Server NICs can come with two (or more) network connectors. Some NICs (built into the motherboard) also provide firewall functionality (e.g. nforce).

- WiFi adapters: what they are, why they are needed, how to choose
- What does a WiFi adapter do?
- Computer or laptop connection options
- What is it for?
- Working Principle and Types
- How do I enable the module on my PC?
- Basic characteristics
- Types of Adapters
- Working with the device
- Classification of network adapters
- First generation
- Second generation
- Third Generation
- Network adapter – what is it in a laptop computer?
- Laptop Network Adapter – Appearance
- Network adapter – what is it in a computer?
- Network Adapter – Appearance
- In DVB-T2 set-top boxes and satellite receivers
- In TVs.
- How to use in dvb-t2 set-top boxes and satellite receivers
- How to Choose a WiFi Adapter
WiFi adapters: what they are, why they are needed, how to choose

No matter how clichéd it may sound, a Wi-Fi router in today's world is one of the most important household devices, especially if we are not talking about connecting a single workstation, but about organizing Internet access for a series of devices. In addition, an increasing proportion of users prefer wireless connectivity due to its simplicity and convenience. And if with mobile devices or Smart TV everything is simple – there is a corresponding module built in by default, then to connect a PC you will need a separate Wi-Fi adapter.
We will dwell on them in more detail later, referring to the peculiarities of the choice.
What does a WiFi adapter do?

As mentioned above, the adapter is needed to connect the device to an existing Wi-Fi network created with a router, access point, or smartphone in the absence of a wired Internet connection. Thus, the adapter allows you to:
- detect available wireless networks,
- provide connection to them via an encrypted channel,
- organize data transfer via a local network (access to other devices, local file storage),
- provide high-speed Internet access without the need to buy patch cords (patch cords) or make them out of twisted pair, lay them and connect.
In fact, WiFi-adapter is a full-fledged additional network card, which takes full control of the network connection. Accordingly, it can be used not only in case of a strong need for wireless connection, but also as a temporary or permanent replacement for the failed built-in network adapter.
Computer or laptop connection options
The computer can be connected to the router in two ways:
- By wire. Of the disadvantages – sometimes it is difficult to pull it if the computer is far from the router. But here there is its overlapping pluses – reliability and speed of connection, besides the network card for the wire is almost any desktop PC.
- Over the air. With the help of that very same Wi-Fi adapter. There is no default adapter in the computer, but it is easily purchased and installed. It is used when you don't want to pull the wire or there is no such an opportunity. Disadvantages are speed limitations and possible problems from using Wi-Fi technology. But sometimes it is still very necessary. Another possible purpose is to perform wireless network analysis from a computer.
In the following we will learn more about wireless modules, their types, connection options and uses. Once again, they can be used not only on PCs, but also on laptops (e.g. if the built-in WiFi adapter is broken, or you need a special one). Some smartphones also support OTG with some wifi adapters – better check with your model.
What is it for?
The main function of our device, for which it is purchased by people:
- Connection to existing Wi-Fi networks from a PC – home router, Wi-Fi modem. The device receives Wi-Fi on the computer.
- Creating a wireless access point from the PC – so that other devices in the house can connect.
- Replacing a failed adapter on a laptop.
- Specific use – like analyzing external networks when there is not enough power or the hardware on the built-in adapter does not fit.
Working Principle and Types
Now let me tell you in simpler terms what a wireless network adapter is. Routers, smartphones, laptops, tablets, TVs have an integrated module. It acts as a receiver (it picks up the signal from the router) and/or a transmitter (it can distribute the signal as an access point). I think everyone knows that.
All equipment that works with Wi-Fi wireless technology has a network adapter!
If your PC or any other device does not have a network module, you can buy one separately. An external (portable) Wi-Fi adapter plugs into a USB port. It works the same way as the built-in one – it receives and transmits the radio signal.

There is another type of network device for connecting to a wireless network – a PCI adapter. Installed inside the system unit, it connects to the motherboard via a PCI slot. Typically, such devices are equipped with an external antenna, which is installed outside of the "system unit". Why do I need such a Wi-Fi adapter? To also receive a wireless signal and connect to the network.

How do I enable the module on my PC?
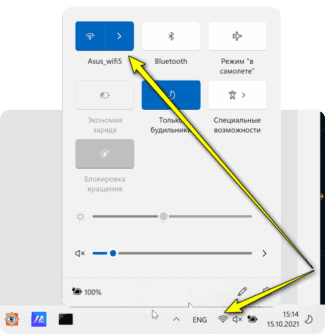
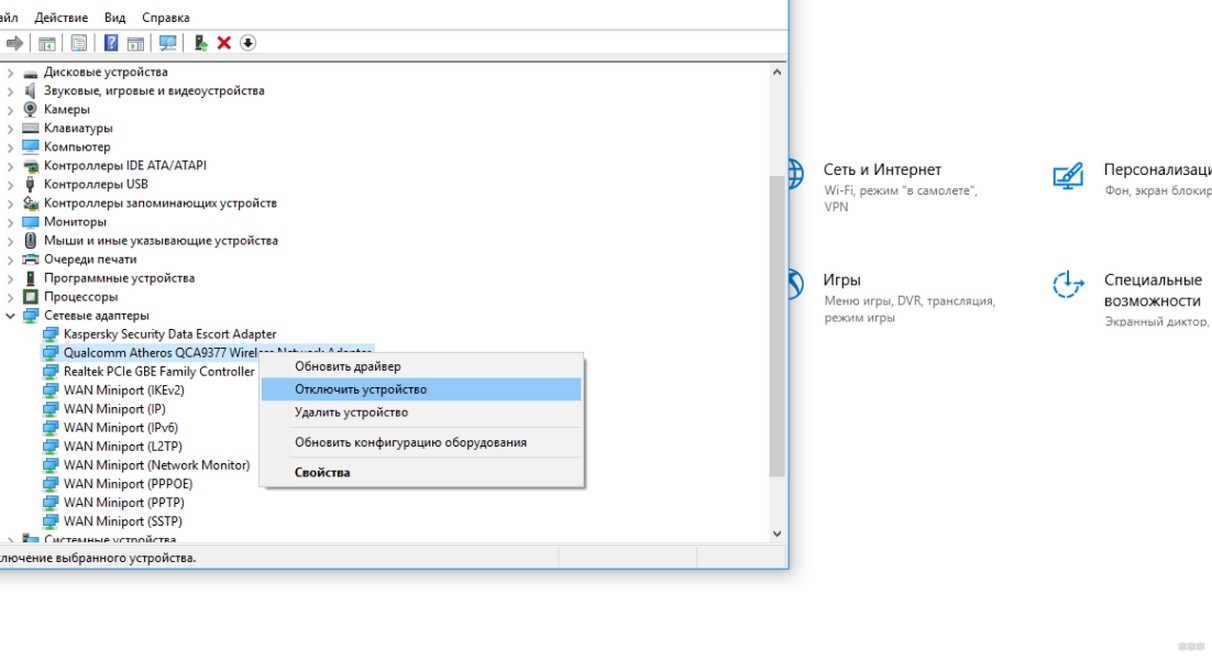
- Built-in module. On laptops can be turned on by "hotkeys" – Fn + one of the function keys (most often with the Wi-Fi icon). Another way is through the "Device Manager". Go to the "Network adapters" section, find the module, press PKM, select "Enable device". Connect to the network.
- External module. Connect to USB port, install drivers. Connection can be done using Utility that is installed together with software or via the Windows system tray (wireless icon).
- PCI adapter. The device is connected to the motherboard and the antennae are installed. Then as for the external one – install drivers and connect via Utility.
Basic characteristics
Wi-Fi adapter – this is a complex technical device and has its own characteristics. The data is usually specified on the equipment or in the user manual. What indicators I want to pay attention to (will come in handy when buying an external or PCI module):
- Connection interface – USB 2.0, 3.0.
- Wi-Fi protocols – 802.11a/b/g/n/ac.
- Range – 2.4 and/or 5 GHz.
- Transmitter power – measured in dBm (preferably at least 20).
- Antenna gain – defined in dBi (not always specified).
- Security type – most reliable WPA/WPA2-PSK.
- Compatibility with operating systems.
All of these characteristics should be considered when buying a Wi-Fi adapter. For example, if your home devices do not support the 802.11ac standard, you do not need to buy a module that supports 5 GHz.
Types of Adapters
In addition to USB adapters, there are PCI, PCI-Express and PCMCI adapters. They are full-fledged network cards capable of transferring data at speeds in excess of 600 Mbps. Such devices are installed inside the computer and are connected via the corresponding slot on the motherboard.
The advantage of USB adapters is their portability – they can easily be transferred and used in other computers. However, the speed of data transfer and the level of signal reception in such devices can be lower than in expensive PCI-E cards. This is due to the peculiarities and limitations of the USB interface. It is worth noting that some USB adapters support connection speeds of 150 and 300 Mbps. This performance is usually enough for home wireless networking and comfortable surfing the Internet.
Working with the device
The adapter is installed in the appropriate slot on the computer chassis according to the instructions that come with the device. Once the device is installed in the slot, configuration is performed, i.e. Installing the necessary driver to support wireless data transfer through the adapter in the system. The driver can be installed either from the disk, which is usually supplied with the device, or by downloading the driver installation file via the Internet from the manufacturer's official website. Once the driver has been installed, you start configuring the network settings, i.e. selecting the available Internet access point. The settings can be applied directly in the system used on the computer.
When choosing an adapter, you should pay attention not only to its speed characteristics, but also to the manufacturer. The most popular and high quality adapters are produced by such companies as D-Link, Asus, TP-Link, Zyxel, LinkSys. The most expensive models of these manufacturers have the ability to not only receive, but also distribute Internet signals. Thus, some adapters can act as a router so that you can connect with your phone or any other device to a Wi-Fi network.
When choosing, also pay attention to the network standard that the device uses for data transfer. For example, the fastest standard is 802.11n, which supports data rates of up to 600 Mbps under ideal conditions.
- How to choose a modem
- How to turn on a wifi adapter on a hp laptop
- How to install a network adapter
- How to connect to a wireless network
- How to turn on a wi-fi adapter
- How to identify your network adapter
- How to set up a wi-fi adapter
- How to choose a modem for your notebook
- How to choose a wifi for your home
- How to set up a WiFi Adapter
- What is a Network Adapter and what does it do?
- Why do you need a network adapter?
- How does your network adapter work?
- How to choose a router
- How to connect to the internet with an adapter
- How to set up Wi-Fi Internet access
