Blocking WAN ping requests from outside, Stealth mode. Since ping requests are often used to determine the availability of a particular host on the Internet, by not responding to such a request, the computer hides its presence on the network. Many routers allow you to block ping requests or, more precisely, to block the responses to such requests by hiding your presence on the network. Content filtering. Content filtering is designed to limit internet users' access to the Internet resources with questionable content. Depending on the version, you can create a black or white list of URLs or IP addresses or use third-party filtering lists. It should be noted that content filtering can be applied to all computers in the local network or only to some of them, in addition, it is often possible to set a schedule for these lists. Access Control, Port Filtering Access Control, Port Filtering. In many small organizations, access to the Internet is limited. One of the options for this might be the use of a router. So, some users can allow access only to e-mail, while others can add access to web-pages and ICQ, and still others can use all services without restrictions. For ease of configuration, routers allow you to create groups of local users, for which you can allow or deny access. In addition, most routers allow activation of scheduled restrictions. Also of interest are the differences in the router's actions when blocking unauthorized traffic. Some simply block, giving the user the impression that the service is unavailable and does not manifest itself in any way, while others transmit a corresponding message to the user and register access attempts in the router's system log. Virtual Private Networking (VPN). Virtual private networking is a rather popular topic related to computer network security. VPN technologies make it possible to use public, insecure networks such as the Internet for secure communications, using encryption and digital signing capabilities. With such a connection, the user can work with the resources of the remote network just as with those of the local network. Many router manufacturers have started to release models with VPN support, ranging from simple VPN tunneling, to full-fledged built-in PPTP or IPSec servers. The following protocols are used to create VPNs: IPSec (Internet Protocol Security), PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol), L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol), SSL. VPN pass through tunnels (VPN pass through) allows VPN tunnels to pass through the router; this has become a de-facto standard, although not all devices could previously be set up for a VPN connection. VPN client Allows you to initiate a connection to a VPN server. It is of interest to subscribers of providers that provide network access via VPN (PPTP is often used), as well as for branch offices of enterprises that need a secure connection to the central office. VPN server Allows receiving connections initiated by clients. Often used in corporate headquarters to connect branch offices and employees. Support for VPN tunnels (VPN Endpoint). Creating a virtual tunnel between router networks most often involves the use of IPSec protocols, which allow transmitted data to be encrypted and decrypted, as well as to verify its immutability and exchange of keys. This is the scenario that is most actively used today to interconnect multiple remote networks.

Table of Contents
In the first article of the series "Local network with your own hands" we found that the router is the main component of the local network and performs most of the basic functions of data exchange. And if so, then its choice should be taken very seriously. It will determine many of the features of your home network, its performance and stability.
To make it easier for you to choose this complex device, let's take a look at the main characteristics of routers and understand what they are responsible for. I will intentionally simplify some of the wording when describing certain functions, trying not to overload inexperienced users with complicated technical information.
Types of routers
Generally speaking, routers can be divided into two large groups – wired and wireless. Already the names show that all devices are connected to the former only with cables, and to the latter, both with and without wires, using Wi-Fi radio technology. Therefore, in the home, it is wireless routers that are most often used to provide the Internet and to network computer equipment using different communication technologies.
Conclusion 1: If you are not pursuing any specialized tasks, it is better to buy a wireless router. This versatile solution will allow you to network equipment using different data transmission technologies.
General
Wikipedia:
Router (router is a network device that, based on information about network topology and certain rules, makes decisions about forwarding network layer packets (Layer 3 of the OSI model) between different network segments.
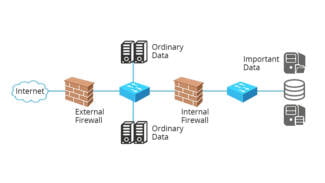
To the average user, a router is a network device that connects between the local network and the Internet. Often the router is not limited to just sending data between the interfaces, and also performs other functions: it protects the local network from external threats, limits access of local network users to Internet resources, distributes IP-addresses, encrypts traffic and much more. FirewallThe firewall is also known as a firewall. Designed to protect your network. It filters traffic between internal and external network segments according to predefined rules. NAT (Network Address Translation) – A network address translation technology. Allows you to translate the IP addresses of computers on your local network into external IP addresses and vice versa. With NAT, you can use one or more external IP addresses given by your ISP to connect almost any number of computers to your network. Most routers are capable of address translation so that they can be used to connect small networks to the Internet with a single external IP address. SPI. SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) technology allows you to further protect against attacks by inspecting the traffic in transit for correctness (operate at the network, session and application layers of the OSI model). Most routers today have SPI firewalls. Web-interface. The Web-interface allows you to control the router using a Web browser. This allows you to work with the router with minimal knowledge in the field of network technology. Almost all models produced today have a built-in Web-interface.
External interface
WAN – is the router's external interface, used to connect to your ISP. Most often the Ethernet (or FastEthernet 10/100 Mbps) interface is used as the WAN port. All parameters related to this section describe the type of connection. There can be several options for the connection type: Dynamic IP (Dynamic IP).Also called "DHCP Client". The router automatically obtains its IP address, default gateway addresses and DNS server addresses. This type of connection is quite widespread and gives the provider sufficient flexibility in configuring his network. In this case, customers may be given both permanent, reserved for clients addresses, and freely selectable from the range of available. Static IP address (Static IP) is most often used by corporate clients who need a permanent IP address. With this type of connection, the client needs to set its own IP address, default gateway address and DNS server address provided by the ISP. PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) This is an authentication method popular with DSL Internet providers. To connect, the user is required to specify a name and password, and authentication, monitoring and control of connections are provided. It is quite convenient for a customer because it requires minimal knowledge when setting up. PPPoE is now supported by almost all routers. PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunnelling Protocol) is generally used to establish a private connection to an ISP over a LAN. It requires a user name and password and a server address to establish a connection. 802.1X – A security standard that provides for user authentication on the network. Typically used in EAP-MD5 mode. Not all routers support this type of connection, so if this is what your ISP uses, you should be especially careful when choosing a router. MTU. The Maximum Transmission Unit parameter is most interesting for those who use PPPoE connection or for those who are trying to set up a VPN connection, or both at the same time. The need to change this parameter is caused by the network settings of some ISPs. You can read more about what these changes mean at speedguide.net, but in our opinion you should not change this setting unless your ISP or manufacturer advises you to do so.
Router
A router is most commonly referred to as a router (although the more correct transliteration is "router"). This device is designed to connect multiple networks of different architectures. This means that the router is capable of connecting your personal home network to a global network (the Internet). This interaction is the third (networking) layer of the OSI model.
A special feature of the router is the ability to configure the rules of data transmission. Most often this is done with the help of a special web interface accessible via a browser.
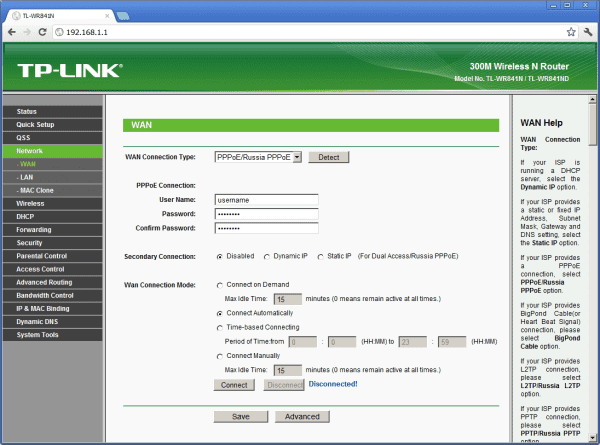
Almost all household ISPs use a similar web interface to allow the user or administrator to adjust the rules of the router
The security of this device is ensured by a built-in firewall as well as data packet filtering. Another common optional feature is a wireless Wi-Fi access point.

A household router is often equipped with a wireless access point
Routers are used not only to access the Internet. Large companies often choose a router to reduce the load of the local network by dividing it into broadcast or collision domains.
Operating Principle
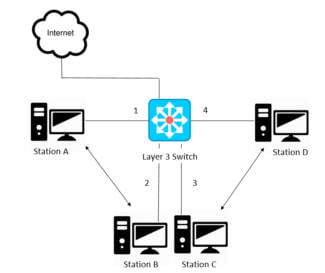
While a switch uses a switching table to identify network nodes, a router uses a routing table. It is more complex than its switch counterpart and contains data such as the address, destination network mask, gateway, interface, and metrics of all network devices, including other routers. Using this table, the router is able to determine the shortest path for transmitting data from one network device (such as a server on some website) to another (such as your personal computer).
What is the difference
Now that we know the basic characteristics and features of a router and a switch, it is not difficult to highlight their differences:
- A switch communicates between devices on only one network, while a router can link several networks;
- data rules can be configured for the router;
- the switch cannot be connected to the Internet;
- the switch uses only LAN-ports, while the router has at least one WAN-port, which provides communication with the global network.
It's easy to make a conclusion: you can't use a switch as a router, but a router acts as a switch. If you disable access to the Internet, the router will be absolutely similar to a normal switch.
A switch and a router are externally similar devices that perform different functions. Knowing their features and functions, it is not difficult to distinguish one from the other.
Read More: