Because it's more complicated, I'll cover it later in my own guide, but TP-Link has included it here as an example.
- What is a vlan: technology and configuration
- Vlan: What is it?
- How does VLAN technology work?
- Switch Port Operation Modes
- Connections and Ports
- WAN and LAN – what is the difference?
- Types of Ports
- Trunk
- Advantages of using VLAN
- About windows vlan
- Popular Related Posts:
- How VLAN works
- Benefits of VLANs
- VLAN Modes
- MTU VLAN (Multi-Tenant VLAN)
- Port-based VLANs
- 802.1Q VLAN.
- DHCP Server Notes
- Trunking and routing between vlan
- Tagging a vlan.
What is a vlan: technology and configuration
We have used the term VLAN many times on our website in instructions for setting up various routers and creating corporate networks. However, modern vlan technology requires a detailed study, so the following series of articles is devoted to characterizing and configuring "vlan" in different devices.
This article is a kind of "introduction" and here we will look at what a VLAN is and how VLAN technology helps in setting up a network.
Vlan: What is it?
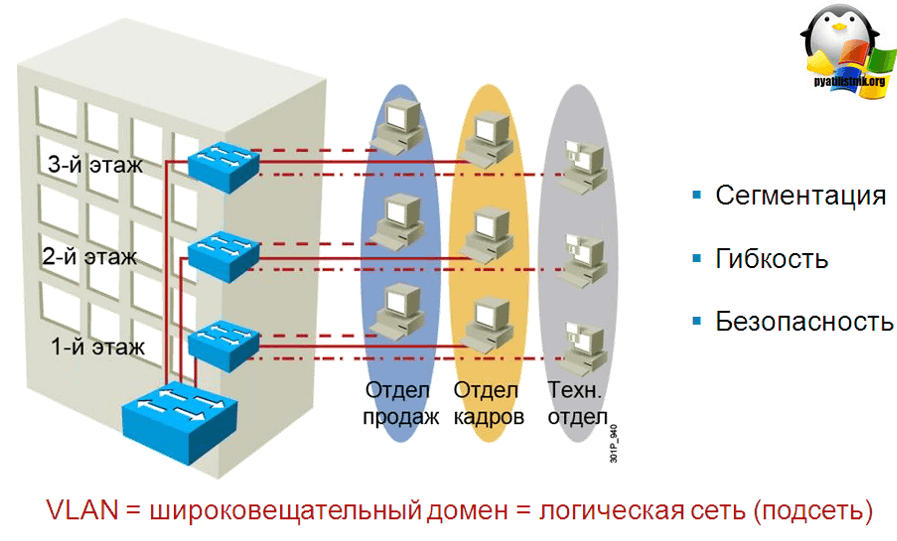
VLAN is a technology which allows you to configure multiple virtual broadcast domains within one physical broadcast domain. In other words, having "flat" physical network of several or one switch, you can divide it into several isolated, full-featured "flat" networksThe network is divided into several isolated, full-featured "flat" networks, thus differentiating users' PCs by departmental affiliation or, in the case of servers, by specific roles and the specifics of their work.

- – It reduces the number of broadcast requests, reducing network bandwidth;
- – improve security of each enterprise departmentIt eliminates the possibility of eavesdropping on traffic by third-party employees who are not members of a particular VLAN;
- – there is an opportunity to geographically separate different departments and divisions on the basis of affiliation. That is, for example, employees of the HR Department, not being in the same building, will be able to "see" each other within their subnet.
The network architecture uses VLANs to provide network segmentation of services, usually performed by routers, which filter broadcast traffic between different VLANs, improve network security, perform subnet aggregation and reduce network congestion. Switches cannot pass traffic between VLANs due to the restriction imposed by the broadcast domain.

Some switches can have Layer 3 networking functions of the OSI model, storing and using routing table to carry traffic between subnets. In this case, a virtual interface of a particular VLAN is created on the switch with a specific ip address и subnet mask. Such an interface acts as a default gateway for devices in a given VLAN.
How does VLAN technology work?
Each VLAN subnet has an identifier that identifies which subnet belongs to which subnet. The identifier information is contained in a tag that is added to the body of the Ethernet frame of the network in which VLAN subnetting is implemented.
The most common standard describing the traffic tagging procedure is the open standard 802.1 Q. There are also proprietary protocols but they are less popular.
The format of Ethernet is the frame after tagging:

A 4-byte tag consists of several fields:
- TPID (Tag Protocol Identifier). – The tagging protocol identifier. For the 802.1Q standard, the TPID value is 0x8100
- P-tag – Defines the priority of a packet. Used with 802.1p to determine the priority of packets
- CFI (Canonical Format Indicator) – The MAC address format identifier that was used for compatibility between Ethernet and Token Ring networks. The CFI field is no longer used due to the abandonment of Token Ring networks
- VLAN ID. – VLAN ID. Determines which VLAN subnet the packet belongs to
It is by the tag the network equipment determines packet belonging to a particular VLAN, filters packets and determines further actions with them: remove the tag and pass to the end equipment, discard the package, forward to the next recipient of the package with the tag saved. The rules defining the actions with a tag-based packet depend on the operating mode of the network equipment port. In turn, the mode of operation is selected according to the characteristics of the connected equipment. The system may contain equipment with or without VLAN technology support.
Switch Port Operation Modes

The Access type is assigned to a switch port to which either a single subscriber device or a group of devices in the same subnet is connected. In addition to selecting the Access port operating mode, you must specify the identifier of the VLAN subnet to which the equipment located behind this port will belong.
When the switch receives data from the subscriber devices connected to the Access port, it adds a common tag with the specified subnet ID to all Ethernet frames and then operates with the tagged packet. In contrast, when receiving data destined for an Access port from the main network, the switch will check the VLAN ID of the received packet with the VLAN subnet number of that port. If they match, the data is successfully sent to the port and the tag is removed, so the devices connected to the port will continue to operate without the need for VLAN support. If, however, the ID does not match the subnet number, the frame will be discarded, preventing a packet from a "foreign" VLAN subnet.
- Trunk port – A trunk port that transmits tagged data packets. It is used to connect VLAN-enabled network devices, most often to connect switches to each other.
- Network size – the Internet is ubiquitous (we are not even talking about Earth anymore, as it is also used in orbit, and in the future, there may be applications on other planets, and it will not limit WAN to our globe), LAN network – limited to the apartment, office, enterprise network (key – not everywhere).
- The number of users – again, the difference in the limitation of the local network.
- Services – local services (printing, files), global services (WWW, global routing).
- Topology – in a LAN, everyone is equal, connected to each other, Peer-to-Peer. The WAN is characterized by client-server connections.
- Tagged port. This is the type of port that is allocated on the switch to verify that the virtual network tag is present in incoming packets. Also, this type of port performs the function of adding these tags. This leads to an internal classification: tagged receiving (which checks for the tag and accepts the packet if it is present) and transmitting (which puts that same tag).
- Untagged ports.. These are the ports whose job is to transmit all types of packets that pass through the switch.
 What is a virtual network adapter and when is it useful?
What is a virtual network adapter and when is it useful? ESXI virtual machine gets incorrect network settings
ESXI virtual machine gets incorrect network settings- Installing esxi 6.5, with proper configuration
 Installing and configuring dongleserver ProMAX
Installing and configuring dongleserver ProMAX Connecting 1C dongleserver dongleserver ProMAX
Connecting 1C dongleserver dongleserver ProMAX- Setting up a network in CentOS 8, in a minute
- Reduced broadcast requests that reduce network bandwidth.
- Increased security of each virtual network. Employees in the same department of the office will not be able to monitor traffic from departments that are not on their VLAN and will not be able to access their resources.
- The ability to split or merge departments or users that are geographically distant from each other. This allows you to involve specialists who are not in the office building to the work process.
- Create a new virtual network without running cables or buying a switch.
- Allows you to connect computers connected to different switches into one network.
- Simplification of network administration. When a VLAN user moves to another room or building, the network administrator does not need to reconnect the cables, just reconfigure the network equipment from his workplace. And in the case of dynamic VLANs, the user will be registered to "his" VLAN at the new location automatically.

In addition to setting the operating mode and VLAN ID, the Trunk ports are configured with a list of VLAN subnets that the switch checks against when it receives packets. This allows packets from multiple VLAN subnets to be transmitted through the Trunk ports.
Switch, after receiving untagged data into the Trunk port, will act similarly to the Access port, i.e. it will mark the packets with the VLAN-subnet identifier assigned to that port and will pass them on into the network. If a packet is received with the same VLAN ID as the port itself, the tag will be removed and the data will be sent to the subscriber's device without the tag. If a tagged packet is received with a VLAN ID that is different from the number assigned to the port, the switch will compare the ID to a list of allowed VLAN subnets. If the number is listed, the data will be sent over the network to the next device without changing the tag. If the ID indicates that it belongs to an unfamiliar VLAN subnet, the packet will be discarded.
Connections and Ports
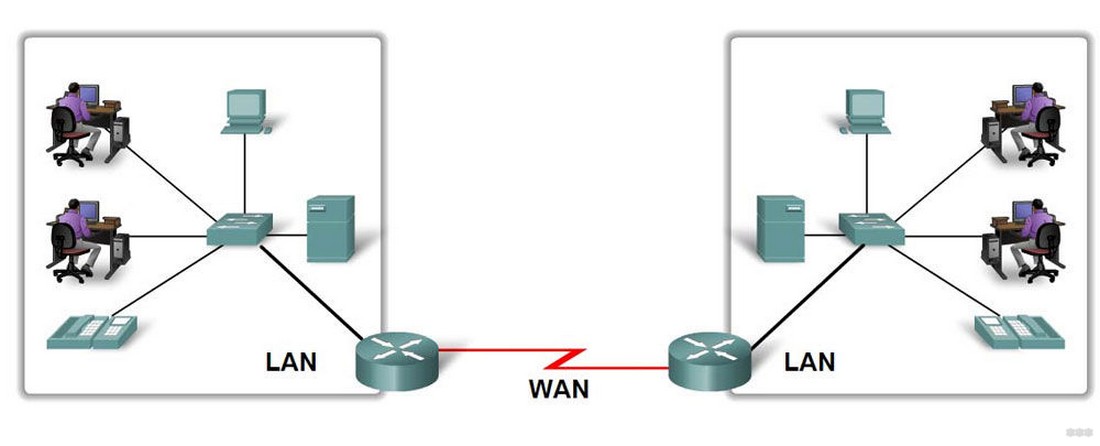
Here I will tell you about the connection to the LAN. There are two variants:
Here it is worth understanding that everything revolves around the router. Everything that connects to the router is a LAN. What the router connects to is the WAN. As an inbound and outbound connection.
The router itself can connect via Wi-Fi, but usually still connect to it. Whoever connects is immediately connected to the local network. Another option is to connect via wire. To do this let's look at the backside of any average router:
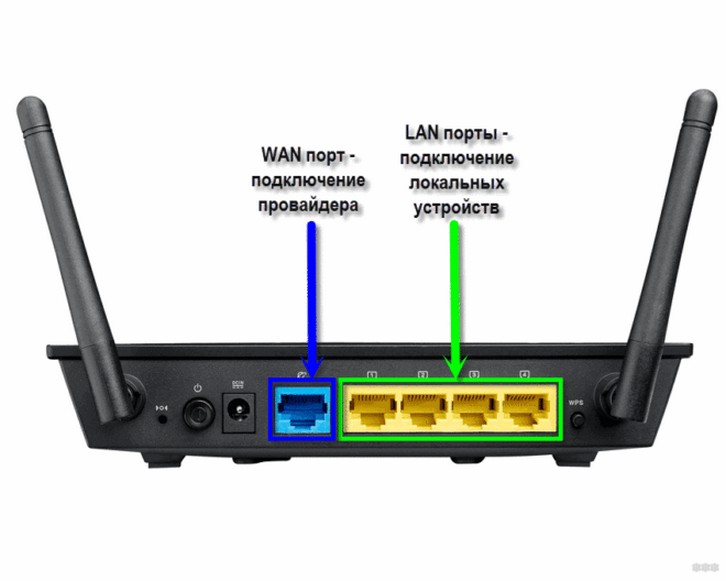

Notice the LAN ports – there are usually several, and they are usually yellow (and not always). They say LAN, or local network, or something else. It is difficult to confuse them with others. The WAN port is specially put separately and allocated. Bottom line – if you want to connect something to your local network – connect only to LAN ports. If you want to connect router to ISP (for internet access, 99% of the time) or another router (e.g. for kinky repeater mode) – use WAN interface.
Now both LAN and WAN ports usually have the same type of connector for twisted-pair Ethernet cable – RJ-45. But this may not always be the case. Thus ADSL modem may use RJ-45 (LAN) for the local network, and RJ-11 (WAN) for Internet access via a telephone cable. The LAN connector is predominantly RJ-45.

WAN and LAN – what is the difference?
LAN – Local Area Network
WAN – Wide Area Network.
There is a broad sense and a narrow one. In the wide sense I have already mentioned above – there is your personal home network, and there is a network to which all devices of the world can connect – the Internet. In a broad sense, the WAN is the Internet. Basically this is the difference and is asked everywhere in schools and universities. That's where the main differences are asked for, too:
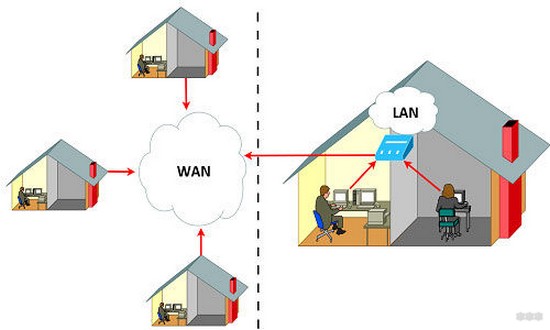
So, if someone asks you what is the difference between WAN and LAN – list the points above, separated by commas, and end the conversation – everyone will definitely be happy.
But there is one more point about the technology. We're talking about the WAN port. As a rule, the ISP cable is plugged into it – to connect to the Internet. The WAN port makes the outgoing connection in the router. And in this approach, the global concept of LAN and WAN in some cases can blur the line between them)
That said, the outgoing connection through the WAN can also be connected to another router in your home (special cases). To connect an external device through the WAN port without dancing with tambourines is not possible.
There is another type of network – MAN (Metro Area Networks). It is something in between – a metropolitan or city network, probably an ISP. That is a kind of local network between all users, for example of one provider. As an advantage – high speed between points. On this basis, it is not bad used to live file sharing.
Types of Ports
Setting up a VLAN is a long and laborious process. It is an action that you have to do once, and then just watch and fix it if necessary. When it comes to a single switch, there is no problem. In essence, it comes out that one port one VLAN and the work is boiling. But when several such devices are brought together, there are different nuances. These have to do with the use of tagged and untagged ports.
Let's start with a simple circuit:
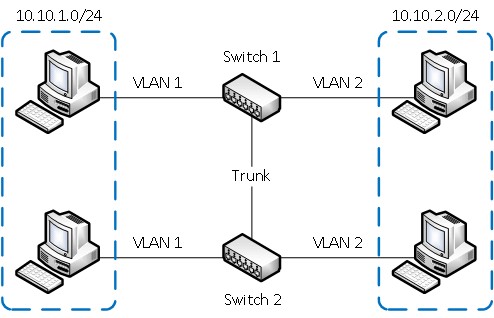
It has has 2 VLANs and a common network (which is represented by a combination of both virtual ones, this configuration can also be implemented). SW1 and SW2 are switches which are connected with tagged ports (21 and 22 respectively). In fact, it comes out that the same ports are used for data transmission (the switches are connected through them).
When transmitting data within VLAN1 a special flag (tag) is put on, which is read by the switch and transmitted to the other. From port 21 to SW1 an unremarkable packet comes out, which is received by port 22 on SW2. Having received the tagged packet, the switch transmits it as VLAN1 component. Thus, this package is available for computers G and Hcomputers, but is not available for E and F .. Both ports are tagged in order to be able to exchange traffic between the networks. Otherwise the tag will be ignored and transmitted to all devices on the switch.
Trunk
This is the type of port in CISCO switches.. It performs the task of passing tagged traffic between different network segments. In a concrete example it looks like this:
Another one is added between the switches where the VLAN is installed. Its task is to to provide data exchange. The trunk ports, instead of checking the tag and broadcasting packets, have the property of checking and transmitting destination. The rest of the traffic is simply ignored. The result is transmission through the trunk with the preservation of the tag (as if there is no intermediate switch). The only difference between a trunk port and a tagged port is that the trunk does not broadcast to the network itself (only transmitting packets if tagged).
Advantages of using VLAN
Flexible partitioning of devices into groups
Typically one VLAN corresponds to one subnet. Computers located in different VLANs will be isolated from each other. It is also possible to group computers on different switches into one virtual network.Reducing broadcast traffic on the network
Each VLAN represents a separate broadcast domain. Broadcast traffic will not broadcast between different VLANs. If the same VLAN is configured on different switches, the ports on different switches will form one broadcast domain.Increased network security and manageability
In a network divided into virtual subnets, it is convenient to apply policies and security rules to each VLAN. The policy will be applied to the entire subnet, not to an individual device.Reducing the amount of hardware and network cable
Creating a new VLAN does not require you to buy a switch and run network cable. However, you must use more expensive managed switches that support VLANs.
How to create and configure a vlan in Cisco, I told you in another article, as you see. the technology is very good and helps to minimize 806 frames (broadcasts) and thus improve the performance of your LAN
About windows vlan
Windows does not come with vlan as built-in support. You can't just say out of the box when you install an operating system that a network card will be in the correct vlan and set a Vlan ID. There are some exceptions which are specialized network card drivers. For example, there is software Realtek Ethernet Diagnostic Utility, as you can see for Realtek network cards, it is able to work with virtual tags. Cards with 802.1Q support, also know how to process tags, for example, can delete them or process them in a special way. I don't know if Windows needs to process vlan on its side because it is better to do it on the switch.
As a rule, in this case, there is a mechanism that allows you to disable the processing of tags by the network card, making it more "dumb" and delivering traffic along with the tags. Usually, this is done by editing the registry by specifying the appropriate key.
xx is the number of the network adapter in the system, I want to point out that each vendor has its own utilities and its own drivers, about their availability, you should read the specification. I hope you will not give up learning about vlan ports technology and study it more thoroughly and put it into practice.
Popular Related Posts:
How VLAN works
Computers on a LAN are connected to each other using networking equipment – switches. By default, all devices connected to ports on a single switch can communicate by exchanging network packets. Any computer can send a broadcast packet addressed to all devices on that network, and all other computers connected to the switch will receive it. Everyone hears everyone. The large number of broadcast packets sent by devices reduces network performance because switches are busy processing data addressed to everyone at once instead of useful operations.
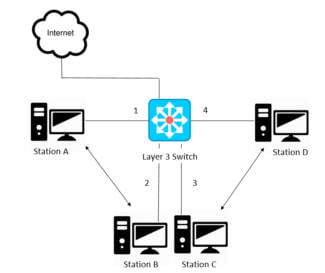
To reduce the impact of broadcasts on performance, the network is divided into isolated segments. In this case, each broadcast packet will be distributed only within the segment to which the sender computer is connected. This can be achieved by connecting different segments to different physical switches that are not connected to each other, or by connecting them through routers that do not allow broadcasts.The figure shows four isolated network segments, each connected to a different physical switch. Interaction between the segments takes place through routers. VLANs allow you to isolate network segments using a single physical switch. Functionally it will look completely similar, but one VLAN-enabled switch is used for each office.
VLAN technology is based on the IEEE 802.1Q standard. It allows you to add information to Ethernet traffic about whether the data being transmitted belongs to a particular virtual network – VLAN tags. With their help, switches and routers can distinguish from the total stream of frames transmitted over the network those that belong to a particular segment. VLAN technology makes it possible to organize the functional equivalent of multiple LANs without the set of switches and cables that would be required to implement them in physical form. Physical network equipment is replaced by virtual equipment. Hence the term Virtual LAN.
Benefits of VLANs
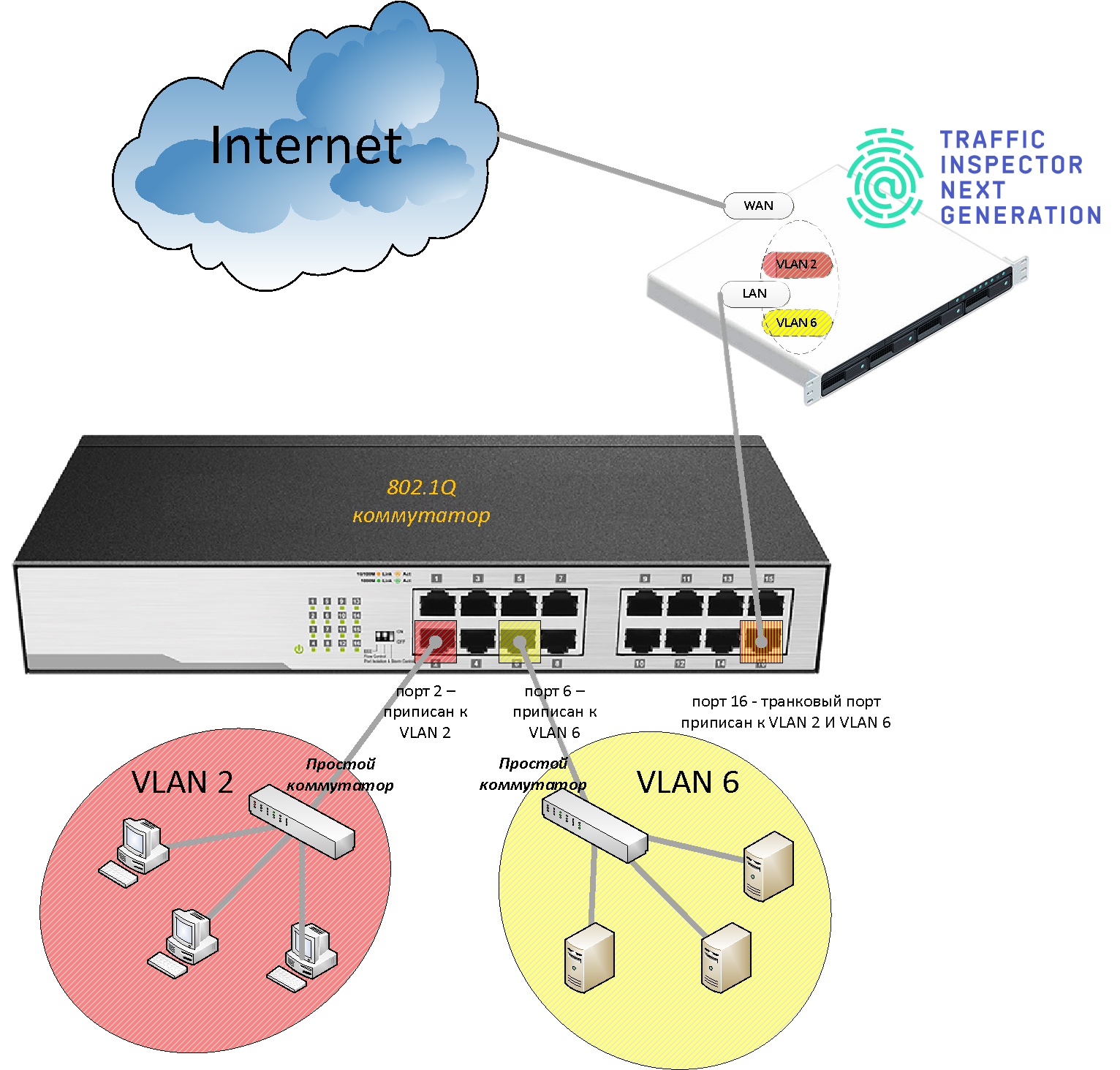
VLAN technology allows a single Traffic Inspector Next Generation device to control Internet access for several departments, and it is possible to set different rules for each segment of the network.
The figure shows a company network connected to the internet via a Traffic Inspector Next Generation server. The network is organized on the basis of one switch with two virtual segments – VLAN 2 and VLAN 6. The first segment contains users' computers, and the second segment contains servers. The Traffic Inspector Next Generation device is connected to the trunk port of the switch, a special port that "hears" packets from all virtual networks. Traffic transmitted or received on the trunk port is always formed by tagged frames.
VLAN Modes
Most devices will support multiple VLAN modes.
The TP link smart switch (TL-SG105E) supports three modes:
Which mode you need to use will depend on your network requirements.
MTU VLAN (Multi-Tenant VLAN)
This uses a common uplink port, which is usually connected to the Internet.
Other ports can send and receive data through the uplink port, but not between each other, as shown in the diagram below:
This is very easy to set up, as all you really have to do is select the uplink port (shared port) and enable it.
Port-based VLANs
In this mode, a VLAN can consist of multiple ports, but a port can only exist in one VLAN.
It is used when you want to create an isolated network.
In this configuration, devices on VLAN 1 can access devices connected to ports 1, 2 and 3, but not devices connected to ports 4, 5 (VLAN 2).
Devices connected to ports 4,5 (VLAN 2) can connect to each other and have no connection to the Internet and cannot connect to devices in VLAN 1.
802.1Q VLAN.
This is the most flexible mode, but also the most difficult to configure.
The IEEE 802.1Q protocol defines a new Ethernet data frame format by inserting VLAN tag into the data frame data frame, as shown in the diagram below:
DHCP Server Notes
The DHCP server must be located on a VLAN that is accessible to all other VLANs, which usually means it is on an Internet router.
If you want a VLAN to use a separate DHCP server other than the one on the router, you can install it on the VLAN without causing problems for machines in other VLANs.
However, since the VLAN has a DHCP server, this does not prevent it from using a central DHCP server, and you cannot guarantee that the client in the VLAN will get an address from the local DHCP server.
Trunking and routing between vlan
The term "router on a stick" is often used to describe the connection of a router and a switch connected by an Ethernet link configured as an 802.1Q trunk. In this case, the switch is configured to use multiple vlan, and the router does all the routing between different subnets/vlan.
This term sounds a bit strange to some users, but it is a very popular and ubiquitous term in networks that do not have switches with Layer 3 features of the OSI network model. A good example of a "router on a stick" configuration would be a Cisco CCME installation, which implies the need to separate the VoIP network consisting of your ip phones from the general network where the workstations and servers are.
Tagging a vlan.
In general, to understand the tagging process, you need to separate data packets into incoming (incoming "off the network wire") and outgoing (outgoing "into the wire") packets.
Incoming un-tagged packets coming into a port are placed in what is called a "native" vlan. If the switch is configured to use more than one vlan, you need to specify which vlan the incoming un-tagged packet belongs to.
Incoming tagged packets coming into the port will be tagged and there is nothing else you can do with them. If the switch does not know how to work with tagging and does not know the exact vlan information, it will discard such packets. You can also force the switch to accept only tagged or untagged packets.
For outgoing untagged packets, you can select one vlan on each port where the packets will not be tagged, because hosts usually do not support tagging and will not be able to decrypt such a packet. Examples of such hosts are PCs, printers, etc.
For outgoing untagged packets the process is as follows: you have to tell the switch which of the vlanes to make available on the port, and if there is more than one, all but one will be tagged anyway.
Read more: How to output an image from your computer to your TV: cable your TV to your computer