- How to choose a wi-fi router
- How does Wi-Fi work
- How to choose the best network card
- How does a wi-fi modem work
- Why do you need a router?
- What does the abbreviation wi-fi mean?
- SMA connector: description, purpose, classification
- How to make your computer give out wi-fi
Classification of network adapters
As an example of classification of adapters we will use the approach of the firm 3Com. The company 3Com believes that Ethernet network adapters have passed through three generations in their development.
First generation
First generation adapters were made on discrete logic chips, which resulted in low reliability. They had a buffer memory for only one frame, which resulted in low adapter performance, since all frames were transferred from computer to network or from network to computer sequentially. In addition, setting the configuration of the first generation adapter was done manually, using jumpers. For each type of adapter used a different driver, and the interface between the driver and the network operating system was not standardized.
Second generation
The second generation of network adapters began to use the method of multiframe buffering to improve performance. In this case, the next frame is loaded from the computer memory in the buffer adapter simultaneously with the transfer of the previous frame to the network. In receive mode, after the adapter has fully received one frame, it can start transferring this frame from the buffer to the computer memory simultaneously with the reception of another frame from the network.
Second-generation network adapters make extensive use of highly integrated chips, which increases the reliability of the adapters. In addition, the drivers of these adapters are based on standard specifications. Second-generation adapters usually come with drivers that work both in NDIS (Network Driver Interface Specification), developed by 3Com and Microsoft and approved by IBM, and in ODI (Open Driver Interface), developed by Novell.
Third Generation
Third-generation network adapters (which includes 3Com's EtherLink III family of adapters) have a conveyorized frame processing scheme. It consists in the fact that the processes of receiving a frame from the computer's main memory and transfer it to the network are combined in time. Thus, after receiving the first few bytes of a frame, their transmission begins. This significantly (25-55%) improves the performance of the chain "RAM – adapter – physical network".RAM – adapter – physical channel – adapter – RAM". Such a scheme is very sensitive to the transmission start threshold, that is, the number of bytes of a frame that is loaded into the adapter's buffer before transmission to the network begins. The third-generation network adapter performs self-tuning of this parameter by analyzing the operating environment, as well as by calculation, without the involvement of the network administrator. Self-tuning provides the best possible performance for a particular combination of the computer's internal bus performance, its interrupt system and the direct memory access system.
Network adapter – what is it in a laptop computer?
The short answer: Is a device that receives an Internet signal and then converts it to familiar data.
In simple words: The network adapter of the laptop is an internal device through which the laptop receives the Internet for further use by the operating system and its applications, such as messengers (Viber/Skype/WhatsApp and others), torrent downloaders (e.g. uTorrent), browsers (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox).
- Wired. When the cable from the provider is connected, the settings of the operating system configure the reception and you can say that the laptop with the Internet.
- Wireless. When a Wi-Fi module is used to receive a wireless network. Here as simply – the module catches Wi-Fi networks. Connecting to the necessary one implies entering a login/password (the network can be passwordless). Often the Wi-Fi network is distributed by the router, sometimes by another laptop or even an Android smartphone.
In other words – just a device that receives the Internet signal (by wire or air) and transforms it into one that is understood by the operating system and the installed applications in it.
Laptop Network Adapter – Appearance
It is a small board inside the notebook casing:

A special Ethernet cable (standard RJ45) is connected to this connector, which actually carries the Internet. Here the connector itself is soldered to the motherboard.

The Wi-Fi module is usually removable and can be replaced. To the module are special wires that serve as an antenna to receive Wi-Fi signal.
Also the Internet can come through a built-in modem (e.g. 3G), which is inserted SIM-card of the mobile operator.
There is also a variant of external device, which is a USB-device, connected to the usual USB-port:

Network adapter – what is it in a computer?
Immediately the short answer: A general name for the devices by which a computer gets the Internet.
In other words: A PC contains various devices, a processor (CPU), a graphics card (GPU), a hard disk drive (HDD), and a device for receiving Internet signals, which are converted into understandable data for the operating system and installed applications.
Without such a device, the PC is almost useless – you can't browse the web, you can't download movies/games, you can't watch YouTube videos, and you can't use e-mail.
Network adapter – the general name for devices capable of receiving the Internet. It can be divided into two types:
- Network card. Standardly it receives the Internet via Ethernet RJ-45 cable. A distinctive feature – stable connection, high speed, availability. Ordinary Internet on the PC – often precisely wired. It may be implemented as a built-in motherboard chip (usually Realtek) or as an external PCI-E card.
- Wi-Fi module. A device that allows to receive a signal over the air, more precisely – to catch the Wi-Fi network. The essence – it scans the space around (the radius is limited) for the presence of Wi-Fi networks and displays a list, after selecting the network you must be authorized, specifying a password and login (the network can be passwordless). The network (or rather access point) is distributed by other equipment – a router, another computer or even a smartphone. The motherboard may contain a module of two variants: built-in (usually a Realtek chip) or external (PCI-E expansion card).
Network Adapter – Appearance
Appearance of the PCI-E wired Internet adapter (installed on the motherboard):

Built-in type (the chip itself is unsoldered on the motherboard, from which the contacts go to the connector):


Installed in the motherboard (similarly put and ordinary network card):

There is a universal option that can be connected to a laptop/computer – USB-adapter, this is a device to which the RJ-45 Internet cable is already connected:

Approximately the same variant exists with the Wi-Fi module, which is also connected to the USB port and can look like a flash drive.
In DVB-T2 set-top boxes and satellite receivers
To receive terrestrial digital channels, or satellite television is not uncommon to buy separate devices. Most often they are called digital set-top boxes, receivers, tuners. So, these devices are also evolving, and many have support for various Smart features. To put it simply, the ability to access the Internet, watch YouTube through an application, etc. For this, of course, you need an Internet connection. Typically, all set-top boxes which have the ability to connect to the Internet are equipped with a LAN input (to connect via cable). But at the same time support USB Wi-Fi adapters. The adapter is plugged into the USB port on the STB and the Wi-Fi connection function appears in the STB settings.
- Be sure to check if your DVB-T2 set-top box or satellite receiver supports Internet connection. Since the USB port can only be used to connect USB memory sticks. Look at the characteristics, read reviews on the Internet, study the menu of the set-top box. If the menu, for example, has YouTube, a browser, "Internet" – then it supports it.
- As a rule, all set-top boxes work with certain Wi-Fi adapters. That is, there is a risk that after buying the adapter the set-top box simply will not see it. You should always be very careful when choosing a Wi-Fi receiver. Usually, a particular model of set-top box supports adapters that are built on a particular chipset. These can be adapters from different manufacturers, but the module (chipset) in them is the same. The best way is to find this information on the Internet according to the model of your DVB-T2 set-top box or receiver. Read the reviews of those who have already bought the adapter.
- If the set-top box is far away from the router and near it there is not a very strong Wi-Fi signal, it is better to take an adapter with an external antenna.
For example, the easiest and cheapest digital receiver DVB-T2 Strong SRT 8203 can be connected to Wi-Fi network via USB adapter and look through it YouTube, or configure IPTV.
In TVs.
- TV with built-in Wi-Fi module – Wi-Fi is built-in, you do not need an additional adapter. These are almost all modern Smart TVs. How to determine whether a TV with Smart TV, or not, I have already written.
- TV without built-in Wi-Fi, there is a LAN, but it is also possible to connect a USB adapter.
- The TV with only a LAN input. Wi-Fi adapters are not supported. As a rule, these are the oldest models of smart TVs.
Even if there is support for USB Wi-Fi adapters, the TVs only work with original, branded adapters, which are very difficult to find, and which are usually expensive. Somewhere I met information that you can pick up some ordinary adapter to the TV, cheaper, but I think it will not work with it. You can google about it, if you're interested.
I think it's better to already use another router, or a repeater. I wrote about this in an article on how to connect a TV without wifi to the internet via wifi.
How to use in dvb-t2 set-top boxes and satellite receivers
To receive digital and satellite channels, a special device is useful. Depending on the set of functions, it may be called a tuner, receiver or set-top box. With the development of technology, they also began to add smart features.
In this regard, it became possible to connect set-top boxes to the network. Then, in addition to the usual channels, the user can add streams, movies and programs from the Internet.
When choosing an adapter, first of all you should check the compatibility. For example, some models have USB ports that support only working with storage devices, but cannot be used to connect wireless modules. The second important point is the remoteness of the set-top box from the router. If the signal is weak, it is advisable to take a powerful adapter with external antennas.
How to Choose a WiFi Adapter
Having answered the question "WiFi adapter, what is it?", you can move on to the selection of the device itself. The buyer should check:

- Compatibility. To avoid the purchase becoming a waste of money, you should check whether the selected option can be connected to a particular device. Especially carefully you should select the adapter for the TV or TV set-top box. It is better to study the experience of other users and consult with the seller.
- Supported standards. Here it is useful to check what standard the router has. Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) is widespread, it is better that the adapter can work with it. Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) has backward compatibility with its predecessor, while supporting higher speeds.
- Frequency ranges. For Wi-Fi, you can use 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz. The former will provide greater range, the latter is able to transmit data faster. For mobile devices, it is useful to be able to work with either one, while for a computer or TV, the one used in the home network is sufficient. You can check the specifics of the connection in the router settings.
- Transmitter power and antenna type. The range of reception depends on these parameters. It is better to choose a variant with a power of 20 dBm, which is able to transmit a signal at a distance of 5 m. Note that walls and other obstacles weaken the signal, thus reducing the maximum range.
- Connection security. To prevent data from leaking to intruders or jokers, secure connections should be used. WPA/WPA2-PSK is used for Wi-Fi because it is considered secure.