If your Internet connection is too slow, or it doesn't cover the surface of your home or office, or there is some speed and coverage issue, the most likely culprit for all these anomalies is a router with outdated technology.
- What is a Wi-Fi hotspot? What is the difference between a router and an access point?
- Wireless Access Point: What is it and why do I need it?
- What is a Wireless Access Point?
- Wireless AP vs. Router: what are the differences?
- Function
- Connecting
- Coverage
- The arrival of routers
- How does the router work and why do we need it?
- Wi-Fi technology
- Types of routers
- What is the difference between a modem and a router, in simple words
- Operating modes and connectivity options
- How the router works:
- What's the difference between a router and a router?
What is a Wi-Fi hotspot? What is the difference between a router and an access point?
To be honest, I'm kind of lazy to write another tutorial today, so I decided to tell you about access points. What is an access point, what they are for, how they differ from routers, and how to make an access point out of a router. There are no specific, step by step instructions in this article. Later, in a separate article I will write about how to use a Wi-Fi router in AP (Access Point) mode.
I think you should first find out what a router is. It is a network device which allows you to connect multiple devices to the Internet. It distributes IP addresses to the devices, connects them to a local network, connects to your ISP, and manages it all. I wrote about this topic in more detail in this article: what is a router.
Wireless Access Point: What is it and why do I need it?
First and foremost, an access point is a separate device. A router and an access point are not the same thing. Yes, in many ways they are similar. You could say that an access point is a stripped down, simpler version of a router. The fact is that a wireless access point is designed to connect devices to an already established network. Its task is simply to organize a connection to the Internet via Wi-Fi. Also, it can work in different modes: wireless client, bridge, repeater, access point. It all depends on the specific model.
The access point does not distribute IP, does not connect to the ISP, does not have a built-in firewall, etc. It simply gets the Internet from a router, or modem, and distributes it over Wi-Fi. Some commercially available wireless access points can distribute IP, set up a separate network, and even connect to the Internet Service Provider. But, only via Static IP, or DHCP. Most likely, you won't need a router or modem anyway. One more important point is that the access point has only one network connector. Therefore it will not be able to deliver Internet via cable.

For example, if you need to distribute Internet via Wi-Fi from an ADSL modem, or expand an existing Wi-Fi network, in this case the access point will be perfect. That's what they're built for. As I wrote above, many models can work in client mode, or in repeater mode. Many modern routers can also work in all of these modes.
In access point mode, we connect it to a router or modem through a network cable, and get access to the Internet via Wi-Fi network. If you want to connect the wireless access point "over the air", you can set it up in bridge mode (WDS) , or in repeater mode. You need to see what works best for you.
What is a Wireless Access Point?
A wireless access point (also called a wireless AP or WAP) is a networking hardware device that adds Wi-Fi capabilities to an existing wired network, connecting traffic from a wireless station to a wired LAN. The wireless access point can act as an independent device or as a component of a router.
Generally speaking, a wireless AP allows devices without a built-in Wi-Fi connection to access a wireless network over an Ethernet cable. In other words, the signal from the router to the AP is converted from wired to wireless. In addition, if future access requirements increase, WAP can also be used to extend the reach of existing networks.

Figure 2: Wireless Access Point Connection Scenario
Wireless AP vs. Router: what are the differences?
Both wireless access points and wireless routers support Wi-Fi network connections and play a similar role. So there's been some confusion. In fact, the two networking devices are more like cousins than twins. The differences between them will be explained below.

Function
Typically, most wireless routers combine the functions of a wireless access point, an Ethernet router, a basic firewall, and a small Ethernet switch. Wireless access points
are usually built-in components of devices such as routers or Wi-Fi extenders. In short, wireless routers can act as access points, but not all access points can act as routers.
There is no doubt that a wireless router, acting as an Ethernet hub, helps create a local network by linking and controlling all the devices connected to it. However, the access point is an auxiliary device in the LAN and only provides access to the network set up by the router. Therefore, if you are a network administrator, you can use a wireless router to change network settings, but a wireless access point does not have this function.
Connecting
Router mode vs AP mode, the connection method is different. A wireless AP cannot connect to a modem. Usually a switch or router will be used as an intermediary. a wireless router has a broadband dial-up function and can be directly connected to a modem to access the internet.
Coverage
Wireless routers are the most common networking equipment today. But if a router can't cover a Wi-Fi signal, it will have weak or no signal. Conversely, wireless access points can be added in places with poor network conditions, eliminating dead spots and expanding the wireless network.
The arrival of routers
As time went on, ISPs started bringing fiber to cities. It's faster Internet, more reliable and cheaper. I remember when I got my fiber optic cable installed, I was surprised that I didn't need the modem anymore, and I had to say goodbye to that little box that I had stuck to. Grudgingly, I gave it to the workmen who were running me the wire.
Now the Internet was transmitted with the right technology, and a modem, which would decrypt the signals over the phone line, was unnecessary. The Internet wire was plugged directly into the computer, there were no breaks, the speed was crazy, and I was happy.
Another 5 years passed, and cool phones with wide displays and the first devices that had a Wi-Fi module – a thing that is able to connect to a wireless network.

At home, everyone was using a smartphone or a tablet. And the question arose as to how to unite all these people so that they have access to the home Internet. After all, mobile at the time was very expensive and, most importantly, not unlimited. Yes, there were such terrible times, when it was a gigabit and expensive.
That's when I first got to know my first router. I brought it home and started fiddling with the settings. My goal was to build a Wi-Fi network, connect it to the Internet and distribute it to all my home devices.
- The Internet cable from the doorway went inside the apartment and plugged into the router.
- From this box went to the usual network wire to my desktop computer.
- Having set up the Internet, it was now on the computer and all the devices that are connected to the wireless wi-fi network.
All the family was happy, because now I had good, stable and fast Internet on my smartphones, phones, tablets and laptops.
How does the router work and why do we need it?
Router has at its root the word "Route" and for good reason. The task of this network apparatus is to properly distribute data flows within. Simply put, to ensure that all devices are fully and quickly receiving information.
The way the router works is based on a routing table. It stores addresses and more detailed information about all devices connected to the network. Imagine a data packet arrives from an external network and you need to send it to the recipient. So in order for the packet to get to the right device, and need this table, and the machine itself.
DEFINITION! Router is a device which builds a local network based on a routing table, receives external packets from the Internet provider and transmits them to the recipient via cable or wireless Wi-Fi technology.
Let's take a look at what a network router looks like.
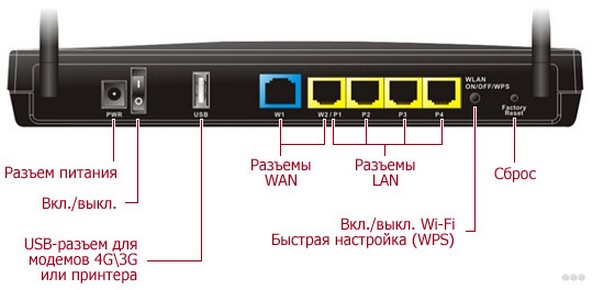
- The first input is for power from a wall socket.
- The USB port allows you to plug in a printer or a flash drive or a hard disk. This is so that all users on the network can have access to the same dedicated space. You download movies there and watch them from your laptop, which is connected to the network. You can also set up a Torrent server and upload movies there offline. You go to sleep, and movies are downloaded. Useful thing. Also we do not forget about 3G/4G modems, which also work through this port.
- The WAN port is blue – this is where the wire from the provider is connected. Roughly speaking, this is where the external Internet streams come in.
- LAN port – is for connecting devices directly to the local network.
- WPS – quick connection to the wireless network without a password.
- Reset – to reset the device to factory settings. It is better not to press it if you do not want to configure it again. But sometimes it's the only way out.
Wi-Fi technology
To imagine the modern work of the router without the implementation of Wi-Fi technology is absolutely impossible. After all, it is the technology that allows you to transmit data wirelessly. In this case, a powerful router provides a certain, sufficiently large coverage area.
If we consider in detail what is Wi-Fi technology, we can distinguish it:
- The ability to transmit a signal without a wire (using radio waves) within a local network.
- The signal transmitted using Wi-Fi technology is not always an access to the global Internet. Sometimes this feature is used to create a local network, within which connected devices can exchange the necessary data with each other.
To use the advantages of wifi is possible only if the device has a special network card that supports wireless communication technology.
Types of routers
To date, on the market of such products there is a large number of routers, which differ both in the way they are connected, and on other principles of their functioning.
If we divide routers according to the method of connection, we can distinguish:
- Mobile devices that offer a number of advantages. For example, such as compact size, the ability to transmit data via USB connection, as well as through wireless technology, i.e. over the air. To make such mobile router work, it is necessary to buy a SIM card of the specific operator.

- Mobile routers connected to the telephone line will be relevant in cities or towns, where there is a wired connection, but there is no opportunity to connect to the Internet in another way. This type of network device uses a pair of ADSL modem, which is connected to the phone line and a router, which will be used to distribute the signal of the Internet.

- Another type of router, in terms of connection, is provided by twisted pair and fiber optic. It is this variety that is the most common, both in offices and when installed in apartments and two-story private homes. Such a connection is simple enough – it is easy to make, even for a beginner. But the router itself can be different. Cheaper router models have a single antenna – although they give a good enough signal, they do not provide much coverage. To get a more powerful device, you should pay attention to models that are equipped with several removable antennas. Such a router is suitable for installation in a two-storey house or where there are quite thick reinforced concrete walls, which somewhat "muffle" the signal. In addition, such a device is able to work in 3G and 4G networks, as this modem is more advanced and new in terms of the introduction of a variety of technologies.
What is the difference between a modem and a router, in simple words
Why do you need a router in the apartment is easy to understand, but some people need constant access to wi-fi at the cottage or in the countryside. In this case, the choice is usually made in favor of a modem.
A router is a device that provides Internet access in the home and by default takes care of distributing information to external devices.
A modem is usually provided by Internet service providers like Megafon, but it can also be purchased separately if the user is familiar with their home Internet network technology. Therefore, a compatible model is needed. The modem takes the signal to one device and does not distribute it to others.
For home users, a modem router, provided by some telephone and Internet companies, is a device that does both the job of receiving an Internet signal and of managing all connected devices, distributing it to all through Wi-Fi antennas.
If the user has a large home or office and uses computers that need fast Internet access, a modem with a router may not be the best option. These devices are usually quite simple and may have a small range, depending on where and how they are installed.
In this case, you need to buy a high-performance router and configure the device to work only as a modem. If the house is small and there aren't many Wi-Fi devices (or if a cable connection is used), a modem with a router is the best option because of space and energy savings.
Operating modes and connectivity options
The Wi-Fi signal passes through the router in radio bands that act as invisible trunks. Each band is an independent path, storing data on separate paths to prevent congestion.
Because some devices require more bandwidth than others, the efficiency of the router depends on the number of bands it handles: single-band, dual-band, or tri-band.
A tri-band backbone (or in this case, a tri-band router) consists of one 2.4 GHz channel and two 5 GHz channels to serve more users simultaneously. This is a big advantage for families with eight or more devices that have high bandwidth.
How Wi-Fi is used also determines which router best suits your needs.
For example, a tri-band router is a great option if the user regularly streams movies or shows on multiple TVs, has an avid gamer in the family, or needs to work from home and have dedicated bandwidth for home office traffic.
On the other hand, if you use the Internet very formally, primarily to send emails or check social networks, a dual-band router will be more than enough.
How the router works:
- Connect to the router the cable that was laid to our house by the Internet provider (or the cable from the ADSL modem). If you have ADSL Internet (by telephone cable), and you do not have a separate modem, you can buy a Wi-Fi router with a lined up modem. To which you can immediately connect a telephone cable. And if you have Internet via USB modem, then connect the modem to the router. But in this case you need a special router with USB modem support.
- Configure the router to work with your provider or modem (ADSL or USB). The best way to do this is to follow the instructions that are written just for your device. You can search for such an article on our site in the section "Setting up the router". Also, you must set the name for your Wi-Fi network, set the password for the network.
- Connect to the router all the devices on which you want to use the Internet. Usually, the router is installed by those who want to use the Internet via Wi-Fi on their mobile devices. Therefore, we connect our phones, tablets, laptops, televisions, etc. to our Wi-Fi network. And those devices that cannot connect wirelessly (usually desktop computers), you can connect to the Internet via a network cable (LAN). As a rule, the router has 4 LAN sockets, which means that 4 devices can be connected via cable.
And if you don't want to bother with cables for a desktop computer, you can buy a Wi-Fi receiver for it and connect it wirelessly.
It turns out that the router just establishes a connection to the Internet and shares it among all the devices connected to it. That's its job.
What's the difference between a router and a router?
If you have read this article from the beginning, you may have noticed that I wrote either a router or a router. Yes, they are the same device. They are absolutely the same and there is no difference between them.

Just router is the English word for router. And in Russian the word is translated as router. That's all. Both are correct. When I write an article, I use both names.
I hope that I have answered the question in the title of this article. If you can somehow add an article, you can write me in the comments, I will be grateful.
![]()
201

343430
![]()
Sergey
![]()
Useful and interesting
Hello. Will this device give out Wi-Fi, if you connect a LAN wire to it.
ru.aliexpress.com/item/FW1S-2016-New-Arrival-High-quality-Mini-3G-4G-WiFi-Wlan-Hotspot-AP-Client-150Mbps-RJ45/32622382063.html
Hello. I think it is. The description says "WAN Ports:1". Maybe it means USB and not LAN.
But it would be a good idea to ask the seller about it.
WAN Ports:1 means that it has one network input (cable internet from ISP, RJ-45 connector)
LAN – this is the output, usually they are from one to four, to connect the network cards of laptops, computers through a patch cord with RJ-45 connector
Hello!
Can you please tell me please, I have a modem without Wi-Fi, can I separately buy a router for Wi-Fi, and keep the old modem?