Sergey

- How to enable, disable and configure the 5 GHz on a Wi-Fi router?
- Operating, Configuring, and Managing 5 GHz Wi-Fi on a Router
- How to choose the right router
- WAN Port Type
- Wi-Fi Frequency Range
- Wi-Fi signal speed
- What is the best router
- Choosing a router for a standard-sized apartment
- Choosing a router for a large apartment or house
How to enable, disable and configure the 5 GHz on a Wi-Fi router?
I very often encounter different questions related to setting up a Wi-Fi network in the 5 GHz range on Wi-Fi routers. I also noticed that some people want to enable and configure 5 GHz on those routers, where it is not possible in principle, because the router simply physically does not support this range. So, I decided to do a separate article on this topic and tell you which routers can enable the 5 GHz frequency, and how to configure it correctly. I will also show you how to disable 5 GHz Wi-Fi on routers from popular manufacturers.
Nothing complicated about it, but first things first. There are regular routers and there are dual-band routers. Regular (aka single-band) routers only give out one 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi network. Dual-band routers have two Wi-Fi networks, one on the 2.4 GHz band and the other on the 5 GHz band. It is always written in the specifications, on the box of the router, in the manual. If it says 802.11ac (or, for example, says AC1200) , or 802.11ax, then the router is definitely dual-band and supports 5GHz, since these Wi-Fi standards work only on that frequency. If the router is not dual-band, supporting only 2.4 GHz, you will not be able to enable 5 GHz. It's not the settings or the firmware, it's the support at the hardware level. It also needs to be supported on the device (client) side. I wrote about it in an article on how to enable and configure 5 GHz Wi-Fi on a laptop or computer and why a laptop, smartphone, or tablet does not see the 5 GHz Wi-Fi network.
Operating, Configuring, and Managing 5 GHz Wi-Fi on a Router
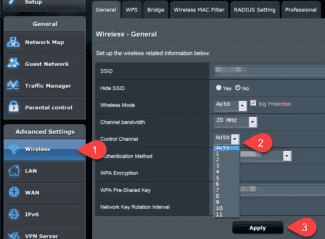
If your router supports 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, its web interface (settings page, or app on your phone) has separate settings for each band. You can set different names and passwords for each network. And separately set the channel settings, channel width, network mode, security settings, etc. In the settings of each router there is an option to disable and enable each band separately. For example, you can turn off the 5 GHz Wi-Fi network and turn it on if necessary. Usually you just need to uncheck/check the box and save your settings.
On all dual-band routers, both bands are enabled by default. If you do a router reset, it will give out two Wi-Fi networks. The factory names of these networks (SSIDs) are usually listed on the bottom of the router on a sticker. The 5 GHz band network name usually has "_5G" at the end. But there are routers, such as Keenetic, that have a feature enabled that combines two Wi-Fi networks (in different bands) into one (two networks with the same name) . The devices see one network, connect to it and automatically choose the best band.
Since you can disable, enable and configure the wireless network in the 5 GHz band on the router is usually possible on one page (in one section of the web interface), I will show you how to perform all these steps on examples of routers from different manufacturers.
How to choose the right router
To know exactly which router is best for your needs, you need to be familiar with some of the technical characteristics common to all models.
WAN Port Type
The WAN port is the place where the cable is connected, brought by the provider to your apartment. The port can be of two formats:
When making a purchase, pay attention to this parameter. The Ethernet format is much more popular now, but it is better to check, so that you do not have to change the device.

Wi-Fi Frequency Range
There are two frequency ranges in which Wi-Fi routers operate – 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The first band is simply older, it is more crowded, so the signal transmission rate is worse than in the 5 GHz band. In turn, routers that support the 5 GHz clock frequency work in a freer range, so they provide a fast and stable connection.
Routers themselves can be single-band and dual-band. That is, either support one of the frequencies or both at the same time.
It is worth noting that both frequencies work well, and you should make a choice based on the number of devices that will be connected to the Internet via Wi-Fi router. If you have, for example, a computer, a phone and a printer, a frequency of 2.4 GHz will be enough. If you need to connect multimedia devices, game and TV consoles, it is better to opt for a version supporting a frequency of 5 GHz.
Wi-Fi signal speed
This point is worth paying attention to if you are going to choose an immodest high-speed tariff from your provider, or if you need the best signal bandwidth with the largest coverage area.
There are certain standards of Wi-Fi networks, which determine the data rate, frequency range and range. The most popular now are 802.11a, 802.11g and the most recent modifications of 802.11n, 802.11as.
What is the best router
And now the information for those who do not want to carefully study the characteristics of the devices, we will tell you which Wi-Fi router is better to buy. It is worth noting right away that you should not chase the most powerful router for home. Within the limits of the apartment, a good model, corresponding to the characteristics that we have given above, is enough.
We also ask you to keep in mind that our opinion is independent and the recommendations of specific models are not intended to identify the best router in the world, but only reflect, in our opinion, the best options in terms of price – quality ratio.
In our practice, these models showed the best results in terms of performance, signal quality and overall functional stability.
Routers from manufacturers TP-Link and D-Link, on the contrary, we do not recommend. The former release a part of customer traffic into an external network, have problems with general technical operation and remote work, and on top of that they lack a normal recovery mode (a restart and recovery option). The latter are not so bad technically, but it is better to avoid buying older models if you need high speed internet connections.
We will be glad if the information was useful! Despite what might seem to be the complexity, choosing a home router is not difficult at all. Follow the recommendations, pay attention to your own needs and requirements, compare opinions and reviews – it will help to make the right good purchase.
Choosing a router for a standard-sized apartment
The peculiarity of apartment buildings is an overloaded network and a lot of interference. Therefore, when choosing a router in 2022, it no longer makes sense to consider single-frequency devices, even if you live in a small studio and alone.
A dual-frequency router is the choice for a typical apartment of up to 80 m². In order to appreciate the benefits of Wi-Fi 6, you need to make sure that your devices (smartphones, laptops, etc.) support this class. But more often than not, as we have already written above, Wi-Fi 5 is quite enough for an apartment.

Choosing a router for a large apartment or house
With large areas the case is more complicated. This applies not only to private houses of different storeys, but also to multi-room apartments. Even a high-performance router can't handle the coverage in such an area. The solution is to install mesh systems.
Mesh-systems consist of a central router and repeaters (adapters). Repeaters do not require a cable connection to the Internet, so they can be installed anywhere in the house or apartment. The signal is transmitted from the central router to the adapters, creating a seamless network. The client device automatically switches to the element of the system that gives the most stable signal. For example, you can video call on your phone and move around the house, including from floor to floor, and your smartphone will switch from one adapter to another without affecting video quality or interrupting the call.

Ready-made mesh kits transmit the signal between the components only through Wi-Fi and have the simplest settings. But you can also create a network from an existing router and a separate repeater, or even two routers from the same company. So you can connect the elements of the system not only via Wi-Fi, but also via cable. The latter option is technically more complicated, since it requires communication, but it allows you to significantly increase the data transfer rate and improve the performance of the entire system. To combine routers, it is necessary that their characteristics were declared to have the appropriate function.

The number of elements in the mesh-system is limited by the number of ports on the router in the case of a cable connection and the capabilities of Wi-Fi in a wireless connection (often it is no more than 3-4 modules).
Read More: