In this article, we will try to understand what a router is and how it is different from a router. I will try to write it as simply as possible. Therefore, if you understand these devices, you are unlikely to find anything new.

- What's the difference between a router and a router?
- Choosing a Wi-Fi Version
- What is a WiFi router and why do you need one?
- Router and router: what's the difference?
- What caused the confusion over the name
- Router and router: the principle of operation, configuration and other features
- How a router works
- Configuring
- What's the difference between a router and a router?
- Where is the confusion?
- Summary
- Choosing
- Settings
- Router buttons and indicators
- Additional Router Features
What's the difference between a router and a router?
First things first: a router and a router are the same thing. Yes, that's right. The English word router means "router. And yet there is a huge variety of models, which can be difficult to understand even for an experienced user. But we're here to help.
A router or router is a device that distributes the Internet to wired and wireless gadgets.
Most often you need an Ethernet cable to connect to the network at home. Less commonly, an ADSL connection is used. Here are the most common types:
– FTTB (Fiber To The Building) is one of the most successful technologies. The provider brings an optical cable into the apartment building, which is fed to the users with a twisted pair – Ethernet copper cable with RJ45 connector. Thus the provider provides a maximum speed of Internet connection up to 1000 Mbps in both directions: from the provider to the user and back;
– ADSL technology (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) allows you to have high-speed access to the network using a standard telephone line already available in your apartment. In this case, the maximum possible speed of data transfer to the consumer is 24 Mb/s, and to the provider – 3 Mb/s. This is noticeably inferior to the FTTB option. If you are connected to an ISP using this technology, choose a router with an ADSL format input (WAN port).
Fiber optic prices are going down. Thanks to this, it is now possible to lay the cable directly into the house. More and more operators are deploying networks in the private sector. In such a case, you need not only a router, but also a media converter. It is a device that converts the fiber optic signal into a digital one. At the output of the media converter is the familiar Ethernet port.
Choosing a Wi-Fi Version
When buying a router, it is important to decide which version of the Wi-Fi standard you need. To do this, you should know a few nuances:
– The newer the version of the standard (Wi-Fi 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac/ax – in ascending order), the faster it is able to transmit data;
– The vast majority of current devices support 802.11n. However, there are already models that support the progressive 802.11ac standard;
– In the near future the market will be conquered by new devices supporting the 802.11ax Wi-Fi standard. The world's leading smartphone manufacturers have begun to equip their flagships with this wireless module.
Almost all routers support not only the main standard listed on the box, but also all previous current versions. Even if you don't have new laptops and smartphones right now, we recommend getting a router that supports 802.11ac.
What is a WiFi router and why do you need one?
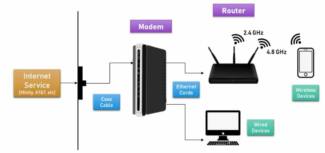
Let's take as an example an ordinary city apartment where one person lives. He has a cell phone with WiFi, a computer (or laptop) and a SMART television. Or maybe also a smart speaker, a tablet, and a security camera. The apartment comes with a cable from the Internet provider. By default, only one device can access the Internet through this cable. But how do you connect another gadget or all of them at once? This is where the router comes in.

From the outside it looks like a small box with a power supply. Sometimes, depending on the model, it may be with "horns" of external antennas, and sometimes without. Routers come for cable provider networks, with one or more ports to connect the appropriate cable. These types of connections include twisted-pair Ethernet line:

A dedicated ADSL line connector looks about the same, just a little smaller:

And this is what the WAN port looks like on optical routers and GPON terminals:

These routers have at least one port to connect the ISP cable, and there will also be one or more to connect home gadgets – televisions, computers, etc. As a rule, all modern models emphasize wireless Wi-Fi network, which provides Internet access for tablets, smartphones, smart watches and other electronics.
There are models for 3G, 4G/LTE and 5G mobile carrier networks:
Router and router: what's the difference?
Well, there is no difference. In fact, there is no difference at all. It's just in the blood of Russian people to use anglicisms. Let me prove it! The word "router" means "router" in English. That's the tricky part. That is, a router is a router, and vice versa, a router is a router. There is no difference!
Now a little bit about why a router? The fact is that in computer networks and directly on the Internet, all of the services are based on routes. Accordingly, the device, which stands at the border of the local and external networks, is busy creating routes for each of the requests in both directions. That is, it routes the traffic.

Example: You type yandex.ru in your PC browser and press Enter. Then, in layman's terms, the computer creates a request and sends it to the network. The router receives this request, gets the IP address of the required service from the DNS server, and sends the request to that server. The server will receive the request, execute it, and send the response that comes to the router, which routes it to the computer that sent it. That's it!
What caused the confusion over the name
What is the difference between these devices? Router and router – the meanings of these words have the same meaning. The confusion arose with the Russification of the designation.

In English, the word "Route" means "route. The addition of the suffix "er" resulted in "Router", the direct translation of which is "router". Accordingly, the question "What is the difference between a router and a router?" can safely answer that there is no difference in the meaning of these words.
A side note! It should be borne in mind that in technical literature the most common is "router".
Router and router: the principle of operation, configuration and other features
A router as a "link" between the network Internet and wirelessly connected devices is known to most users.

How a router works
The distribution of the Internet signal starts from the router (or router) and goes to all the devices of the users connected to it – smartphones, computers, tablets, etc. That is, the router works as a merger of several devices into one network, which can be local or with Internet access.

All devices can be connected via Ethernet cable or wirelessly – via Wi-Fi.
For your information! The home use of a router is a local network.
- The Internet service provider or ISP sends the signal via a special cable. This is the same wire that you wind from the entrance or from the street to the apartment and connect to the router or computer.
- How to connect the router is through a special WAN port on the back.
- The router functions as an intermediary between the network and the end consumer.
Configuring
The router as a link does not connect automatically and does not start distributing a signal when you dock a cable to a port – you must configure the access point and other network settings.
- You need to check your operating system settings. Relevant for all computers that have previously connected to the network, and they may have changed the basic settings.
- Install the router and connect all wires.
- Enter the admin panel on the computer and the router settings.
- Connect the Internet and Wi-Fi.
- Set or change passwords.
- Use the interface prompts to enter any additional settings.
What's the difference between a router and a router?
If you've read this article from the beginning, you may have noticed that I wrote either a router or a router. Yes, they are the same device. They are absolutely the same and there is no difference between them.

Just router is the English word for router. And in Russian the word is translated as router. That's all. Both are correct. When I write an article, I use both names.
I hope that I have answered the question in the title of this article. If you can somehow add an article, you can write me in the comments, I will be grateful.
![]()
201

343430
![]()
Sergey
![]()
Useful and interesting
Hello. Will this device give out Wi-Fi, if you connect a LAN wire to it.
ru.aliexpress.com/item/FW1S-2016-New-Arrival-High-quality-Mini-3G-4G-WiFi-Wlan-Hotspot-AP-Client-150Mbps-RJ45/32622382063.html
Hello. I think it is. The description says "WAN Ports:1". Maybe it means USB and not LAN.
But it would be a good idea to ask the seller about it.
WAN Ports:1 means that it has one network input (cable internet from ISP, RJ-45 connector)
LAN – this is the output, usually they are from one to four, to connect the network cards of laptops, computers through a patch cord with RJ-45 connector
Hello!
Can you please tell me please, I have a modem without Wi-Fi, can I separately buy a router to distribute Wi-Fi, while leaving that old modem?
Where is the confusion?
It comes from nowhere, a lot of people are used to both names by now. Most people call this home device a router, that's how we got used to it. This is an example of taking the word "modem" – at home means and dial-up, and 3G USB and ADSL. That is a true people's word – "router. And the pros use it much more often.
On the other hand, there is the official part. So in high school we were taught the competent word "router". That's how they write it in technical literature, where a formal syllable is required. That's also how the stores picked up on it:
At the same time, the consultants of these same stores themselves will call them "routers". So on paper it's a router, in words it's a router. Rather, the popular confusion arose precisely on this contrast. Rather, no one has written about such an addiction yet, so it's almost primary source)
Summary
The full answer was given above, here I will leave brief information about routers for survivors. There's almost endless talk about them – the types, features, and setup. And with professional equipment, you can get hooked for more than a year. You can read a lot on our WiFiGid pages, but for the sake of this article, let's talk about router routers.
A router acts as an intermediary in your home network. It takes the Internet from your ISP and distributes it to the local network it creates. All the devices connected to it via Ethernet or Wi-Fi connect to that local network and access the Internet.
That's probably the best way to put it. That is, you can somehow think of everything manually, and assign the same functions, for example, to a laptop. But nowadays it is already a noble perversion – all the routing functions in the home network are taken over by this little box with antennas.
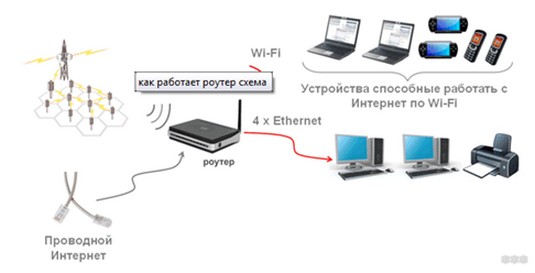
- We connect the ISP cable to it (WAN port).
- Configure Internet connection via ISP cable (many models have settings on our site).
- Set up the Wi-Fi connection and wireless protection from the neighbor.
- Then connect all home devices via Wi-Fi or cable (LAN).
- Now you can enjoy its stable operation 24/7.
And given the fact that the routing function can be used in a software environment, you can sometimes call a router even the classic ADSL or 3G/4G modems. If you are confused any further, that's not the subject of this article) The main thing is that router and router are not different in any way. And neither of them is better – you can safely choose both a router and a router, no matter what it says in the store.

Choosing
Depending on the design, routers are divided into industrial and household. In the first case, it is a specialized device. They are most often used to organize corporate networks, and the right choice is the responsibility of the network administrator, who is a technically trained specialist. On the other hand, with household routers, things are much more complicated. They are purchased by ordinary users, who are not well trained and knowledgeable specialists in this field. Therefore, we can give them the following recommendations:
- First of all, pay attention to the manufacturer. The best are considered to be the routers of D-Link, Asus and Zyxel brands.
- We pay attention to the maximum wireless network transmission speed. In most cases it is 150 Mbit/sec. But there are also devices capable of transmitting 300 Mbps. The more the better.
- Don't forget to check the package contents. Be sure to have, in addition to the router, power supply, user manual in Russian, one meter twisted pair cord for connection and initial setup, and a disc with drivers.
- Then we look at the modes of operation of the wireless network. There are only two options: "abg" and "bgn". If your smartphone is equipped with an "a" standard transmitter, it will not work in a router of the latter type. In general, everything must be coordinated and work in the same mode. Otherwise there may be problems with the connection.
Some stores, in order to confuse the ill-informed buyer more, tend to call network devices differently on the price tags. In this case, those that come with a foreign word are more expensive. If you ask a salesperson in such a store: "What is the difference between a router and a router, and why does the former cost more?", in most cases you will not be able to get a coherent answer. That is why it is better to avoid such outlets. The quality of products in them is usually questionable.
Settings
As mentioned earlier, the difference between the router and the router is only in the origin of the words. From a technical point of view, these devices are identical, and the configuration procedure is not different. It consists of the following steps:
- Connecting the power supply, the input wire from the provider and a meter twisted pair to the computer or laptop.
- Switching on your computer and router. Be sure to wait for each of them to finish loading.
- Start your browser and enter the network address: "192.168.1.1" (in some cases, the last two numbers may be "0.1" – see the manual).
- Specify the network name, the password to access it and the encryption method (it is best to choose WPA2 – the maximum security level).
- Reboot the router, everything is ready.

Router buttons and indicators
All routers are designed similarly and have a similar set of buttons. There are 3-4 light indicators on the front panel:
- indicator of equipment on and off (newer models are not equipped);
- presence or absence of Internet;
- presence or absence of the local network;
- direct connection via LAN port.
On the back of the router the following buttons and connectors:
- reset button (looks like a small hole);
- "Fn" or the button that automatically searches for updates and installs them. To reset the settings, you need to insert a paper clip or other thin sharp object into the hole and hold it for 15 seconds. This will reset all settings to the factory settings;
- "ON/OFF""ON/OFF", turn on, turn off the equipment;
- "WPS" (Wi-fi Protected Setup), this is a rare button that allows you to connect to the network without a password. On both devices: the router and the smartphone, this button is pressed simultaneously and the pairing takes place without asking for a password;
- Connector for connecting to the power supply.
In addition to the buttons, there are WAN and LAN connectors on the rear panel. The first input is always the same. The ISP cable (blue) is connected to the WAN socket. Pay attention to the declared by the manufacturer speed of the WAN-port, if it is less than the provider's, it will be reduced in the local network, in fact you will overpay for what you will not receive.

LAN connectors are 4, rarely fewer or more, always yellow. These are for wired connection of computers, televisions and other local devices. The button arrangement of different manufacturers will not necessarily be in the same order, but the connectors are always on the back panel.
Additional Router Features
Modern models of routers are equipped with a huge number of additional "chips" that simplify the use of the device, namely:
- USB-connector. Through it you can connect a hard drive, 3G/4G modem. If you connect an external hard drive, you can set up a torrent file viewer without connecting a PC.
- Mobile App, which can be installed not only on your PC, laptop, but also on your smartphone. The program allows you to configure the router from anywhere in the world.
- IPTV. This plushka is usually found in routers from providers. IP TV gives you a wide range of possibilities, from watching hundreds of channels to the highest quality video.
- The Qos (Quality of Service) feature Allows to cut off the users and limit the bandwidth in order to give the priority to the more necessary destinations (devices).
- Control technologyBlocking individual sites. Setting up individual filters allows you to protect your household from unwanted content and dangerous sites. This feature is relevant for families with children and older people, who still have little understanding of the Internet and are often victims of scammers and hackers.
- Multi WAN function makes it possible to connect to several providers at once. It allows you to stay online even if one of the providers has problems. There is no need to change the cable or reconfigure the equipment. Routers with this technology usually have two or more WAN slots of different colors.
- MU-MIMO or acceleration technology. Popular among gamers who reduce latency and ping from transmissions over a wireless network. The technology makes it possible to increase IEEE 802.11n transmission speeds up to 450 Mbps.
Antivirus software can be installed on some powerful router models. This reduces the load on the PC and protects not only the PC from viruses but also the local network.
Read More: