First of all, you need to find a suitable place for the AP. It is recommended to install the router on an elevated location in the center of your home, apartment or office. Make sure that there are no high-frequency interference emitters, such as TVs or radios, near the router.
- The difference between LAN, WAN, WLAN, WiFi – Russian Blogs
- What is a WAN?
- WLAN vs. Wi-Fi
- Comparison table
- WLAN and Smartphone.
- What does it mean if the WLAN is blinking on the router?
- How WLAN and Wi-Fi are related
- Russian Blogs.
- WLAN and WI-FI
- How to connect and configure
- PC-based software to support different WLAN drivers
- The main purpose of this product is to
- Release Date, Operating Systems and Memory Requirements
- WLAN and WI-FI 2022
- What is the difference between Wlan and Wi-Fi and what they have in common
- What is a wireless LAN
- What WLAN and Wi-Fi have in common
- Features of wireless LS in the phone
The difference between LAN, WAN, WLAN, WiFi – Russian Blogs
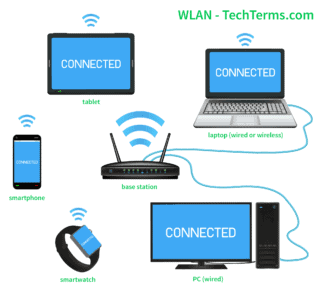
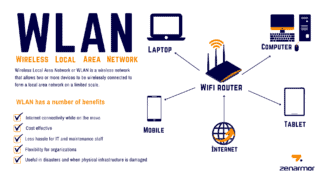
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) is a wireless local area network. In this way of networking, data transmission is carried out over the airwaves; connecting devices into the network takes place without the use of cables….
The main advantages of this technological solution are as follows:
- Convenience. This advantage applies to both network owners and end users. For the first ones, installing and configuring WLAN is cheaper than laying cables. In addition, in some cases, installation of cable is simply impractical or impossible due to the peculiarities of the terrain, the location of buildings and communications. Users get the opportunity to use a stable high data transmission in a certain area of coverage.
- Network expansion. Technology can be easily expanded by installing additional access points.
- Mobility. Coverage virtually ignores obstacles, allowing users to use the network equally well on the move, on different floors or levels, in different rooms.
- Ease of installation. It's much easier to build than laying cables.
- High speed and considerable coverage. The speed is comparable to cable connection and reaches 100 Mbit / s. Reliable signal reception is achieved within a radius of 150 m, with the presence of additional access points can expand and more.
- Simultaneous operation of several subscribers with the same signal level for each.
- Unification. WAN is perfectly compatible with numerous devices from a wide variety of manufacturers.
What is a WAN?
"WAN" literally means "Wide Area Network". Which can be translated into Russian as "Global Area Network". Such a network combines a huge number of different nodes, located in different places and at different distances from each other. It can connect cities, countries and even continents. In other words, " WAN " is what we used to call the Internet.

WLAN vs. Wi-Fi
The difference between WLAN and Wi-Fi is the type of technology used. WLAN, known as wireless local area networking, is used to connect multiple devices using technology that minimizes the use of wires and creates a local area network, while Wi-Fi is also a wireless technology that depends directly on IEEE 802.11. standards.

Want to save this article for later? Click on the heart in the bottom right corner to save to your own article block!
WLAN is also known as wireless local area network, as well as wireless WLAN.
It is a network of computers that use high-frequency radio waves to transmit signals over a distance of several hundred feet.
Several computers can be connected to a central data system, a printer, or even a scanner through the network.
This provides mobility on the network (Internet) and avoids the use of cumbersome and inconvenient interconnecting cords.
The abbreviation WI-FI stands for "Wireless Fidelity. The word is really a trademark that is used to refer to items belonging to a specific category of WLAN devices.
The standards set by IEEE 802.11 are used in gadgets or equipment marked with the WI-FI trademark. Most people think that WI-FI is the same as the present standard.
Comparison table
| Comparison options | WLAN | Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A wireless network is a network that connects multiple devices using wireless technology to create a local area network. | Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that depends on IEEE 802.11 standards. |
| Range | 2.4 GHz 100 meters (300 feet) | The Wi-Fi range for the 2.4 GHz band can range from 150 to 300 feet outdoors. |
| Obligatory devices | Devices within WLAN technology use proprietary WI-FI products | Devices in Wi-Fi do not use proprietary Wlan products |
| Full form | Wireless LAN | Wireless precision |
| Other name | Wireless | Wi-Fi, Wi-Fi, Wi-Fi or Wi-Fi |
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a wireless network that connects multiple devices using wireless technology. It allows Wlan to create a local area network (LAN).
It is within a specific region, which can be a residence, institution, computer room, campus or office complex.
This allows users to travel throughout the region while remaining connected to the Internet. The WLAN can also provide access to the rest of the Internet through the gateway.
The most widely used networks in the world are wireless LANs based on IEEE 802.11 standards. They are often called Wi-Fi, which is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance.
They are used in home and small business networks to connect laptops, scanners, cell phones, Internet TVs, and gaming gadgets to the Internet through a wireless network. router.
People can use portable wireless devices to access Internet services through the many access points provided by routers in many places, such as restaurants, cafes, hotels, universities, and airports.
WLAN and Smartphone.
Technology is advancing at a rapid pace, so having a WLAN access point on your modern phone is a must. Cell phone is no longer just a tool for calling and messaging, but a full-fledged device for work and entertainment. IOS, Microsoft mobile version, whether Android is installed on the device, the WLAN will definitely be available there.
What does it mean if the WLAN is blinking on the router?
The indicator of the wireless network WLAN. And if it is not lit, it means that the Wi-Fi network is disabled by the button on the router, or in the settings. LAN ports. If it is not lit, it means that nothing is connected to the port, if it is lit – the device is connected but not active, if it is blinking – data transfer is going on.
Why divide one network into several isolated parts? For example, when building a network for a large company, it is known that each department wants to have its own network that is separate from the others.
Of course, you could build a separate physical network based on separate switches. But if we build a network of a huge business center, we will not know in advance how many tenants there will be, how many square meters they will need. Consequently, you need to build one large network for the entire business center, and then logically divide it into separate parts, depending on the needs of tenants.
How WLAN and Wi-Fi are related
WLAN and Wi-Fi are often thought of interchangeably. Let's understand why this is wrong and what the difference between the two is. As mentioned above, a WLAN is a wireless local area network .
The abbreviation Wi-Fi stands for Wireless Fidelity, and literally translates as wireless precision. This term refers to a family of standards for transmitting digital information over the air. That is, Wi-Fi is a way to implement WLAN.
Communication between the server and end users is established in one of the two available frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The Internet is more stable in the 5 GHz band because these networks have less radio interference.
Russian Blogs.
With the rapid spread of smartphones, almost everyone has a cell phone in their life. Wherever they go, the first thing they do when they walk in the door is usually ask if there is Wi-Fi. This shows that Wi-Fi has begun to slowly penetrate human life.
However, a careful friend may find that the Internet at home uses WLANs and cell phones use Wi-Fi. It's the same with wireless Internet access. What's the difference between Wlan and WiFi?
Simply put, WLAN refers to a wireless LAN, and WiFi is an acronym for Wireless Fidelity, which is a technology that can wirelessly connect computers and cell phones. Wi-Fi is a subset of WLAN, which refers to short-range wireless communication technology that is typically applied to mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets; while Wlan can create a powerful carrier-class interconnection network and organize multiple access points (hotspots). It is used in large public places such as libraries, cafes, and homes.
The biggest feature of WiFi is that the transmission speed is very high, up to 11 Mbit/s, and the effective distance is also relatively long, the range can be up to 90 meters, and it is compatible with a variety of 802.11DSSS devices. The WLAN coverage area is larger than that of WiFi, and with an antenna it can reach distances of up to 5 kilometers.
With the rapid development of Internet technology, Internet surfing has become a common way of life in modern society. However, with the development of Internet data services and the development of video services, bandwidth has become an important factor. Network speed is directly related to bandwidth. For faster and more convenient access to the Internet, Wi-Fi is sufficient. Wi-Fi has the advantages of high access speed and low cost, and is also an important means of offloading data traffic. Nowadays, Wi-Fi is widely used in entertainment, business, education and other areas and it has penetrated almost all areas of life. Therefore, people are under the impression that "Wi-Fi is a wireless network".
WLAN and WI-FI

Trying to improve data technology is more about ease and convenience. Whenever possible, we always want less effort to communicate with others. Today's technological advances allow us to transmit and receive digital information without the physical connection of wires or fiber optics. Of course, for network administrators and engineers, nothing presents greater ease and comfort than wireless means of connecting devices.
WLAN, short for wireless LAN and sometimes called wireless LAN, is a network of computers a few hundred feet away that uses high-frequency radio signals to send and receive data. The network can also connect multiple computers to a central information system, printer, or scanner. This provides mobility on the network (Internet), which also helps avoid the use of bulky and inconvenient cables for communication. IEEE 802.11 is the primary standard for wireless LANs.
In principle, WLANs allow peer-to-peer data transfers and/or two-point transfers, such as LAN-to-LAN, WLAN-to-LAN, or even WLAN-to-WLAN, in a relatively small area (building or campus). Conventional LANs typically use twisted pair, coaxial wires, or in some cases, optical fibers. WLAN gets rid of these physical connections and instead uses electromagnetic waves to transmit and receive data on the network. Potentially, the transmission is not as fast as the speeds provided by a conventional LAN, but for most users, medium and professionals in the industry, the slow transmission speed is a minor limitation.
WI-FI stands for Wireless Fidelity. The term is actually a brand name used to label products belonging to the category of WLAN devices. Devices or equipment branded with the WI-FI trademark are based on the standards specified in IEEE 802.11. In most cases, WI-FI is considered by most to be synonymous with the actual standard itself.
How to connect and configure
To install a wireless home or office network, you will need a router, a personal computer or laptop with a network adapter, and an Ethernet cable from your Internet service provider.
First of all, you should find a suitable location for the AP. It is advisable to install the router on an elevated location in the center of the house, apartment or office. Make sure that there are no high-frequency interference emitters, such as TVs and radios, near the router.
Once you have decided on the location of the AP device, you can proceed to the direct setup of the access point. Connect the cable coming from the ISP to the WLAN connector on the router. The computer connects to the AP with an Ethernet cable, which is included in the package.
To configure the AP, follow these steps:
- Press the power button on the router. Open any browser on your computer (e.g. Chrome) and enter the IP specified in the user manual in the top line.
- Enter the login and password (they are also specified in the manual).
- Check the "Wireless access" checkbox and enter an arbitrary network name. Switch on the automatic mode and save the settings.
- Select the information security protocol in the radio network settings section. Set the password, confirm it, and save the settings.
- In the advanced settings section, list the types of devices that can be connected to the wireless network.
- Enable access control by selecting the appropriate check box.
- If desired, you can configure the VPN (network for secure connections) section.
- To connect user devices to the Internet, you will need the network name and password that you specified when you set up the router. For example, to activate a connection on an Android smartphone or tablet, you need to go into its options, open the "Wireless Networks" section and select the newly created access point from the list.
PC-based software to support different WLAN drivers
It is not possible to connect to the Internet if the appropriate network drivers are not available or are not recognized. The software package known as "WLan Driver 802.11n Rel. 4.80.28.7.zip" can support many wireless LAN (WLAN) drivers.
The main purpose of this product is to
WLan Driver 802.11n Rel. 4.80.28.7.zip can work together with many Broadcom network drivers. Some of these include compatibility with the 802.11 infrastructure. Support is offered for 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11a, and 802.11n. Note that this software suite is also applicable to 802.11 multiband network adapters. This package was developed by Acer and it is for Broadcom network adapters only.
Release Date, Operating Systems and Memory Requirements
The WLan 802.11n Rel. 4.80.28.7.zip driver was first released in June 2006. It is intended for use with various Windows operating systems, including Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows 2003, and Windows NT4. Note that newer systems may require a different set of drivers. This program will require at least 9.48 megabytes of free memory and can be downloaded in ZIP format.
WLAN and WI-FI 2022

Trying to improve data technology is more about ease and convenience. Whenever possible, we always want less effort to communicate with others. Today's technological advances allow us to transmit and receive digital information without physically connecting wires or fiber optics. Of course, for network administrators and engineers, nothing presents greater ease and comfort than wireless means of connecting devices.
WLAN, short for wireless LAN and sometimes called wireless LAN, is a network of computers a few hundred feet away that uses high-frequency radio signals to send and receive data. The network can also connect multiple computers to a central information system, printer, or scanner. This provides mobility on the network (Internet), which also helps avoid the use of bulky and inconvenient cables for communication. IEEE 802.11 is the primary standard for wireless LANs.
In principle, WLANs allow peer-to-peer data transfers and/or two-point transfers, such as LAN-to-LAN, WLAN-to-LAN, or even WLAN-to-WLAN, in a relatively small area (building or campus). Conventional LANs typically use twisted pair, coaxial wires, or in some cases, optical fibers. WLAN gets rid of these physical connections and instead uses electromagnetic waves to transmit and receive data on the network. Potentially, the transmission is not as fast as the speeds provided by a conventional LAN, but for most users, medium and professionals in the industry, the slow transmission speed is a minor limitation.
WI-FI stands for Wireless Fidelity. The term is actually a brand name used to label products belonging to the category of WLAN devices. Devices or equipment branded with the WI-FI trademark are based on the standards specified in IEEE 802.11. In most cases, WI-FI is considered by most to be synonymous with the actual standard itself.
What is the difference between Wlan and Wi-Fi and what they have in common
To set up a local network, it is necessary to understand the concepts of WLAN and WiFi, what the difference and similarities between them are. Wireless coverage has made it possible for a large number of users to access the Internet. It is difficult to do this with a cable connection for technical reasons.

The term WLAN stands for wireless local area network. The technology is designed to transmit data packets over radio signals, thus eliminating the need for a cable connection.
What is a wireless LAN
In the past, all local area networks were cable networks. They were used to connect desktop personal computers (within the same home or office) and exchange data between them.
What WLAN and Wi-Fi have in common
Wireless Fidelity is a brand name used to refer to devices that connect to a wireless network. More often than not, the term WiFi is considered synonymous with WLAN.
Companies around the world have formed an alliance that supports wireless technology and related devices. This association grants certificates for products, provided they meet international standards for interoperability. However, you can find devices on the market that fit this criterion, but are deprived of certificates and WiFi logos because of the high cost and complexity of the registration procedure.
Features of wireless LS in the phone
The Wi-Fi module is installed on any smartphone, but not all owners of gadgets use the capabilities of wireless connection to the fullest extent. With this technology, Android or iOS devices can be connected to access points not only at home, but also in public places for free.