But this mode has positive aspects, or rather there are only two. The first is the simplicity of configuring the router.
- How do I enter the router in the repeater, bridge or access point mode? I can't open the settings after changing modes
- Restoring the router to default mode via reset
- Setting up Wireless Router Modes of Operation over WiFi – How to Enable
- Access Point.
- Modem mode (ADSL Modem)
- Repeater
- How to configure the Asus router mode?
- Operating modes and router settings
- Bridge .
- Access point, client, repeater
- Router – bridge mode.
- Setting up a router in bridge mode
- Router Modes
- The disadvantages of bridge mode
- In addition to the fact that the router does not know how to establish a connection itself, it also ceases to perform the following functions:
- Configuring routers
- Setting up bridge mode
- Setting in router mode
- What to set in the router settings to get the highest speed
- Setting the wifi standard on Keenetic
- Peculiarities of the access point mode and router mode
- Comparing access point mode to router mode
- Depends on your ISP's requirements
- Working with traffic
How do I enter the router in the repeater, bridge or access point mode? I can't open the settings after changing modes
In this article, I'm going to talk about solving a problem when you can't access the settings of a router that has had a mode change. When we configure a regular router as a Wi-Fi signal booster, wireless bridge (WDS) , receiver, access point, or just manually disable the DHCP server. And after that we can't open the settings of this router, or it opens the settings of another router. I have already written many instructions on how to change the mode on routers from different manufacturers. I have shown you how to configure different routers as a repeater (signal booster) , wireless bridge, access point, etc. And one of the most common questions in the comments to these articles is "What to do if you can't access the settings after changing the router mode.
In fact, it's very simple. When we change the mode of the router, then after changing the mode (for example, to "Wi-Fi signal booster") on the router the DHCP-server is automatically turned off. And it is responsible for issuing IP addresses to the devices that we connect to the router. Since the DHCP server, the device (the same laptop, or PC) can not get an IP address from the router and connect to it. And if the device is not connected to the router, then we will not be able to enter the settings from it. The same story with setting the bridge mode (WDS). For example, on TP-Link routers. In the configuration process, I recommend manually disabling the DHCP server. After that, the connection with the router is lost, and we can no longer enter its settings (web interface).
So the main reason is that in amplifier, bridge, access point or receiver mode, the DHCP server does not work on the router. This is the story with all routers that have different modes of operation: ASUS, TP-Link, D-Link, Tenda, Zyxel Keenetic, Netis, Mercusys, Totolink, etc. There are several solutions:
- Simply do a factory reset of the router. By default, the device is in router mode, DHCP server is enabled. Then you can open the settings and try again to configure the desired mode of operation, or make other settings. I often recommend this way. It is the easiest.
- On the device (computer, laptop, phone) from which you want to go to the router settings (which was changed mode and lost communication), you must manually enter the IP-address, mask and gateway. When the DHCP server works on the router, the device obtains these addresses automatically. And since the DHCP server is disabled after the mode change, you must manually assign them directly on the client.
- If the router was not just switched to another mode, but the connection with the main router was made (for example, the second router in the repeater mode is connected to the first one) , then you can see the IP address (which can be used to enter the settings) in the web interface of the main router. In the list of connected devices. But this method does not work in all modes and not all routers.
Restoring the router to default mode via reset
After configuring the WDS (wireless bridge) , or changing the mode, you can always reset the router to its original state simply by doing a reset. You don't even have to go into the web interface to do that. The reset can be done with a button. Every router has one. It is usually labeled Reset (RST, Default) .

The resetting process varies from model to model. But in most cases the following scheme works:
- Turn on the router and wait about a minute.
- Find the Reset button. If it is recessed in the case, we will need a paper clip, toothpick, or other thin object.
- Press the button and hold it for about 10 seconds.
- At this point (while holding the button) look at the indicators. According to them you will be able to understand that the reset occurred.
- The router will be as good as new after the reset.
After these steps, you can connect to the router and open its settings via a browser. As an example, here is a link to an article where I showed you in detail how to reset your TP-Link router.
Setting up Wireless Router Modes of Operation over WiFi – How to Enable
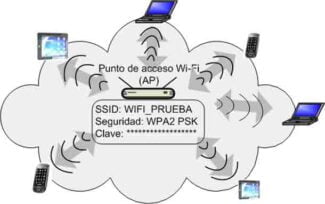
The question on the agenda is how to configure a WiFi router mode? If you are going to set up a wireless network in your home, I recommend choosing a router rather than an access point, modem, repeater, or anything else. Why? Because it is a multifunctional device and it takes the place of all of these things. In this article, we will look at its main modes of operation and see how they are set up using the Asus model as an example.
First of all, we need to understand the concepts. The router has a total of four main modes:
Access Point.
In Access Point mode, or as it is called by foreigners "Access Point", the router works as a device which transforms a cable signal into a wireless signal. The main difference between a router in access point mode and another network device, which is actually called "access point", is that it not only distributes WiFi, that is, turns the wired Internet into a radio signal, but also has the functionality to distribute IP addresses and port forwarding, which is the main function of the router.

Modem mode (ADSL Modem)
In pure video, the modem is a device that is designed to work with providers who provide access to the World Wide Web via a telephone cable using ADSL technology. And for nothing else – the modem itself in router mode or just can not work. But a router in the router mode with ADSL support can not only get the Internet via telephone cable, but also retransmit it wirelessly and assign IP to other clients.

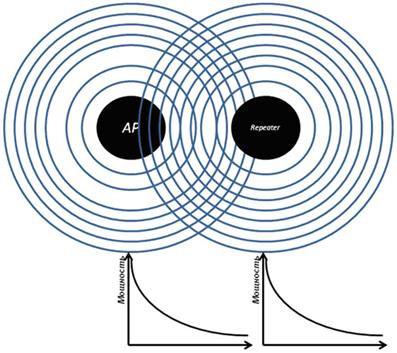
Repeater
Generally speaking, a "repeater" is a wireless signal extender or repeater that extends the signal from a wifi hotspot by some distance to connect computers that are in an area of uncertain reception to the Internet. If our favorite wifi router has repeater mode, it means it can do the same thing – extend the wireless signal, thereby extending the reception area. In addition, repeater mode is useful if you need to bypass some obstacle when creating a wireless bridge, when there is no line of sight between the two access points. Then we put the router in repeater mode within line of sight of both access points and transmit the signal through it.
How to configure the Asus router mode?
In different models, the configuration of the router mode is different. We will need to connect to some existing wifi, which is distributed by some other router, and distribute it already in our apartment. I will show you the example of Asus RT-N10U B in the new firmware.
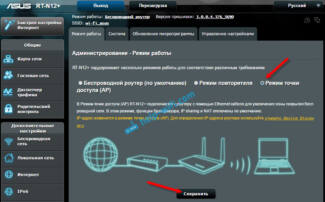
Go to admin (http://192.168.1.1), "Administration" tab, "Operation mode" tab (in red), or immediately click on "Wireless router" at the very top of the settings page (in green).

At the moment, "Wireless Router" mode is activated by default. You'll find its settings in this article, and we'll put a check mark on the second-to-last one, repeater mode. And we press the "Save" button.
A page will open displaying all wireless networks within range of the router. Choose the one to connect to and enter the access key, if it is password-protected.

Click connect. After connecting to the third-party router, you can make another interesting setting: either use the data to access the existing network that we are extending. Or set your own – then we connect to ours with one data (SSID and password), and to the second, which is directly plugged into the Internet cable and whose signal we extend – with others.

Then it's a matter of waiting until all these settings are applied, and you disconnect from the network. Then in the list of available wireless connections appears the new one you just created. Then connect to it and go forward to the open spaces of Runet!
Operating modes and router settings
One of the main advantages of modern routers is their multitasking. Today it is difficult to find such devices as a connection point, modem or repeater separately. Any Wi-Fi router supports bridge mode and router mode, can become a connection point or perform the function of a repeater signal.
According to the way they are used, it is customary to distinguish all wireless Wi-Fi devices into the following categories:
1. Bridge;
2. Router; 2;
An access point;
4. Client;
5. Repeater.
Bridge .
This method is used to join two networks into one. Two devices with this bridge mode are used in the connection. This method is suitable, for example, to connect two neighboring buildings. You therefore do not need to wire them together.
Router
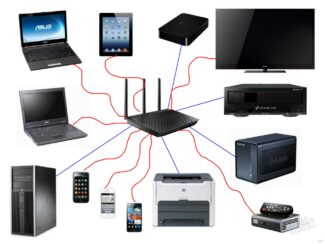
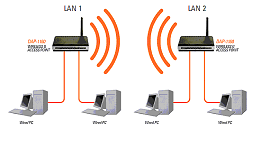
Most routers work in this mode. It can convert the IP address of the Internet service provider into an internal address and distribute it to devices within range. The router can forward ports, share network printers and file storage.
It can automatically authenticate so that the user doesn't have to do it every time he tries to access the Internet. After all, the router in this mode can be used like a normal switch.
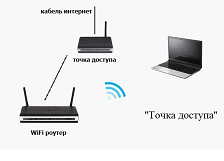
Access point, client, repeater
This method is confused with the previous one. Unlike Router mode, this method is simpler and consists only in the fact that the device receives a wired signal and converts it into a wireless signal.
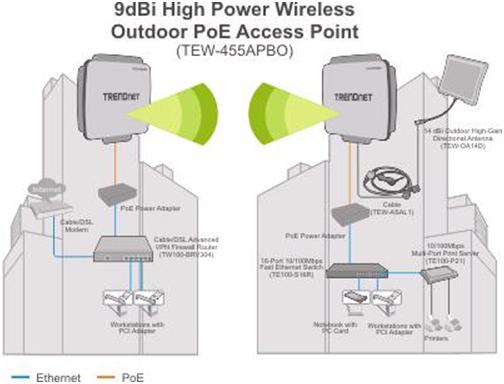
Router – bridge mode.
This mode allows you to connect two remote Ethernet segments via radio if you cannot run a wired connection in certain places or simply do not want to run a cable. When you bridge two access points, the network they form will be invisible. This feature greatly increases the protection of your network from outside connections.
Setting up a bridge router requires that the SSID, channel, and encryption type of these devices match.
Setting up a router in bridge mode
To set up a router in bridge mode you first need to change the password on the router, configure the Wi-Fi. And then go into the router settings and open the SETUP menu and select Network Setting. In the window that appears, set the Wan Port Mode to Bridge Mode.
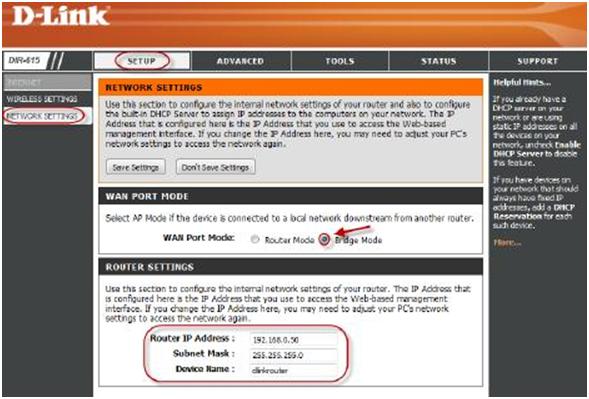
The same functionality can be created by
The same functionality can be created by making a scheme of two devices. On one side there must be a device that works in AP mode and on the other side there must be an access point that works in AP-client mode.

This connection can provide very good performance. The only drawback here is that the network SSID is broadcasted, depriving your network of its stealth property.
Router Modes
Almost all ADSL routers can work in two modes – bridge mode and router mode. If your model does not have both modes, it means that you either need to update the firmware or it is a quite rare case and your model does not support both modes.
Let's look at what these modes are, their pros and cons. Let's start with the bridge mode.
This word translates to bridge, which means that the router works in what is called transparent bridge mode.

This mode "turns" the router into a silly intermediary between your computer and ISP, it does not perform any functions, only forwarding the data stream from the telephone port to the computer connection interface and back. In bridge mode the router can only work with one computer, it is not possible to create a local network or access point. And that means that you can't connect a computer and, for example, a smartphone to the router at the same time. This is the first "minus" of this mode.
The disadvantages of bridge mode
As already mentioned, in bridge mode the router does not perform any functions other than uncontrolled traffic transfer. This means that the router will not be able to connect to the ISP itself when it is switched on. This is the second disadvantage.
Now when you turn on your computer, the user must manually establish a connection to the ISP, and therefore to the Internet, through the operating system, by entering the username and password in the appropriate fields and clicking "Connect".
In addition to the fact that the router does not know how to establish a connection itself, it also ceases to perform the following functions:
- DHCP-server. As you know, this service automatically assigns IP addresses to the devices connected to the router. In bridge mode DHCP makes no sense (no more than one computer can be connected);
- Built-in firewall, also called firewall or firewall, does not work. Now firewall threats and attacks will have to fend off the computer;
- The router also does not provide additional services (depending on the model), such as time synchronization, DNS server, address translation (NAT), network printer and hard drive.
Configuring routers
In this chapter we turn to the practical part and look at specific settings in both modes. Let's take the different routers as an example.
Let's start with configuring the devices in bridge mode.
Setting up bridge mode
We will take the ZyXEL router as an example.
Any router adjustment starts with entering its web interface, which provides us a graphical menu of the settings. Open a web browser and go to the settings at 192.168.1.1.
If you have a different router, the address may be different, check the configuration manual. Next, enter the administrator password, and in the settings menu that opens, go to "Network", submenu "WAN", tab "Internet Connection".
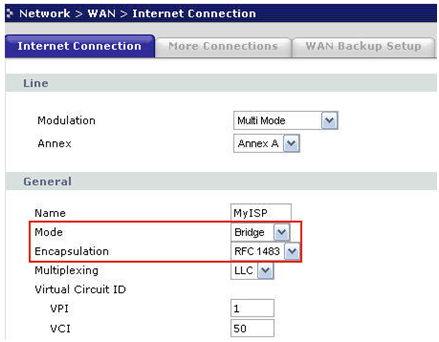
In the "General" area we see the "Mode" line – it is the point to choose the mode of the device. Choose "Bridge" and set the Encapsulation to RFC 1483. The rest of the values are set according to the contract with the provider. Click "Apply", the configuration is done.
We remind you that in this bridge mode the router only establishes an ADSL connection with the ISP, while the authorization of the client must be set by the operating system.
Setting in router mode
Repeat the previous entry steps to configure the router. We go to the same submenus and tab, but in the line "Mode" now select "Routing" mode.
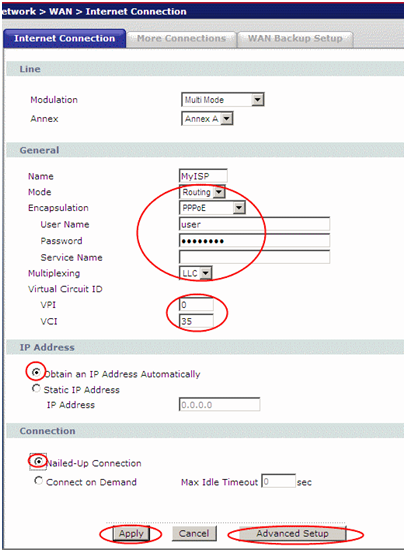
The settings window will immediately change its appearance, there will be much more settings. In the encapsulation we choose the PPPoE mode (or the one supported by your provider), in the fields "User Name" and "Password" we enter the login and password for Internet access issued by your provider. We also set the IP address to automatic. Click "Apply".
What to set in the router settings to get the highest speed
WlanSvc wireless autoconfiguration service is not running – solution
To get the maximum speed, the following settings should be specified in the router settings:
- Use only one wireless mode, 802n.
- Set the encryption type to WPA2 AES.
- TP-LINK routers allow you to disable the speed limit option.
- Set the bandwidth to 20MHz.
- Install new driver updates for the Wi-Fi controller.
- Install the router away from televisions, microwave ovens, and radiotelephones.
When selecting the wireless mode, take into account the specifications of the router and the devices connected to it. To increase the data transfer rate, it is better to set mixed settings. To improve the quality of signal reception, you should choose the channels with the lowest load.
Setting the wifi standard on Keenetic
To specify wifi mode on your Keenetic router, you need to go to "Home network" in the control panel and open the "Advanced settings" link

Here in the item "Standard" put on "802.11bgn", and the channel width denote as 40 MHz





Peculiarities of the access point mode and router mode

When a router supports multiple modes of operation, you may wonder what the difference between them is. In this article, a brief overview of the two most common and most popular modes is made, and features of each of them are pointed out.
The final result of the device configuration is a stable working Internet everywhere. Unfortunately circumstances do not always allow to achieve this. Let's look at each mode in turn.
Comparing access point mode to router mode
A wireless access point allows all devices to connect to a wired network, it serves as a kind of bridge for those devices that are physically unable to do so. Of course, you can find several adapters to connect your phone to a wired network, but it's much more convenient to use a wireless connection. An access point can be compared to just such a set of adapters, only it works for more devices. Router mode offers more options than access point mode, it is more versatile, but may require more effort to set up.
Depends on your ISP's requirements
You may need to configure your connection to access the Internet. In access point mode, these settings have to be done on each device, such as entering a login or password. You only don't have to do this if the connection to the Internet is established immediately when you connect the cable. If, on the other hand, the Internet works immediately with a cable connection, the ISP may limit the number of devices that can be connected. In this case, the Internet will only work on one device and will either be tied to a specific device, or the first connected computer or phone will get access.
In router mode, everything is much easier, because all the settings are made only once on the router. All other devices have to do is connect to the wireless connection.
Working with traffic
In access point mode, the device has no protection against network attacks, unless this is provided, and there is also no possibility to limit traffic. On the one hand this may not be very convenient, but on the other hand – everything works "as is", you do not need to configure anything additionally.
In router mode each connected device has its own "internal" IP address. Network attacks from the Internet will be directed at the router itself, the probability that they will detect a particular computer or smartphone is extremely low. In addition, some routers are equipped with a built-in firewall, and this is an additional protection, which is undoubtedly a big plus.
Read More: