The WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) quick setup function is supported by many modern Wi-Fi networking devices (e.g., smartphones, tablets, SMART TVs, printers). … WPS can be used with Microsoft Windows, Android and WPS-compatible devices.
- The difference between LAN, WAN, WLAN, WiFi – Russian Blogs
- What is a WAN?
- What is a WLAN in a router
- Pros and cons of use
- Advantages of the technology
- What is WLAN on a router and why do you need to know about it?
- Enabling and disabling the feature on your router
- TP-Link
- ASUS
- Zyxel Keenetic
- D-Link .
- Result
- What are the buttons
- Power
- Turning Wi-Fi on and off
- WPS (QSS)
- What is WLAN on a router and why do you need to know about it?
- Wireless data transfer operating frequency
- How many lights should the router have on?
- WLAN support in software
- Connecting and configuring a WLAN
- Step by step guide
The difference between LAN, WAN, WLAN, WiFi – Russian Blogs
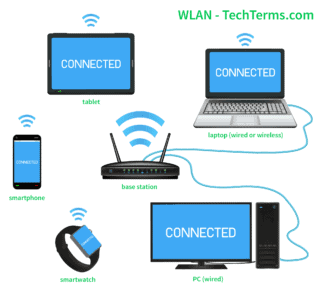
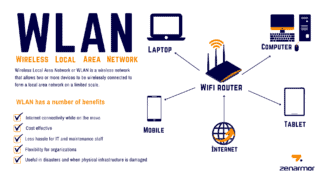
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) is a wireless local area network. In this way of networking, data transmission is carried out via radio; the networking of devices takes place without the use of cable connections….
The main advantages of this technological solution are as follows:
- Convenience. This advantage applies to both network owners and end users. For the first ones, installing and configuring WLAN is cheaper than laying cables. In addition, in some cases, installation of cable is simply impractical or impossible due to the peculiarities of the terrain, the location of buildings and communications. Users get the opportunity to use a stable high data transmission in a certain area of coverage.
- Network expansion. Technology can be easily expanded by installing additional access points.
- Mobility. Coverage virtually ignores obstacles, allowing users to use the network equally well on the move, on different floors or levels, in different rooms.
- Ease of installation. It's much easier to build than laying cables.
- High speed and considerable coverage. The speed is comparable to cable connection and reaches 100 Mbit / s. Reliable signal reception is achieved within a radius of 150 m, with the presence of additional access points can expand and more.
- Simultaneous operation of several subscribers with the same signal level for each.
- Unification. WAN is perfectly compatible with numerous devices from a wide variety of manufacturers.
What is a WAN?
"WAN" literally means "Wide Area Network". Which can be translated into Russian as "Global Area Network". Such a network combines a huge number of different nodes, located in different places and at different distances from each other. It can connect cities, countries and even continents. In other words, " WAN " is what we used to call the Internet.

What is a WLAN in a router
First, let's break down what a WLAN on a modem is, and what "it's eaten with". Wireless routers (routers) are used as the main point in the WLAN network. The functioning is based on the IEEE 802.11 standard, and the system itself is sold under the better-known brand of Wi-Fi.
When considering what WLAN on a router means, it is also important to understand how the system works. It uses radio waves that pass through walls, slabs, or other obstacles. The range and coverage is up to 160 m, depending on the type of router and the existing interference in the signal path.
Another point is the WLAN button on the router. It is not used on all routers and is designed to enable the option. There is also a WLAN indicator, but its designation can be different. Its image has the form of several semicircular waves (Wi-Fi symbol). In normal mode, the indicator should be lit or blinking.
Pros and cons of use
Having considered the question of what WLAN means on the router, you can summarize the advantages and disadvantages of the technology.
- Usability. This advantage applies only to the owner of the WLAN, as well as consumers of the service. For the former, installing and configuring WLAN on a router costs less when compared to running wire. Sometimes the use of wire is impractical because of the location, topography, position of buildings and communications.
- Network Extension. If you set up WLAN in the router, you can increase the coverage of the Internet in the area up to 150-300 m. If desired, you can connect additional routers or repeaters to increase the coverage area. With some skills you can make your own repeater from a router, it is not as difficult as it seems.
- Ease of installation. Setting up a WLAN is easier than running a cable down the street or indoors.
- Mobility. Wi-Fi networks don't fear obstacles, allowing you to connect to the Internet in the presence of partitions, walls or other obstacles.
- Simultaneous connectivity. Large numbers of users can connect to the Internet at the same time after preconfiguration.
- High speed. In the section on what is a vlan on the router, we have already noted that the connection speed can reach 108 Mbit/s. The final parameter depends on the total load on the Internet.
- Compatibility. The WLAN system successfully works with devices from different companies-manufacturers.
The listed advantages make the Wi-Fi networks a really convenient solution for home and business.
The technology has a number of disadvantages, which should be taken into account:
- Short data transmission distance. This disadvantage is characteristic of routers working on old protocols. Other parameters also affect the operating range, for example, the nature of the area. So, in open areas the signal can reach 300 m. In the presence of obstacles the distance is limited to 100 m. In a large office the range is even less – 20-40 m.
- Low speed. In older WLAN protocols on the router (802.11n), the connection speed is limited to 100 Mbps. For comparison, in cable networks this parameter can reach 1 Gbit/s. The only hope is the introduction of the new 802.11ax protocol.
- Health Risk . Many studies have been done regarding WLANs. A number of scientists declare that Wi-Fi networks are dangerous to health. For example, it is not recommended to work near signal sources (routers) and try to turn them off at night. But such statements are more in the realm of speculation, because the real facts have not yet been provided.
- The level of security. In terms of protection against hacking wired network wins. But if you know how to configure the WLAN on the router, know what kind of network it is, and how to protect it, you can minimize the risk of hacking. Existing WEP encryption protocols imply encryption with keys of up to 40 characters. But even that protection can be cracked by sniffing packets. To guard against the risks, it's important to avoid working on public Wi-Fi networks.
- High energy consumption. Laptops, smartphones, tablets, and other devices connected to a WLAN router waste more power. As a result, you have to charge the power supply more often.
- Incompatibility of some WLAN equipment. Before setting up a WLAN network, compatibility issues need to be sorted out. Difficulties may arise only if you use equipment from different manufacturers. But this is not always the case.
Advantages of the technology
The main advantages of such a technological solution are as follows:
Technology is currently developing rapidly, which makes having such an access point as WLAN in a modern phone a necessity. The cell phone now is not just a tool for calling and messaging, but a full-featured device for work and entertainment. Whether you have iOS, Microsoft's mobile version or Android installed in your gadget, WLAN will definitely be available there.
What is WLAN on a router and why do you need to know about it?

Internet users often ask what WLAN on a router is, how to enable it, and what the pros and cons are. Wireless Local Area Network mode is a system that allows you to share data and is designed as an alternative to wired networks. It is used in offices, homes, apartments and other facilities for wireless connection to the Internet without using cables and at high speeds.
Enabling and disabling the feature on your router
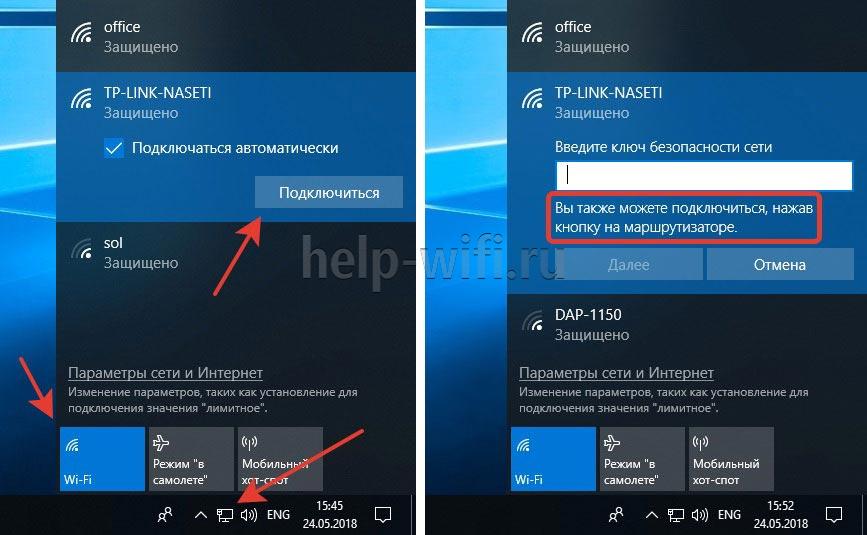
Some routers don't physically have a UPN button, but the technology itself is supported by such wireless routers. Here's how to connect devices to a wi-fi network via WPS if there is no button on the router.
TP-Link
If the TP-Link router doesn't have the button, we open the router web-interface and click the WPS/QSS function. For instructions on how to access the TP-Link router control panel, click here.


By default, this technology is always enabled and you click the "Disable WPS" button to disable it. The software connection is made by means of a PIN-code, which is indicated on the bottom of the device. Usually it is a combination of 8 digits. In these settings you can view the PIN-code and generate new values.
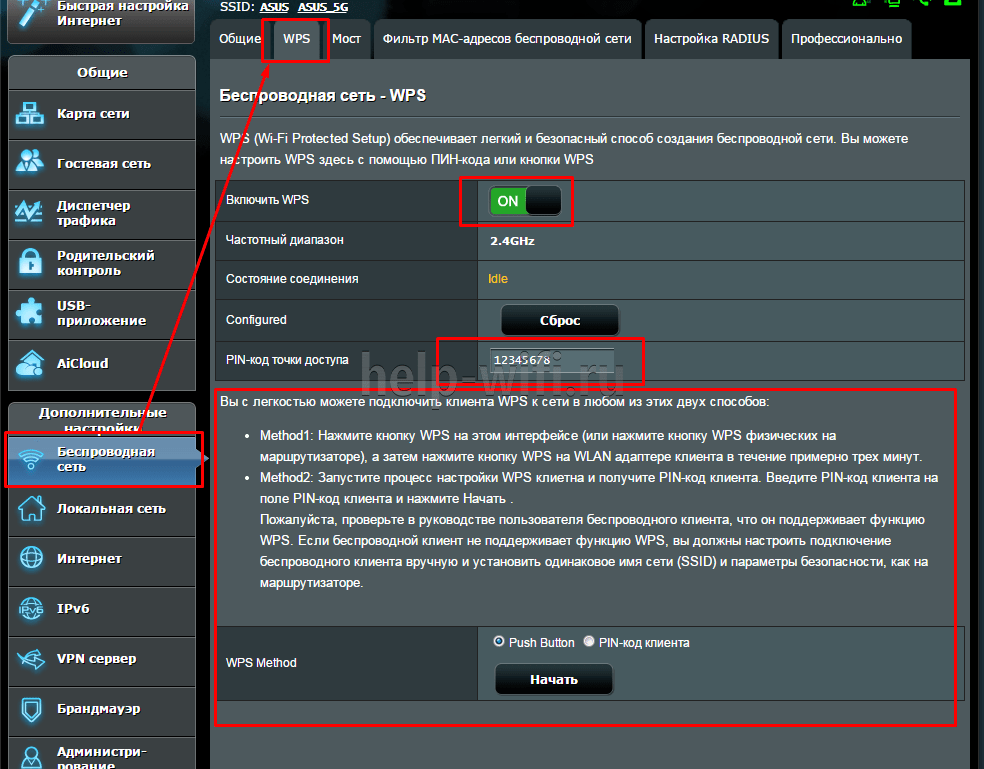
ASUS
The principle of setting the UPU on Asus is similar. Enter the router web interface at 192.168.1.1. Open the tab "Wireless Network – WPS" and set your parameters.
Zyxel Keenetic
To set up WPS on Zyxel Keenetic router, do the following. In web-interface you have to open "Wi-Fi" tab and switch it on. To disable WPS on the router, proceed the same way.

D-Link .
Open the router control panel, where we find the menu "WPS Wi-Fi" to enable WPS. In the tab that opens, turn on the technology, as this device leaves it disabled by default.
Result
Knowing the features of Wi-Fi and the purpose of the WLAN button on the router, figuring out what it is and how it works, you can forget about wires and replace them with a wireless connection. The main thing is to enter the settings correctly and remember about security, which can be provided by setting a strong password.
Modern routers can be equipped with buttons that perform various functions and simplify the work with the device. The list of them is not long, but not all users are aware of their purpose. In this article we will tell you what are the buttons on routers and what they are for.
What are the buttons
Usually they are located on the back panel. But there are some that need to be accessed at all times. They can be placed on the front panel of the device.

Let's look at what are the buttons on Wi-Fi routers and what they mean.
Power
It is used to turn on/off the power. It is not found on all router models. It is usually located on the back panel next to the power adapter jack. Allows you to turn the device off without disconnecting the adapter from the outlet. This is convenient, especially if you need to reboot the device. If your router doesn't have it, you'll need to unplug the adapter from the power outlet and then plug it back in to reboot. It's not very convenient if the outlet is located in a hard-to-reach place, behind a cabinet or under a desk. Sometimes it is used to turn off the router at night.
Turning Wi-Fi on and off
Some routers have a button that you can press to turn off or turn on the wireless broadcast. Just as with the Power button, it is not available on all router models. It is labeled WLAN or a wireless network connection icon. It is usually located on the front of the device, on the top or on the side. If it is not available, to disable and enable Wi-Fi you will need to log in to the web interface of the device and do it from there. Having a hardware button simplifies this procedure.
On ZyXEL routers, the Wi-Fi button is located on the front panel. When pressed briefly, it acts as a WPS button, which we'll look at below. If it is held down for more than 3 seconds, it will turn Wi-Fi on and off. You can see the current status on the WLAN indicator.
WPS (QSS)
This button is available on most modern routers.
On TP-Link routers, it is referred to as QSS. It is located on the top or on the side, sometimes on the back panel and is often marked with two arrows. Behind the abbreviation WPS stands Wi-Fi Protected Setup, a technology of simplified connection to Wi-Fi network. It allows you to connect to a wireless network without entering a password.
What is WLAN on a router and why do you need to know about it?

Internet users often ask what is WLAN on a router, how to enable it, and what the pros and cons are. Wireless Local Area Network mode is a system that allows you to exchange data and is designed as an alternative to wired networks. It is used in offices, homes, apartments and other facilities to communicate wirelessly with the Internet without using cables and at high speeds.
Wireless data transfer operating frequency
Let's start with selecting a wireless operating frequency.
Since this router is dual-band, it can broadcast two Wi-Fi networks:
If you don't need a particular network, you can go to the "Select Working Frequency" tab, and disable the network on that frequency. Uncheck the box next to the network you don't want and save your settings.
But you can leave both networks. For example, connect older devices to 2.4 GHz, and those that support it to 5 GHz Wi-Fi.
How many lights should the router have on?
Modern Wi-Fi routers have light indicators on the front panel. Usually there are 8-9 of them, on some models there may be more, depending on the hardware configuration. The lights may glow or flash with varying degrees of intensity.
802.1ad -is an open standard (similar to 802.1q) that describes a double tag (Fig.4). Also known as Q-in-Q, or Stacked VLANs.. The main difference from the previous standard is the presence of two VLANs – external and internal, which allows you to split the network is not 4095 VLANs, but 4095×4095.
Also, the presence of two labels allows you to organize more flexible and complex networks of the operator. There are also cases where the operator needs to organize L2 connection for two different clients in two different cities, but the clients send traffic with the same tag (Fig. 5).
Client-1 and client-2 have branches in city A and B, where there is a network of the same provider. Both clients need to connect their branches in two different cities. In addition, for their own needs, each client tags traffic with 1051 VLANs. Accordingly, if the ISP will pass the traffic of both clients through itself in one single VLAN, the failure of one client can affect the second client. Moreover, one client's traffic can be intercepted by the other client. The easiest way for an operator to isolate client traffic is to use Q-in-Q. By adding an additional tag to each individual client (e.g., 3083 to client-1 and 3082 to client-2), the operator isolates the clients from each other and the clients do not have to change tags.
WLAN support in software
- BSD family operating systems (FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD) can work with most adapters since 1998. Drivers for Atheros, Prism, Harris/Intersil and Aironet chips (from the respective Wi-Fi device manufacturers) are usually included in BSD OS starting with version 3. In OpenBSD 3.7, more drivers for wireless chips were included, including RealTek RTL8180L, Ralink RT25x0, Atmel AT76C50x, and Intel 2100 and 2200BG/2225BG/2915ABG. This has partially solved the problem of the lack of open source wireless chip drivers for OpenBSD. It is possible that some drivers implemented for other BSD systems may be ported if they have not already been created. NDISwrapper is also available for FreeBSD.
- OS X (formerly Mac OS X). Adapters made by Apple have been supported since Mac OS 9, released in 1999. Since 2006, all Apple Inc. desktops and laptops (as well as the later iPhone phones, iPod Touch players, and iPad tablets) have come standard with Wi-Fi adapters, the Wi-Fi network is now Apple's primary solution for data transfer, and is fully supported by OS X. It is possible to have the computer adapter act as an access point, allowing Macintosh computers to be linked into wireless networks in the absence of infrastructure if needed. Darwin and OS X, while overlapping with BSD, have their own, unique implementation of Wi-Fi.
- Linux: Since version 2.6, support for some Wi-Fi devices has appeared directly in the Linux kernel. Support for Orinoco, Prism, Aironet, Atmel, Ralink chips is included in the main kernel branch, ADMtek and Realtek RTL8180L chips are supported by both closed manufacturer drivers and open, community written drivers. Intel Calexico is supported through open source drivers available at SourceForge.net. Atheros is supported through open source projects. Support for other wireless devices is available using the open source NDISwrapper driver, which allows Linux systems running on Intel x86 computers to "wrap" vendor drivers for Microsoft Windows for direct use. At least one commercial implementation of this idea is known. The FSF has created a list of recommended adapters, more information can be found on the Linux wireless website.
Connecting and configuring a WLAN
What is a Home Wireless LAN and what are its components? It will consist of a modem/router (access point) and one or more computers (clients). Assuming that you already have a modem or router, a fixed Internet connection and the necessary WLAN driver (if required, it can be easily downloaded online for any model of wireless adapter).
- It is desirable to raise it higher so that the signal is well distributed throughout the living space;
- Remove to the maximum distance from various equipment also using the 2.4 GHz frequency (TV, microwave, etc.), so as not to interfere with the connection.

Step by step guide
Moving on to the configuration of the access point (ie, router):
- Go into any browser and in the address bar enter the IP-address of our modem. Find it in the documentation supplied with the device. We will press the Enter button.
- We will be prompted to enter a username and password. You can also find them in the corresponding documents. The default is usually admin/1234 (but may be different).
- Then we get to the main menu and find the WLAN item. How do I connect the wireless network? Next to Wireless Lan, check the box to activate it. In the next line Name (SSID) enter the name of your network (under which it will be shown in the list of available networks). Then write the name of the region, and in the Channel field put Auto. Press "Apply".
- Go to the encryption settings (different methods). Open the tab Wireless Settings and select WPA (or WPA2) – this protocol is better than the outdated 802.1x. Then you need to enter the password (depending on the router model it may be called differently – Pre-shared Key/Security Ecryption, etc.). It must be at least 15-22 characters long. Click on "Accept".
- Now you need to enter the names of the devices which will be allowed to access your wireless network. Select them from the list of connected equipment in the Setup Access List (Advanced/Wireless Settings menu).
- The final touch: put a checkmark in the Turn Access Control On checkbox. You are now ready for your secure WLAN.
- What is a VPN? It is a private virtual network between the access point (router) and your computer, which it is recommended to use for secure data transmission within the network. There is a program called Hotspot Shield for this.
- To configure all the client computers on the network, use the setup wizard and set all the parameters that the access point uses.