LAN port – the connector through which client devices are connected to the router by means of a cable. The standard number of LAN ports on most models of modern routers is four. But there can be variants. For example, there are budget models with only two LAN-ports or even one. And there are routers where there are six or eight ports.
- Router speed
- Hardware capabilities
- Wi-Fi transmission protocols
- Which router to choose
- Power and standards
- Does the speed of the Internet depend on the router
- On what it depends.
- Ports and connectors
- What are the differences between routers?
- Connection technology
- Basic indicators
- advertisement
- advertisement
- advertisement
- advertisement
- Replacing a router
- TOP-5 routers by the end of 2020, beginning of 2021
- Conclusion
- Router in the bedroom
- How to minimize the damage from the router
- Reducing the speed of traffic due to Wi-Fi congestion and ways to fix this problem
- advertisement
- Reducing the speed of traffic of all devices because of one low-speed device.
- What to look for when buying
- Wi-Fi parameters
- Operating range
- Recommended models of home routers
- TP-LINK TL-WR841N
- ASUS RT-AC51U
- Netis WF2411E
- Effects on the body
- How to protect yourself?
Router speed
Most users are guided by the internet speed, which is claimed by the provider. And they are perplexed when the actual speed is significantly lower. In this case, the first thing they do is to flood the provider's tech support with complaints, losing sight of the fact that various factors can affect the speed of the Internet. For example, a wrongly selected or configured router.
Many people simply do not think about this issue. But it often happens that before acquiring a router, the Internet was working fine, but after the router appeared on the network, the speed dropped dramatically. What is the reason?
Hardware capabilities
First and foremost, performance and speed depend on the hardware capabilities of the router. A router is actually a mini-computer with a processor, RAM, a network card and the firmware that manages it all.
These parameters determine the cost of the device. The more expensive models accordingly have more powerful hardware. But most users choose budget models. But you should not expect miracles from a device for 10-20 dollars.
When working on the Internet, the speed will inevitably be lost when routing, that is, when transferring traffic from the WAN port to the LAN port or Wi-Fi adapter of the device. Routers with weak processors and small RAM are simply unable to cope with large amounts of data.
Wi-Fi transmission protocols
In addition, it is important to know what data transfer protocols the router supports. Because the manufacturer's claimed 300 or 600 Mbit/sec in a wireless network is the maximum possible speed. In practice, it will be lower. For example, the fastest standard 802.11n with all the antennas of the router working at full power can give you up to 600 Mbps. But this is theoretical. In practice, depending on the transmitter power, antennae gain and device stability, the actual speed may drop to 60-80 Mbps or even lower. If your ISP gives you an Internet connection at 100 Mbit/sec, the router won't give you more than it can anyway, i.e. it will cut the speed of the Internet connection. And then there are the old standards such as 802.11g. Here the declared maximum speed is 54 Mbit/sec. And in practice it rarely exceeds 20 Mbit / sec..
Which router to choose
So there's no point in buying cheap routers at all? Not at all. If your connection speed is not critical and you only have two or three devices in your network that are close to the router, you can get by with a budget model. Powerful, high-performance routers may be needed for a large network with a heavy load.
When buying a router, especially if you decide to save money and buy a used device, you should pay attention to its hardware. Sellers rarely inform you about the parameters of routers, so it is better to study the description of the specific model on the manufacturer's website beforehand. For comfortable work today, it is recommended to use devices with at least 128 megabytes of RAM and a processor with a frequency of at least 500 megahertz. Budget models may have a weaker processor and a small amount of memory, which significantly reduces performance. With a 240 megahertz or less processor and 64 megabytes of RAM, any normal work with a VPN or PPPoE connection is out of the question.
Power and standards
You should also pay attention to the transmitter's power. It is desirable that it was not less than 16 dBm. If the router will be used in a small apartment, one or two antennas will be enough. But if you have a private house or just a big room with internal partitions, it makes sense to buy a device with more antennas and maximum gain.
The router must support the high-speed 802.11n standard. Standards g and b will not provide maximum data transfer speeds. They can only be justified if you have older laptops or smartphones on your network that do not support 802.11n. But this is very rare today.
For maximum wireless performance, it is best to purchase a router that operates on the 5 GHz band. The speeds in this range are faster, the channel is wider, and it's not as congested. Such routers support the 802.11ac standard, which can provide speeds up to 6.77 Gigabits/sec.
Does the speed of the Internet depend on the router
The job of network equipment is to act as an intermediary between the ISP and the recipient of the service. In other words, the wire enters the WAN connector, and the next step is to distribute the global network to PCs, laptops and other equipment by wired and wireless. The question arises whether the router affects the speed of the Internet. In theory, this parameter does not depend on the router, because it simply distributes a global network. But in practice, the network equipment affects the speed of the Internet.
- The WiFi standard provided on the router. For example, if the router only supports 802.11g, it will cut the speed parameter to 15-20 Mbps. This is true even if your ISP gives a lot more. So think about whether it's worth saving money on this.
- Frequency. When considering whether a router affects Internet connection speeds, it's important to consider the frequency of operation. If the device supports the 5 GHz setting, it helps speed up data exchange.
- The square footage and organization of the apartment, wall thickness and material. The quality of the Network depends on the square footage, number and composition of partitions. So, to cover an area of more than 50 square meters will require more powerful equipment. To solve the problem you may need to buy a repeater or another router configured in bridge mode. But before doing so, make sure you can cover the entire area.
- Location. Many people wonder if a router's location can affect Internet speeds. As in the previous cases, the answer is yes. This parameter directly depends on the place where the network equipment stands. For example, if you put the router in a metal panel or a cabinet, the quality of WiFi connection will deteriorate noticeably.
- Interference from WiFi networks. Another point is whether the Internet speed can depend on another router. Here also the answer is positive, because a lot of interference in the network leads to a deterioration of the connection and, consequently, a deterioration in speed performance.
- Type of connection. It's no secret that when using a dynamic or static IP, the speed will be higher than in the case of PPTP, L2TP or PPPoE.
On what it depends.
Above, we have considered how the router and its characteristics affect the speed of the Internet. But there is a number of other factors on which the parameter in question depends:
- Provider. The quality of the connection to the WAN depends on the channel load of the service provider, the quality of equipment at the nodes and in the home. Equally important is the integrity of the cable and the quality of the connections made. It is important to keep in mind the quality of network equipment provided by the provider for rent. Consider whether to save money or buy a router yourself.
- Equipment. In addition to the effect of the router on the speed of the Internet, there are other factors concerning the hardware used. Thus, the speed depends on the quality of the communication, the parameter of the receiving equipment (computer, laptop, phone), as well as the timeliness of software updates. No less worthy of attention are malicious programs (Trojans, viruses), which also depends on the parameter of interest. So check if there are any malicious programs on your PC, and only after that take other steps.
- Extraneous factors. Knowing how your Wi-Fi router affects your Internet speed can help you eliminate the cause and make the right settings. But there are a number of factors that are independent of the subscriber and the service provider. We are talking about the load of servers on the Internet, the quality of communication lines, the presence of interference from household appliances and other points.
When considering the reasons that determine the reception / transmission of data over a global network, many people forget about the tariff plan. When connecting the Internet, the user specifies the speed he should get from the Network and, accordingly, from the router. But here think about whether it is worth overpaying for the extra speed.
Ports and connectors
Here we take a look at what the Wi-Fi router looks like: this photo and the captions under it will help you understand what the inputs and connectors are for.
- Power indicator . When the device is working, it should light up;
- Power . Input for connecting the power supply. Some models are equipped with a built-in power supply;
- Reset . Button for resetting to factory settings;
- USB 2, USB 1 . Ports for connecting USB devices, such as a printer, modem or storage device;
- LAN ports . They are needed to connect local network devices – laptop, TV, computer;
- WAN . Socket for connecting a network cable – ADSL line or Ethernet port. With the help of this wire the Internet gets into the room.
What are the differences between routers?
But what kind of devices are there, and what is the difference between different types of routers? Read about it below.
Connection technology
There are several technologies and accordingly types of equipment: ADSL, Ethernet, GPON and 3G/4G. Now let's find out how they differ from each other.
- The data channel is asynchronous;
- The receiving speed is up to 30 Mbit / sec;
- Transmission speed – up to 3-5 Mbit/sec. You can try to increase the speed of the modem, but note that this is not always effective;
- Mainly presented in the average price segment;
- Work on the basis of telephone lines.
- Connection is made by means of twisted pair;
- The minimum number of clients to be connected is 10;
- The maximum speed reaches 1 Gbit/sec;
- The presence of antennas – up to four;
- The presence of one or more USB-ports.
There is no way to say that any of them are better or worse than the others, so when choosing, you need to be guided only by your own needs and financial capabilities. However, even if you choose the most expensive device, it will not insure you against the fact that the Internet speed through the router can be reduced.
Basic indicators
In this section we will consider the main indicators that are worth paying attention to when choosing equipment.
- Cheap models operate at speeds up to 150 Mbit/sec;
- More expensive devices reach speeds exceeding 3000 Mbps;
- The optimal number is 300 Mbps. – In fact, this will be quite enough for the average user.
advertisement
Typical signal strength of the problematic network -80dBm
However, with variable intervals, usually in a few seconds, the signal strength of this network, increases sharply on the client side (which is my laptop). Namely, the signal power grows to -22dBm (!). Of course, in this case the laptop is in the same place.

Signal power of the TOTOLINK_XXX network.
advertisement
And such a strong signal holds for quite a long time, acting as an excellent "jamming" neighboring networks in the frequency bands 1-6, because the owner of the unfortunate network "stretched" its width to 40 MHz.
But the communication problems in neighboring networks are not the worst of it. I'm just afraid to imagine what peak power of radiation this network's home (!) router (probably malfunctioning) produces, instead of the standard 100 mW (20dBm). In the following I will try to explain to you why this is dangerous and why you should not live near such routers.
A lyrical digression. All my life I thought Wi-Fi was a completely harmless feature. Until I got a laptop Acer Nitro AN515-55 (you can read about it here) with an excellent Intel AX201 wireless adapter. So, I noticed that when I was sharing torrents via Wi-Fi from this laptop, I started to get a headache. I even made a series of experiments to be sure of that, but not to write it off as an accident. The reason for this is clear – if in usual laptop's mode the wireless adapter mainly works as a receiver, then during the distribution of torrents via ah network (Wi-Fi 6) the laptop turns into a powerful radio transmitter with a very heavy traffic. Moreover, in a transmitter located right in front of your face. Even reducing the transmit power to medium had no positive effect. And this despite the fact that the torrent traffic on every home computer, including this laptop, has strict limitations, so as not to "clog" the narrow external 100 Mbit channel to the ISP. This is how I empirically realized that Wi-Fi is not so harmless. In general, now my laptop gives out torrents only when I'm not sitting at it.
Contrary to popular belief, the government is no fool. And the standards on the power of radiation for routers government set not in vain.
Lyrical digression 2. Why high-powered routers at home are unnecessary and useless is detailed here.
advertisement
That said, wireless routers/TDs always have a CCA Threshold – a signal audibility threshold, and if the signal level does not exceed this threshold, the router/TD considers it noise. Suppose this threshold is 82 dBm. Thus, our conditional router with 5 dBi antennas will work with devices, the signal level from which at the location of the router is at least -87 dBm (-87 dBm signal + 5 dBi gain router antenna = -82 dBm).
Note: Of course, this is just a tentative example with all parameters conditionally-typical and given to understand the situation; your router may have antennas with the gain different from 5 dBi, and different threshold, for example – for some Ubiquiti equipment in general stable connection is guaranteed at -70dBm signal level; threshold for 5GHz networks is lower than for 2,4GHz even on the same equipment, etc., but these are nuances, we will not go into details.
In general for the router and the client we can be guided by a simple rule: all other things being equal, the signal loses 6 dB of power (i.e. 4 times as much) when the distance from the transmitter is increased by a factor of 2.
However, as mentioned above, the signal strength of the router/TD is usually 2-8 times higher than on the clients. And with the distance from the router/TD inevitably there will be a situation where the client will hear the signal of the router well, but the router will hear a weaker client signal at the "edge" of possibilities or not hear at all (because the client signal level will fall below the CCA Threshold of audibility). And there will be a strange situation when the Wi-Fi signal from the router on the client device seems to be caught, but there is no connection or it constantly "fails".
advertisement
The reason is the asymmetry in the "strength" of the connection: for example, when a 14 dBm client hears the router/TD at -84 dBm (-84 dBm + 2 dBi client antenna gain = conditional hearing threshold -82 dBm), the signal from the client reaches the router/TD only at -90 dBm, which is below the hearing threshold. Under these conditions, the wireless connection is guaranteed to break down.
That is, in wireless communication channels already at the typical standard parameters of the routers / TDs there is a significant problem with the connection, caused by the asymmetry of the power of Wi-Fi emitters. And if you additionally increase the signal power on one side (router/TC), the problem will only worsen. Moving with mobile clients, you will increasingly often encounter a situation where a Wi-Fi router "loses" devices, and that's because it has a significantly stronger signal. The client will "hear" the router/TD, but the client's router will not. This is why serious equipment manufacturers do not recommend using Wi-Fi routers and access points at maximum power. To prove this, here is a fragment of a Cisco presentation (you can read the full presentation here).

Even on the contrary, to eliminate asymmetry and obtain a stable connection, it is recommended to reduce the Wi-Fi transmitter power in the router/access point.
But if not signal strength, then what determines the speed and reliability of a Wi-Fi connection?
The connection speed, which doesn't tell you anything.
Three parameters determine Wi-Fi connection speed: modulation type, number of streams (depends on the number of antennas) and radio channel width.
But the "theoretical" connection speed based on the above parameters has little to do with the actual speed of the wireless network. What affects this speed?
The fact is that modulation in the network is not constant. The most advanced modulations today are 256 QAM and 1024 QAM (the modulation determines how many bits are transmitted in one radio symbol). But! These dense modulations are very sensitive to noise. And they are only achieved at high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) when the client is close to the Wi-Fi router/TD. With the distance from the router/TD increases noise, SNR drops, modulation is simplified for the reliability of the connection and, as a consequence, the communication speed drops. Plus, interference adds to the network problems.
Replacing a router
There are router problems arising from a weak logic part, lack of memory or manufacturer savings in the hardware component of the interfaces. Here only replacing it with a better model will help.
TOP-5 routers by the end of 2020, beginning of 2021
| Name | Number of LAN | Outer line | USB | WIFI | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi Router 4 | 2 | RJ-45 | No | Yes | 2450 |
| Xiaomi Mi AIoT Router AC2350 | 3 | RJ-45 | No | Yes | 3630 |
| Keenetic Giga KN-1010 | 4 | RJ-45/External 4G modem | Yes | Yes | 8369 |
| TP-LINK TL-WR840N | 4 | RJ-45 | No | Yes | 1200 |
| Tenda AC5 | 3 | RJ-45 | No | Yes | 1690 |

Conclusion
Router – a kind of "window" to the Internet and connecting all the nodes of the local network. The speed of connection between each of them and the outside world is a burning question for any user. All problems with poor performance are solvable, unless of course you have an extremely unfortunate router model. We hope that the ways listed in the article helped you to get rid of the strong negative factors, in which the router reduces the speed of the Internet, regardless of the method of connecting to it: directly, via modem or via Wi-Fi.
Router in the bedroom
Let's ask ourselves the question, how harmful and dangerous to your health to put a router in the bedroom.

Most often, a router is installed in the bedroom. Because people like to lie in bed with a tablet or watch a movie online. But it's not a good idea to stay close to a switched on router, and here's why.
Scientists did this experiment. They observed two groups of people. One group slept under normal conditions. The people in the other group were put next to their bed at night with a device with Wi-Fi turned on, and then, in the morning, their condition was compared with the subjects from the first group. They found that Most of the people in the second group experienced cerebral vasospasm, fatigue, and decreased attention span.. People who had spent the night without Wi-Fi were much less likely to have these symptoms.
It is believed that Wi-Fi radiation has a much greater impact on the brains of children, as children's skulls are thinner than those of adults and have less protection from radio waves. Therefore, if a child sleeps in the room, you should remove or disable all devices that use Wi-Fi at night.
In addition, the indication of the router, constantly flashing lights, especially in the dark, can have an irritating effect on the psyche, interfere with sleep.
Therefore, it is strongly not recommended to place the router in the bedroom, let alone next to the bed.
You can also read in a separate article on our site where it is better to place the router in the apartment.
How to minimize the damage from the router
Of course, the best way to minimize the harm from Wi-Fi is not to use a router at all. After all, after all, a computer or laptop can be connected to the network by wires. But it is unlikely that Internet users are ready for such a radical solution. And if you follow this method in everything, then you will have to give up television, radio and mobile communications.
So let's look at how you can continue to use a wireless network at home and still reduce the harmful effects of router radiation on the body.
Household routers are usually not very powerful. They operate at frequencies up to 5 GHz and their radiation power does not exceed 100 mW. However, there are more powerful devices used to transmit data over long distances when organizing large networks. Such powerful routers are not needed in an apartment. So use an ordinary router. Its effect on your body will be minimal.
Place the router away from your workplace. Especially away from the bed where you sleep.. In general, if possible, install it in the room where you are least present. For example, in a hallway, in the attic of a private home, or in any non-residential room. Radio waves are much less dangerous at a distance. Of course, the farther away the router, the weaker the signal, but for a city apartment in most cases it is irrelevant. If you are not happy with the signal quality, you will have to find a reasonable compromise.
The fewer devices – the better. It is better to use one powerful router, if necessary, than two or three weaker devices. If you can't do without repeaters in your case, try to keep their number to a minimum.
In normal operation, the router emits radio waves all the time. If its continuous operation is not necessary, it makes sense to reduce its active time. Most routers can be configured so that the Internet will connect only if there are active client devices. All the rest of the time the router will be in passive mode and the intensity of its radiation will be significantly lower.
Reducing the speed of traffic due to Wi-Fi congestion and ways to fix this problem
advertisement
Many users have faced the situation when a router, which used to work normally, suddenly started reducing the speed of the Internet connection (cut the speed), for seemingly incomprehensible reasons. Such a situation often occurs in a widespread and already quite outdated wireless access standard at a frequency of 2.4 GHz.
Usually users, after installing a router and making sure that it works, do not even think about what channels it works on, whether they are free or already occupied by neighbors, what settings it has, optimal or not. Most often they leave the settings set to "default". And without figuring out why the speed has decreased, and how to change the settings of their router to fix the problem, they immediately begin to blame the provider for providing them with poor service in the form of low-speed Internet traffic. Or conclude that the router is faulty. But more often the reason lies in something else, in the "littering" of Wi-Fi networks, that is, in the overlapping of Wi-Fi channels of your router and your neighbors' routers.

In this case, the drop in the speed of the Internet connection occurs because the terminal device (traffic consumer) begins to receive overlapping, distorted data packets that cannot be processed. In this case the terminal device sends a request to the router called a retry to retransmit these packets. If a repeated data packet is received again with distortions, it will be retransmitted again, and after several unsuccessful retransmissions the packet will be ignored altogether. This is the reason why there can be constant disruptions of the Internet connection, freezes and scattering of the viewed video online, brakes in browsers, and the like.
Reducing the speed of traffic of all devices because of one low-speed device.
I want to mention one more reason for the decrease in traffic speed. If your router is set to "802.11 b/g/n" or "Auto" in the wireless mode settings, this can play a cruel trick on you. In the case of a router supporting only devices with protocol "802.11 n" everything will be fine, the maximum data transfer speed of this protocol version will be provided (up to 150 Mbps). But as soon as an ancient device with protocol "802.11 b" connects to your router's network, or even just tries to connect, the speed of your whole network (for all connected devices) will decrease to the speed of this protocol version (up to 11 Mbit/s.). In this case, you will need to set the communication protocol in the router settings to "802.11 n". But it should be remembered that in this case the devices with the old protocol "802.11 b" will not be able to connect to Wi-Fi network.
Write in the comments whether your Wi-Fi network is heavily overloaded, and whether it does not interfere with its work.
Subscribe to our channel in Yandex.Zen or telegram channel @overclockers_news, which are convenient ways to keep up with new content on the site. With pictures, extended descriptions, and no ads.
What to look for when buying
Let's look at the main points to pay attention to in order to choose a good router for an apartment or home with great Wi-Fi coverage.
Wi-Fi parameters
Once upon a time there were routers, to which you could connect only by cable. Now they are produced very rarely. Almost all modern routers are equipped with a Wi-Fi module. It would seem that everything is easy – you can buy and connect as many wireless devices as you want. But in fact, the capabilities of different router models are different.
Operating range
Most router manufacturers claim a range of up to 150 meters outdoors and up to 50 meters indoors. However, these figures are taken from the ceiling and are calculated from the maximum power of home routers – 100 milliwatts (20 dBm). However, the actual range depends on the actual power of the transmitter, the antenna, and the frequency range being used.
20 dBm is the maximum power allowed, but it can actually be lower. Unfortunately, manufacturers do not always indicate the real power of the transmitter. If you can find this parameter in the documentation – good. But even if your router is operating at its maximum power, do not be fooled. After all, the transmitter power of the client device – a laptop, a smartphone – may not exceed 30-40 mW. In the apartment, because of this there may still be places where the client device sees the router, and the router device does not. There is a dead zone, which can be overcome by installing repeaters at the problematic points.
The range of the router also depends on the antenna gain. Yes, there are different antennas. In addition, modern router models can have two, three, or more antennas. Antennas provide not only more or less bandwidth, but also signal strength. It is also possible to boost the signal with an additional external antenna. But you can connect it only if the antenna on your device is removable. That is, it can be disconnected and replaced with another one with a higher gain. This point is also worth paying attention to, because many models are equipped with a non-removable antenna. At the same time, the higher the frequency at which the device operates, the stronger the signal attenuation. When using routers that work on high frequencies, you should take this fact into account.
Recommended models of home routers
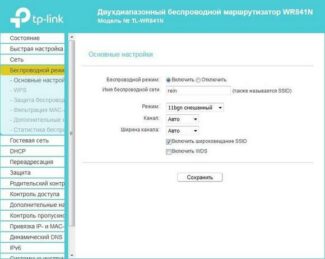
TP-LINK TL-WR841N

Not bad functionality for reasonable money.
A good functional router for the home. It is equipped with four LAN-ports and a WAN-port for Ehternet connection.
Minus – there is no USB port. So if your network is supposed to have a 3G modem or a network printer connected directly to the router, this model will not suit you.
The router has two antennas and, according to the manufacturer, provides wireless speeds of up to 300 Mbps. The router is working on the frequency of 2,4 GHz.
ASUS RT-AC51U

This is a most affordable dual-band router.
Router works in two bands – 2.4 and 5 GHz. It is possible to work in two bands simultaneously. At the same time, the manufacturer declares the maximum wireless data transfer speed of 733 Mbit/sec. However, this is the total speed in both bands. The actual data transfer can be carried out on the 2.4 GHz frequency at 300 Mbit/sec, and on the 5 GHz frequency 433 Mbit/sec.
The router is equipped with a universal USB port to which you can connect a printer, a flash drive, an external hard drive and a 3G/4G modem. You can also use the USB port to charge mobile gadgets.
Netis WF2411E

This is a very cheap router!
A very budget model in terms of price, while having quite decent basic functionality.
Of course, on this device you will not find USB ports, but four LAN ports. There is only one antenna and Wi-Fi data transmission speed is claimed to be up to 150 Mbit/sec.
If you are on a tight budget and are looking for a budget model, this device is not bad for its money and will serve the basic needs of the undemanding user.
Effects on the body

Any electromagnetic radiation, regardless of its source, is able to affect the human body. Wi-Fi is no exception.
High frequencies of radio wave radiation can provoke conditions such as
- sleep disturbance;
- a loss of appetite;
- headaches;
- decreased ability to work;
- Increased fatigue and weakness;
- abnormal changes in blood pressure;
- excessive excitability, nervous overstrain.
The issue of harm from electromagnetic waves becomes particularly acute in the apartment. Since most living quarters are relatively small in size, the router is quite often located close to the place of permanent residence of family members. This raises legitimate questions about whether the radio waves emitted by the router are harmful.
This question is also very worrying for parents, because children's bodies are not fully formed and are more susceptible to any negative influence from the outside.
There is currently no clear answer on this point, so the danger from Wi-Fi belongs to the group of unproven risks.
It is worth understanding that the impact of the router, as a single unit, is unlikely to have a serious impact on health. But its combined effect with other devices, such as phones, microwave ovens and computers, can really cause tangible harm to the body.
Watch the program "About the most important", where they tell the whole truth about the harm Wi-Fi:
How to protect yourself?
Electromagnetic fields are as integral part of our lives as the Internet, so unfortunately you can not fully protect yourself from their effects. But it is possible to minimize the harm from Wi-Fi routers. To do this, you should follow some recommendations:
- It is recommended to install the router in the room where family members spend the least amount of time.
- You should not stay near the router for a long time. It is desirable that it is located away from the workplace.
- It is best to unplug the device at bedtime.
- If the device is characterized by high power, it is recommended to try to turn it down. The signal level will not be affected, and the impact on the body will be minimal.
Unlike the detrimental effects of mobile communications, which has been officially proven, the harm from Wi-Fi is not fully confirmed. Personal safety measures will not be superfluous, even if there is no real danger from the routers:
- It is desirable to wisely distribute the time allocated to the use of electronic devices.
- Alternate it with rest in the fresh air, physical activity.
- Do not forget about the existence of real life.
That's such a serious article our authors wrote today. And what do you think, is Wi-Fi dangerous for a man? Share your thoughts!
Read More: