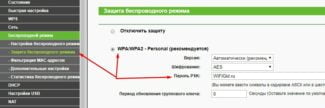
Step 1. Changing router IP. Go to the web interface of the second router and enter the local network parameters – LAN ..
- How to configure the Wi-Fi router correctly, if you know nothing about it
- Installation and connection
- Troubleshooting the problem with the inability to access the router settings at its network address 192.168.0.1
- If the router settings are not saved
- Powerful Home Router with your own hands
- Xakep #279. Shell Code Fluctuation.
- Handmade Wireless Router
- Cascade (according to theory).
- The second option
- How to connect two routers to the same network via cable
- Scheme 1: Connecting router to router via LAN ports
- Using the router as a repeater
- Types of routers
- What to pay attention to when choosing
How to configure the Wi-Fi router correctly, if you know nothing about it
In the menu of each router you can find dozens or even hundreds of parameters. But only a few are necessary for every user on a daily basis. Something unknown is better to ignore at once. The names and locations of some items may vary depending on the model. But there are general principles that everyone can follow. Below we will tell you how to configure routers in different situations.
The general algorithm of working with any router can be described as follows:
- First, check the settings of the operating system itself. The main thing is to make sure that the network parameters are not changed in any way.
- Installing the router. Be sure to connect the wires and take the device, with which you will set the parameters.
- Next, you will need to find the panel with the necessary parameters.
- Connect the Internet.
- Configure the connection.
- If necessary, change the passwords themselves.
- Set additional parameters that may be needed in the future.
Further each item of router settings deserves a separate consideration. You can watch a short video on configuring a TP-Link Wi-Fi router.
Installation and connection
It depends on the Internet providers, which technologies will be supported in this or that case.
The most common option for router setup is when a cable from the provider goes directly to the computer. You will only need a network card, no additional devices. No problems should arise with the self-configuration. The operating system already has everything you need.

- The ISP cable is removed from the network card on the computer, switch it to the router, in the WAN socket.
- Connect the router's free socket to the socket in the computer with the cable that comes with it.
- Connect the power supply.
- Turn on the computer and the power supply.
- Wait for both devices to boot up.
The main thing is not to forget to look at the password and network name on the sticker to the router. It remains to connect to the network, and then complete the setup by setting the parameters to the desired value.
Additional ADSL-modem for connecting to the Internet is another solution that is often used in practice. This is a great option for those who are thinking about how to connect a router.
- The router and the phone line are connected to each other.
- Connect the computer's network connector to one of the ports on the router.
- Turn on the computer.
- Insert the power supply into the connector, then plug it into an outlet.
- Press the power button, if there is one.
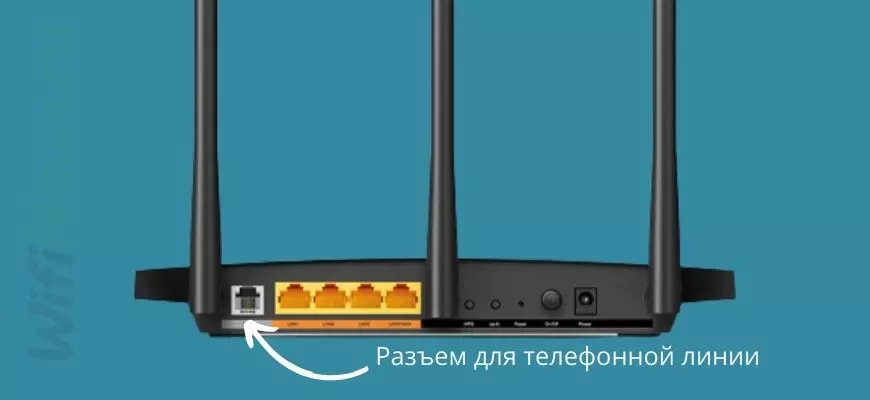

It remains to figure out how to connect yourself to a WiFi router.
Troubleshooting the problem with the inability to access the router settings at its network address 192.168.0.1
If after typing in the router's network address in the address bar the router settings page will not open, then to solve the problem you should do the following steps:
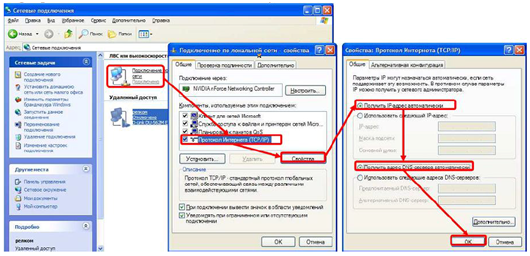
- If the network card settings are correct, then you need to use the Run command (press Win+R), then type – cmd and press enter. Now at the command line, you must enter ipconfig.
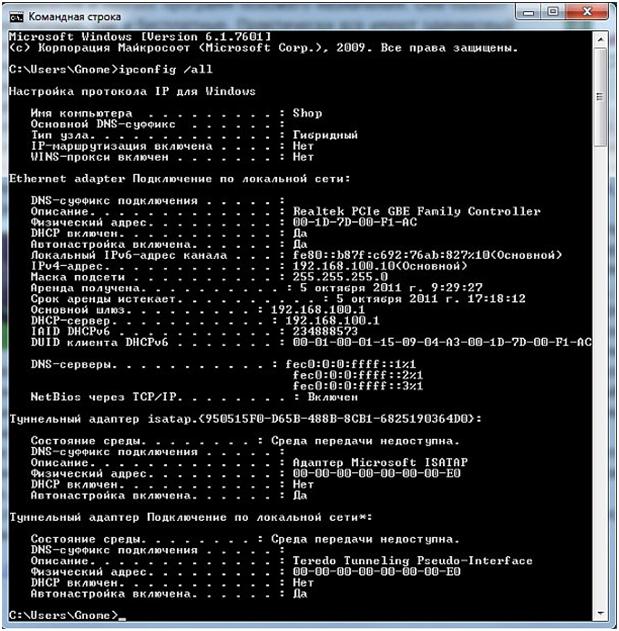
In the settings displayed, you need to see what value is against the inscription – Main Gateway. This address is used to access the router's settings. If the value of this address does not match the default value, perhaps the router has been configured for a specific network with its own requirements. If this is the case, you need to reset this value to the factory defaults. Sometimes this field may not have an address at all, in which case you also need to reset the router. To reset the router, press and hold down the Reset button on the router for a while. Usually five or ten seconds is enough. The hole in the button is fairly narrow, so you can use a ballpoint pen, needle, or paperclip to press it.

If resetting your router doesn't help, disconnecting the ISP cable from your router may help. Pull the ISP cable out of the router's connector, and configure the router without the cable connected. You can then reconnect the cable to the router.
Also check the firmware version installed in the router. Check the latest firmware version on the manufacturer's website and update it if necessary. You can also check the drivers of your network card on your computer and reinstall them if necessary.
If the router settings are not saved
To troubleshoot the problem with not saving the router settings or if you cannot restore the settings from a separate file, you can try to perform these operations by opening a different browser. This method can help with other router faults as well.
There can be many reasons for this malfunction and they are all about the same frequency. Let's consider the main possible causes.
If your laptop does not display your router's network in the list of available networks, you need to check that the wireless network module is enabled. You can do this by looking at the adapter settings in the Network Control Center on your laptop. The wireless connection should be enabled. When it is off, it will be grayed out and you will need to enable the wireless connection. If you can't turn it on, you'll need to check if your laptop has a Wi-Fi switch and turn it on.
If, despite the fact that the wireless connection remains on, but shows the status – No connection, then you should check whether the correct drivers are installed for the Wi-Fi adapter and, if necessary, put them. Drivers should be downloaded from the site of the manufacturer of your equipment. This allows you to avoid possible problems with incompatibility of drivers.
In addition, you can try to go to the menu of the router and change the value for the settings there and change the parameter b/g/n to b/g. If this change helps, it means that 802.11n is not supported. You can also look in the same settings to see how the wireless network channel is specified, and if it is set to Automatic, then select a channel from the list.
Powerful Home Router with your own hands
Xakep #279. Shell Code Fluctuation.
Although there are all kinds of network equipment in online stores, but still there will be lovers of doing things their own way. For example, engineer Nick Pegg was very unhappy with the limitations of the classic WRT54GL home router with 4MB of flash memory and a weak CPU. At the same time, being very tight of funds, he could not afford a professional router.
The way out was found: to build a device with his own hands from computer parts that he could find in his closet or second-hand on the Internet.
He needed something cheap, low-powered and with multiple network adapters.
Nick opted for a Mini-ITX motherboard, which was ideal for the task. For his case, a board with two network connectors was sufficient, but it was not difficult to get a board with more NICs.
The engineer took an Intel 7260-ac Mini-PCIe adapter for wireless networking, though he later realized the mistake of this decision. Due to the specific firmware and the Linux driver, the card stubbornly refused to work in the 5 GHz band.
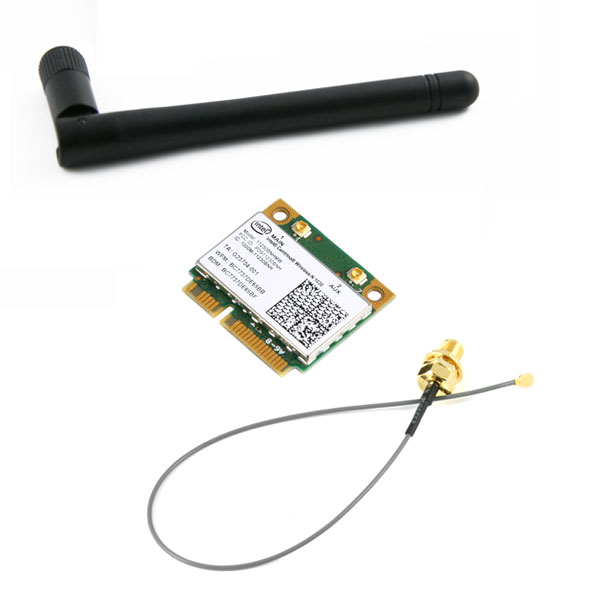

Intel 7260-ac Mini-PCIe card
In the back of his mind he realized that it is better to use a card with an Atheros chipset and with a normal driver. In any case, you should definitely check on the Internet beforehand if other hackers have successfully solved the problem and pumped OpenWRT firmware.
Anyway, Nick Pegg's instruction on network setup and hardware configuration will be very useful when trying to implement a similar project.
Handmade Wireless Router

For the last ten years I bought cheap networking hardware and put DD-WRT on it to get back the $500+ "features" removed from the Linux kernel on which the stock firmware was based.
Despite unstable builds, uncorrected bugs, and controversy, DD-WRT is still preferable to stock firmware. But now decent components are cheaper than ever, and the DIY community has moved to Linux (I'm looking at you, Mr. Raspberry), so why not build your own wireless router once and for all?
Cascade (according to theory).
If the number of routers is more than one, you can cascade them together. There is nothing complicated here: the LAN-port of the "head" router is connected to the next (second) router via its WAN-port.
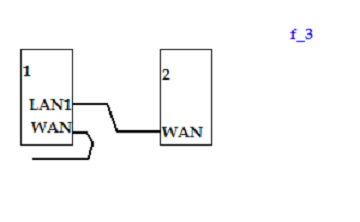
In this case, the DHCP-server mode is enabled on the second and on the first, but the range of IP-addresses should not "cross" (for example, on the second enough to set DHCP 192.168.0.(150-199), if the first "exposed" 192.168.0.(100-149). The second router gets IP dynamically from the first one (that is, in the WAN settings we specify "DHCP" type, and as an "alternative" DNS server – the IP address of the first router). Finally, on the second, as a gateway (Gateway) – specify the IP of the first router. In theory, it should work.
But – does not work ). This scheme of connecting a Wi-Fi router to another router is called "cascading".
The second option
Above, considered only one of the connection schemes. But no one prevents you from turning on the other way:
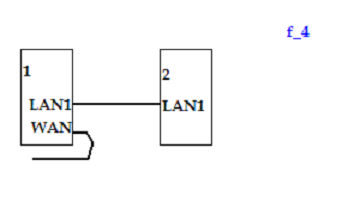
In the configuration, this option – very simple. The disadvantage is that one hardware port is lost (wan router port "2"). Moreover, the properties of the connection (wan-port), any way to configure the second router will not be necessary.
Only one thing is needed: turn off the DHCP server on the second router.
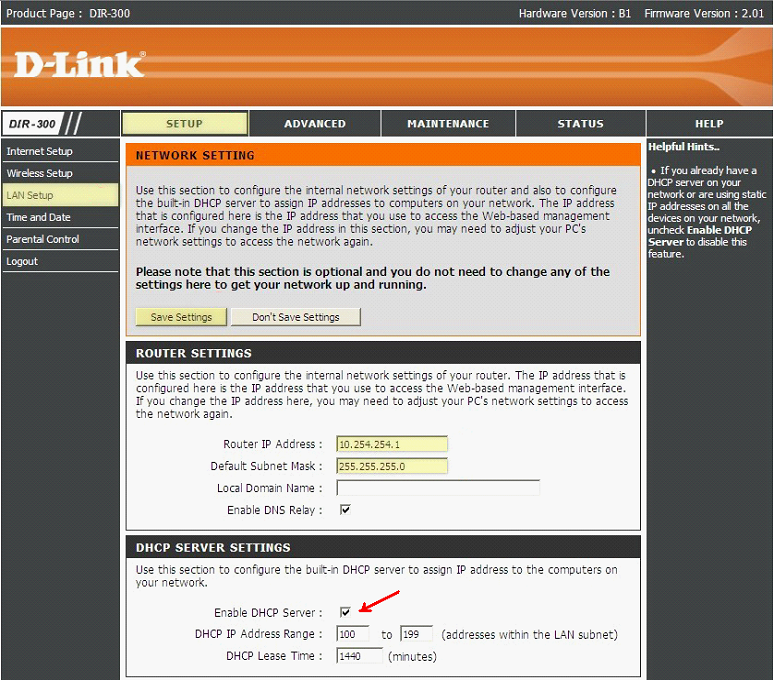
Usually, the tab is called "LAN". The DHCP server should not be reconfigured, but turned off completely (by unchecking "Enable"). After that, the second router will become an ordinary "switch", and will work with the remaining 3 ports and its wi-fi point in this simple mode.
One thing (important!): If you disable DHCP service, remember the IP-address of the router to have access to it! You can see it in the "Status" tab, and the network card of the "control" PC is set like this:
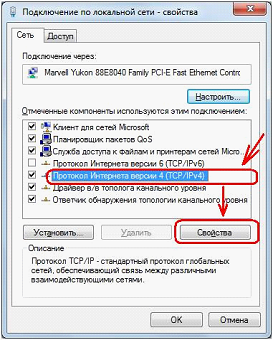
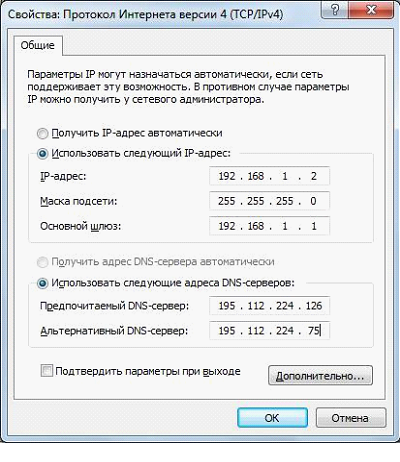
DNS – can be any "left". And the IP (static), mask and gateway – according to the example (here – the router with an address of 192.168.1.1). Another example: 192.168.0.1, then – 192.168.0.2 (in the first line), the mask – the same, 192.168.0.1 (in the third line). The principle is clear.
Here, another disadvantage of this connection scheme appears: to configure the second router, each time you will have to reconfigure the PC card.
Note: In the network, created under this scheme, each device will receive its own dynamic IP sent from DHCP-server of the first router.
How to connect two routers to the same network via cable
So we have two wireless routers and we need to connect one to the other so that physically we have the same local network. It is not possible to simply connect two devices with a network cable – the circuit will not work without additional configuration. Before you can do this configuration, you must decide on the connection scheme. There are only two schemes. The first one is LAN-LAN, i.e. it is necessary to connect the routers through LAN ports. This is the easiest and most convenient cable connection that will work in most cases. The second scheme is LAN-WAN, where LAN-port of the first device is connected to WAN-port of the second one. A rarer case is when it is necessary to divide one physical network into several logical ones. Let's consider each scheme in detail.
Scheme 1: Connecting router to router via LAN ports
The simplest scheme is to connect the router through the router by connecting its LAN ports with a cable. Thus the second device extends the network of the first and works as a standard switch-switch combined with an access point of Wi-Fi. The connection scheme looks like this:
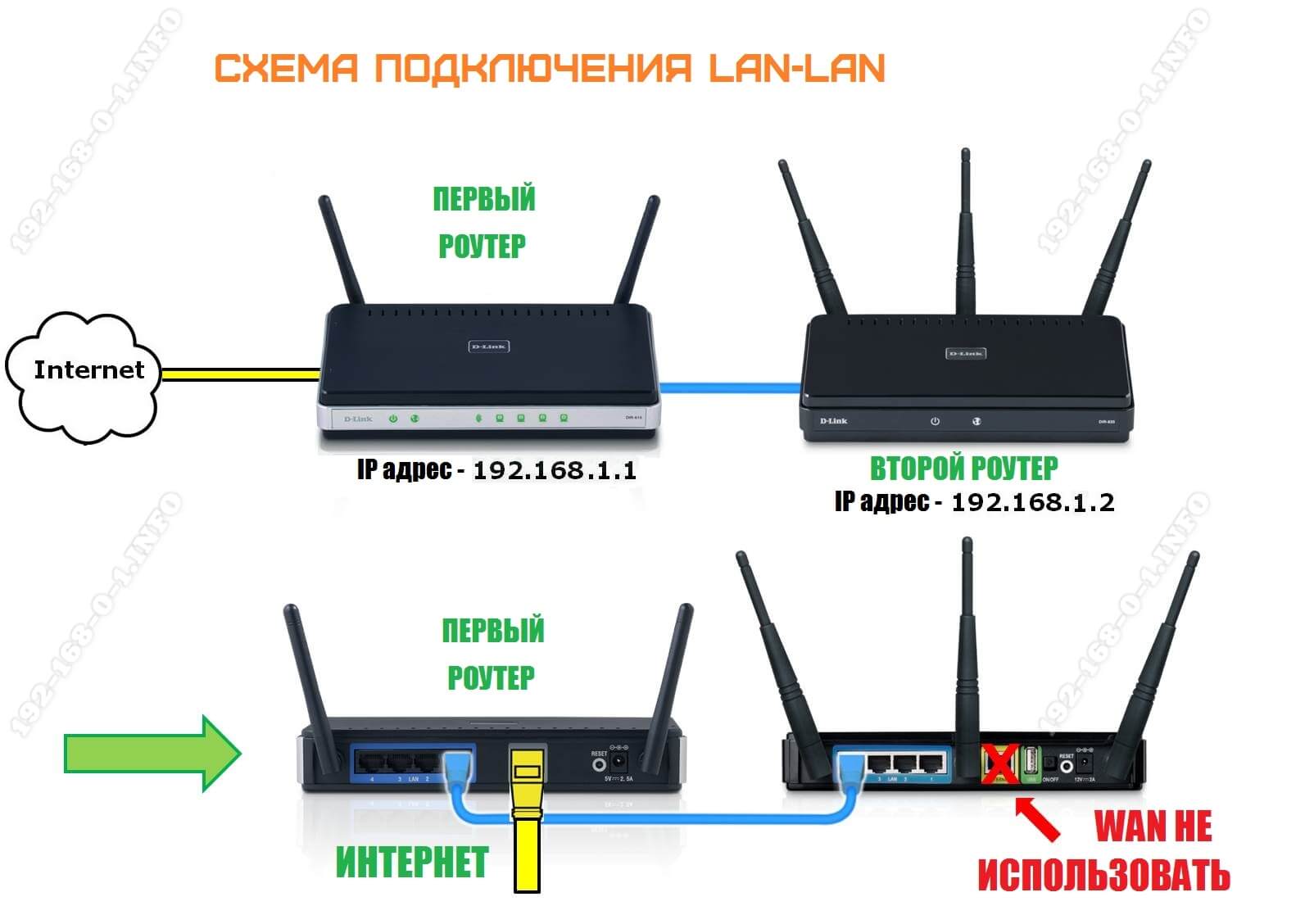
In this case, both routers are connected to the same network both physically and logically – there is one segment. The first router manages the network – raises the connection to the ISP and distributes the Internet. It is the master in this connection. From the same router IP addresses are distributed to the client devices via DHCP. Please note that the WAN port on the second router is not used at all.
Attention! For such connection to work on the first router there is no need to make any adjustments – it has worked and will work as well.
But on the second router, you will have to do quite a lot of work. Moreover, it must be preconfigured and only then connected to the first one. Let's proceed step by step:
Using the router as a repeater
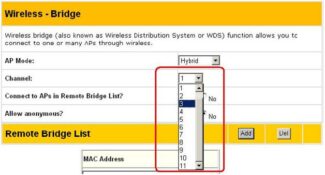
It is not always necessary to bother trying to connect a router via cable – you can do the same via WiFi. To do this, the second device must be able to work as a Wi-Fi Repeater or support WDS technology. The second router connects to the wireless network of the first one and extends it to the range of its signal. This is what it looks like schematically:

On the first device, we do not change anything in the schematic. It works in the same mode as it did before, we will just connect to its WiFi and transmit the network further. Let's take a look at setting up the second router as a wireless repeater.
Unfortunately, not all modern routers support this mode. For example, my TP-Link Archer does not. That is why I will show you an example of repeater mode settings on Asus RT-N10U WiFi-router. Due to its rather low price it is perfectly suited to these purposes. The sequence of actions is the following. Reset the settings with the Reset. After that you should enter the web interface of the device, using its IP 192.168.1.1.
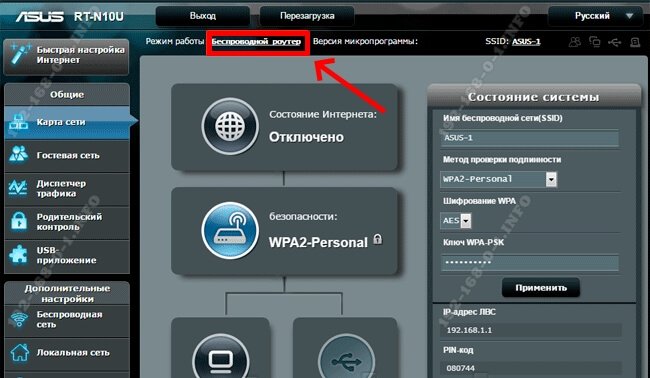
On the main page of the web interface, find the line "Operation mode". The default setting is "Wireless router". Click on it and go to the page of selecting the mode of the device:
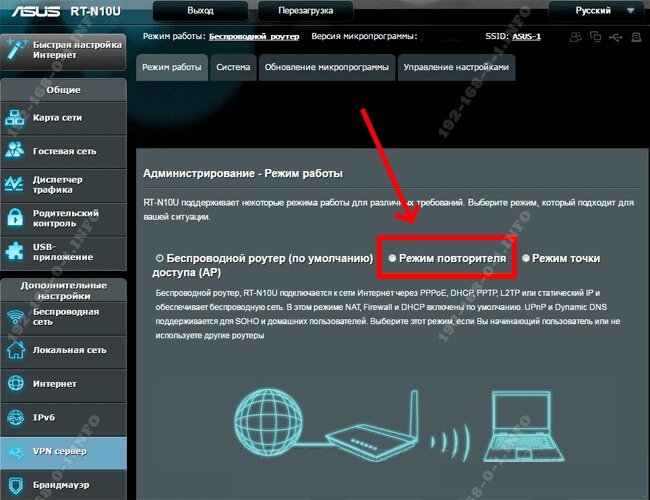
Here we need to tick the "Repeater mode" checkbox. Click on the save button.
Next we should see a selection of available wireless networks:
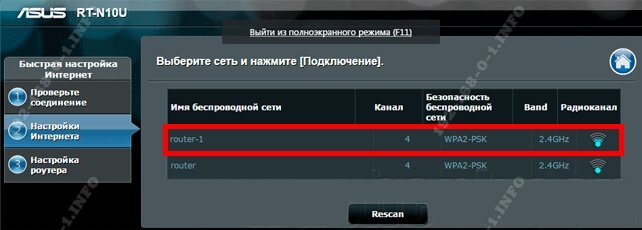
Types of routers
Nowadays on the market of such products there is a large number of routers that differ both by the way they are connected and by other principles of their functioning.
If you divide routers by the way they are connected, you can distinguish:
- Mobile devices, which have a number of advantages. For example, such as compact size, the ability to transmit data via USB connection, as well as through wireless technology, that is, over the air. To ensure the operation of such a mobile router, it is necessary to purchase a SIM card of a particular operator to the device.

- Routers connected to the telephone line will be relevant in cities or towns, where there are means of wired communication, but there is no possibility to connect to the Internet in another way. This type of network device uses a couple of ADSL modem connected to the telephone line, as well as a router, which will be used to distribute the signal of the Internet.

- Another type of router, in terms of connection, is provided by twisted pair and fiber optic. It is this variety that is the most common, both in offices and for installation in apartments and two-storey private houses. Such connection is simple enough – even a novice can easily make it. But the router itself can be different. Cheaper router models have a single antenna – although they give a good enough signal, they do not provide much coverage. To get a more powerful device, you should pay attention to models that are equipped with several removable antennas. Such a router is suitable for installation in a two-storey house or where there are quite thick reinforced concrete walls, which somewhat "muffle" the signal. In addition, such a device is able to work in 3G and 4G networks, because this modem is more advanced and new in terms of the introduction of a variety of technologies.
What to pay attention to when choosing
- Determine its main purpose – for home or office.
- Pay attention to the indicators of Wi-Fi speed. Especially this can be clearly felt if the router will be connected to the TV, and it will be watching videos in Full HD and 4K.
- Pay attention to how many GHz the router has. Some are only capable of operating in one of two possible bands – 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz. Although, there are models that operate simultaneously with two frequencies.
To choose a router that will not disappoint the consumer, it is necessary to take into account:
- The power of the transmitter, since it is this indicator that provides the expansion of the signal coverage area. But it should be understood that it is also possible to increase the coverage area by correct placement of the sensor. But still, it is better to pick up initially a device with appropriate parameters.
- If you need to provide maximum coverage in one plane, ie at the level of 1 floor, you should prefer models with a large number of antennas. They have a high gain, distributing the signal to the sides, but not allowing it to penetrate significantly up or down.
- If you need to provide a quality signal on different floors of the building, you should pay attention to router models with a coefficient close to 1. In this case, the coverage area of the device is a sphere.
- Some routers may have additional antennas, as this may be required by specific building construction or the use of building materials with absorbing characteristics.
Considering all the above points, it is possible to choose a suitable router for different purposes. It will work well in a small apartment, in a large office or in a country house.
If you have any ideas or have any doubts on the choice of router – feel free to write in the comments on our site and our team will help you.
Read More: