Well, as we have already said above, in addition to the hardware part, there is also the software part. Its quality has a direct impact on how often you will have to reboot the router, which settings and features a particular router model can provide, and how easy it will be to configure. Here, alas, only usage experience can tell you the difference.

- The pitfalls of high-speed Internet providers
- Why do I need Internet speeds over 100 Mbps?
- How to choose a router – types and characteristics of equipment
- Types of equipment
- Find your provider by name.
- Specifications
- Finding out a router's bandwidth
- Frequently asked questions
- How to set or change the channel width on your router
- TP-Link
- Asus .
- Choosing a router for a standard apartment
- Choosing a router for a large apartment or house
The pitfalls of high-speed Internet providers
In the race for market leadership, ISPs offering wired Internet use different strategies. Many of them are going the usual way: cheaper rates, better equipment and support for local media resources with free content. But there are also providers who are trying to win their place under the sun with ambitious tricks like delivering high-speed Internet – connections at speeds exceeding 100 Mbit/s. In some CIS countries (for example, Kazakhstan) it is still rare to find Internet speeds offered by ISPs greater than 150 Mbit/s. But the websites of Internet service providers in Russia, Ukraine and Belarus offer plans at speeds of 200, 300, 500 and even 1000 Mbps, which are not uncommon. High-speed plans cost more than regular plans, which usually promise unlimited traffic and speeds of up to 100 Mbit/s. High-speed plans cost more than regular plans, but the prices are not directly proportional to the multiple of the speed increase. For a 200 Mbit/sec speed plan providers ask for 100 Mbit/sec speed with an average markup of 30-40%. And in promo tariffs, to which you have to urgently switch before so-and-so date, otherwise the chance will be missed, the markup may be even less. What is the secret of such generosity? Is it all explained by the strategy of "cheaper in a big package"? Here's a look at the pitfalls of high-speed plans.
Why do I need Internet speeds over 100 Mbps?
High speed Internet – more than 100 Mbit/s – is not relevant in every case. A tariff plan with 100 Mbit/sec speed will be enough for comfortable web surfing, online gaming, watching IP-TV or Internet video, including HD-quality. Problems may arise only in the case of connecting by Wi-Fi such a number of devices, at which the router begins to severely reduce the speed for each of the users of the home network. For an average router, that's usually more than 10 devices (including TVs, fridges, and other Smart House appliances).
Internet speeds over 100 Mbps make sense only when downloading heavy files to your computer – distributions of operating systems or other software, high quality video, audio collections, etc. Only when constantly downloading large amounts of files can payment for a high-speed Internet connection be justified. For example, if members of the whole family are actively downloading files from torrent trackers and file storages in the evenings at the same time. But even then we are talking only about those tariff plans, the speed of which due to technical reasons can be used on computer and mobile devices in the house. After all, in order to unleash the potential of a high-speed plan, you need to have the equipment in your home that would, in fact, ensure the unleashing of this potential. And not even all modern equipment is geared to the possibility of using high-speed Internet.
How to choose a router – types and characteristics of equipment
Types of equipment
There are different ways of wired connection to the Internet, the main ones are via telephone line, Ethernet cable, fiber optic. Certain types of routers are used for each method. The main difference between the devices is the type of cable connectors. In the case of DSL routers, the WAN port is adapted to a telephone cable with an RJ11 connector, in Ethernet FTTB – RJ45. Recently, devices for connecting to fiber-optic cables, they are designed to connect to the optical pigtail.
Along with models of narrow application, there is universal equipment. These routers have several WAN-ports at once, adapted to different connectors, for example, DSL and Ethernet connection or Ethernet and USB.
Consider the type of connection you are using when choosing the right model. If in doubt, check with your ISP for information.
Find your provider by name.
Specifications
Routers can be compared to each other based on several criteria:
- Throughput (maximum data rate).
- Wi-Fi signal coverage radius.
- Number of USB, LAN and WAN ports.
- Support for the required Wi-Fi standard.
- Understandable interface and availability of technical support.
Each router has a bandwidth capacity. This is the maximum speed that you can get through the device under ideal conditions.
Bandwidth is important to pay attention to if the rate implies a high data rate. A router with less bandwidth slows down the data rate. So, if your rate pays 100 Mbps, but the router maxes out at 50 Mbps, the actual internet speed will be less than 50 Mbps. It is also not recommended to choose a router with the same bandwidth as the internet speed according to the tariff. In fact, the data will be transferred slower.
How to choose a router for the apartment, which will not affect the speed? Choose equipment from well-known manufacturers, such as ASUS, TP-LINK, NetGear. You can also get advice from your provider about the technical compatibility of the model of interest with the operator's equipment, read user reviews on forums, or check the speed from your own experience. If you choose the latter option, you will need to compare the data transfer speed through the router and through a wire connected directly to your computer. If there is a big difference, you should probably change your router.

This characteristic is important if you plan to use wi-fi in a large area, such as a vacation home. The coverage radius depends on the number of antennas on the device.
Finding out a router's bandwidth
When testing wireless networks, it is important to consider that the bandwidth depends primarily on interference and obstacles between the router and the laptop. Therefore, it is important to place the device close to the router (in the same room). Also make sure that the Wifi signal strength is as high as possible. If there is RF interference, partitions between the wireless signal receiver/transmitter, the index will not be accurate.Scan your PC for malware (for example, with DrWebCureIt). They often take up quite a bit of traffic, reducing the overall data transfer rate. Several ways to measure Wifi bandwidth.
- Running a bulk data stream copy. Conveniently calculating the speed at which the broadcast occurs.
- Using the LAN Speed Test utility, NetStress, NetMeter. Disable torrents, downloaders, messengers, mail client. Close unnecessary browser tabs.
- The administration client-service program Iperf or the graphical shell Jperf.
Testing is better to repeat several times at different times of the day. The result will vary, which depends on the server, caching, website traffic, etc.
Frequently asked questions
This is a measure of the maximum speed that the router is capable of delivering when it wirelessly connects your computer. It should not be confused with the concept of Internet speed.
Why do I have a speed of 200 Mbit/sec according to my tariff, but in practice all tests show no more than 90 (wireless connection)?
Perhaps the problem is with your router. Some models have a bandwidth of 90 Mbps, so they are not able to provide higher performance. Even if your rate is 300 Mbps, you won't be able to get speeds higher than what the router claims.
The tariffs and services of Net Buy Net Holding LLC are subject to change by the operator. Full actual information about tariffs and services in section "tariffs" or by phone indicated on the site.
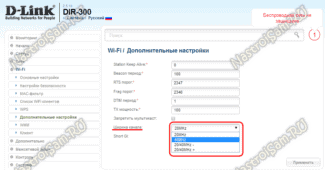
How to set or change the channel width on your router
Any router can broadcast in 2.4 GHz mode. The most modern devices also support 5 GHz mode. Few of the wireless standards work only in this band, but they are also backwards compatible with 2.4GHz gadgets. Before specifying bandwidth, you should pay attention to the Wi-fi specification in the settings. The wrong communications standard may make the configuration of the desired bandwidth unavailable.
The location of the channel width, channel number, and wireless standard settings in the router configuration depends on the firmware version.
Older equipment may not be able to access the Internet after configuration if the Wi-fi channel width is 40 MHz or more. If the router is not working in a suitable mode, the devices are able to recognize the network without actually accessing it. Such a connection is only suitable for exchanging system data between the router and the device.
To change the bandwidth value, you first need to open the router settings. To do this, connect it to the system unit, turn it on, and enter the IP address of the device in the address bar. It is usually listed along with the default username and password on the bottom or back of the case.
The bandwidth settings are determined by the router model, version and localization of the firmware. The Channel Width or Bandwidth settings may also be named Channel Width and Bandwidth.
TP-Link
To set the wifi channel width in the TP-Link interface, one has to go to the "Wireless Mode" tab in the left-hand menu and choose "Wireless Mode Settings".

Asus .
Configuration of the frequency range for devices of this company can be found in the item "Wireless network" of the list "Additional settings".
Choosing a router for a standard apartment
The peculiarity of apartment buildings is overloaded network and a lot of interference. So when choosing a router in 2022, it no longer makes sense to consider single-frequency devices, even if you live in a small studio and alone.
A dual-frequency router is the choice for a typical apartment of up to 80 m². In order to appreciate the benefits of Wi-Fi 6, you need to make sure that your devices (smartphones, laptops, etc.) support this class. But more often than not, as we have already written above, Wi-Fi 5 is quite enough for an apartment.

Choosing a router for a large apartment or house
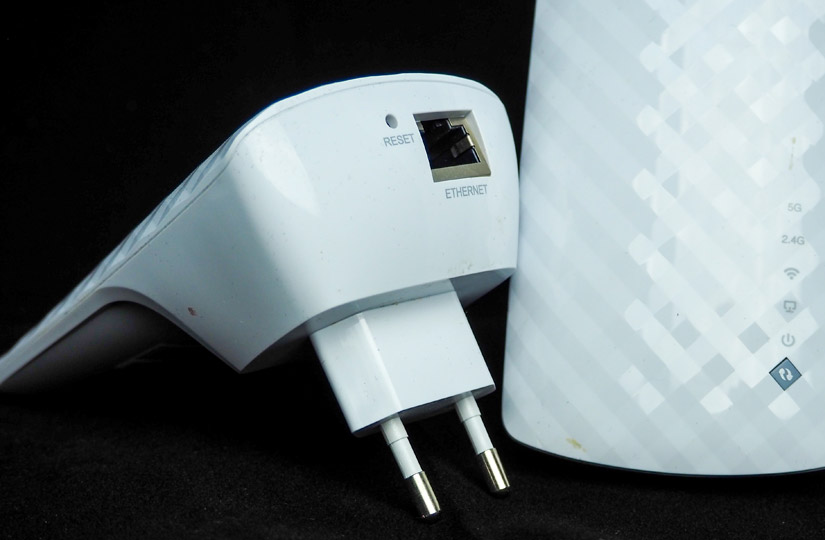
With large areas, the case is more complicated. This applies not only to private houses of different storeys, but also to multi-room apartments. Even a router with high performance can't handle the coverage in such an area. The solution is to install mesh-systems.
Mesh-systems consist of a central router and repeaters (adapters). Repeaters do not require a cable connection to the Internet, so they can be installed anywhere in the house or apartment. The signal is transmitted from the central router to the adapters, creating a seamless network. The client device automatically switches to the element of the system that gives the most stable signal. For example, you can video call on your phone and move around the house, including from floor to floor, and your smartphone will switch from one adapter to another, without affecting the quality of the video call and without interrupting the call.

Ready-made mesh-systems transmit the signal between the components via Wi-Fi only and have the simplest settings. But you can also create a network from an existing router and a separate repeater, or even two routers of the same company. So you can connect the elements of the system not only via Wi-Fi, but also via cable. The latter option is technically more complicated, because it requires communications, but it allows you to significantly increase the data transfer rate and improve the performance of the entire system. In order to combine routers, you need to have the corresponding function in their characteristics.

The number of elements in a mesh-system is limited by the number of ports on the router itself in the case of a cable connection and the capabilities of Wi-Fi in a wireless connection (often it is no more than 3-4 modules).
Read More: