This is a rather long test, but if you need to check the basic parameters of the local network, it is indispensable. It is also one of the best tests to check the performance of routers.
- Testing networks and routers
- Checking with utilities
- Ping
- Drivers
- Indicators
- Transferring a file
- Programs
- How to choose the right WLAN router
- Security Issues
- Endpoint support for 802.11ac
- Automating it
- Method 2: Using the Command Line
- Method 3: Using Web UI Diagnostic Tools
- Method 2: The tracert utility
- Method 3: The router's web interface
- All ways of testing
- Via Windows
- File transfer
- Online services
- How to increase the speed
Testing networks and routers
Internet technology is all around us. We use it all the time: at home, at work, on the bus, or in the subway. It's hard to imagine today's world without wireless technologies like Wi-Fi. This article describes the tools used to test networks both during deployment and in use. What tests are used and how to perform them. Testing routers and switches during design and to verify their functionality is also covered.
Network and router testing is performed in the following cases:
- To To verify the provider's compliance with the terms of the contract To verify the provider's compliance with the terms of the contract for communication services.
- After the network is deployed, before putting it into operation.. For example, a new building is built, a new bus with Wi-Fi is developed, and IP video cameras are installed. Here we can distinguish between long-term measurements and short-term measurements. If a new network has been developed, it should be tested in the long term. If similar networks have been deployed before, short-term tests are conducted.
- For to verify the performance of routers and switches.. These tests should be carried out during their development, as well as during the testing of finished products.
- When creating communications equipment. For example, to test a new Wi-Fi receiver.

The quality of communication provided by the provider can be measured by yourself, but it is desirable that this is done by an independent organization. You can monitor the quality of the channel provided all the time. For this purpose, "probes" are used. They are installed by the monitoring organization at the nodes of the network. The control system configures the probes and periodically tests them. If faults are found, a report is generated and the provider is notified to fix it.
Checking with utilities
You can check the bandwidth through standard utilities. This method is good if you need to roughly estimate the quality of the connection between two computers.
For this purpose the following cross-platform iperf utility. On one computer you start the server with "iperf -s", after that, the client "iperf -c server_ip". The utility runs the test and displays the results: time in seconds since the start of the test, number of bytes transmitted, transmission speed.
The current version is version 3. If you are a Windows user, download the utility and run it from the command line. On one computer the server "iperf3.exe -s". On the second one the client. This is how the output log looks like, if no additional options are set:

With the keys you can configure the transmission protocol (TCP/UDP, and in version 3 also SCTP). It is possible to test not only the transmission from the client to the server, but also in both directions. It is possible to choose the ports on which the server will run.
The main disadvantage of such testing is, first of all, that testing is on Layer 4 of the OSI model, that is, only the data transmitted through TCP/UDP is recorded without considering ip headers and control packets. The telecom operator, in turn, usually guarantees the bandwidth, including IP headers.
Since this testing is done using a computer, any application or service may be running at any time and affect the test results.
Ping
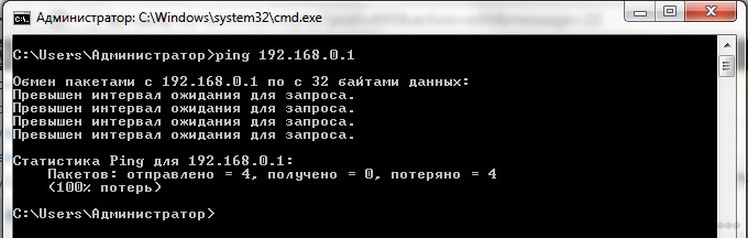
You can check if the router is working properly from the computer to which it is connected via the LAN. Run the command line and run the command: "ping.router.address". The address can be found on a sticker on the bottom of the device. It is used to access the router's parameters. Thus we can see whether the PC connects to the access point.
The response time should not exceed a couple of tens of seconds. The loss is 0%, if the value is greater, repeat the operation several times. In case of a similar result, you can either reflash the device yourself or immediately take it to the service center, where the router will be tested, find out the cause of the failure and, if possible, eliminate it.
Drivers
The software that allows the router and the computer to "communicate" can cause the former to malfunction. The driver should be updated or rolled back to a previous version if a newer version is not available.
If this does not help after rebooting the computer, roll back the software to the previous version in the same way.
This is not the best way to search for updates. The optimal way to solve the problem is to visit the official site of the device's developer and download the latest driver release from there.
Let me take TP-Link as an example. Information about the current version of the driver for your model can be found on the website tp-link.com . Here you can also download the software you need.
In order to fully check the status of your router, regardless of its model, and to identify ways to solve problems,
you need to carry out the following tests and actions one by one:
- analyzing the state of the indicators;
- checking the router's power supply;
- Determine the availability of the ISP's network;
- test the speed of the Internet;
- check the network card drivers;
- searching for viruses;
- router reset;
- device reflash.
Let's take a closer look at how the router is checked at each of these steps.
Indicators
The easiest way to start diagnosing routers from TP Link and other manufacturers is to check the LEDs on the front of the router.
If the router is working properly, the power LED on the router is constantly lit green and the following indicators are blinking green all the time:
- settings (usually looks like a gear, may not be present on some models);
- Wi-Fi;
- WAN connector (indicates the presence of a signal from the provider through the cable connected to the WAN port, most often looks like a circle combined with an oval);
- connected computers (for each of the computers connected via LAN-connectors the corresponding indicator should blink).
Lack of lighting of all indicators indicates power problems or complete failure of the device. If the Wi-Fi indicator light is not lit, it means that the wireless network is disabled in the device's settings. If the WAN light is off, it means that the router is not receiving a signal from the ISP. If the LEDs of the connected PCs do not light up, it means that there are problems with cables, connectors or the PC itself.
Transferring a file
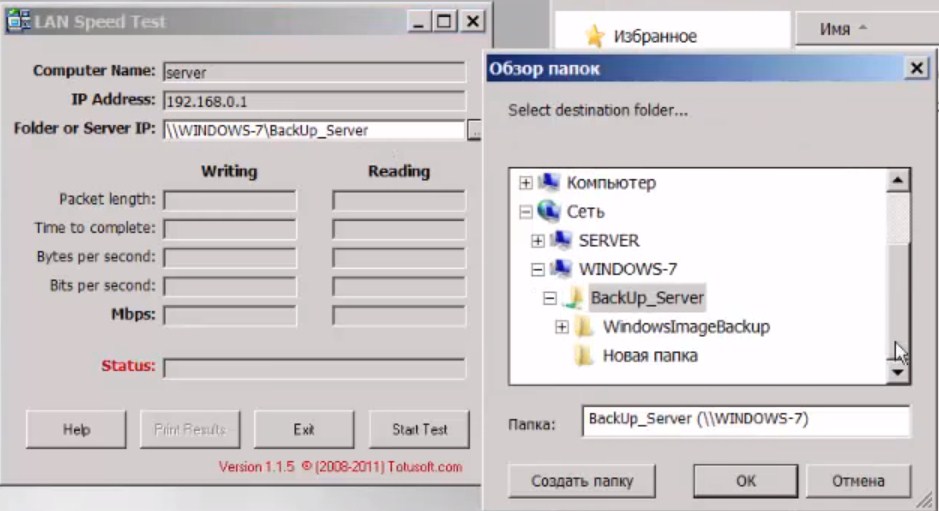
Our task is to create a local network between two laptops. They are both connected to the same router using wireless technology. On one of them we will throw a pretty fat file and just time it. Now more details and pictures. All I will describe now, you will have to do on two laptops.
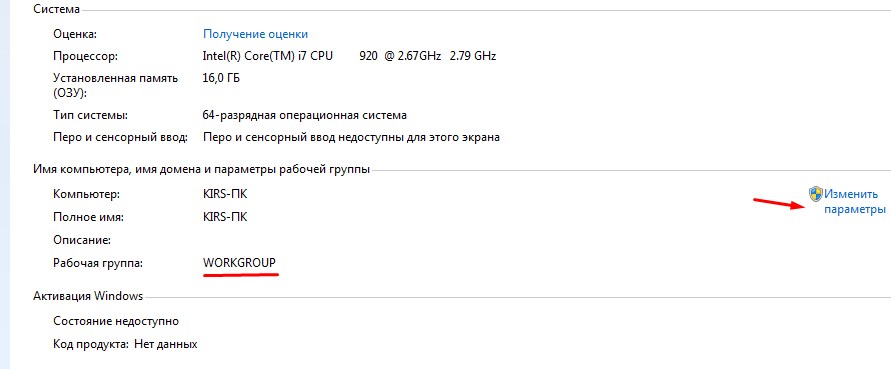
- Right click on "My Computer" and go to properties. Make sure that the two laptops in the line "Workgroup" is the same value. If this is not the case, correct it by clicking "Change settings".
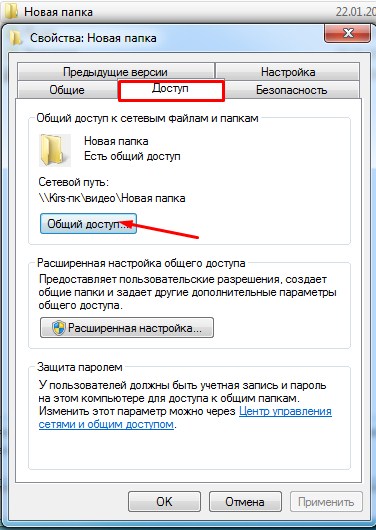
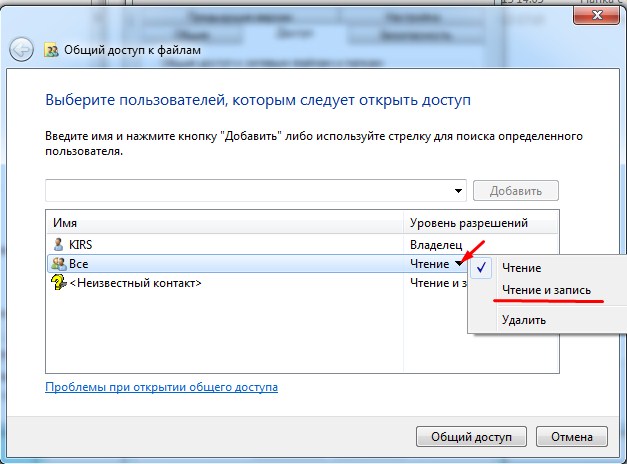
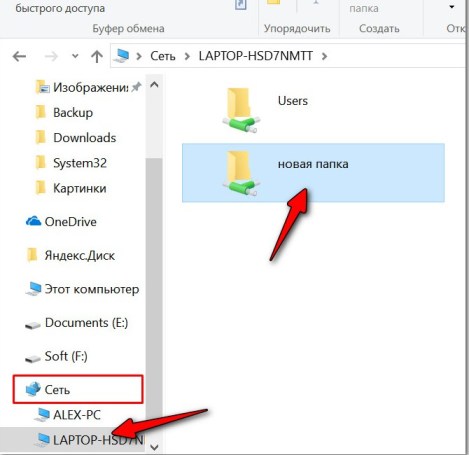
- Now open "My Computer" on the laptop that has no shared folder, go to the network and open the second laptop. You will see the created folder. Now take any large file – it is better to take a movie of 10 gigabytes and drop it into this folder. Then you will see a window with the download and the transfer rate.
Programs
The following software can be useful not only for measuring Wi-Fi speed, but also the local wired network and bandwidth in general. Useful utilities for system administrators.
This is a program that, offline, does what we did in the last chapter.
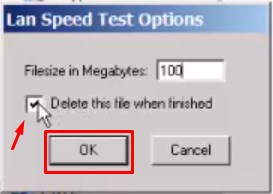
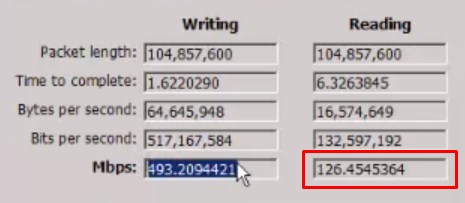
- At the very end we should look at the line Mbps (megabytes per second). The first column will be the recording result, i.e. how fast the file was recorded. But it is better to start from the reading of the file, where you will get the approximate speed in the local network. The speed itself should be multiplied by 8 to convert megabytes into megabits.
How to choose the right WLAN router
Data transfer speed is undoubtedly an important, but not the only factor when choosing a router. We assess the equipment and functionality as carefully as the performance. To better navigate in the richest assortment, you need to look first at the equipment. For instance, if you are connected to the Internet via DSL and you do not want to have several devices in your house, you better buy a router with a built-in modem – from those tested these are FritzBox devices and the winner of the ASUS test. All other routers require a separate modem.
But if you need a router with additional support for VoIP telephony or with DECT technology for radiotelephones, even ASUS has to give up. From tested devices only FritzBox 7490 performs this practical function. However, by equipment we mean some other features, such as Dual Band support for parallel operation in two frequency bands – 2.4 and 5 GHz. All the devices we tested managed to do this, and D-Link has three access points at once – two for the 5 GHz band and one for 2.4 GHz (Tri Band technology). The advantage of this solution comes first and foremost when several devices with different speeds are working in the same wireless network.
Another important feature is that the router supports the full bandwidth of the 5 GHz band. Apart from TP-Link, which uses channels from 36 to 48, all the devices we tested were able to cope with this.
Security Issues
Wireless network security is no less important. Therefore, all related presets deserve separate points, because not all users are aware of the relevant encryption algorithms and password protection and not everyone wants to do it. Advanced router settings can sometimes be extremely confusing. Only four routers that, among other things, imply using individual WPA2 keys deserve a full security score: AVM, Zyxel, D-Link and TP-Link. At the same time all the routers allow creating guest networks in which you can surf the Internet, but have no access to internal resources like network storage.
Endpoint support for 802.11ac
High-speed 802.11ac networking can of course only be used on 802.11ac-capable clients, that is, on almost all modern mobile devices. While older smartphones and tablets cannot be retrofitted, PCs and laptops can be fitted with adapters that connect via USB 3.0 or PCIe (see table above) and provide 802.11ac support. USB is the easiest: you need to install the manufacturer's software driver, connect the device via USB and configure it, then disable the former wireless network (by the switch on the device or via "Control Panel | Network and Sharing Center | Change adapter settings", right-clicking on the name of the old adapter and clicking "Disable").
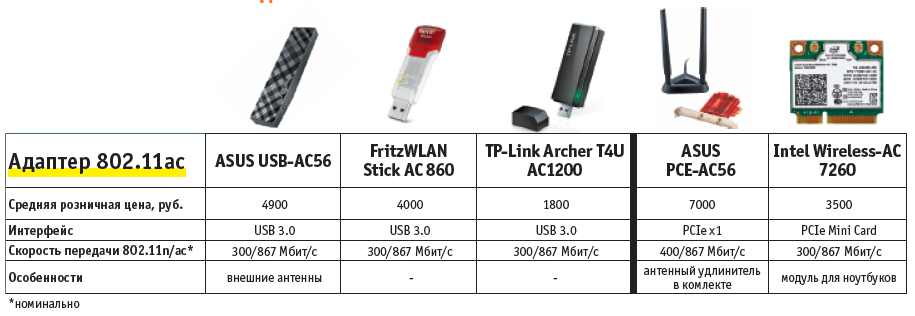
For desktop PCs, it is more logical to use such adapters, since they can be connected via a USB extension and can be placed higher up. PCIe expansion cards with external antennas and extenders, which can weaken the signal, are quite rare. In the CHIP test center they gave very erratic results. In laptops, hobbyists may well replace the 802.11n module with the only available Intel Wireless-AC 7260 adapter if the computer is equipped with 5 GHz antennas and the BIOS will allow it, which you should first find out about on the Internet.
Automating it
Running the commands manually is inconvenient, so I wrote a script in python that automatically collects all the necessary diagnostics from macOS and Linux. Windows is in the plans.
It also checks the availability of user-selected resources (gateway, 8.8.8.8, facebook.com, etc.) and saves a handy report on disk in several formats (markdown, json, plaintext).
All source code is open, MIT-licensed – use it at your pleasure, or better yet, come back to counter-buy it.

As I wrote, this question could be worth a separate article. Or a series of articles.
I'll leave the canonical diagram from the WirelessLANProfessionals trablushing guide as an introduction.
Method 2: Using the Command Line
Sometimes you want to check access to the router and check for errors in processing packets without starting the browser. A simple console command that runs like this will help:
- Open Open the "Start" menu.Open "Start" and look for the application "Command Prompt" and run it.
- Enter the command ping 192.168.0.1 or ping 192.168.1.1, depending on the router address that appears on the sticker on the back. To confirm the command, press Enter ..
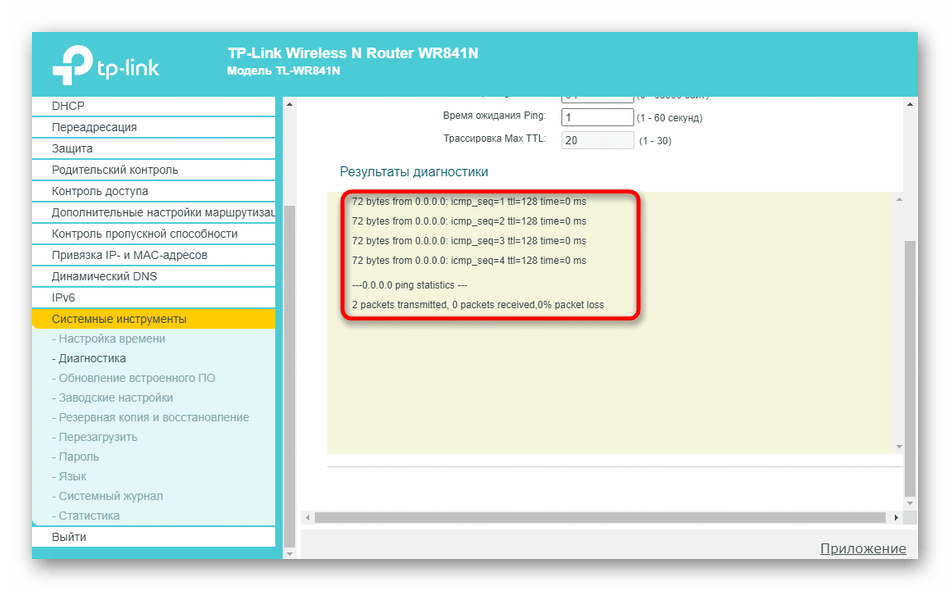
- Wait for the packet exchange to complete and check the responses. If everything is working correctly, four packets should be successfully sent and received without loss and the latency should not exceed 150 ms.
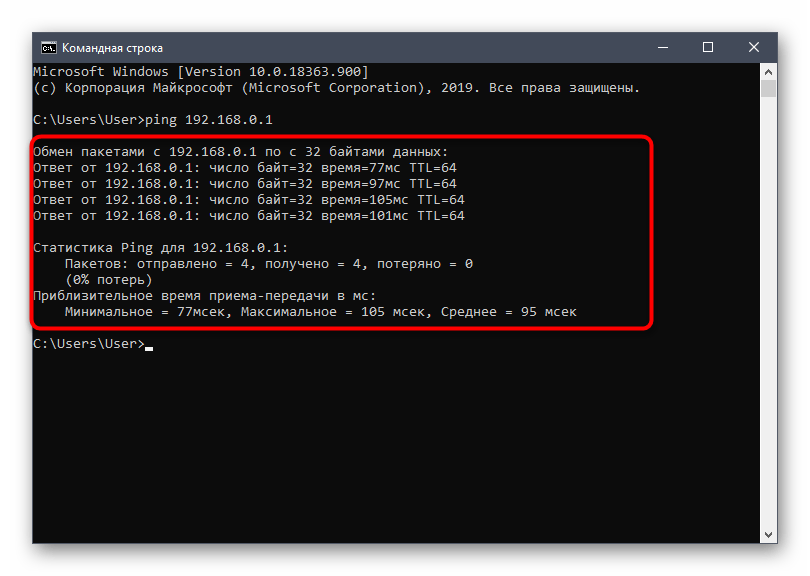
Loss or excessive delays indicate that there is a problem with the LAN cable or the quality of the wireless connection, or that the router is malfunctioning. If no packets were sent and received at all, then the computer does not see the router or the address you entered at the beginning is not correct.
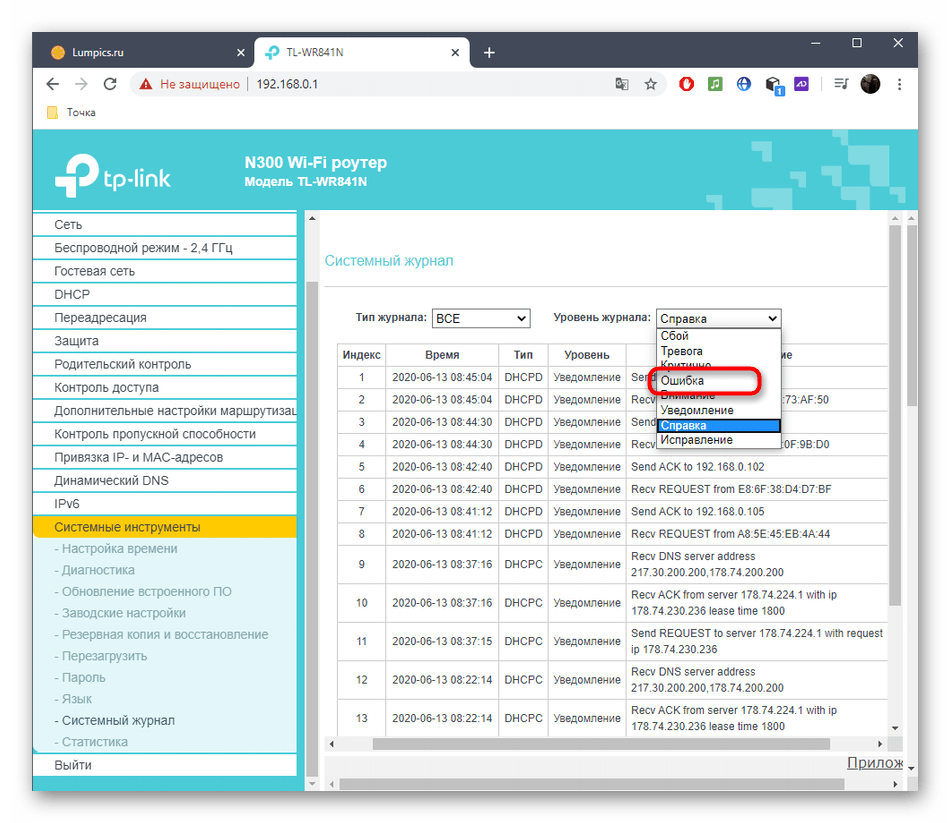
Method 3: Using Web UI Diagnostic Tools
Almost every router has a separate function in the web interface that allows you to test the network, but to do so you first have to connect the router to your computer and authorize it in the Internet center.
-
Use the instructions at the link below if you have not previously accessed the router's web interface.

Method 2: The tracert utility
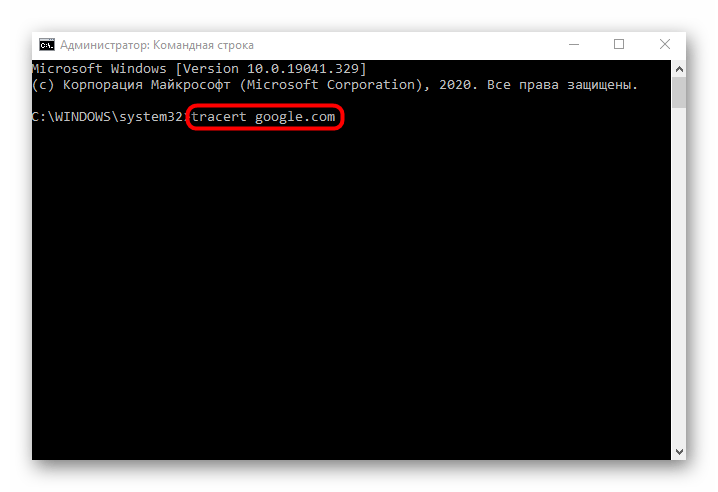
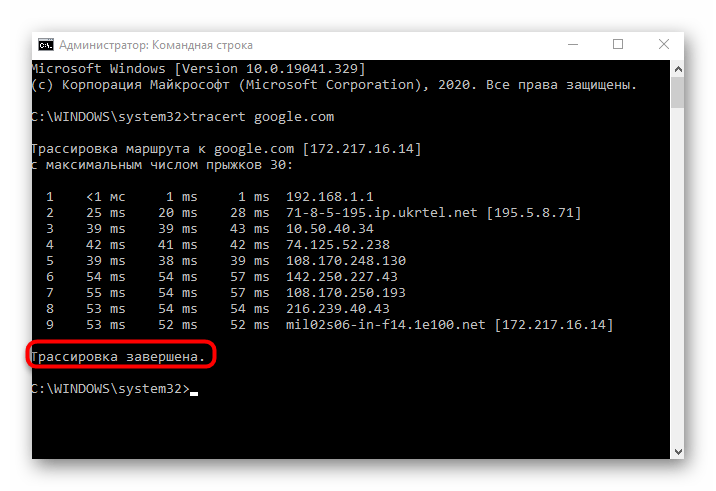
Another system utility called tracert is used to trace, i.e. it shows how fast a request goes from your PC to the router. This command should be used in situations where the main purpose is to determine the stability of the router's connection to the computer and to see if there are any wireless or LAN problems.
- To perform this method, you will again have to run "Command Line.". There, type tracert google.com and press Enter. In the same way as with the previous utility, you can use any domain or IP address for tracing.
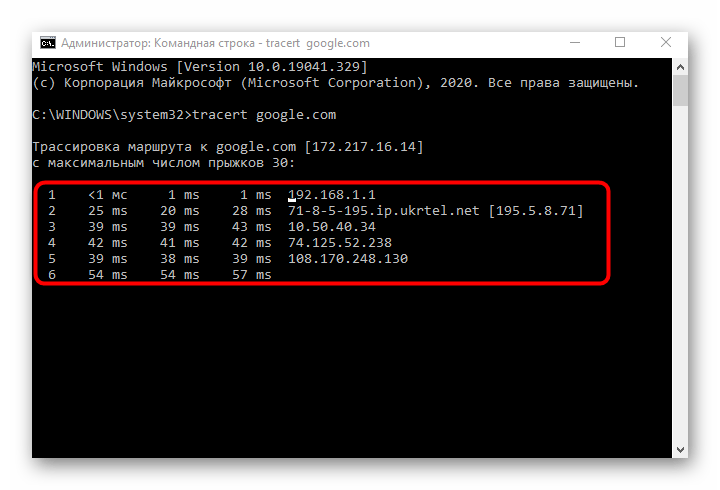
- The route tracing process will start, which may take some time. Do not close the console until the check is complete.
Method 3: The router's web interface
Most router web interfaces from different manufacturers can perform Internet diagnostics using roughly the same pinging and tracing utilities. First, authorize in the Internet center, which you can read about in more detail below.
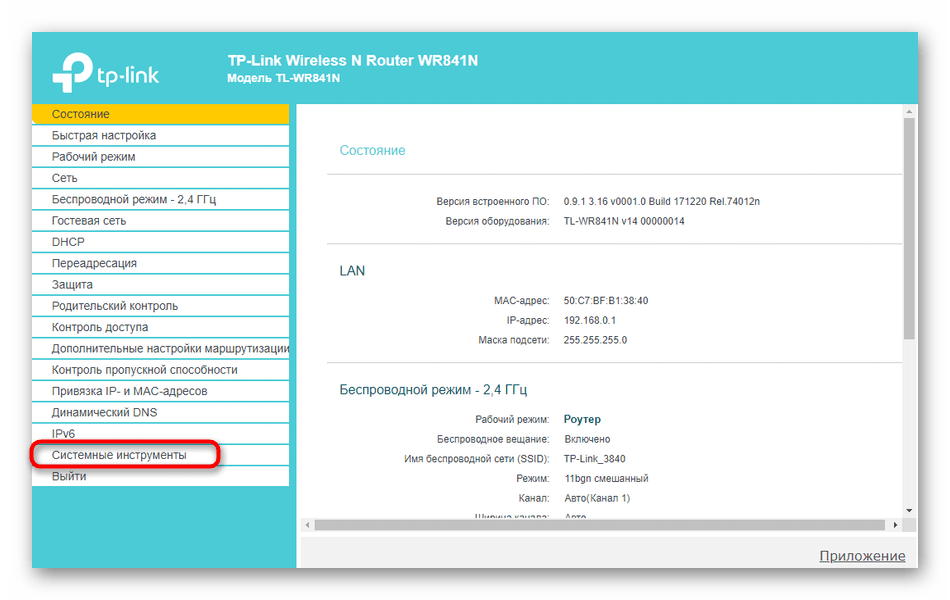
After that, there are only a few simple manipulations to perform. We suggest to disassemble it on the example of the TP-Link model, and all you have to do is to orient yourself in the available web-interface and make the same actions.
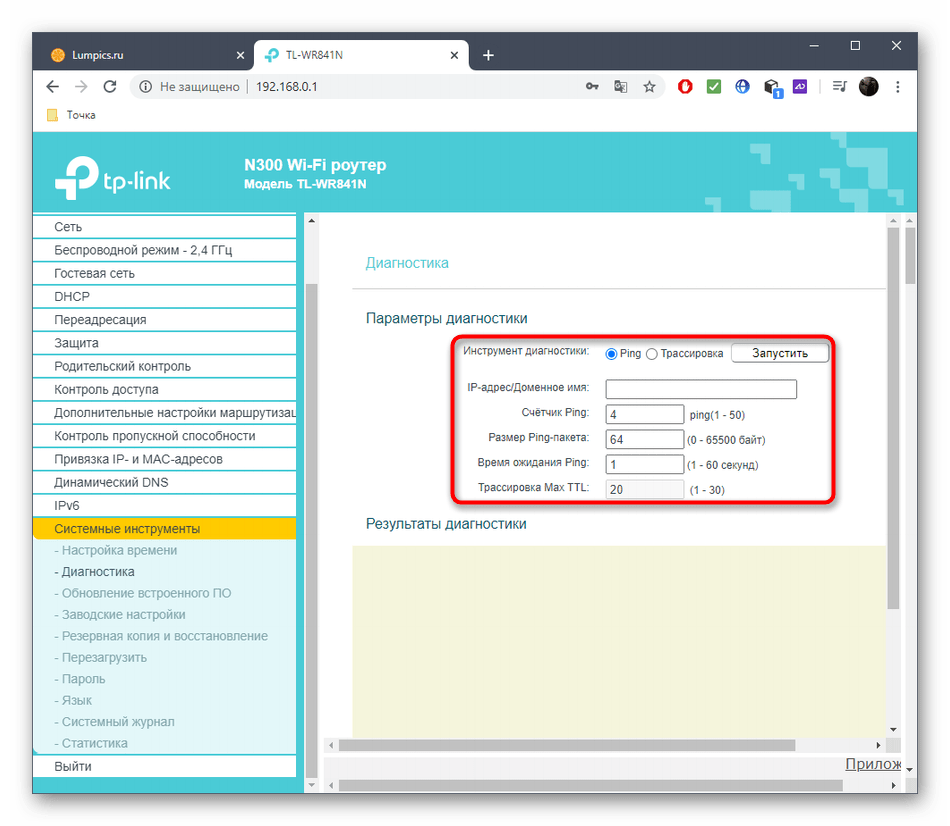
- In the left menu go to "System Tools.
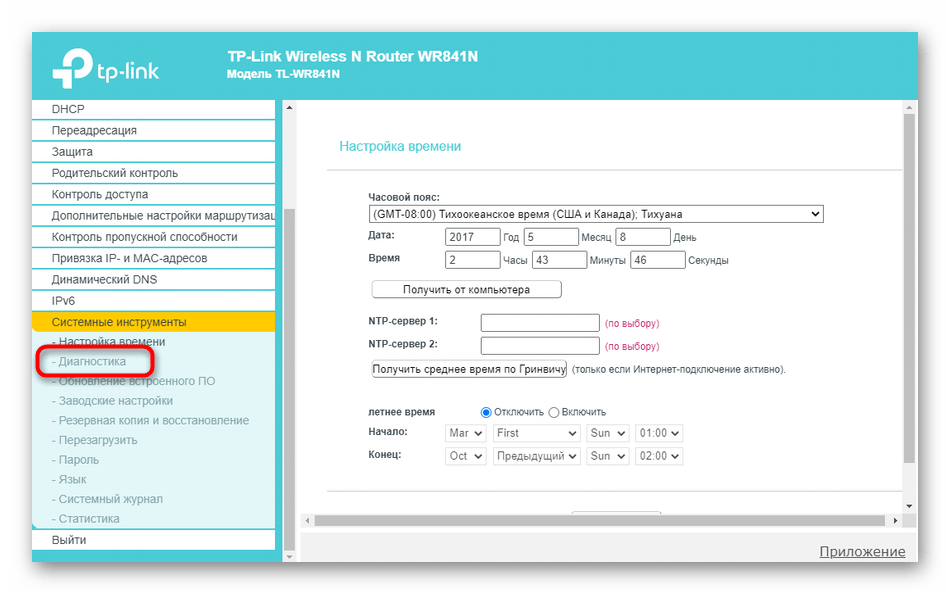
- There you are interested in the section "Diagnostics"..
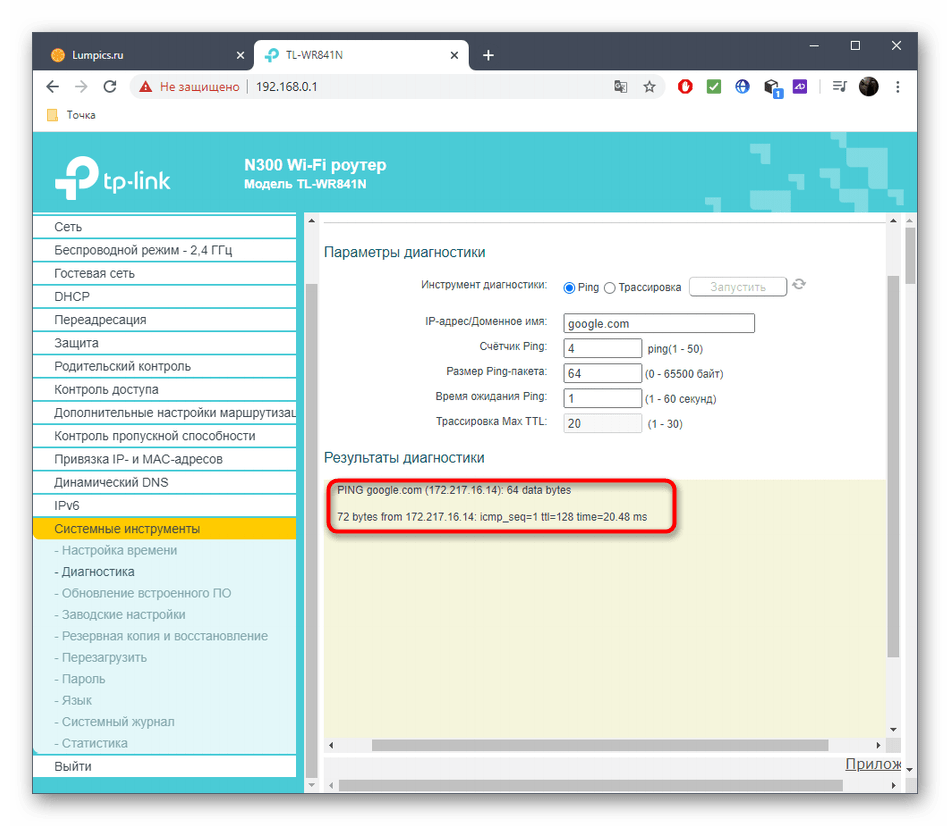
- Mark the marker next to the test you want to perform. As you can see, it may be pinging or tracing, and also specify the IP address or domain of the site to test.
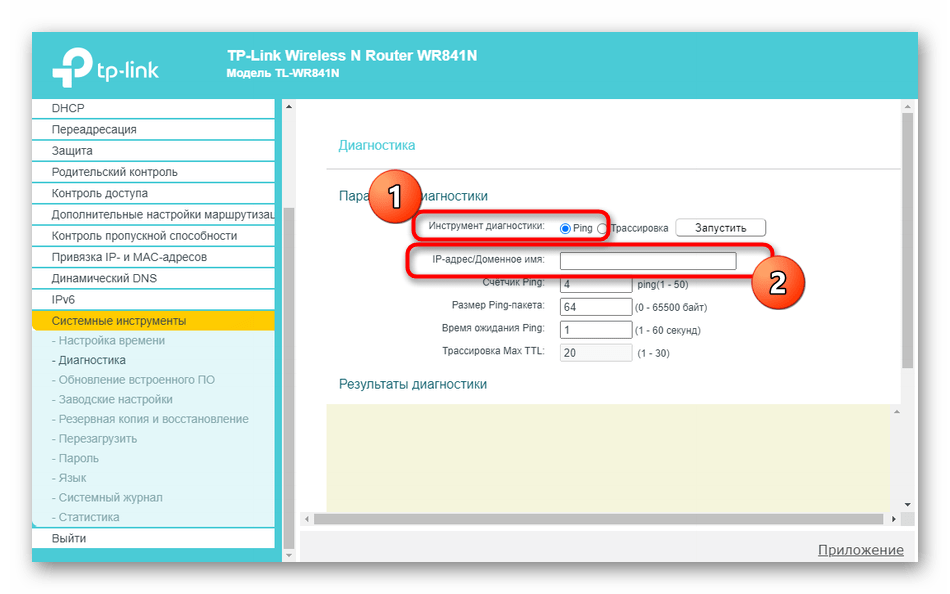
- Read the results and analyze them as described in the methods above.
All ways of testing
At home, the most striking parameters that affect your wi-fi remain the range and power. Sometimes the test shows significant improvements after the router is properly configured.
Testing options vary depending on what you plan to test your wi-fi speed with – smartphone, laptop, tablet.
Via Windows
There are special desktop gadget programs online. If the question of speed arises frequently, it is necessary to install one or two of these gadgets.
The essence of their work is simple: on schedule or at the request of the user, they test wi-fi, showing the test results in real time. These include Systometer, Netwotk Urilization and others.
File transfer
There are three nuances to consider before using this method:
- The method is ideal for testing speeds between devices on a home network – a router without an external hard drive plugged in is not one of them;
- If laptops were previously configured on a wi-fi connection to the router, they must be reconfigured to a direct connection, bypassing it;
- The method is a bit inflated, it will affect every extra link in the chain of connections.
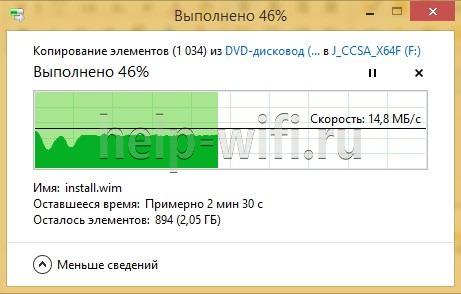
The test is simple. You copy a file from one computer to another. The file must be big, e.g. a disk image of the OS. The copy window will show the speed in Mb/sec along with the process graph. By solving the arithmetic example (multiplying the number by 8 to convert megabytes into megabits), we get the average wi-fi speed.
Online services
If it can be difficult to reconfigure computers, there are options for checking online. One of them – the service Npnerf – is presented above.
The Speedtest.net meter, familiar to all experienced users, is also suitable for one-time measurements. If you use it regularly, it is recommended to register on the resource, the choice of settings will be larger.
How to increase the speed
In many cases, the quality of the wireless connection depends only on the correct settings and location of the router.
- The most common way to solve the problem is to increase the transmitter power. This can be done in the router settings. How exactly depends on the model. For example, in Tp-Link routers you have to enter the menu "Wireless", select "Wireless Advanced", then "Transmit Power". You can set the reception level there to High, Medium, or Low.
- If your home is large, you'll need to find a more convenient location for the router, closer to the center.
- The antenna will broadcast the signal 360 degrees. And if the router is in a corner, it is turned (if it is supported by the design) in the direction of the receivers – deep into the house. Sometimes checking the Internet speed even after such a simple change shows completely different results.
- Connect to a different provider or choose a different tariff. For example, the ISP has 100 Mbit, it is connected to the router port at 100 Mbit too. Even if the manual for the device says 1000 Mbit (1 Gbit), the actual speed of the devices connected to it, both by wire and wirelessly, will not be more than 100 Mbit.
So, there are many programs and applications that estimate the speed of a wireless connection. It is useful to know it in order to properly configure the router and make networking more comfortable.
Read More: