Some of the chipset supported by Kali Linux include:

- Article Guide 2020 on starting monitor mode in TP-LINK TL-WN722N v2/v3 Kali Linux Wardriving
- Installing dependencies in Kali Linux
- Installing the driver for TP-Link TP-WN722N V2-V3
- Conclusion
- You might also like
- Installing the unofficial Figma client on Linux
- Installing the Sublime Text Code Editor on Debian/Ubuntu
- Live Wallpapers on Linux systems
- 26 Comments to " Kali Linux monitoring mode for TP-LINK TL-WN722N V2/V3 "
- Connect a Wireless Adapter to Kali Linux Virtual Machine (VirtualBox)
- Automatically Connect the WiFi Adapter to a VirtualBox VM
- Connect a Wireless Adapter to Kali Linux Virtual Machine (VMware Player)
- Enable Monitor Mode
- Troubleshooting When Enabling Monitor Mode
- Categories
- Useful commands
- How
- Reconnaissance
- Provide USB privileges to guest
- Provide USB recognition to guest
- Blacklist Wifi Module on Host
- TP-Link WN722N monitor mode on Kali Linux
- Setting up TP-Link WN722N in monitor mode on Kali Linux
Article Guide 2020 on starting monitor mode in TP-LINK TL-WN722N v2/v3 Kali Linux Wardriving
Today in the program, transforming the monster into a beauty, let's make the manufacturing bug work to our tune. We will not talk about TP-LINK TL-WN722N v2/v3 for a long time, let's get down to business.
What would you have everything worked, follow strict requirements and follow the instructions, because I can not guarantee the performance of this instruction for any other distribution / kernel, actually about the distribution version, download Kali Linux 2019.2, if already installed, make sure you are on the kernel 4.19 if not, here's a link to download Kali Linux 2019.2
Under no circumstances do not update any packages, do not enter update && upgrade commands, they will update the kernel of your Kali Linux 2019.2 distribution and it has to be 4.19! Do not touch the terminal after installing the OS, follow the instructions!
After complying with all the requirements, proceed to the instructions, first go to the terminal and enter the following commands:
Finishing, after all these steps strictly according to the manual, do not enter anything else into the terminal until you have rebooted Kali Linux recall that the kernel must be 4.19. After rebooting the operating system, disconnect the TL-WN722N v2/v3 from the USB and re-insert.
ifconfig wlan0 down airmon-ng check kill iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor ifconfig wlan0 upiwconfig wlan0 IEEE 802.11b ESSID:"" Nickname:"" Mode:Monitor Frequency:2.447 GHz Access Point: Not-Associated Sensitivity:0/0 Retry:off RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off Encryption key:off Power Management:off Link Quality=0/100 Signal level=-100 dBm Noise level=0 dBm Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0 Tx excessive retries:0 Invalid misc:0 Missed beacon:0 eth0 no wireless extensions. lo no wireless extensions.Congratulations, now you can make the beauty dance to your tune and justify your $10.
Thank you all for your attention, thank you for the motivation to move and design the manual @f22. Thank you @The Codeby for your understanding. Thanks to all the moderation members and forum members and haters for their help in finalizing the "Article".
I'm sure a lot of people could use material like this.
You could also add a scan screen, like airdump-ng or wifite.
I haven't quite figured out the forum engine yet, but somehow I managed to add a screenshot)
Is it possible that you have a third version?
Good for a year on the forum debate on the topic v.1 VS v.3 )))
I propose to attach the same poll. Was the article useful?
Exactly, I was thinking that I should buy it for nothing, but I remembered the words of Elon Musk "I'll give up when I die or will not be usable" and decided not to let go of the hands and yet it worked!) I started it and tested, the capture of handheaks from "their" Wi-Fi networks was successful as well as brute-force using Hashcat on CUDA cores where the selection was 450-500k combinations per second and all this on kali linux version is not the latest, can even say the last year))))
true speak!) I often came across your forum when googling manuals to run the adapter and tried almost all methods described here to start the tl-wn722n v2/v3 in monitor mode unfortunately none of the topic did not help, after I could do it myself I decided to share this manual on your forum so that to help those many young hackers do not let go and give hope)!
by the way who found the passchalk put a mark under this comment and do not palim where it is)
Installing dependencies in Kali Linux
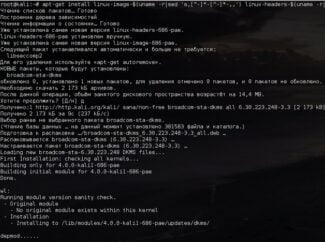
And so, the first thing to do is to update the system to the current one, this is done by commands "sudo apt update && sudo apt dist-upgrade". Then install the necessary dependencies to build the modified TP-Link TP-WN722N V2-V3 driver:

When the dependencies are installed, you need to restart Kali Linux, this can be done by "sudo reboot" or from the menu, whichever is more convenient… Next update the kernel headers, at the time of writing this article, Kali Linux 2021.4 has kernel 5.15 installed:
The next step towards our goal is to create the file realtek.conf and put the following content into it "blacklist r8188eu". But before that, we need to switch to root user mode with the command "sudo -i". Execute the following sequence of commands:
sudo -i echo "blacklist r8188eu" >> "/etc/modprobe.d/realtek.conf"Installing the driver for TP-Link TP-WN722N V2-V3
Let's proceed to installing the modified driver for TP-Link TP-WN722N V2-V3 adapter, you can take it from Aircrack-ng developers' github, where it is freely available. For this purpose we will use "git" utility and clone it into our system by running the command:
When the cloning process of this repository is completed, we move to the directory "rtl8188eus" using the command "cd", which has a separate article available at this link. Well, we go to the directory "rtl8188eus":
Next, it is necessary to build the driver from the sources that we received, to do this we execute the command:
When the process of building the driver for TP-Link TP-WN722N V2-V3 is completed, we will install it:
Reboot the system, as you remember, it can be rebooted with the command "sudo reboot". Actually, when you boot into Kali Linux again, you can put our adapter into monitoring mode.
Conclusion
TP-LINK TL-WN722N Wi-Fi adapter has on-board Realtek RTL8188EUS chip, in fact, it (the chip) and plays a big role when choosing a Wi-Fi adapter for pentesting. Professionals, who earn their bread by this hobby, most likely will buy Alfa Wi-Fi adapter for their business. But that's not necessarily worth it, because as already mentioned, there are plenty of alternatives. TP-LINK TL-WN722N Wi-Fi adapter is one of them. Taking into account that it is not expensive and is suitable for scanning networks, it will be enough for beginners.
That will be all for today. I hope this article will be helpful for you.
Cyber-X Magazine
You might also like
Installing the unofficial Figma client on Linux
Installing the Sublime Text Code Editor on Debian/Ubuntu
Live Wallpapers on Linux systems
26 Comments to " Kali Linux monitoring mode for TP-LINK TL-WN722N V2/V3 "
In case of the "/lib/modules/5.7.0-kali1-amd64/build" error, install the 5.8 kernel with the commands:
sudo apt install linux-image-5.8.0-kali2-amd64
sudo apt install linux-headers-5.8.0-kali2-amd64
sudo apt-get install linux-headers-$(uname -r)
After that you can move on to the "make" command
To enable monitoring mode in Kali 2020.4, run the following commands:
sudo apt install linux-headers-$(uname -r) dkms bc
git clone https://github.com/aircrack-ng/rtl8188eus.git
cd rtl8188eus
sudo -i
echo "blacklist r8188eu" >> "/etc/modprobe.d/realtek.conf"
exit
sudo make
sudo make install
It is necessary to look what kind of chip is installed in V1 version and whether it is possible to switch monitoring mode on it somehow. In the case of versions V2 and V3 it is the same chip
Kali Linux 2020.3 sudo ifconfig
sudo airmon-ng check kill
sudo airmon-ng start wlan0 sudo airmon-ng start wlan0 PHY Interface Driver Chipset phy0 wlan0 8188eu TP-Link TL-WN722N v2 Newly created monitor mode interface wlan0mon is *NOT* in monitor mode.
Removing non-monitor wlan0mon interface… WARNING: unable to start monitor mode, please run "airmon-ng check kill".
Did you did everything exactly as described? I mean, did you install modified driver? Is it the same Wi-Fi interface? Maybe you just pointed the wrong interface. And you have the wrong command sequence:
sudo ifconfig wlan0 down
sudo airmon-ng check kill
sudo iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor
sudo ifconfig wlan0 up
sudo iwconfig Your message says that your interface is not switched to monitor mode
I did, the issue is that it asks me to authenticate myself as a user. It says Username for 'https://github.com'.
Please help me, my make install says this:
cut: /etc/redhat-release: No such file or directory
install -p -m 644 8188eu.ko /lib/modules/5.10.0-kali3-amd64/kernel/drivers/net/wireless/
/sbin/depmod -a 5.10.0-kali3-amd64 Заранее спс
Connect a Wireless Adapter to Kali Linux Virtual Machine (VirtualBox)
To connect a wireless adapter to your Kali Linux virtual machine, when using VirtualBox, you can go in the Oracle VM VirtualBox menu > Devices > USB > [select_your_adapter].
It may not list the name of the WiFi Adapter, but something related to the chipset, instead. Here, I’m using a TP-LINK TL-WN722N 2.4GHz v2/v3, and as you can see, it’s displaying Realtek 802.11n NC.
Automatically Connect the WiFi Adapter to a VirtualBox VM
You can also automatically connect a wireless adapter to your Kali Linux virtual machine, when running VirtualBox. This way, you don’t have to manually connect it every time
- Shutdown the Kali virtual machine if it was already running
- Connect your Wireless USB adapter to your PC
- Right-click on your Kali Virtual machine and select the Settings option. A window will open displaying all the different configuration options.
- Click on the USB option and check the Enable USB controller check box.
If you are not sure of the adapter’s name, just remove it, and you will notice the name that will disappear from the VirtualBox USB list.
Your wireless adapter will be listed under the “USB Device Filters” section.
To finalize everything, right-click on your newly added USB filter and select the Edit Filters option.
A window will open listing all the details about your wireless adapter. Then, on the Remote option, click on the dropdown and select Yes.
Connect a Wireless Adapter to Kali Linux Virtual Machine (VMware Player)
To connect a wireless adapter to your Kali Linux virtual machine, when using VMware Player, you can go to the VMware Player menu > Player > Removable Devices > [your_adapter] > Connect (Disconnect from host).
It may not list the name of the WiFi Adapter, but something related to the chipset, instead. Here, I’m using a TP-LINK TL-WN722N 2.4GHz v2/v3, and as you can see, it’s displaying Realtek 802.11n NC.
You should then receive a message informing you that the device will be safely stopped and disconnected from the host machine, so it can then be connected to Kali Linux in the VMware player.
I’m not sure of an easy way how you can automatically connect a WiFi Adapter with VMware Player, as we did with VirtualBox. The solution in VMware knowledge base seems to involve a bit of work https://kb.vmware.com/s/article/1648 , and I haven’t tried it myself. If anyone has an easier solution for this and would like to share, then we’d love to hear from you.
Enable Monitor Mode
Here’s the output you should be seeing. You can see that the adapter is set to Mode: Monitor .
Troubleshooting When Enabling Monitor Mode
In some cases it doesn’t work right away. For example you may get the error Error for wireless request "Set Mode" (8B06) : SET failed on device wlan0 ; Operation not permitted.
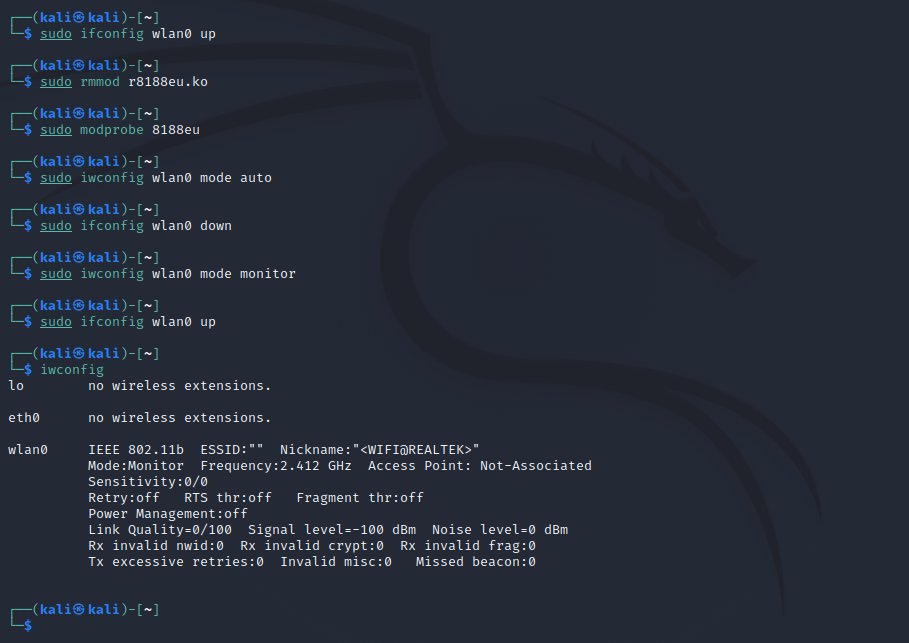
The solution that has worked for me every time is the following (credit to this Github user’s comment ).
sudo ifconfig wlan0 up sudo rmmod r8188eu.ko sudo modprobe 8188eu sudo iwconfig wlan0 mode auto sudo ifconfig wlan0 down sudo iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor sudo ifconfig wlan0 upNow when you check iwconfig you should see the adapter is in monitor mode.
Categories
I have a problem with Tl-wn722n on kali VM. The make comment doesn’t work; an error shows up at the end: make: *** [makefile: 1368 modules] error 2. how should I solve it?
On the last Kali version, when i execute “Make” i have errors.
Probably its caused because the “make” command runs a scripts that looks into the build folder on the linux kernel headers.
This error occurred to me on Kali 2022.3. The way that I managed to workaround was installing the linux headers from the Kali repositories on this link: https://http.kali.org/kali/pool/main/l/linux/
You can know which one you should install by using the “uname -a” command and looking which distro you have. The file which you need to install begins with a “linux-headers” prefix and a extension “.deb”.
After downloading it, you could run the command “dpkg -i .deb”. You could run into some dependencies problems, and for those you need to search on the internet to see which packages you need to install.
After you manage to run the above command without errors, you should be fine to run the “make” command again.
This works on kali-virtualbox, one of the comments didnt work though $ sudo rmmod r8188eu.ko but carried on with the next comment ($git clone https://github.com/aircrack-ng/rtl8188eus ) and it’s all working using TL-WN722N V2.
Nice! Thanks for commenting! Very glad to hear you got it to work!
Thank you very much. Your guide is very detailed. It also works with TL-WN722N V4.
There is only one note that when I run Wireshark from Kali menu the wlan changes to Managed mode. Running wireshark from terminal “sudo wireshark” is the correct way to capture packets.
Cheers!
does the packet injection also work on this method?
Anyone else running into this error? E: Package ‘bc’ has no installation candidate
Does this affects the process?
It shows the following error while I executed
$ sudo iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor
Error for wireless request “Set Mode” (8B06) :
SET failed on device enp0s3 ; Operation not supported.
Useful commands
- iwconfig
- ifconfig
- sudo lshw -C network
- iwlist scan
- lsusb
- dmesg | grep -e wlan -e ath9
- contents of /var/log/syslog
- lsmod
- Release DHCP assigned IP. Similar to Windows ipconfig /release
dhclient -r [interface-name] - Renew DHCP assigned IP. Similar to Windows ipconfig /renew
dhclient [interface-name]
I want to be able to access the internet on my laptop at the same time that I’m penetration testing a client network. I use my phone as a wireless hot-spot to access the internet. The easiest way to do this is to use the laptops on-board wireless interface to connect to the phones wireless hot-spot and pass the USB Wifi adapter straight to the guest.
Taking the following statement: “The preferred way to get Internet over wlan into a VM is to use the WLAN adapter on the host and using normal NAT for the VM. Passing USB WLAN adapters to the guest is almost untested.” from here, I like to think of more of a challenge than anything else. It can be however, something to keep in mind. if you’re prepared to persevere, you’ll get it working.
How
Reconnaissance
When you plug the Wifi adapter into your laptop and run lsusb , you should see a line that looks like:
ID 0cf3:9271 Atheros Communications, Inc. AR9271 802.11n
The first four hex digits are the Vendor ID and the second four hex digits are the Product ID.
If you have a look from the bottom up of the /var/log/syslog file, you’ll see similar output to the following:
kernel: [ 98.212097] usb 2-2: USB disconnect, device number 3 kernel: [ 102.654780] usb 1-1: new high-speed USB device number 2 using ehci_hcd kernel: [ 103.279004] usb 1-1: New USB device found, idVendor=0cf3, idProduct=7015 kernel: [ 103.279014] usb 1-1: New USB device strings: Mfr=16, Product=32, SerialNumber=48 kernel: [ 103.279020] usb 1-1: Product: UB95 kernel: [ 103.279025] usb 1-1: Manufacturer: ATHEROS kernel: [ 103.279030] usb 1-1: SerialNumber: 12345 kernel: [ 103.597849] usb 1-1: ath9k_htc: Transferred FW: htc_7010.fw, size: 72992 kernel: [ 104.596310] ath9k_htc 1-1:1.0: ath9k_htc: Target is unresponsive kernel: [ 104.596328] Failed to initialize the device kernel: [ 104.605694] ath9k_htc: probe of 1-1:1.0 failed with error -22
Provide USB privileges to guest
First of all you need to add the user that controls guest to the vboxusers group on the host so that VM’s can control USB devices. logout/in of/to host.
Provide USB recognition to guest
Install the particular VirtualBox Extension Pack on to the host as discussed here. These packs can be found here. If you have an older version of VirtualBox, you can find them here. Don’t forget to checksum the pack before you add the extension.
- apt-get update
- apt-get upgrade
- apt-get dist-upgrade
- apt-get install linux-headers-$(uname -r)
- Shutdown Linux guest OS
- Apply extension to VirtualBox in the host at: File -> Preferences -> Extensions
Blacklist Wifi Module on Host
Unload the ath9k_htc module to take effect immediately and blacklist it so that it doesn’t load on boot. The module needs to be blacklisted on the host in order for the guest to be able to load it. Now we need to check to see if the module is loaded on the host with the following command:
TP-Link WN722N monitor mode on Kali Linux
The fact is that TP-Link WN722N version 1 comes with an Atheros AR9002U chipset and supports monitor mode. Versions 2 and 3 already come with the Realtek RTL8188EUS chip and do not support monitor mode and packet capture. TP Link N150 TL-WN722N version 1 is hard to find now, so a solution must be found.
The TP-Link WN722N version 2 Wi-Fi adapter fell into my hands. After connecting it, it worked and I was able to connect to my Wi-Fi network, but I need monitor mode and packet injection.
Let’s open the Kali Linux terminal and check the wireless network interfaces:
In my case, wlan0 is the built-in wireless interface and wlan1 is the adapter’s network interface.
Run the following command to check if the adapter supports monitor mode:
The screenshot above shows that the WiFi adapter does not support monitor mode, and to solve this problem, you will have to use the TP-Link WN722N driver to solve this problem.
Setting up TP-Link WN722N in monitor mode on Kali Linux
sudo apt install dkms bc build-essential libelf-dev -y
The screenshot below shows that we are already on the updated core:
echo "blacklist 8188eu" >> "/etc/modprob.d/realtek.conf" echo "blacklist r8188eu" >> "/etc/modprob.d/realtek.conf"
After that, the old drivers will be deleted and a reboot will be required.
After the reboot, you need to install a driver that supports monitor mode and TP-Link WN722N packet capture. To do this, we clone the aircrack-ng driver from GitHub:
The compilation process may take a couple of minutes depending on system performance. Then run the command to install the compiled driver:
Let’s restart the system. After the reboot, check the network interfaces:
Enable monitor mode on the wlan1 interface (in my case). To do this, we run the following commands one after the other:
sudo ifconfig wlan1 down sudo iwconfig wlan1 mode monitor
Now you can check the status of network interfaces:
Now the wlan1 WiFi adapter can work in monitor mode.
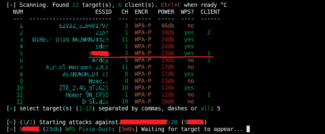
Let's check the operation of the adapter by scanning Wi-Fi networks:
We see that TP-Link WN722N version 2 can scan networks.
Read More: