To improve the reliability of your home network, we recommend considering a MoCA-enabled Wi-Fi network extender if your home has coaxial wiring. A good alternative is a MoCA network adapter.
- What WiFi bands are available: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz Explanation
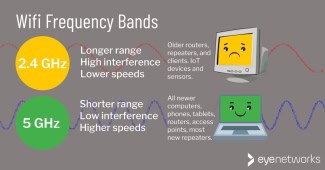
- 2.4 GHz band: more coverage, but less speed
- What's the difference between 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi and 5 GHz?
- 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi – Interference
- Which Wi-Fi range should you use?
- How do I choose a WiFi range to connect to on my Android?
- Wireless Frequency: What It Is
- What is frequency crossover
- Speed or range
- How to choose the best range
- 1. The size of your home
- 2. Interference and Obstacles
- 3. type and scope of client devices
What WiFi bands are available: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz Explanation
We are all very familiar with Wi-Fi networks today, as there is a very big trend toward wireless Internet connectivity today. We've probably heard of the 2.4 GHz band and the 5 GHz band, formerly known as Wi-Fi N and Wi-Fi AC, as in 2018 the WiFi Alliance decided to change those names to simpler nomenclature, Wi-Fi 4, Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6. Today, we're going to talk in more detail about the newest member of the family, the 6 GHz frequency band, which introduces the new Wi-Fi 6E standard, as well as all the features of the entire family.
As the speed requirements increased, there was a significant improvement in the standard, and Wi-Fi 5 was launched, which used only the 5 GHz band to communicate with various devices. Years later, the wireless standard was further improved to increase bandwidth and efficiency, while the theoretical performance of the Wi-Fi network was slightly increased, leading to Wi-Fi 6 . This new standard uses 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks simultaneously, This allows us to take advantage of both: the coverage of the 2.4 GHz network, which is larger than the 5 GHz coverage, and the speed of the 5 GHz network, which is much faster than the 2.4 GHz network.

Wi-Fi 6E was born out of the need to connect a large number of devices with Internet access to the Wi-Fi network. The novelty that. Wi-Fi 6E standard is the addition of the 6 GHz band. To Wi-Fi 6. Up until now, we've had Wi-Fi 4, which can use the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz band , although Wi-Fi 4 in the 2.4 GHz band has almost always been used, but it is true that there have been selectable dual-band and simultaneous dual-band routers with Wi-Fi 4 broadcasts in the 5 GHz band.
2.4 GHz band: more coverage, but less speed
This band is the oldest of all, all routers on the market use it, it ranges from 2.412 MHz to 2.472 MHz, it is divided into 13 channels of 20 MHz each, which overlap each other, as we can see in the picture. Subsequently channel 14 was added which was quite far from the 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi spectrum and not all the devices were compatible with this channel which operated at 2.484 MHz, reaching 2.495 MHz and only overlapping channel 12. and 13 was a measure which was used to avoid the oversaturation which this band represented very early on.


As you can see, the closer we get to the center of the spectrum, the more channels overlap each other.
The company The 2.4 GHz band is used by Wi-Fi 4 and Wi-Fi 6 standards. . It has 3 channels of 20 MHz or 1 separate channel of 40 MHz. In this case, the part of the frequency spectrum assigned to this band will remain free if our router chooses to use only the 40 MHz channel, but it will not affect our connection.
This strap is by far one of the most commonly used, it has high device compatibility because all WiFi devices today have access to the 2.4 GHz band , while many are not compatible with the 5 GHz band. The most cost-effective devices will stick to using this band, while it is more economical to manufacture them with compatibility for 2.4 GHz and excluding other bands. On the other hand, this is the band with the highest saturation. Many devices operate on the same frequency as this Wi-Fi frequency band, devices such as wireless keyboards and mice, TV controls or cordless phones use this frequency, this does not mean that they share the technology, that is, operate over Wi-Fi. Fi. But if a device is operating on 2.4 GHz, no matter how much Wi-Fi or other radio frequency technology, they will use the same airwaves and some connections will overlap each other.
What's the difference between 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi and 5 GHz?
Both are. 2 GHz Wi-Fi and 5 GHz – should be evaluated with the factors already mentioned in mind, namely the number of channels and signal strength, popularity of use, and possible speed.
First of all, comparing 2.4 and 5 GHz Wi-Fi, you can see the difference in the popularity of using a particular Wi-Fi band. The 2.4 GHz band is much more popular and most devices can be connected to it. In turn, the 5 GHz band is still rare these days.
As for the number of channels, the 5 GHz band is characterized by a greater number of channels. This makes the router faster, because more channels means less interference in the network.
It is very important to emphasize the ability of the generated signal to overcome physical obstacles. The 2.4 GHz band definitely has an advantage here, because it will work much better in conditions where you need the equipment to work in different rooms without problems.
When choosing any of the available frequencies, you should consider the factors that guide your network use. If you want to work easily or use the Internet for a variety of purposes, think about mobility or speed.
The 5 GHz Internet is definitely the best option for anyone who needs a fast connection when you need to seamlessly use multiple resources or transfer more files. In terms of mobility, however, the 2.4 GHz band will allow you to use the Internet without much hindrance in rooms other than the one where the router is located.
It's worth noting that it's currently advantageous to purchase dual-band routerwhich operates on two frequencies simultaneously.
2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi – Interference
If you have a lot of devices in your area using the same Wi-Fi band, you could have interference. The 5 GHz band, which is less popular and less common on devices, is not a serious problem.
Wi-Fi frequencies that are classified as 2.4 GHz and have fewer channels are prone to more interference due to the fact that the emitted signals overlap. Due to the fact that 2.4 GHz is a fairly popular band, the risk of certain connectivity limitations will be more likely. You may not feel this while surfing the Internet, but certainly the quality and buffering speed of the FullHD movie you are watching will be at a low and unsatisfactory level.
In today's world of the Internet and various technologies, a great solution is to use the previously mentioned dual-band router.
Which Wi-Fi range should you use?
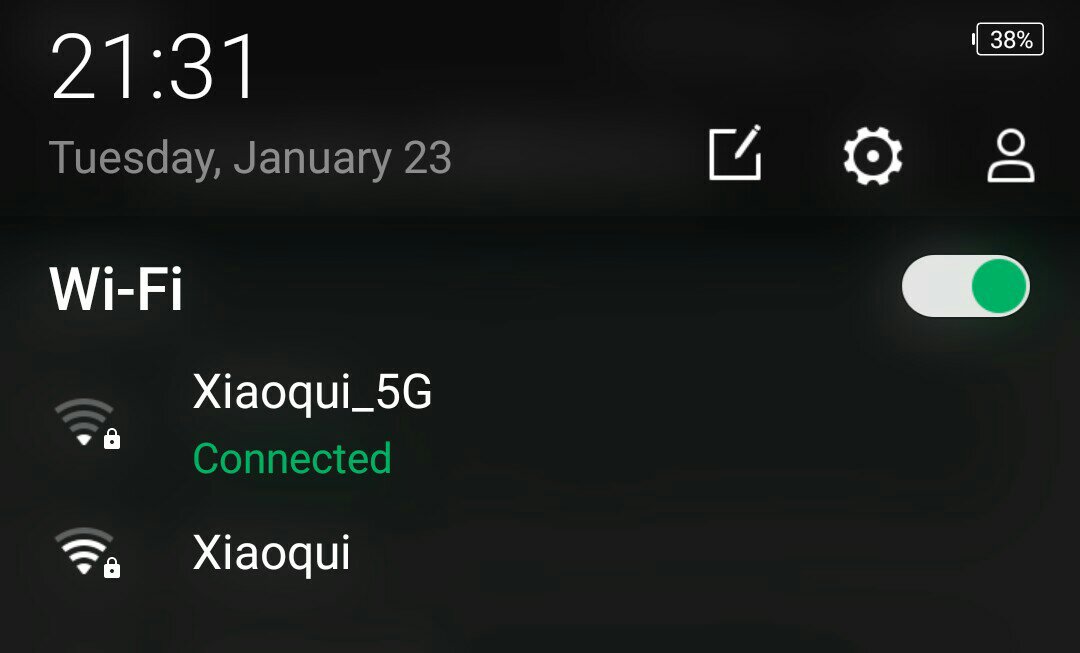
The choice depends greatly on the group's purpose for you. The need for higher speeds makes 5 GHz a better choice than 2.4 GHz. If wireless range is more important to you, 2.4 GHz is a better choice. If you have many devices that use 2.4 GHz and are experiencing interference or connectivity issues, you are better off switching to the 5 GHz band.
Note that while a Wi-Fi network can use both bands, your personal devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops will only connect to one radio band at any given time. Each device has basic band selection rules for connecting. Perhaps your phone connects to the 2.4 GHz band and your laptop connects to the 5 GHz band. So your device will decide which band to use for connection, depending on certain conditions, such as range and interference. Your device should support dual-band mode so that you can easily switch between 2.4 and 5 GHz.
Devices that only support the 2.4 GHz band will automatically connect to that band. Dual-band devices that support both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz automatically select the band, or you can set it up to select a specific band to your liking. This is only possible if the Wi-Fi network provides a 2.4GHz band SSID or a Wi-Fi name and a 5GHz band SSID, as you can see in the screen shot of my Android smartphone above.
How do I choose a WiFi range to connect to on my Android?
Yes, depending on the device. Older devices are tied to the 2.4 GHz band, but there are Android devices that allow users to specify the band that will be used for connection. All you need to do is follow a simple procedure; Open your Android device's settings menu, tap Wi-Fi, then the three dots in the top right corner, tap " Advanced" > « Wi-Fi frequency range", select the desired radio band.
Finally, choose the WiFi range carefully. Note that the 5 GHz band just because it is theoretically faster does not always mean that it is better. Sometimes you will have a terrible experience with the 5 GHz band. Test the performance of both bands on your device and in different locations in your home or office and choose the best one.
Wireless Frequency: What It Is
In this section, we'll talk not only about what frequency is, but also about frequency crossover and wireless channels.
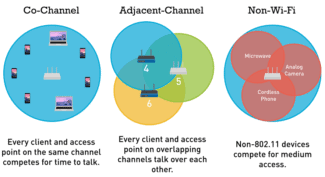
So, let's compare data packets to cars traveling in two directions: from point A (your PC) to point B (your router). The frequency is the road from the router to your PC. However, our apartments, offices often have many roads, and some of them intersect with each other. For example, it can be a road from the radiotelephone to the base, from the remote control to the TV/air conditioner. In addition, there are cars that drive aimlessly in one direction, such as the radiation coming from the microwave – radio interference.
What is frequency crossover
Imagine that you are sitting at your computer and you see several networks running simultaneously on it. First of all, this means that there are other cars driving down your road besides your cars. Only they are headed from your neighbors' computers to another access point. You all use the same road – the frequency – to pass cars (packet passing). Also, since the wireless environment is a distributed one, cars can often collide with each other if they have little room on the road.
To make it easier for cars to drive on the road, they divided the road with a lane. That way they don't interfere with each other. The same situation happens with radio waves: the frequency is divided into channels. This avoids collisions and traffic deterioration.
Thus, if your neighbor configures his router to another channel, you both although you will be in the same frequency range, but will not collide. Thanks to this, no loss of traffic will occur.
Speed or range
The main difference between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands comes down to the difference in wireless speed and range (coverage) of the network: if you want more range, use 2.4 GHz; if faster connections are a priority, use 5 GHz.
The technical capabilities of the newer 5 GHz band allow you to reduce interference with large numbers of devices served and maximize network performance. Which makes this band preferable for games, for example, where it is important that latency is as low as possible.
The 5 GHz band offers more communication channels, and it generally does not have significant problems serving many potentially competing devices. But technically, the 5 GHz band does not offer as much range as 2.4 GHz. Newer routers are usually dual-band and give you the choice of using 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz.
How to choose the best range
1. The size of your home
Larger homes need more coverage, so 2.4 GHz is the best option here.
As for smaller homes or apartments, the 5 GHz band will not only provide faster connections but also reduce interference from neighboring networks.
If you want to take full advantage of the 5 GHz band and still increase your Wi-Fi network coverage, then it makes sense to look into Wi-Fi network extenders.
2. Interference and Obstacles
The 2.4 GHz band is more susceptible to interference because many types of devices operate on this frequency. These include older models of routers, microwave ovens, Bluetooth devices, baby monitors, garage door openers, etc.
From this perspective, 5 GHz is the best option if the subscriber device is close enough to the router/access point. In addition, a large number of dedicated subscriber channels are available in the 5 GHz band. Less overlap between these channels means better interference immunity, which ultimately means better Wi-Fi network efficiency.
3. type and scope of client devices
The 2.4 GHz band uses longer wavelengths that are better suited for long-range signal transmission, including through walls and other solid objects in the signal path. The 2.4 GHz band would be ideal for connecting clients that do not require high bandwidth connections; it is a suitable option for web surfing, for example.
On the other hand, the 5 GHz band is better suited for high bandwidth client devices and loads such as online gaming or HDTV broadcasts.
Read More: