices to provide faster connection speeds as well as more stable Wi-Fi network operation. But we should not forget that there are many other factors that also affect the performance of Wi-Fi networks:
- Other Wi-Fi devices that are a short distance away.
- Bluetooth devices that are operating somewhere within your Wi-Fi network coverage area.
- Excessive distances between Wi-Fi devices in use.
- All sorts of obstacles, such as furniture, walls and ceilings that constantly absorb the radiated radio signal.
- A variety of appliances that work directly within your network coverage area.
- Devices that operate via the USB 3.0 standard.
The last point may surprise many users, but it's true, USB 3.0 devices do interfere with 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi.
If you end up configuring everything correctly, you can safely count on the fact that your overall Internet speed is guaranteed to go up. Many users are not even aware of these features, using the default settings, when in fact the potential of their connection allows for much faster speeds.
Read More: