The speed also depends on the device that you connect to the Wi-Fi router. It depends on the signal strength of the wireless network, on interference, and to some extent on the settings of the wireless network.

- How can you increase the speed of the Internet via Wi-Fi router
- Configuring via the web interface
- Channel width
- advertisement
- advertisement
- Speed generation mechanism
- Causes of poor communication via cable
- How to organize a Wi-Fi network, so that the speed loss would be minimal?
- Why is the speed lower than what is stated on the box with the router and in the specifications?
- What causes speeds to drop through a Wi-Fi router?
- Frequency crossover with the neighbor's network
- Programs, overloading the channel
- Check the speed online
- Internet speed and wi-fi – what's the difference
- Update the router firmware
- Remove "unnecessary" users from the network
How can you increase the speed of the Internet via Wi-Fi router
In the minds of the mass consumer Wi-Fi-router is a device that only transmits the Internet connection received via ethernet cable wirelessly to other devices. Therefore, when there are problems with network quality, few people turn to changing router settings to increase the speed of receiving and transmitting information. Although there are many ways you can improve your Internet connection with this device.
Most users think that the Internet connection speed is the sole responsibility of the ISP and the ethernet cable installed in the house. However, the quality of reception and transmission of information is greatly influenced by the equipment for transmitting a wireless signal. Thus, the following parameters of a Wi-Fi router affect the connection speed:
- The quality of the router parts;
- the technical settings of the equipment;
- the channel for transmitting information;
- the security of the Internet connection;
- the workload of the device;
- location of the device.
Let's take a look at how to increase the speed of the Internet through a Wi-Fi router.
Configuring via the web interface
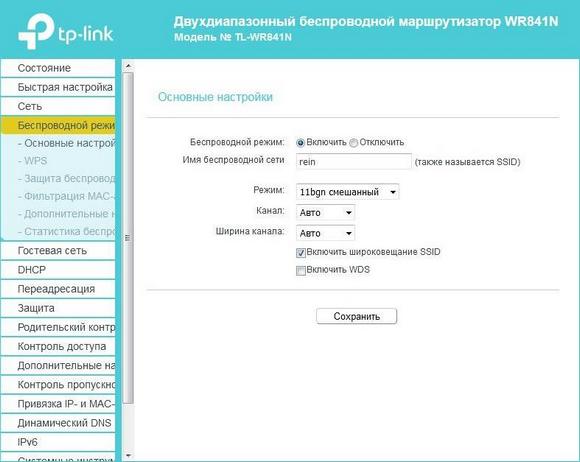
You can increase the speed of a Wi-Fi router by changing the width of the traffic channel and the mode of the device. This process is performed via the router's web interface. To open the router system settings, follow a series of steps:
- Start your Internet browser on your PC.
- Enter an IP address, e.g. http://192.168.0.1/, into the address bar of the software.
- Login to the system. To do this, enter the "User name" and "Password". Their values can be found on the underside of the router or you can enter the defaults "admin" and "admin". But they may be different from the ones given.
If all steps of the instruction have been performed correctly, the web interface page will open in the Internet browser. In it you need to perform the following actions:
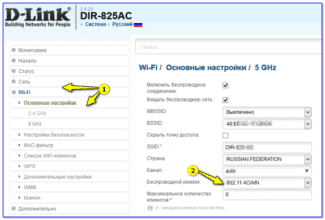
- Go to the Wi-Fi settings. For example, in TP-Link models, this menu is called "Wireless mode".
- Select the "Main settings" subsection.
- Find "Mode".
- Select the "11n only" option. The device will change the operating mode, which will increase the operability with incoming traffic.
- After making the changes you must press the "Save" button, otherwise all the settings will be reset.
Channel width
If changing the operating mode did not help, you should pay attention to the channel width of the router. This parameter will depend on the mode previously selected ("Mode") in the router.
For the "11n only" option, it is better to reduce the width to 20 MHz. If using another mode of operation, increase the parameter to 40 MHz.
To find the "Channel Width" tab, do the following:
- Open the web interface of the device.
- Go to the Wi-Fi settings. For example, in TP-Link models, this menu is called "Wireless mode".
- Go to the "Main settings" subsection.
- Find the "Channel Width" item.
- Click the tab and change the values.
- After entering the new data in the equipment settings, be sure to save the parameters, otherwise all the changes will not be valid.
advertisement
Wireless routers/TDs always have a CCA Threshold – a signal audibility threshold, and if the signal level does not exceed this threshold, the router/TD considers it noise. Suppose this threshold is 82 dBm. Thus, our conditional router with 5 dBi antennas will work with devices, the signal level from which at the location of the router is at least -87 dBm (-87 dBm signal + 5 dBi gain router antenna = -82 dBm).
Note: Of course, this is just a tentative example with all parameters conditionally-typical and given to understand the situation; your router may have antennas with the gain different from 5 dBi, and different threshold, for example – for some Ubiquiti equipment in general stable connection is guaranteed at -70dBm signal level; threshold for 5GHz networks is lower than for 2,4GHz even on the same equipment, etc., but these are nuances, we will not go into details.
In general for the router and the client we can be guided by a simple rule: all other things being equal, the signal loses 6 dB of power (i.e. 4 times as much) when the distance from the transmitter is increased by a factor of 2.
However, as mentioned above, the signal strength of the router/TD is usually 2-8 times higher than on the clients. And with the distance from the router/TD inevitably there will be a situation where the client will hear the signal of the router well, but the router will hear a weaker client signal at the "edge" of possibilities or not hear at all (because the client signal level will fall below the CCA Threshold of audibility). And there will be a strange situation when the Wi-Fi signal from the router on the client device seems to be caught, but there is no connection or it constantly "fails".
advertisement
The reason is the asymmetry in the "strength" of the connection: for example, when a 14 dBm client hears the router/TD at -84 dBm (-84 dBm + 2 dBi client antenna gain = conditional hearing threshold -82 dBm), the signal from the client reaches the router/TD only at -90 dBm, which is below the hearing threshold. Under these conditions, the wireless connection is guaranteed to break down.
That is, in wireless communication channels already at the typical standard parameters of the routers / TDs there is a significant problem with the connection, caused by the asymmetry of the power of Wi-Fi emitters. And if you additionally increase the signal power on one side (router/TC), the problem will only worsen. Moving with mobile clients, you will increasingly often encounter a situation where a Wi-Fi router "loses" devices, and that's because it has a significantly stronger signal. The client will "hear" the router/TD, but the client's router will not. This is why serious equipment manufacturers do not recommend using Wi-Fi routers and access points at maximum power. To prove this, here is a fragment of a Cisco presentation (you can read the full presentation here).

Even on the contrary, to eliminate asymmetry and obtain a stable connection, it is recommended to reduce the Wi-Fi transmitter power in the router/access point.
But if not signal strength, then what determines the speed and reliability of a Wi-Fi connection?
The connection speed, which doesn't tell you anything.
Three parameters determine Wi-Fi connection speed: modulation type, number of streams (depends on the number of antennas) and radio channel width.
But the "theoretical" connection speed based on the above parameters has little to do with the actual speed of the wireless network. What affects this speed?
The fact is that modulation in the network is not constant. The most advanced modulations today are 256 QAM and 1024 QAM (the modulation determines how many bits are transmitted in one radio symbol). But! These dense modulations are very sensitive to noise. And they are only achieved at high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) when the client is close to the Wi-Fi router/TD. With the distance from the router/TD increases noise, SNR drops, modulation is simplified for the reliability of the connection and, as a consequence, the communication speed drops. In addition, interference adds to the network problems.
Speed generation mechanism

The paths of digital data between all interfaces and addresses are built on the basis of a routing table. The latter can be created automatically or entered manually. The density of transmitted information, at any given time and for a particular channel, is controlled by a software mechanism generally referred to as QoS (Quality of Service or Quality of Service). It is he who sets the system parameters for each interface, which must be the same on the receiving side and on the sending side. Otherwise there is a collision (mismatch) with the rate adjustment procedure until its quality characteristics do not meet QoS.
The quality of service mechanism is focused on the number of packets of the network, passed in both directions without breaking the structure of the data. With slow transmission – a higher chance of sending them to the integrity than with a faster. Depending on the number of losses QoS and sets the minimum hardware speed of the interface.
The procedure is performed simultaneously, on the receiving and transmitting sides, until the best balance of values is achieved. In this case, if the interface is asynchronous, then the speed can be different for the moment of receiving and transmitting, and thus doubles the number of conducted synchronizations. Setting a single value is not a panacea. Technically: each mode's operating scheme is implemented by its own method. Accordingly, the correct transmission and reception speeds are different, even within a single set of hardware interfaces.
QoS operation also affects the priority of the received data. All incoming information goes to a special processing queue. Some of the packets may be of higher importance. If there is an error, they will be retrieved again. If the priority is low, they are simply discarded. On some routers the function is disabled or not implemented at all.
Causes of poor communication via cable
- Errors of setting on client devices;
- Switch service settings;
- Manual setting of invalid interface values on the router;
- Physical faults in the cable line (electromagnetic interference, breaks, short circuits) with a corresponding increase in collisions;
- software errors in the router, including firmware problems;
- Weakness of the hardware component of the router.
The reasons why the speed cuts, except for the first one listed, concern all parts of the network, since a data packet passes through many intermediary devices on its way from one point to another.

This is what lines of communication from routers look like.
How to organize a Wi-Fi network, so that the speed loss would be minimal?
As for your Internet Service Provider: If you have not yet connected to the Internet, and if possible, choose an ISP that uses Dynamic IP connection technology, or Static IP. This will make it easier for the router, and it is much easier to set up such a connection.
Choosing a router: If you want minimal speed loss, you'll have to splurge on a router. My recommendation is to buy a router which can run at 5GHz (GHz), and support the new 802.11ac standard. The 5GHz frequency is practically free now, which means there won't be much interference there. After all, for now, mostly all Wi-Fi networks operate at 2.4GHz. And the new 802.11ac standard, even compared to the currently most popular 802.11n, allows you to transmit information at as much as 6.77 Gbps. This is, of course, in theory, with special equipment.
The devices that you will connect to the network: As I wrote above, the speed also depends on the network clients. It is desirable that your devices are new, with support for the modern standard 802.11ac, or at least 802.11n. If it is a computer, update the driver on your Wi-Fi adapter. I wrote about this in a separate article.
Check your internet speed, share your results in the comments, and tell me if your router is slowing down too much. Have a nice day!
Why is the speed lower than what is stated on the box with the router and in the specifications?
Why? Why does it say N150, N300, N450, or even N600 and higher on the box of the router, but my Internet speed is so low? About this question very often suffer from the support service employees of online stores, router manufacturers, or innocent consultants in the stores 🙂 .
Now I will explain, and we will close the subject with these figures, which are listed on the box, or in the characteristics to the router. Many people also see the item "Speed" in the properties of the connection on a computer or mobile device, and do not understand why the data is so different.

Each router has a certain index of Wi-Fi network speed. This is one of the main indicators and criteria when choosing a router. If we consider routers, which work only in the 2.4 GHz band, the speed there is from 150 Mbit/s, and it seems up to 600 Mbit/s (4 antennas). If we consider dual-band routers, with 5 GHz frequency support, the speed will be higher.
So, all these numbers, up to 150Mbps, up to 300Mbps, this is the maximum, theoretically possible speed of your wireless network, which this router can give you in ideal conditions and only in theory. I have already written in an article that these numbers have nothing to do with the actual speedas it depends on many factors.
For example: an 802.11n router, which can deliver speeds up to 300 Mbit/s (they are the most on the market now) in theory, in reality can squeeze out a maximum of 100 Mbit/s. But even that is practically impossible. I'm not even talking about budget models with the index N150. There's a maximum of 50 Mbps.
It turns out that if you have a rate of 100 Mbit/s, and you bought a router with speeds up to 150 Mbit/s, then the maximum you can get through Wi-Fi is 50 Mbit/s.
What causes speeds to drop through a Wi-Fi router?
Now for the most important part. Why is it that the direct speed is the same as promised by the provider, the cable from the router is the same or a little bit lower, but via Wi-Fi the speed slows down. Sometimes even very much.
Everything is kind of clear here without any complicated explanations. A cable is a cable. Through it our Internet is strictly by the appointed route "flies in" to the devices, and not dispersed across the room, apartment, etc., as in the case of Wi-Fi.
Let's take a closer look, and look at the main factors that cause wireless connection speeds to drop.
- Let me tell you a little secret. A router is like a small computer. It has the main board, the processor, the RAM, the RAM, the wireless module. As with a computer, the performance of a router depends on the amount of memory, the performance of the processor, and the quality of those elements. The more memory, the more powerful the processor and the wireless module, the faster the router can process data. And this directly affects the speed of the Internet and the stability of the work even under load. It is not uncommon that the speed seems to be good, but as soon as there is a load on the router, it immediately slows down. This is due to weak and not very high quality hardware, which is often installed in budget models.
- If our computer runs on Windows, the router also runs on its operating system. Simply put – the firmware. And the firmware also has a lot to do with it. If the software is poorly made, then even a powerful iron will not save. And if the firmware is buggy, raw and unfinished, it can also affect the connection speed. Always update the firmware on your router. This does not always have a positive effect, but sometimes the router starts working better and faster. You have to update the firmware!
- Each ISP uses a specific type of Internet connection. If you have set up a router yourself, you probably know what I mean. So, Dynamic IP (DHCP) and Static IP are the easiest and simplest protocols. With them, the router will cut speed the least. If you connect PPPoE, it is more complicated here, the router will spend its resources to connect to this protocol, and the speed will sag. And in the case of PPPTP – the speed will drop even more.

So it is better to choose a provider who gives addresses automatically, or requires you to write them manually, but without authorization by username and password. - Wi-Fi client. Simply put, the device that you connect to the router. For example, if you measure the speed from a laptop (via Wi-Fi) , it may be 15 Mbit/s, and from a phone – 70 Mbit/s. Or vice versa. Why so? It's very simple, the speed is limited to the slowest device in the network. And if the router will give even 100 Mbps, and the module in a laptop or any other device has a speed limit of 24 Mbps (this is the maximum real speed for 802.11g), then we will get the same speed. Outdated Wi-Fi module, the lack of support for new standards and technologies, outdated software (drivers) – all this directly affects the speed of connecting to the Internet. And the router, as you understand, has nothing to do with it.
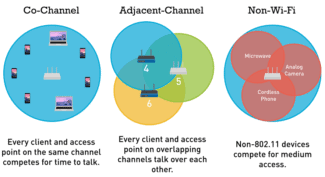
- Other external factors. For example, the worse the signal strength on your device, the slower the connection may be. Each Wi-Fi network works in a certain range and on a certain channel. And when there are a lot of these networks around, they start to overlap and interfere with each other. I would also add here the interference from various household appliances, obstacles in the form of metal in the walls, etc.
- Router settings. From the factory, the router is configured by default to be as compatible as possible with a variety of devices. Including older devices that you may not have. For example, the network mode is set to auto mode (b/g/n) . And the channel width is 20/40 MHz. But, if you do not have old devices that support only wireless g mode, then it makes sense to set the router to n mode (only n) , and the channel width to 40 MHz.
 Perhaps the speed of the Wi-Fi network will increase decently. All of these settings can be changed in the web-interface of the router, in the section with the settings of the wireless network. I wrote about this in the article how to increase the speed of the Internet via Wi-Fi through a router.
Perhaps the speed of the Wi-Fi network will increase decently. All of these settings can be changed in the web-interface of the router, in the section with the settings of the wireless network. I wrote about this in the article how to increase the speed of the Internet via Wi-Fi through a router.
Frequency crossover with the neighbor's network
Sometimes a defect appears, which looks strange: everything is configured, the distance from the router is minimal, the signal is maximal, but the speed is still weak. One meter away from the router the speed becomes several times higher. The explanation for this paradox is simple: 2 routers next to each other, working on the same channel, interfere with each other.
If the neighboring router works with identical settings, there is a problem in the signal crossover zone, where the interference is higher. The easiest and fastest solution is to switch the operating frequency from 20 to 40GHz. Be careful: it is not the width of the channel that has to be changed, but its number.
Inssider, a Windows-based program, is available to help you detect interference.

Some problems with Wi Fi speed are not related to the router: they can also create a receiving device – your "laptop". Do not rush to carry it to the service center, you can solve the problem at home.
Programs, overloading the channel
One of the reasons for the speed drop on the laptop is the loading of the channel with programs. We are talking about updating programs and the OS, which requires significant Internet resources. Let's imagine a situation where the channel is simultaneously loaded by several devices downloading updates. Poor speed in such a case is guaranteed.
You should set up manual updating or set the devices to update on a time interval: the devices update one by one, relieving the channel. The drop in speed falls on the set time intervals. Late time is the best time for this.
And some programs even load the channel without user's knowledge. You should find the list of programs in the Task Manager and see who has an excessive appetite. If speed is more important to you than this app, disable it.
Check the speed online
Check your internet and wi-fi speed with the Npnerf service. It is free.
- You have to select a server or leave the "automatic selection";
- Clicking on the wrench under the speedometer, select Mbps (top right corner);
- "Start testing". Scanning will take some time;
- Get the result.
Perform the measurement twice. For the first test, connect your computer or other device to the Internet via cable. Do the second test with a wi-fi connection. If the difference is noticeable, look for a problem with the wireless connection.
Internet speed and wi-fi – what's the difference
It is worth understanding the difference between the speed claimed by the provider and the actual speed of the device and the access point from which the user will be surfing the Internet. The provider will never guarantee that they will be equal. If you measure the speed of the Internet under normal conditions, it will be, for example, 50 Mbit/sec. But if you move the pointer to the characteristic icon in the system tray, there will be quite different data.

The explanation is very simple: the connection to the ISP's server is limited only by the equipment, and the speed at which the sites are opened is stated in the tariff, and there is no correspondence between them.
The situation is the same in the case of the router. The speed of the wi-fi connection is one thing, the speed of your connection to the ISP is another, and the speed at which the Internet sites are opened is a third. It's easy to check. What opens faster – the server provider or the main Yandex?
People often do not understand also that the connection speed DEFINITELY depends on the port through which the router communicates with the service provider. The latter promises 1 or more Gbit/sec. But if you have a mid-range router and use a port of 100 Mbit for the Internet connection, you cannot get higher than this mark, no matter what speed of the wireless network is mentioned in the instructions.
Often the wi-fi connection will also depend on the signal strength of the transmitter. Routers have a function to adjust the power, and if your laptop thinks the signal is weak, it will automatically run slower.
This also includes the range of reception. The farther your laptop is away from the access point, the slower the connection.
Update the router firmware
Keeping the router software up to date is important for stable operation. Often users forget about it. And outdated firmware is the cause of many problems. Including the speed degradation.
To get rid of bugs and speed up the router, open the "Firmware Upgrade" item in the "System Tools" section.

Everything can be done online. Just click the "Check for updates" button. If newer firmware is available than already installed, a window will appear in which you should click "Update". The router will download and install the firmware itself. The main thing during this process is not to disconnect it from the electricity and the Internet.
You can also update the firmware manually: download it from the official TP-Link web-site, write the path to it with the help of the "Browse" button and click the "Update" button. However, this way should be used only if the online update doesn't work for some reason.
Remove "unnecessary" users from the network
The cause of the drop in speed can be the freeloader neighbors. Such unscrupulous fellows pick up the password to the router that gives out the Internet, and download files or watch videos. As a result, your speed drops because the router divides it between you and "that guy". This is a very common problem in apartment buildings.
By blocking such freeloaders, you can immediately increase the speed of the router. It can be done in different ways. For detailed instructions on how to disconnect users from Wi-Fi router, read the link. Here is a brief algorithm of actions.
Firstly, change the router administrator password. Go to "System Tools" under "Administration", enter the old password and the new one twice. Save the changes.

Second, change the Wi-Fi password in the wireless mode settings.
Create a whitelist, as I described above, under "Security". Add all of your devices to it. A client with a MAC address that is not on the list will not be able to connect.
Another way is to find an outsider in the list of connected devices, create a black list and put it there. Devices blocked in this way will not be able to connect to your network, even if they have the correct access password. But there is a way around this protection – to change the MAC address. So be sure to change all passwords on the router.
Read More: