If most of your devices can be used near a router, the best choice is 5 GHz because it gives you the advantage of faster connections. For example, if you're doing several types of "high-frequency" scenarios online, such as gaming or video conferencing, it's best to connect in the 5 GHz band and be as close to the router as possible. (It's even better to connect devices directly to the modem via Ethernet cable, since wired connections are always faster and more stable than wireless ones.) Or, as noted above, if you live surrounded by neighbors and their devices, the 5 GHz band can help you avoid problems with air congestion.
- What is the real difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
- What are dual- and tri-band routers
- What's 5G?
- What is 5GHz?
- How do I change my band settings?
- How to know if your device supports 5 GHz Wi-Fi
- How do I know if my laptop supports the 5 GHz band?
- Laptop does not see Wi-Fi 5G network
- Using External Wi-Fi Adapters for Laptops with 5GHz Support
What is the real difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
These numbers refer to the two different "bands" your Wi-Fi can use for its signal. The biggest difference between the two is speed. Under ideal conditions, 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi will support speeds up to 450 Mbps or 600 Mbps, depending on the class of router. 5 GHz Wi-Fi will support up to 1300 Mbps.
Of course, there are some caveats here. First, the maximum speed you can see also depends on which wireless standard the router supports – 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n or 802.11ac.
The second big caveat is that important phrase we mentioned: "ideal conditions."
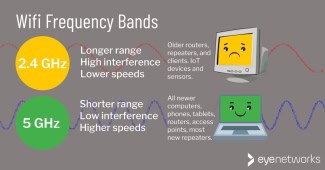
The 2.4 GHz band is a busy band because it's not just used by Wi-Fi. Older cordless phones, garage door openers, baby monitors and other devices tend to use the 2.4 GHz band. The longer wavelengths used in the 2.4 GHz band are better suited to longer ranges and transmitting through walls and solid objects. So, it may be better if you need more distance on your devices or have a lot of walls or other objects in the areas where you need coverage. However, because many devices use the 2.4 GHz band, the resulting congestion can lead to dropped connections and slower than expected speeds.
The 5 GHz band is less congested, which means you are likely to get a more stable connection. You'll also see higher speeds. On the other hand, the shorter wavelengths used in the 5 GHz band make it less able to penetrate walls and solid objects. It also has a shorter effective range than the 2.4 GHz band. Of course, you can also reduce this shorter range by using range extenders or Wi-Fi mesh systems, but that would mean a big investment.
What are dual- and tri-band routers
The good news is that most modern routers act as dual- or tri-band routers. A dual-band router is one that broadcasts 2.4GHz and 5GHz signals from the same device, giving you two Wi-Fi networks and the best of both technologies. Dual-band routers come in two varieties:
- Selectable Dual-Band. A selectable dual-band router offers a 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi network, but you can only use one. You must use the switch to tell the group what you want to use.
- Simultaneous dual-band. The simultaneous dual-band router simultaneously broadcasts separate 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi networks, giving you two Wi-Fi networks that you can select when you set up the device. Some brands of routers also allow you to assign the same SSID to two bands so that devices can only see one network, even if they are still running. These tend to be slightly more expensive than selectable dual-band routers, but not by much. The benefits of both bands working simultaneously usually outweigh the cost difference.
A tri-band router broadcasts three networks simultaneously – two 5 GHz signals and one 2.4 GHz signal. The reason for this is to help reduce network congestion. If you have multiple devices that do use the 5 GHz connection heavily – like streaming high-definition video or even 4K video – you could benefit by spending a little more for a tri-band router.
What's 5G?
5G stands for fifth generation; it refers to the cellular communications standard. This standard allows you to access the Internet with your smartphone from anywhere with a cellular signal, even if you don't have Wi-Fi access.
The naming principles remain the same and 5G came after 4G, 3G and 2G. Some of these standards have other names that not everyone is aware of.

The 2G standard was also known as EDGE (short for Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution). This was an update of the original 2G standard. 4G you may know as LTE (Long Term Evolution). This term was first used for connections at speeds much higher than 3G, even if they did not reach the requirements of the 4G standard.
5G networks have no other names yet. That may change as the technology develops.
What is 5GHz?
Unlike the 5G mobile standard, 5GHz is a short-range wireless band in home networks. All modern routers have at least two bands, that is, they can transmit on two different frequencies.
One of these bands is 2.4 GHz and has been in use for a long time. Because of this, this band works on so many devices. Broadcasting on the 2.4 GHz band is done over longer distances, but the data rate is not very high.
The 5 GHz band supports faster data rates than the 2.4 GHz band. A more modern network is less susceptible to interference because there are fewer devices operating on this band. Smartphones, laptops, and computers on the 2.4 GHz band can be disturbed by microwave ovens, baby monitors, and other household devices. This can cause data transfer rates to drop.
The 5 GHz band has a greater choice of Wi-Fi channels, allowing you to change channels if your current channel is overloaded by your neighbors' devices.
Some routers transmit on both frequency bands on the same network and automatically select one of them to connect devices. Others operate on the 5 GHz band with a separate SSID and have -5G at the end of the network name, which contributes to confusion about the two terms.
How do I change my band settings?
Whichever band you choose – 2.4 or 5GHz – you need to make sure your wireless modem/router is also configured for that band. Check which frequencies your particular router model supports.
In the case of a dual-band router, you can configure it to transmit on both bands at once. In this situation, you will usually see two networks (SSIDs) with the same name, but with "5G" or "2.4G" at the end. Accordingly, you can optionally connect each specific device to one or the other network.
On most new modems, you can find the best – specifically for your current environment – Wi-Fi channel, and then change that channel in the modem's wireless settings as needed. This option allows you to make the most of the various advantages of the 2.4 and 5 GHz Wi-Fi bands.
How to know if your device supports 5 GHz Wi-Fi
Based on the rule above, in order to work on the new frequency, you need both devices to support it. Accordingly, you need to check the router and the laptop itself. To find out whether the router is equipped with the necessary characteristics, you can do the following:
- Go to the settings (the address to enter the parameters is written on the device: 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
- Enter your login and password (the data is also specified there).
- Open the tab with the wireless settings.
- Find the frequency switch button.
Pay attention! Another method is to go to any online electronics store and find your router. In the specifications column there is a list of supported bands. You can also open the manufacturer's website. If there is a list of router models, there will probably be the necessary device and information about it.
How do I know if my laptop supports the 5 GHz band?
There is no such way. But it is worth opening the Windows Device Manager. To do this, you need to click on the "Start" menu and write there "Device Manager". You can also press the shortcut "Win + R" and write in the input field "devmgmt.msc" (without quotation marks). In the list you will need to find the network adapters. In the branch that opens, select the wireless network module. As a rule, the name is Wireless, Wi-Fi, WAN. Next – find the characteristics of the adapter in the search engine. If it works with the standard a or ac, then the desired frequency is definitely supported.
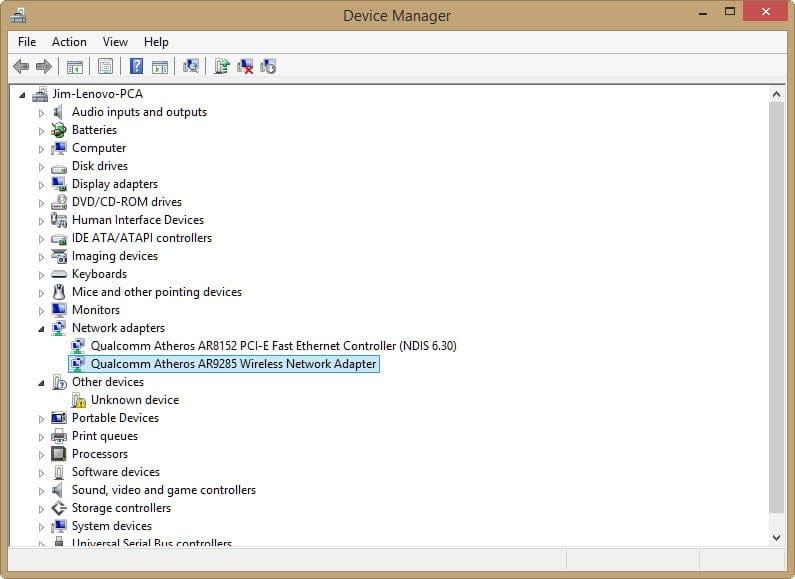
Pay attention! Determine whether there is support on the smartphone side, you can, by connecting the device to the wi-fi. If everything works, the gadget is equipped with the necessary module.
Laptop does not see Wi-Fi 5G network
The cause of the problem in 90% of cases is the laptop's lack of support for higher frequency. If one device works with 5 GHz, and others do not, and you want to use a faster Internet, it is worth buying a dual-frequency router.
Using External Wi-Fi Adapters for Laptops with 5GHz Support
If the devices do not work with a higher range, it is worth using the following way – to install a special external adapter. The only condition is the presence of a USB port in the laptop. In addition, such gadgets are compact and do not catch the eye.
It happens that the laptop does not see the connected device. In this case, it is worth looking for drivers on the manufacturer's website or another forum. But you should not download files from unknown sources, so as not to infect your computer with malicious software.
Wi-Fi is an integral part of modern people's lives. Everyone wants a high-speed connection. 5 gigahertz frequency can help with that. The main thing is to know the basic nuances. And this article will help with that.
Read More: