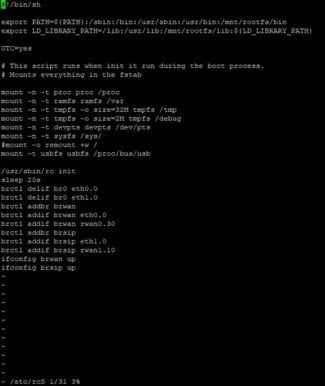
Next, you need to cut the wires so that they are the same length and insert them into the connector. At the same time, they have to be placed so that a small piece of insulation also goes into it. After crimping, and then the Internet cable can again be inserted into the WAN connector.
- WAN-port on the router: what it is and what it looks like
- Deciphering WAN and LAN in the router
- What does the WAN connector look like on the router
- What is the difference between WAN and LAN connection on the router
- WAN on the router
- What is a LAN port?
- Display
- WAN network
- WAN IP
- Connections and Ports
- WAN and LAN – what is the difference?
WAN-port on the router: what it is and what it looks like

Your Internet router probably has a WAN port and several LAN ports. They may seem completely identical, but the WAN and LAN interface perform different functions. Therefore, if you have decided to connect to the Internet, it is very important to understand what the WAN connection type is and how it differs from the LAN connection.
Deciphering WAN and LAN in the router
LAN stands for Local Area Network, which means local network. In simple words, it is the joining of several devices into a network in a small area so that files can be exchanged between gadgets. The LAN port is for connecting devices to the web router with a web cable.
What is the difference between a WAN port and a LAN port? WAN stands for Wide Area Network, that is, global network. The WAN port is designed to connect an Internet wire that provides access to the World Wide Web, and this is the difference between the WAN and LAN connector.
What does the WAN connector look like on the router
Each router has one or two wan ports. The port must be marked with a different color from the others, usually blue, as well as put next to the port the word "WAN", "Internet", "Ethernet" or just a pictogram of the planet.
When you plug a cable into the WAN port, the corresponding indicator light comes on. It starts blinking when the ISP approves the wan network settings and starts transmitting data from the WAN.

Each wan connector of the router has its own address – wan ip to identify it with the global network.
What is the difference between WAN and LAN connection on the router
The main difference is the purpose of these ports. WAN is the port to connect the Internet, that is, the external network, and LAN is the port to connect all home devices into a single local network. There are a few more key features, let's look at them:
- WAN port is one and its color is blue, and LAN ports are several and their color is usually yellow.
- Network coverage, WAN covers the whole world, while LAN is limited territorially, for example to an apartment, house or office space.
- Network speed, in the LAN between devices is faster and limited only by the type of router, now the standard speed of 1000 Mbit/s, and the WAN depends on the provider and the selected tariff ( from 1 Mbit/s to 1000 Mbit/s).
- In the local network we can use printer management services, file sharing, DLNA technology. In the wide area network VPN services and routing services are available.
WAN on the router
As you can easily guess, the WAN port (WAN port) on the router is used to connect a cable with the Internet signal. It is in this port (or ports, if the router supports the connection of two communication channels) and you need to connect the WAN cable coming from the equipment of the Internet service provider. Because only on this port there is an opportunity to make all the necessary settings such as login, password, IP address, and others.

Also some router models allow you to use LAN to connect the Internet. This is relevant for old-fashioned DSL routers, because they have no WAN and you can connect there only with this function to the modern high speed Internet via FTTx technology. To use it, you will need to choose one of the LAN ports in the router settings and set it as WAN. Then you have to plug a cable into this port and configure it for Internet access.
What is a LAN port?
LAN" stands for "Local Area Networks" or "Local Area Network". It connects nodes that are a short distance from each other. An example of such a network would be a network in an office or university. In other words, computers can be connected directly to one another via a LAN.
There are specially designed devices for this – hubs and switches. These are such switches with network connectors, which help to create huge local networks. Also if you use a router, you can give such a private network access to the global Internet.
Display
On each of the WAN and LAN ports there are two LEDs, which can show whether or not there is a link – whether or not the other device is connected, the speed of the connection, usually:

Some devices may not have a yellow LED at all. It can be arranged in such a way that one indicator lights up green only in case of a 1 Gbit/s connection, and the indicator on the right side lights up when a data packet is transmitted.
In addition to the indicators on the connector, very often they also make indicators on the case, for the WAN it is usually depicted as a planet, for the LAN it is depicted as a computer. If all is well – it lights up or flashes green.
WAN network
Another option for theorists. WAN is a global area network. A network that connects several other networks together. A little bit of theory can be taken from the following video:
For a brief understanding. There are usually 2 types of networks, but sometimes they try to add a third one:
- WAN – read "WAN" – Wide Area Network – a global network – meaning that all-encompassing Internet. One World Wide Area Network.
- LAN – read "LAN" – Local Area Network. The key here is closed. Maybe a home, maybe a huge enterprise with tens of thousands of computers and distributed all over the world. But not everyone has access here from the outside.
- MAN – read "MAN" – something in between and in between – the Metropolitan Area Network – an urban network. The concept of "metropolitan" is also blurred, I would think here more to understand the networks provider – when everyone completely can not see each other, but when downloading from local file sharing provider speed between members of this non-global network is still higher, because it is essentially the same large local network, but with built filters.
Sometimes, these networks are also classified by radius (like MAN – 5-50 km), but nowadays it is already outdated nonsense – there are different networks. Classify them to understand WHY they are created.
The differences between WAN and LAN are relevant for students in this segment as well. Under the record:
- The size of the network – the global one is not even limited by space, the local one is limited by its architect. In theory, it can also go into space, but it does not belong to the whole world and will always be smaller than the global one.
- The number of machines – everyone connected to the Internet is a member of the global network. Local networks are disparate, and there are always fewer in a single network.
- Services. On a local network, folders and printers fumble. On a global network everything is built on a client-server architecture – global routing, WWW, etc.
WAN IP
In addition to the article. Some readers don't understand what a WAN IP is. And some router interfaces add LAN IP in the same place. In this case, one computer shows 2 different IP addresses. Let me help you to understand:
- WAN IP is your external IP address on the Internet, issued by your ISP. You can check it on the same 2ip.ru or inside the settings of the router. For more information: if it is displayed in the router as 0.0.0.0 – it means that the router was unable to connect to the provider for some reason (maybe the connection is temporarily down somewhere in the area, or maybe the settings are wrong, this is a topic for a separate article). All devices in your home network connected to the router will always have the same external WAN IP.
- LAN IP – your local IP address given by the router itself. Usually it looks like 192.168.X.X – each device in your local network has its own.
That is all! We have looked at the question from both sides. If you have any doubts or don't understand anything, just post the question below. That's all for now, your Nerd from megakool portal about Wi-Fi and other wireless networks WiFiGid.ru. See you later!
Connections and Ports
Here I will tell you about the LAN connection. There are two options:
Here it's worth understanding that everything revolves around the router. Everything that connects to the router is a LAN. What the router connects to is the WAN. Like an inbound and outbound connection.
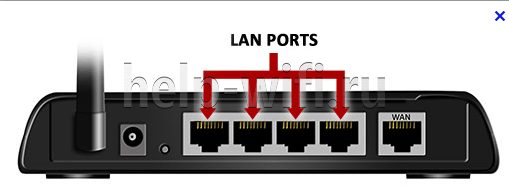
The router itself can connect via Wi-Fi, but usually still connect to it. Whoever connects is immediately connected to the local network. Another option is to connect via wire. To do this let's look at the back of any average router:
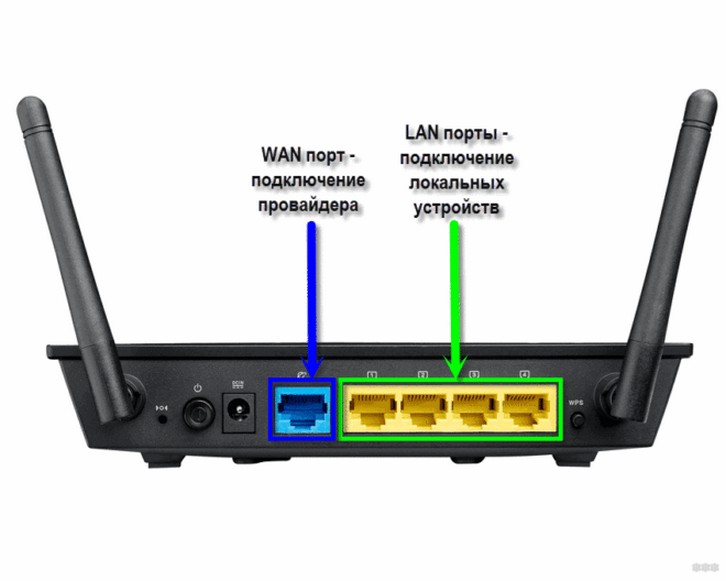

Notice the LAN ports – there are usually several, and they are usually yellow (and not always). They say LAN, or local network, or something else. It is difficult to confuse them with others. The WAN port is specially taken out separately and allocated. Bottom line – if you want to connect something to your local network – connect only to LAN ports. If you want to connect router to ISP (for internet access, 99% of the time) or another router (e.g. for perverted repeater mode) use WAN interface.
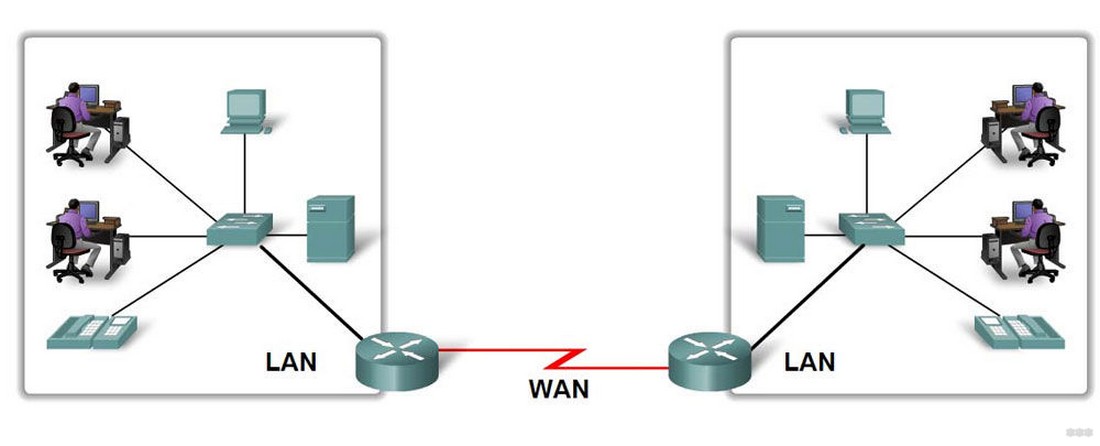
Now both LAN and WAN ports usually have the same type of connector for twisted-pair Ethernet cable – RJ-45. But this may not always be the case. So ADSL modem can use RJ-45 (LAN) for the local network and RJ-11 (WAN) for the Internet connection via a telephone cable. The LAN connector is predominantly RJ-45.

WAN and LAN – what is the difference?
LAN – Local Area Network
WAN – Wide Area Network.
There is a broad sense and a narrow one. In the wide sense I have already mentioned above – there is your personal home network, and there is a network to which all devices of the world can connect – the Internet. In a broad sense, the WAN is the Internet. Basically this distinction and is asked everywhere in schools and universities. That's where they ask for the basic distinction as well:
- The size of the network – the Internet is ubiquitous (we are not even talking about Earth anymore, since it is also used in orbit, and in the future, there may be applications on other planets, and this will not limit the WAN to our globe), LAN network – limited to the apartment, office, enterprise network (key – not everywhere).
- Number of users – again, the difference is the limited nature of the local network.
- Services – local services (printing, files), global services (WWW, global routing).
- Topology – in LAN all are equal, connect to each other, Peer-to-Peer. The WAN is characterized by client-server connections.
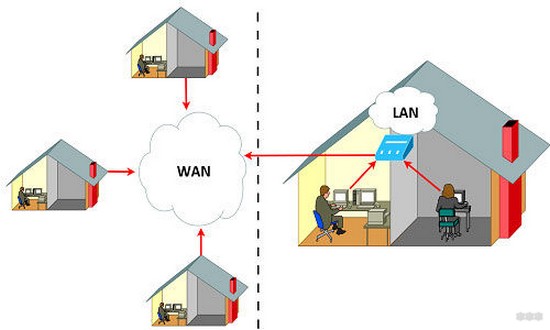
So, if someone asks you what is the difference between WAN and LAN – list the points above, separated by commas, and end the conversation – everyone will definitely be happy.
But there is one more point about the technology. We're talking about the WAN port. As a rule, the ISP cord is plugged into it – to connect to the Internet. The WAN port makes the outgoing connection in the router. And in this approach, the global concept of LAN and WAN can in some cases blur the line between them)
That said, the outgoing connection through the WAN can also be connected to another router in your home (special cases). Connecting an external device via the WAN port without dancing with tambourines is not possible.
Read More:There is another type of network – MAN (Metro Area Networks). This is something in between – a metropolitan or city network, perhaps an ISP. That is, it is a kind of local network between all users, for example, one provider. As an advantage – high speed between points. On this basis, not bad used to live file sharing.