The controller settings are complete, now we have to move on to the access points.
- What is OneMesh from TP-Link? How to set up a seamless Wi-Fi network using TP-Link Archer A7 v5 router and TP-Link RE300 amplifier as an example
- OneMesh and TP-Link Mesh – what are they?
- Setting up a Seamless WiFi Roaming Network for your Apartment or Country Home – TP-Link, Zyxel, Keenetic, Tenda
- How to make a seamless wifi?
- Mesh Systems
- TP-Link Deco
- Important – before setting up
- Basic Configuration
- How do I connect two Zyxel Keenetic routers into one mesh network?
- TP-Link devices supported by OneMesh
- Creating and configuring a OneMesh network between a TP-Link router and computer from a computer
- How do I enable or disable "Fast Roaming" in the Wi-Fi Mesh system settings?
- Netgear Orbi
- Band steering
- Technology and standards
- 802.11k
- 802.11r
- 802.11v
- What is a Mesh
- Applications
- How to make a seamless wifi at home on the equipment
- TP-Link
- Keenetic
- Creating a network based on two routers
What is OneMesh from TP-Link? How to set up a seamless Wi-Fi network using TP-Link Archer A7 v5 router and TP-Link RE300 amplifier as an example
In this article, I would like to talk in detail about TP-Link's OneMesh product line and TP-Link Mesh technology itself. I will also take a look at the setup process for a OneMesh enabled Wi-Fi router and amplifier. Let's take a look at a real-life example and see how it all works. But I want to start by saying that the process of amplifying (extending) a Wi-Fi network always has a downside. We increase the range of the network, but the connection speed drops and the stability of the devices on that network deteriorates. Technologies such as TP-Link Mesh are designed to optimize the performance of a Wi-Fi signal booster. For devices in such a network to get a fast and stable connection.
Until recently, there was only one way to enhance Wi-Fi network (without using wires) – to install a conventional signal booster (repeater). Yes, they strengthen the signal, but the devices in such a network very long and unstable switch between the router / repeater. The connection speed also drops a lot. Then came Wi-Fi Mesh systems, with which you can create a large, seamless Wi-Fi network. And it's just perfect for big houses and apartments. The Wi-Fi network that the Mesh system's modules create supports fast roaming. Devices switch between modules with virtually no loss of connectivity. In the whole area, house, apartment, office – one Wi-Fi network. Such a network is fast and stable. Now the manufacturers of network equipment sort of began to transfer the technology from Wi-Fi Mesh systems to conventional Wi-Fi routers and Wi-Fi signal amplifiers. TP-Link calls this technology TP-Link Mesh. And the devices that support this technology are part of the OneMesh line.
OneMesh and TP-Link Mesh – what are they?
TP-Link Mesh – is a mesh technology that allows you to connect devices (routers, signal boosters, powerline adapters) into a single, seamless Wi-Fi network. To ensure stable and fast connectivity of devices within this network.

OneMesh – is the name of a line of devices that have support for TP-Link Mesh technology.
This technology is designed so that we have the opportunity to expand our Wi-Fi network and do it effectively and on a budget. We don't have to spend money on the same Wi-Fi Mesh system. If, for example, we have a router from the OneMesh line, we simply buy an amplifier from the same line of devices, install it and get a wider range of a seamless Wi-Fi network. Without noticing any change in network performance. It just increases its range. You can connect multiple amplifiers. But TP-Link does not advise to install more than two pieces.
We know that fast roaming in Wi-Fi network works due to the support of three standards: 802.11k, 802.11r and 802.11v (I wrote about it in more detail in the article Seamless Wi-Fi. Fast roaming (802.11r) in Wi-Fi Mesh systems settings ) . In theory, all OneMesh enabled routers and repeaters should support these standards. But for some reason I have not found this information anywhere. It is not listed in the specs of the devices of this line. I will try to find out this information and supplement the article.
At the time of this writing, support for OneMesh is on a small number of devices from the company TP-Link (for Ukraine and Russia):
- Regular Wi-Fi routers: Archer A7 (V5.0), Archer C7 (V5.0), Archer C6 (V2.0), Archer A6 (V2.0).
- 3G/4G routers: Archer MR600 (V1.0), Archer MR200 (V4.0), Archer MR400 (V3.0)
- Wi-Fi signal boosters: RE300 (V1.0), RE200 (V3.0), RE305 (V3.0).
Setting up a Seamless WiFi Roaming Network for your Apartment or Country Home – TP-Link, Zyxel, Keenetic, Tenda
In a typical apartment, one more or less powerful router is enough for many wireless Internet users. However, if we are talking about a whole country house or office, when you need to cover a large enough area with wifi signal, the issue of organizing a network with seamless roaming becomes acute. In this article we will discuss in detail what it is, how to build and configure a wifi network with seamless roaming in an apartment or a country house using several sets of equipment from TP-Link, Tenda and Keenetic (former Zyxel) as examples.
In simple words, seamless roaming is a function of automatically connecting your device to the nearest access point within the same wifi network without losing your connection to the Internet.

The scheme works as follows. You install several compatible wireless access points in your apartment or house that are set up in a certain way. You connect your smartphone or laptop to the Internet via wifi.

And as you move from one room to another, it connects to one signal source or the other, depending on which one is closer and which one is less loaded with connections to other devices. And it goes completely unnoticed by the user. As a result, we get a single wifi coverage over a large area.
How to make a seamless wifi?
There are currently three ways to set up a wifi network with seamless roaming within it:
- A separate set of multiple access points called a "mesh system"
- Multiple routers that support seamless roaming
- Router and repeaters that support mesh technology
The seamless WiFi roaming feature is available these days not only in sophisticated professional equipment like Ubiquiti, Cisco and Mikrotik, but also in the mass segment among TP-Link, Keenetic, Asus and Tenda models. About some of them we will talk in this article.
Mesh Systems
Some of the first to hit the market were the so called "mesh systems". That is two or three access points which are set up from the factory. All we need to do is to plug Internet cable into one of them or connect it with wire to the main wifi router. Then to install these modules in different rooms of the apartment, house or office.

The advantage of this method is that it does not require any additional settings, except to come up with a name for the network and password. Also, depending on the model, you can connect several additional components to such a system and thereby further expand the network coverage area.

The main disadvantage may be their cost. That is, you already have a WiFi router at home, but you need to buy more separate equipment, which can be very expensive.
We have reviewed many models of mesh systems from different brands. Here are the ones that seemed to us the most interesting in terms of price/quality ratio.
TP-Link Deco
TP-Link Deco E4 is a relatively inexpensive set of 2 or 3 access points. The model has 5 GHz frequency range support, ability to connect additional modules and remote management via a cell phone application. However, it has no web-interface, which means that it is impossible to work with its control panel via a computer.
Important – before setting up
Before we start, here are some important points so that there are no problems:
- Before you start, update RouterOS everywhere – it has been supported since version 6.22rc7 (we're talking about version v2 – we won't dwell on the earlier one, because there are much fewer bugs).
- The required license level on the devices is at least 4.
- The connection to the controller network is via twisted pair. At the same time the controlled points can be connected to each other via twisted pair.
Introduction is over, it's time to go to the official website and check for firmware updates for your equipment! I won't dwell on the update process here.
Basic Configuration
We will not dwell on the moments of entry – everyone here is competent. If not – search our site for the instructions you need, or ask for them in the comments. For reference – no web interfaces, just WinBox. Move on to the basic configuration of the router, which will manage all the access points.
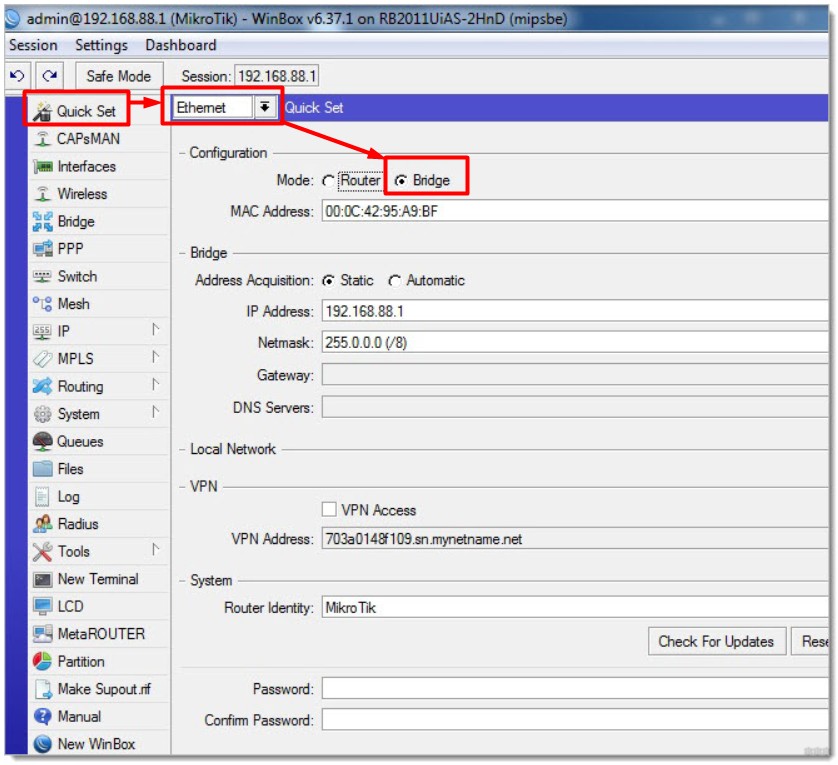
- Now, in theory, we should combine all the ports and Wi-Fi into one bridge – so that third-party points can connect in any way and see each other. Let's do that. Go to the tab Interface and add your new interface:
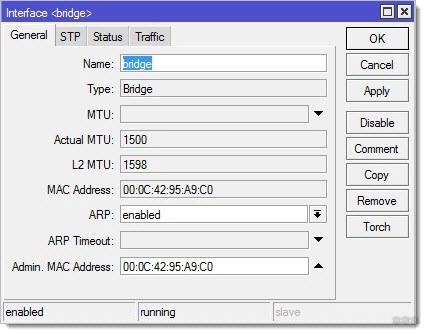
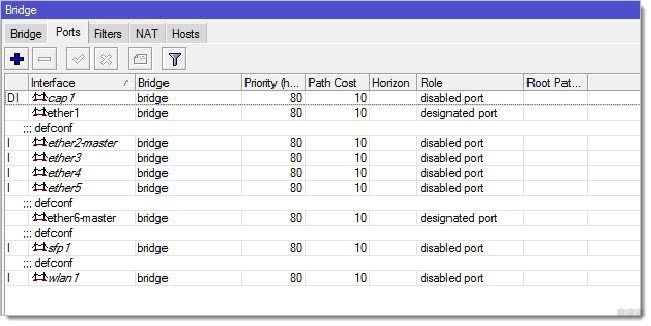
Repeat the steps on the master router and on all the access points in the network.
The management router here set the address 192.168.88.1. The rest are distributed at its discretion.
How do I connect two Zyxel Keenetic routers into one mesh network?
So we already have a Keenetic Viva router connected to the internet. To make it work as a mesh network controller, you have to go to the settings at the address my.keenetic.net and install the module of Keenetic OS, that allows you to connect several routers to one mesh network. To do this, go to the menu "Management – General Settings" and click on the "Change Component Set" button on the page


Save the changes and wait for the module to download and reboot the router to install it. After that, a new item will appear in the wireless settings menu – "Wi-Fi system"
TP-Link devices supported by OneMesh
Since OneMesh is very new and is just being introduced to TP-Link network devices, there are not many supporting devices yet. Among them are the Archer AX10 router and the MR200 modem that we have already published reviews and user manuals about.

However, it's nice that TP-Link does not forget about its already released models of routers, modems, repeaters, adapters and gradually expand the line of devices that support OneMesh. If you own a relatively new router, you can check the official website for the availability and description of the latest software version – it should indicate that after the TP-Link firmware will appear OneMesh.

There are only 2 devices that can be networked together – one of the OneMesh routers and several wifi repeaters or PowerLine adapters, including the TP-Link RE300 and TL-WPA4220. The disadvantage of the whole system is that you cannot connect two or more different routers to each other. Only 1 router and wifi repeaters. However, the repeater can be connected to any router, including from another manufacturer, but OneMesh will only work with TP-Link from a limited list of models.

I think that this situation will change over time, and any modern router can be combined with another in a single seamless network. One of the undoubted advantages is the fact that you can configure the OneMesh network in three ways:
Read More:Setting up a OneMesh network can be done not from the control panel of the main router, but through the web-interface of the signal booster.
Creating and configuring a OneMesh network between a TP-Link router and computer from a computer
I don't know about people, but personally I continue to use the old-fashioned way when connecting a device – through the web interface from a computer or laptop. It allows you to configure all the settings in more detail and control the entire process from start to finish. Let's start with it.
Creating a seamless OneMesh network begins with connecting the wifi repeater to a power outlet.
Right after that it will start transmitting a wireless signal which is not protected in any way. That means you can open the list of wifi networks on your computer or laptop and connect to it without entering a password.
After that we launch the browser on the computer and type tplinkrepeater.net into the address bar to enter into TP Link amplifier settings. The first thing you need to do is to come up with an administrator password to protect the web configurator.
It is advisable to memorize it in the browser or write it down on paper, as it is impossible to restore the authorization key later. You will have to do a TP-Link factory reset.
The next step will open a list of wireless signals that you can connect to. As already noted, any network can be connected and extended. But seamless roaming will only work with those marked with "Mesh". In our case it is "TP-Link_355E".
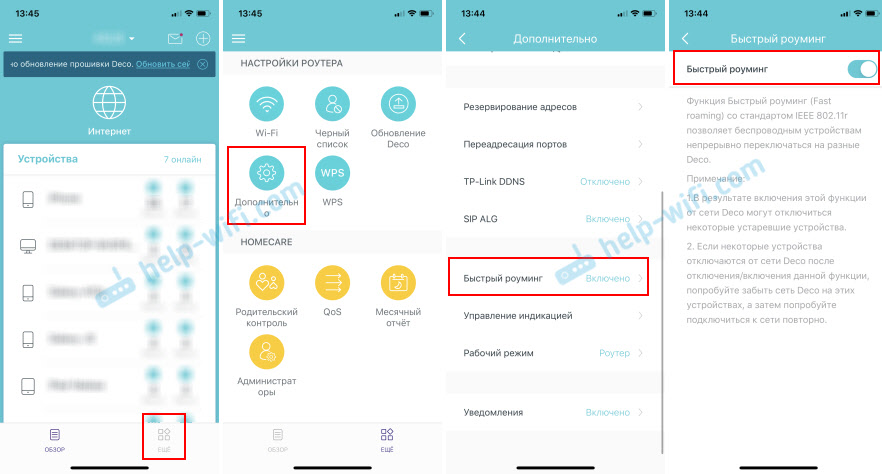
How do I enable or disable "Fast Roaming" in the Wi-Fi Mesh system settings?
Since the configuration and management of Mesh systems in most cases is done through the application from mobile devices, then you can enable/disable "Fast roaming" in the proprietary application, which is used to manage your system.
In the Deco app, go to settings, open "Advanced" – "Fast roaming". There will be a description of the function, a warning about possible problems with older devices and an option to turn on/off. Fast roaming.
If you activate this function, I immediately recommend that you check how the connected devices behave. Especially not the newest devices.
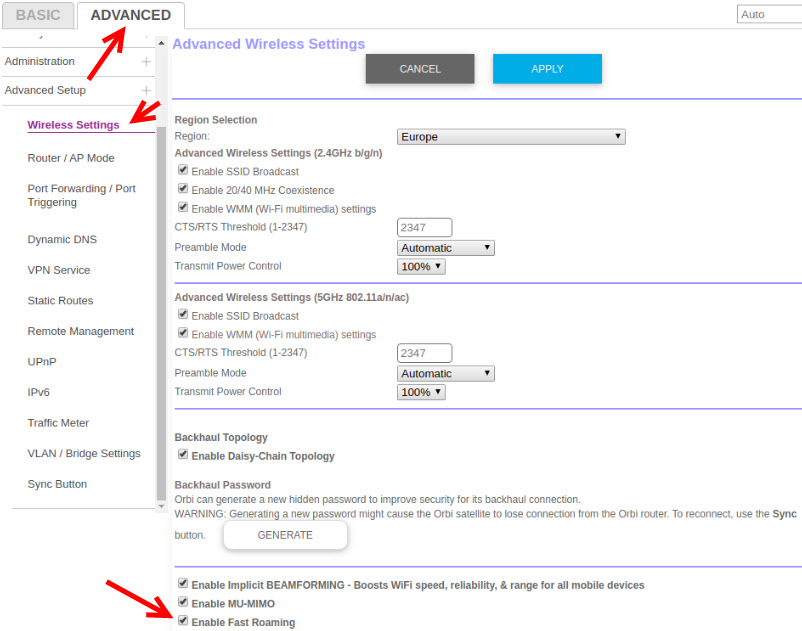
Netgear Orbi
In the web interface, under "ADVANCED" – "Wireless Settings" there is a setting "Enable Fast Roaming".
I don't know how these settings are on other Wi-Fi Mesh systems, no way to check. If you have a Mesh system Asus Lyra Home, Zyxel Multy, Linksys Velop, etc., you can share a screenshot of the settings in the comments. Also, write how your devices reacted to turning on or off the feature "Fast roaming".
8
12462
Sergey
Useful and interesting
Band steering
Band steering technology allows a wireless network infrastructure to move a client from one frequency band to another, usually this involves forcing the client to switch from the 2.4 GHz band to the 5 GHz band. Although band steering is not directly related to roaming, we decided to mention it here anyway because it is related to switching the client device and is supported by all of our dual-band access points.
In what case might it be necessary to switch the client to a different frequency band? For example, such a need might be related to moving a client from the congested 2.4 GHz band to the freer and higher speed 5 GHz band. But there are also other reasons.
It's worth noting that there is currently no standard that strictly regulates the described technology, so each manufacturer implements it in its own way. However, the general idea stays more or less the same: the access points will not announce to the client which carries out an active scan SSID in the 2.4 GHz band if the activity of the client on the 5 GHz frequency has been noticed for some time. That is, access points, in fact, can simply be silent about the presence of support for the 2.4 GHz band, in case it was possible to establish the presence of the client's support for the frequency of 5 GHz.
- Forced connection. In this mode, the client is basically not told if the client has support for the 2.4 GHz band, of course, if the client has support for the 5 GHz frequency.
- Preferred connectivity. The client is forced to connect in the 5 GHz band only if the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) is above a certain threshold value, otherwise the client is allowed to connect to the 2.4 GHz band.
- Load balancing. Some clients supporting both frequency bands are connected to the 2.4 GHz network, and some are connected to the 5 GHz network. This mode will not overload the 5 GHz band if all wireless clients support both frequency bands.
Technology and standards
Now back to the process of switching between access points itself. In the default situation, the client will maintain the existing association with the access point for as long as possible. Exactly as long as the signal strength allows it to do so. As soon as the situation arises that the client can no longer maintain the old association, the handover procedure described earlier will be initiated. However, handover is not instantaneous, it usually takes more than 100ms to complete, which is a noticeable amount. There are several IEEE 802.11 working group radio resource management standards aimed at improving wireless reconnect time: k, r, and v. Our Auranet product line has 802.11k support on the CAP1200 access point, and our Omada product line has 802.11k and 802.11v support on the EAP225 and EAP225-Outdoor access points.
802.11k
This standard allows the wireless network to report to client devices a list of neighboring access points and the channel numbers on which they operate. The generated list of neighboring points makes it possible to speed up the search for candidates for switching. If the signal of the current AP weakens (e.g., the client is removed), the device will look for neighboring APs from this list.
802.11r
Version r of the standard defines the Fast Basic Service Set Transition (FT) feature to speed up client authentication. FT can be used when switching a wireless client from one access point to another within the same network. Both PSK (Preshared Key) and IEEE 802.1X authentication methods can be supported. Acceleration is achieved by storing encryption keys on all access points, i.e. the client does not need to go through a full authentication procedure involving a remote server when roaming.
802.11v
This standard (Wireless Network Management) allows wireless clients to exchange service data to improve overall wireless network performance. One of the most used options is BTM (BSS Transition Management).
Typically, a wireless client measures its connection to an access point to make a roaming decision. This means that the client has no information about what is going on with the access point itself: the number of clients connected, device load, scheduled reboots, etc. With BTM, the AP can send a request to the client to switch to another AP with better operating conditions, even if with a slightly worse signal. Thus, the 802.11v standard is not directly aimed at speeding up the process of switching a wireless client device, but when combined with 802.11k and 802.11r it provides faster software and improves the convenience of working with Wi-Fi networks.What is a Mesh
A Mesh is a meshed computer network topology. It is a mesh network in which workstations are connected to each other and can assume the role of a switch for the other participants. This organization of the network is quite difficult to set up, but with this topology is implemented fault tolerance.
To briefly explain what a mesh is, it is a wireless network that is fault tolerant and has a larger coverage area. On the user side, the differences between mesh and Wi-fi will be minimal. The complexity of the technology and configuration processes in Wi-Fi Mesh systems is taken care of by the Mesh router or master router.
From the Wi-Fi side, the mash system looks like one router and several transmitter devices. Some would recognize this as a router and repeater circuit, but in principle these circuits are different. A Mesh network does a much better job of transmitting the signal, which makes it more reliable and faster than repeaters. The components are more complicated to make and configure, so they are more expensive.
Applications
This networking principle is used wherever a good seamless and uniform coverage of the wireless network is needed. This can be a company that requires constant exchange of information over the network, a large apartment with thick walls that do not penetrate the wi-fi, home or site. There are many options when a constant internet connection is required. The whole question here is how even coverage is required and how much you are willing to invest in it.
To create your Mesh network, you will need multiple devices that work with Mesh technology. There is no difference between the devices, each of them is able to act as a Mesh router and as a transmitter. But still we need to distinguish the seamless Mesh router and those devices that transmit the signal further. The router is connected to the Internet, and the other devices are placed within range of the wireless network.
How to make a seamless wifi at home on the equipment
While Wi-Fi roaming in corporate and public environments requires separate equipment, any user can build it in the home environment.
It takes time and following simple instructions. The algorithm is similar for setting up most routers of well-known brands. The only difference is in the nuances outlined below.
TP-Link
The company TP-Link is one of the manufacturers of network equipment. Wi-Fi roaming technology has been implemented in the Auranet hardware and software system. The controller can operate autonomously after one-time configuration "out of the box".
Access points for the internal infrastructure and the external perimeter of the building of the ceiling type. A gigabit router model AC1200 from the described brand can be responsible for Internet distribution. It operates in two wireless network bands. All devices are compact, easy to install and configure.
TP-Link's minimum seamless Wi-Fi kit consists of such equipment:
- Omada OC300 hardware controller;
- TD EAP660 HD for dorms and apartments;
- TD EAP245 for access to the wireless network in the corridor or private house.
The software part of the devices is implemented in such a way that the access points are also capable of working offline in case the network core hangs up, shuts down or temporarily fails. The controller and DT can be controlled both from a PC and mobile devices from anywhere in the world.
Keenetic
Keenetic brand equipment is popular for implementing seamless Wi-Fi network access. The system can be set up in the web interface of the Keenetic configurator.
Creating a network based on two routers
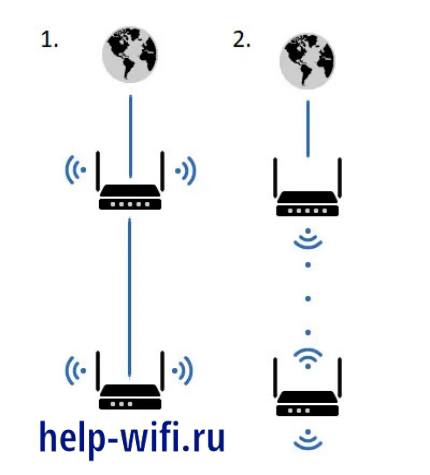
You can organize a seamless home Internet connection using two routers. At the very beginning you need to determine which method of connection between the two routers will be the most convenient.
There are two ways to connect the devices: via cable or via Wi-Fi connection. Each of them has advantages and disadvantages.
Cable connection of routers is not always convenient and quick to do, but it is the most reliable and durable type of connecting devices. If the need is primarily for reliability, high speed and continuity, this method is preferred.
Wi-Fi-connection of routers is carried out by a WDS bridge. In this case, the equipment is configured in client (repeater) mode. At the same time, you should note that the interfaces of different brands of devices may have different settings of these modes.
For example, you can use the settings of TP-Link routers. As an alternative, you can use Zyxel equipment, but the company described is more common in the home segment. TP-Link devices are the most common and understandable for home users.
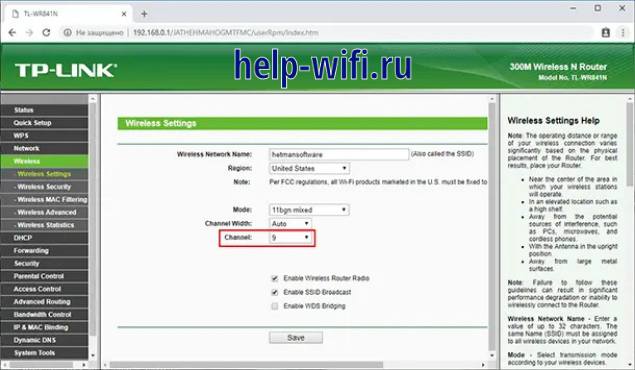
First, you need to configure the basic router so that it distributes the Wi-Fi network. A static connection channel must be set up. Then you have to connect to it by SSID name.
Channel is changed in the menu Wireless -Channel. In this item, you must specify a channel from 1 to 9. After completing the steps router settings must be saved.