Although a wi-fi router performs the same functions as a router, it is ideal for mobile devices without the need for a cable connection to the Internet. Also, the number of devices that can be connected is not limited by the number of ports on the router.

- Wireless hotspot vs router: what are the differences?
- What is a wireless access point?
- Router or router – what's the right one
- How a router works
- Switch – purpose and principle of operation
- What can be connected to the router
- Wi-Fi routers .
- Stylish and Compact – Wi-Fi Router HUAWEI WS7200 AX3 Pro
- Reliable and safe – HUAWEI WS7100 AX3 Wi-Fi router
- Indicators and buttons on the router
- Router and modem: the differences
- Wi-Fi Technology
- Main modes of operation, what you can connect
- Why do we need antennas, wi-fi technology
- Wireless network standards
- Modem and Router
- What routers are there
- Twisted pair and fiber optics
- A phone line
- Mobile .
- Why do you need a router in your apartment?
- How to use a router
- What's the difference between a modem and a router?
- Bottom line
Wireless hotspot vs router: what are the differences?
9:00 AM: You are having a video conference in the office through your laptop. 9:00 PM: You're watching a live stream on your cell phone at home. Wait a minute, have you ever wondered what wireless devices are running on your unhindered network? Surely you've heard people around you talk about the router from time to time. What about wireless access points? Is it just like a router? Absolutely not! Below, we'll help you distinguish between two different wireless networking devices.
A router is a network device that can transmit data wired or wirelessly. As a smart device, a router can efficiently direct incoming and outgoing traffic on a network. The traditional router was connected to other local area network (LAN) devices via Ethernet cables for a wired network. Over time, wireless routers, which provide a convenient installation without wiring, have gradually become a favorite in many homes and small offices.
A wireless router refers to a networking device that acts as a router by wirelessly connecting WiFi-enabled devices (such as laptops, smartphones and tablets). For corporate routers, they support IPTV/digital television services and can be used for VoIP. In addition, they also have a firewall and password protection to protect against potential threats outside the local network.
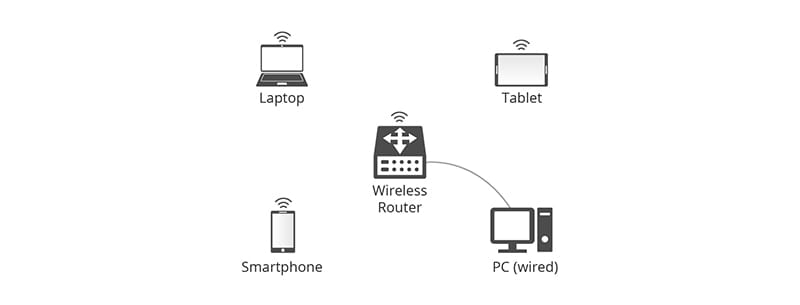
Figure 1: Wireless router connection scenario
What is a wireless access point?
A wireless access point (also called a wireless AP or WAP) is a network hardware device that adds Wi-Fi capabilities to an existing wired network by connecting traffic from a wireless station to a wired LAN. A wireless AP can act as an independent device or as a component of a router.
Generally speaking, a wireless AP allows devices without a built-in Wi-Fi connection to access a wireless network through an Ethernet cable. In other words, the signal from the router to the AP is converted from wired to wireless. In addition, if future access requirements increase, WAP can also be used to extend the reach of existing networks.

Figure 2: Wireless Access Point Connection Scenario
Router or router – what's the right one
There are no differences. Router – English, router – Russian version. The devices are also known as Internet gateways, Internet centers, and gateways. And a router differs from a modem fundamentally. The first receives the signal from the provider and decrypts it into a code that can be understood by a single computer. And the second one distributes the received information between several devices connected to the same network.
It is possible to classify router models in several ways. The main criteria are the area of use and the connection method, where the routers themselves and the user devices are connected differently.
Depending on the area of use, routers are divided into:
- Top. These are the most powerful models, which are used by large corporations. Routers with up to 50 ports, support a variety of interfaces and protocols, including non-standard.
- Medium. They allow you to form small networks for small businesses. Have up to 3 global and 8 local ports.
- Bottom. Designed to make connections in individual offices or homes. Have up to 2 global and 4 local ports.
According to the method of connection to the Internet routers are divided into wired and wireless. There is also a difference in the distribution to user devices – by cable or via Wi-Fi. Wired routers are usually used in offices or at home to connect to the network from 2 to 8 desktop computers or laptops, located in one room. You can also use such routers to set up access, for example, from a PC to a printer or other device.

Wireless (Wi-Fi) routers transmit data with or without cables. This is useful for connecting stationary computers, laptops, printers, phones, Smart TV, and other devices to a common network and Internet connection. Here you need to have one access channel and sufficient connection speed.
How a router works
The router establishes a connection to the Internet and distributes data to each connected device. To set up the router, you need to connect a cable from your ISP or ADSL modem (you can also buy a router with USB modem support). Then set the necessary settings – it is easiest to do this with the help of a wizard or by following the instructions to the device. Then connect all devices that need the Internet to the router via Wi-Fi or LAN network cable. You can also buy a wireless receiver for your PC and use it to connect to the router.
This unit will tell you the difference between a router and a switch. Outwardly they are similar – a box with many inputs and outputs, but their work is based on different principles.
Switch – purpose and principle of operation

The second name of a switch is a switch. The device connects several network nodes within a single segment. It processes information at the data link layer of the OSI network model and works with the MAC addresses of user hosts. Computers that the switch connects to a single local area network are not able to connect directly to the Internet. To access the World Wide Web, you need to configure one PC – the main one. And from it, using the switch to distribute traffic to the connected devices.
This scheme has its disadvantages – complex settings and permanent work of the main computer (otherwise the rest of the devices will be left without Internet). There is an alternative: go online with the router and connect all the PCs to it via the switch. If you have enough ports on your router, you don't need a switch in your scheme.
The switch has an undeniable advantage over the router – faster transfer of information within the local network. Therefore, if Internet access is not needed, it is possible to connect all the PCs with a switch. This way they will exchange information with each other faster.
What can be connected to the router
The list of network devices that can be connected to the Internet via a router is quite big. And it keeps growing! If you have a router, you can get a connection for several computers, laptops, smartphones, TVs with network access, camcorders and printers. And it will also provide Internet access for your smart fridge and kettle (if they have network connectivity).
Depending on the design, routers can be divided into four types.
Wi-Fi routers .
These "boxes" have a special WAN port – a cable with an RJ45 connector is connected to it. The same one, which previously had to be connected directly to the computer.
Once connected and configured, such routers are ready to distribute wireless Internet to all devices – just find the signal source in the list and enter the password. And usually such routers are able to work in a hybrid mode, i.e. they can both distribute Wi-Fi and transmit the signal over the wire. For example, let's look at several models of such routers.
Stylish and Compact – Wi-Fi Router HUAWEI WS7200 AX3 Pro

Look at the product
This router provides a high data transfer rate – up to 2402 Mbit / s. This is more than enough for gaming and streaming. For fast connection of several devices at once OFDMA-modulation technology is responsible, and there are four antennas for signal amplification. The neat white housing fits any interior, and the small size (22,5 × 40 × 15, 9 cm) will place the router in any corner of your home. You can set up the router yourself without the help of a specialist.
Reliable and safe – HUAWEI WS7100 AX3 Wi-Fi router

Shop by Product
This model allows you to receive the Internet both over the wire and without it – a hybrid method of receiving the provider's signal is available. Harmony Microkernel architecture ensures the security of the connection, all received and stored data will be reliably protected. The signal is amplified by four fixed antennas. It comes with a cable and power supply – nothing extra. The maximum speed is the same as in the previous device – 2402 Mbps.
Indicators and buttons on the router
All information icons are usually displayed on the front panel. This is where the device's power-on sign and network status icons are displayed. If the sign of receiving a signal is not lit, then you should check the reliability of the cable connection to the router before you panic.


You can't get any faster. 21 Ways to Speed Up Your Home and Mobile Internet
Router and modem: the differences
A router is not always enough to connect the Internet, sometimes you have to use a modem. A router is designed to "redistribute" the Internet to several devices, but even without it everything will work, for example, if you just plug a cable into your computer.
The difference between a modem and a router is that it converts the Internet from other types of connections.
Its principle of operation is to convert a signal not intended for computer use directly into a form that it can understand. To cite an example of those which are commonplace, they are USB modems (3G/4G "whistles" from mobile operators), inserted into the computer, which convert the cellular network signal into a format understandable to the computer.
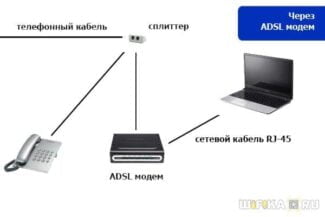
Earlier examples of modems can be considered ADSL-modems, used when the Internet first appeared. They were connected to the telephone network and transmitted signals through it. The computer did not "understand" such signals without special boards and programs, so the conversion was done by the modem on the user side.
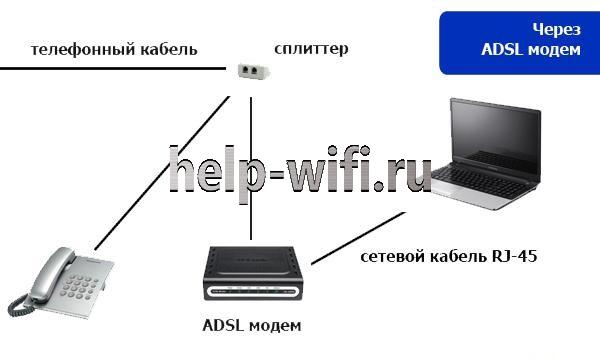
Nowadays there are almost no simple modems, except for 3G/4G modems from operators and small mobile "boxes". Most modems are combined with a router, which saves time and nerves.
Now you don't need to first put the modem on the phone line and then the router to distribute it to several computers. All you need is to buy a model with a built-in modem, connect it to the telephone or mobile network and distribute Internet via wires or Wi-Fi.
Wi-Fi Technology
Wi-Fi router is a router with a small addition. It is a radio module that converts the signal it receives into a wireless wi-fi network. To transfer data to the Internet, it still needs a connection from the provider, but those gadgets that are inside the network will be able to communicate without it. For example, the absence of the Internet will not prevent you from transferring files from your phone to your TV.
Bluetooth is a different technology. It also uses wireless data transmission over radio waves, just like wi-fi. They even have a similar range of radio frequencies, but one technology will not replace the other. In addition, the latest wi-fi models have new frequencies that allow it to not overlap with other wireless technologies.
This provides more communication stability, there will be more free channels for each router, so they won't interfere with the transmission of information. In densely populated houses, there was often a problem with transmission speeds due to the fact that there were many Wi-Fi routers next to each other, which blocked the signal to each other, and the transmission speed dropped.

Main modes of operation, what you can connect
The unit can play different roles, depending on user preferences, the option of connecting to the World Wide Web and other nuances. The list of the most common is presented:
- conventional connection – through a cord, followed by distribution of information via wi-fi or through wires connected to the LAN ports;
- WISP mode – receiving a signal from the service provider is through the air instead of the wires, this approach is often used in country houses where it is impossible to run a cable line;
- repeater or repeater – the system has two units, one main and one additional, the last one helps to pull the net to the distant equipment when the Wi-Fi coverage is insufficient (large offices, houses with several floors or large apartments);
- Bridge mode – used to build a local mesh, aDSL modem is used as a signal receiver.
The main difference between a switch and a router is that the former works with physical and the latter with logical IP addresses.
Many devices can be connected to a common line, popular options are represented by:
- laptops, tablets, personal computers, smartphones;
- printers – depending on the version, support a wired or wireless connection, universally used in homes and offices;
- TV sets – devices with Smart functionality have a built-in module that allows you to access the Internet, watch movies, serials, etc. through it.
If there is no module in the receiver, there is a replacement in the form of a Smart set-top box. It allows any receiver to connect to the network without loss of function.
Why do we need antennas, wi-fi technology
Many users confuse the concept of the Internet and wi-fi. In the latter case, data transmission is done without cables using radio frequencies. One equipment sends a radio signal, the task of the second is to receive and decode it.
Stable communication requires powerful antennas in the adapter (router). The index is measured in decibels, the more radio antennas, the wider the coverage.
On home units are usually installed additions of 2 to 3 dB. With a large house, their power is not enough, the owner will have to look for amplified variations from 7 to 10 dB.
In order not to wonder what a home router is and what it is intended for, it is enough to study the varieties of devices and their intended purpose. The means to visit the World Wide Web in most cases is provided by the service provider, and the installation is performed by technical support specialists.

Certified specialist in computer network security. Routing skills, creating complex network coverage schemes, including seamless Wi-Fi.
Wireless network standards
When buying a router, you should first familiarize yourself with its specifications and capabilities.
Wi-Fi standards determine speed and security. They have evolved historically. New requirements for the equipment were gradually added to the already existing standards.
By now, the following types have been defined: 802.11 b, 802.11 g, 802.11 i, 802.11 n.
The first of these is still in use where consumer equipment does not support more advanced standards. It is characterized by low communication speeds (up to 11Mbit/s) and a low level of security. Range is limited to 50 meters..
The 802.11g standard has significantly increased the data rate (up to 54Mbit/s). Security has increased by being compatible with new encryption protocols.

With 802.11 n the declared speed is 600Mbit/s. A high level of protection. The range reaches 100 meters.
Routers supporting the latest standards require proper configuration and compatibility with the equipment with which you plan to work together.
Modem and Router
Today, these two terms absolutely different in nature devices are misleading for many.
The purpose of a modem is to provide information to the consumer. The fact is that the messages transmitted from the network provider in analog form are not available to the computer. The modem converts this information into a form that the computer can already work with.
The input information comes to the modem through various communication channels: telephone line (ADSL), twisted pair (Ethernet), via radio waves of the appropriate range (3 G /4 G), fiber optic cable to the house.
The purpose of the router is to distribute the information received from the modem between the consumers, created on its basis local network. This distribution takes place both over cable lines (LAN) and over the air via Wi-Fi. There are practically no wireless routers in their pure form.
All of them have a modem of input information, which is then distributed between the consumers of the local network according to its routing using internal IP-addresses.
Modems in its pure form are used only to convert the information transmitted over telephone lines.
A wireless router receives the Internet not because it is a router, but because it is a built-in modem.
The modem does not have its own IP address on the Internet. It is defined by the address of the only computer it is connected to.
The router, on the other hand, has an address through which it is identified in the wide area network. The addresses it creates in the local network are intended to assign routes to all of its participants.
The modem does not require additional settings from the user. It is configured once in the factory.
The router has many individual settings. Their number depends on the network architecture, its composition and priority of participants.

What routers are there
Most often we deal with Wi-Fi router which is connected to the provider via cable (Ethernet connection) and sends Internet to the client devices via cable or wireless network. But actually routers are different and differ in the way they connect to the Internet.
Twisted pair and fiber optics
The most common router, as already mentioned, connects to the Internet via cable (twisted pair). But instead of twisted pair, fiber optic (GPON) can be used. This method of connection provides a much higher speed and a number of additional features. Accordingly, the router used here is different – it has a built-in port for connecting to a fiber-optic line. Otherwise it works in the same way – it gets the Internet via cable and distributes it to the devices in the apartment.
A phone line
A telephone line can be used to connect to your ISP. This kind of connection is called ADSL. Usually in this case one uses either an ADSL-modem with a router function or a pair of ADSL-modem + a regular router. In the first case the router is directly connected to the phone line, and the Internet is distributed via cable or Wi-Fi. In the second – ADSL-modem is connected to the phone line and to it via twisted pair ordinary router that distributes the Internet.
Mobile .
And there is a separate group of devices – portable 3G/4G routers, designed to connect to mobile networks. In this case, the router connects to the Internet over the air. Client devices are connected via Wi-Fi. But some mobile routers are able to distribute the Internet, for example, via USB cable.
Some models of regular Wi-Fi routers are also equipped with a 3G module. And, in addition, a router with a USB port can be connected to a 3G modem and receive Internet from the mobile operator.
In all cases, routers work the same way: being between the Internet and the home network, they receive the traffic from the outside and distribute it among the user's devices.
Why do you need a router in your apartment?
In the past, when there was only one computer connected to the Internet, there was no need to use a router. The cable from the provider was connected directly to the network card of the PC, and the Internet was coming directly. But today it is very common to have more than one device in the apartment. This can be a desktop PC and a laptop. And also a smartphone or tablet, which also want to be connected to the Internet. In addition, for example, modern set-top boxes also use an Internet connection. There is only one cable from the ISP. In addition, the ISP usually provides only one IP address. This means that only one device can connect to the Internet, to which this address is assigned. You can, of course, get additional addresses, but you have to pay extra for them.

To solve the problem with connecting several devices at the same time, a router is used. It is given an IP address by the provider and, using it, the router connects to the Internet. And the devices in your home network, it assigns internal IP addresses and at these addresses redirects the received traffic.
In addition, the router allows you to share network resources. If you have a printer, there is no need to lug files for printing from your computer to your computer on a flash drive. The printer can be connected directly to the router, if available, or you can simply enable printing over the network on the PC to which it is connected. Now you can print a document from any device on your home network, whether it is connected to the router via cable or Wi-Fi. In the same way, you can access files, such as a movie folder on your computer, and view them online without having to copy them to your laptop or tablet.
In short, if you have more than one computer at home, and you want them to be able to connect to the Internet at the same time, you can't do without a router.
How to use a router
Once you understand why you need a router, you need to configure it properly. Ideally, you should look for as central a location as possible, and place the device in a slightly elevated position (such as on a desk) and without obstructions.
Wi-Fi waves are donut-shaped and move with a slight dip effect, so placing the router in a low position is not a good idea.
Obstacles significantly reduce signal strength. It's true that its effect depends on the material – a simple thing like a drywall wall can reduce Wi-Fi signal strength by 50%.
On the other hand, interference from certain electrical appliances can also negatively affect the connection. That's why it's so important to place your router in a location free of obstacles and interference.
How to use a router is easy to understand. To connect to the Internet and use a router, follow these steps:
- Insert one end of the network cable into the router's Internet/Wan port.
- Connect the other end of the network cable to the modem.
- Connect the power supply to the router and modem.
- If you want the connection to be direct to the PC, connect the network cable to one of the Ethernet ports on the router. The other end must be connected directly to the PC's Ethernet port.
If your Internet connection is too slow, or it does not cover the surface of your home or office, or there is some speed and coverage issue, the most likely culprit for all of these anomalies is a router with outdated technology.

Certified Computer Network Security Specialist. Routing skills, creating complex network coverage schemes, including seamless Wi-Fi.
What's the difference between a modem and a router?
- the first device distributes the internet to connected devices, while a modem makes a connection to the internet;
- a router can be connected to several devices, while a modem is designed to work with only one;
- to distribute the Internet, the router must be connected to it by cable or modem, and for the modem itself to be connected to the Internet, a SIM card must be inserted into it.
That is, the main difference between the devices is that the router is a device that distributes the Internet (to which it can be connected in several ways), while the modem is a device designed to connect to wireless Internet, and is not able to distribute it.
Bottom line
We have answered the question what is the difference between a router and a router – absolutely no difference. Many people make the mistake of calling a router something more complicated and expensive, used for industrial purposes. So there is no point in asking which is better – it is the same thing.
Setting up the router D-Link DIR-300-enter settings, basic parameters, creating a WiFi network, router protection
The main advantages of mobile application development for business
How to configure your Windows 10 home network via a WiFi router – step-by-step instructions
What is the best WiFi router for your home: what you need to pay attention to, top 15 best models
Read More: