Hello! Internet service provider says that, for example, if there are several devices in an apartment, it can not be such that they both work via wifi and cable from one router.
- The type of security and encryption of the wireless network. Which one should I choose?
- Wi-Fi security: WPA3, WPA2, WEP, WPA
- IEEE 802.11 standards are Wi-Fi
- Wi-Fi Channel List
- 802.11b/g/n
- 802.11a/h/j/n/ac.
- 802.11y
- Setting up WiFi Router Wireless Modes – How to Enable
- Access Point.
- Modem mode (ADSL Modem)
- Repeater
- How to configure the Asus router mode?
- Which mode to use
- TP-Link
- "Asus".
- Keenetic by Zyxel
- D-link
- Wireless Mode on D-link.
- Radio Frequency Range on the Netis Router
- What is a multiple SSID?
- Why change the wireless mode
- Setting the wifi standard on Keenetic
- Why change the mode of the wireless network?
- QuickSet Internet Setup with QuickSet.
- Configure the WiFi.
- Configuring Bridge mode operation
- History
- Simplification of names
- Which operating mode should I set for 5 GHz wifi – ac or ax?
The type of security and encryption of the wireless network. Which one should I choose?
To protect your Wi-Fi network and set a password, you need to choose the type of wireless network security and encryption method. And at this point many people have a question: which one should I choose? WEP, WPA, WPA2, or WPA3? Personal or Enterprise? AES, or TKIP? What security settings will best protect your Wi-Fi network? In this article, I will try to answer all of these questions. Let's take a look at all of the authentication and encryption methods that are available. Let's find out what Wi-Fi security settings are best for your router.
Note that security type, or authentication, network authentication, security, authentication method are all the same thing.
Authentication type and encryption are the basic security settings for a wireless Wi-Fi network. I think we should start by figuring out what they are, what versions there are, their capabilities, etc. After that we will figure out what type of security and encryption to choose. I will show you an example of some popular routers.
I strongly recommend that you set up a password and protect your wireless network. Make it as secure as possible. If you leave your network open and unsecured then anybody can connect to it. This is not very secure in the first place. As well as the unnecessary load on your router, connection speeds drop and all sorts of problems with the connection of various devices.
Wi-Fi security: WPA3, WPA2, WEP, WPA
There are three security options. Of course, not counting "Open" (No protection) .
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is an outdated and insecure authentication method. It is the first and not very successful method of protection. Attackers have no problem accessing wireless networks that are protected by WEP. You do not need to set this mode in your router's settings, although it is there (not always).
- WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) – reliable and advanced type of security. Maximum compatibility with all devices and operating systems.
- WPA2 – Improved and more secure version of WPA. There is support for AES CCMP encryption. This is the current version of the protocol, which is still used on most home routers.
- WPA3 – is a new standard that allows for greater protection against attacks and provide stronger encryption than the previous version. OWE encryption also increases the security of public open networks. It was introduced in 2018 and is already actively used on almost all modern routers and clients. If your devices support this version, use it.
- WPA/WPA2 – Personal (PSK) – is a common method of authentication. When you only need to set a password (key) and then use it to connect to the Wi-Fi network. One password is used for all devices. The password itself is stored on the devices. Where it can be viewed or changed if necessary. It is recommended to use this option.
- WPA/WPA2 – Enterprise – A more sophisticated method used mainly for securing wireless networks in offices and institutions. It provides a higher level of security. It is only used when a RADIUS server (which issues passwords) is installed for device authentication.
IEEE 802.11 standards are Wi-Fi
Developers of routers are aware of the issue of the changing market and offer combined devices (Mixed) for a guaranteed connection of the user to the Internet. Before proceeding to the settings, you need to determine which mode to choose for your Wi-Fi router.
Learn more about the IEEE 802.11 set of standards, Wi-Fi bgn – what does this combination mean?
- 802.11b – slow up to 11 Mbps, 2.4 GHz band.
- 802.11g – speeds up to 54 Mbps, 2.4 GHz range, compatible with the b standard.
- 802.11n – speeds up to 600 Mbps, 5 GHz band and 150 Mbps on 2.4 GHz band, compatible with standard b,g.
Please note! Wi-Fi b, g, n differ in transmission speeds. Each subsequent one connects to the preceding one without any additional settings.
Another newest standard – 802.11ac – works only on dual-band routers with speeds up to 6.77 Gbps, 5 GHz band, the presence of 8 antennas provides MU-MIMO.
The Wi-Fi ace mode broadcasts the network in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
Note! Modes of operation of the router – the letter values that the device supports are spelled out in the specifications for the device next to the mark Wi-Fi 802.11.
A complete list of standards has more than 30 items. The rest are not basic. They are amendments or additions to functions. Two of these standards are of interest specifically for their additional capabilities.
802.11.y offers a data transmission range of up to 5 km and uses pure range.
802.11.ad offers super speeds over short distances.
Wi-Fi Channel List
Typical routers receive 1-14 channels. The number depends on the router model, frequency, and country. Channel represents a "sub-frequency" of the main frequency on which the device operates. A kind of "air corridor" from the router to the receiver wi-fi.
Pay attention! The more devices on the same channel, the more interference and the lower the bandwidth.
802.11b/g/n
Channels 1-14 are the 14 channels for 802.11b/g/n. Radio frequency bands 2400-2483.5 MHz, transmitter emission power not more than 100 mW. Short range.
802.11a/h/j/n/ac.
Channels 34-180 are the 38 channels for 802.11a/h/j/n/ac frequencies. The frequency is 5170-5905 MHz.
802.11y
Channels 131-138 are 14 channels for 802.11y. Operates at 3.65-3.70 MHz up to 5000 m (open space). Additional communication channel. In the U.S., channels are available at 5;10;20 MHz.
Please note! Before you decide to change the channel, you need to check what channels are busy, collect statistics on the signal strength, the protocols used, and only then switch the router to the right position. Acrylic Wi-Fi Home program (free download) will help to collect statistics.

Setting up WiFi Router Wireless Modes – How to Enable
The question on the agenda is how to set up a WiFi router mode? If you are going to set up a wireless network in your home, I recommend choosing a router for this purpose rather than an access point, modem, repeater or anything else. Why? Because it is a multifunctional device and it takes the place of all of these things. In this article, we will look at its main modes of operation and see how they are set up using the Asus model as an example.
First of all, we need to understand the concepts. The router has a total of four main modes:
Access Point.
In Access Point mode, or as it is called by foreigners "Access Point", the router works as a device which transforms a cable signal into a wireless signal. The main difference between a router in access point mode and another network device, which is actually called "access point", is that it not only distributes WiFi, that is, turns the wired Internet into a radio signal, but also has the functionality to distribute IP addresses and port forwarding, which is the main function of the router.

Modem mode (ADSL Modem)
In pure video, the modem is a device that is designed to work with providers who provide access to the World Wide Web via a telephone cable using ADSL technology. And for nothing else – the modem itself in router mode or just can not work. But a router in the router mode with ADSL support can not only get the Internet via telephone cable, but also retransmit it wirelessly and assign IP to other clients.

Repeater
Generally speaking, a "repeater" is a wireless signal extender or repeater that extends the signal from a wifi hotspot by some distance to connect computers that are in an area of uncertain reception to the Internet. If our favorite wifi router has repeater mode, it means it can do the same thing – extend the wireless signal, thereby extending the reception area. In addition, repeater mode is useful if you need to bypass some obstacle when creating a wireless bridge, when there is no line of sight between the two access points. Then we put the router in repeater mode within line of sight of both access points and transmit the signal through it.
How to configure the Asus router mode?
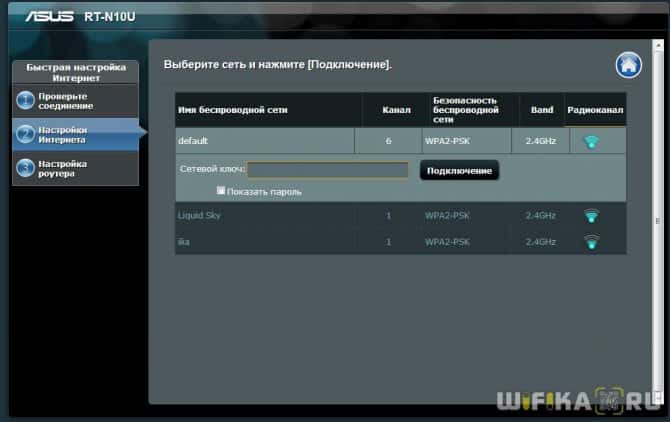
In different models, the configuration of the router mode is different. We will need to connect to some existing wifi, which is distributed by some other router, and distribute it already in our apartment. I will show you the example of Asus RT-N10U B in the new firmware.
Go to admin (http://192.168.1.1), "Administration" tab, "Operation mode" tab (in red), or immediately click on "Wireless router" at the very top of the settings page (in green).

At the moment, "Wireless Router" mode is activated by default. You'll find its settings in this article, and we'll put a check mark on the second-to-last one, repeater mode. And we press the "Save" button.
A page will open displaying all wireless networks within range of the router. Choose the one to connect to and enter the access key, if it is password-protected.

Click connect. After connecting to the third-party router, you can make another interesting setting: either use the data to access the existing network that we are extending. Or set your own – then we connect to ours with one data (SSID and password), and to the second, which is directly plugged into the Internet cable and whose signal we extend – with others.

Then it's a matter of waiting until all these settings are applied, and you disconnect from the network. Then in the list of available wireless connections appears the new one you just created. Connect to it and go forward to the Runet!
Which mode to use
The basic settings of the routers have already been configured. Often 802.11b/g/n mixed, or 802.11n/ac mixed is chosen. This means that the standard is of the mixed category. It is used so that the router can connect to a very old device as well as to the most modern one.
Each router has its own interface that allows you to change the protocol at the user's discretion. This is done to increase bandwidth.
TP-Link
Important! If the device can operate in two bands, you can also change the frequency.
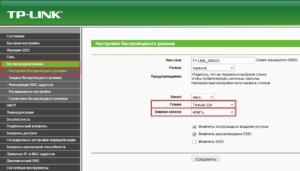
"Asus".
In devices of this manufacturer, it is necessary to follow the following order:
- Open the web interface of the router by going to 192.168.1.1;
- enter the "Wireless Network" section, where the necessary menu is located;
- choose from three formats: "Auto", which corresponds to b/g/n. Maximum compatibility. "N Only", the ability to work only in n mode, maximum performance. No support for legacy devices. "Legacy", meaning devices can connect according to b/g/n, however, the speed of 802.11n will be limited to 54 Mbps. It is not recommended to use this option.
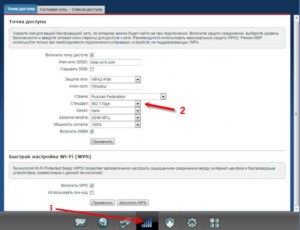
Keenetic by Zyxel
It is necessary to enter the interface of the router and find the "Wi-Fi network" section. There will be a menu on the right side of the screen called "Standard". Be sure to save the changes when the desired standard is set, otherwise the changes will not be saved.
D-link
There are several variants of the interfaces on the devices of the represented manufacturer. However, there is not much difference between them. It is necessary to find the section with the name similar to "Wireless Standard" and set one of the four proposed options in the menu.
Wireless Mode on D-link.
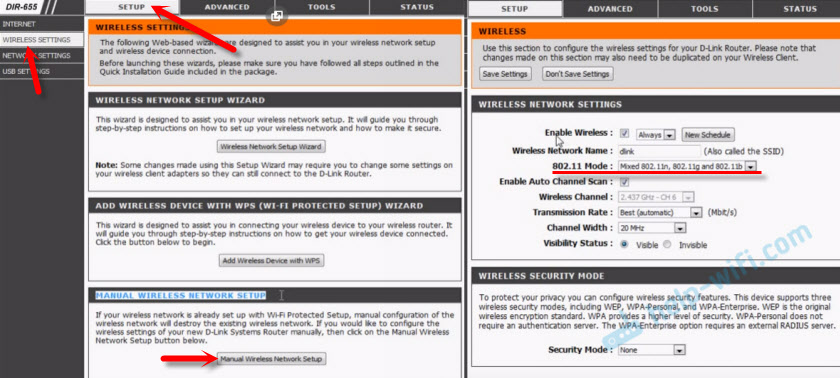
Open the control panel on your D-link router at 192.168.1.1. (read more in this article) or see how to enter the settings of your D-Link router.
Since they have many versions of the web interface, let's look at a few of them. If your case is a light web interface like the one in the screenshot below, then open the "Wi-Fi" section. There will be a "Wireless Mode" item with four options: 802.11 B/G/N mixed, and separately N/B/G.


Radio Frequency Range on the Netis Router
Open the settings page in your browser at http://netis.cc. Then go to the "Wireless mode" section.
There will be a menu called "Radio Frequency Diapason". Here you can change the standard of the Wi-Fi network. The default is "802.11 b+g+n".

It is not difficult. Just remember to save your settings.
What is a multiple SSID?
Users can assign their VLAN ID to a specific Wi-Fi network ID. This allows TP-Link access points to work on networks with different access levels and credentials.
Can I make a copy of a photo? Can I change the wallpaper on my iPhone? Can I take a screenshot of my Insta story? Can I take a screenshot on Instagram? Can I make a private Facebook account? Can I make a recording of a Skype conversation? What do I use to make a presentation? What can I do a presentation on? What website to do a presentation on? What website can I use to make a presentation?
Why change the wireless mode
Wi-Fi modules built into devices support certain standards. New TVs, computers, phones, etc. connect to wi-fi mode b/g/n/ac, frequencies of use range 2.4 and 5 MHz. Not all models support the ac standard. As a rule, these are low-priced products.
Technics with wi-fi reception of earlier years of release assumes support for b/g. Accordingly, when you need to access the Internet, and Wi-Fi works in n mode, you will not be able to connect to the Internet.
When you try to connect, the device displays one of the error status of the inability to connect to the network.
Pay attention! To solve the issue, you need to configure the automatic wifi 11n g b mode.
Setting the wifi standard on Keenetic
To specify wifi mode on your Keenetic router, you need to go to "Home network" in the control panel and open the "Advanced settings" link

Here under "Standard" we set it to "802.11bgn" and mark the channel width as 40 MHz

Why change the mode of the wireless network?
It's very simple. Let's look at an example. Here we have an iPhone 3GS and it can work in Wi-Fi only in b/g mode (if the specs don't lie). That is, in the new, high-speed mode n mode, it can't work, it just doesn't support it.
And if you have the router, as the wireless mode will be nAnd if you have a router with n , without any mixed, you will not be able to connect the phone to Wi-Fi, you will have to bang your head against the wall :).
But it does not have to be a phone and especially the iPhone. Such incompatibility with the new standard may be observed in laptops, tablets, Wi-Fi receivers, etc.
Several times I've already noticed that with a variety of problems with the connection of phones or tablets to the Wi-Fi – change the mode of the Wi-Fi.
If you want to see what modes your device supports, look in its specifications. Usually supported modes are listed next to the "Wi-Fi 802.11" mark.
On the package (or on the Internet), you can also see in what modes your router can operate.
Here is an example of the supported modes which are printed on the TP-LINK TL-WN721N:
QuickSet Internet Setup with QuickSet.

In the Quick Setup Wizard "Quick SetQuickSet" wizard provides you with several modes of the router:
- CAP .CAP: A controlled access point which is controlled by a CAPsMAN server
- CPEClient mode which connects to an AP.
- Home AP.: The Home AP. This mode is suitable for simplified Internet access configuration.
- PTP Bridge AP.: Creates an access point for a remote PTP Br > client to connect to.
Select Home AP mode and proceed to set up the router as a regular Internet access point, which can be used for a small office or home.
Configure the WiFi.

Network NameName of the network. This is the name that will be visible to whoever is connected to your WiFi network.
Frequency: Normally, it is best to leave it set to Auto .The router will select the optimal frequency.
Band .Bandwidth range for your home router 2GHz-only-N. If you have legacy 802.11b or 802.11g devices in your network, then you will need to select 2GHz-B/G/N mode, but you will lose connection speed.
Use Access List (ACL).: Used to limit WiFi access. Before enabling this option, it is necessary to create a list of clients who are allowed access. Select from the list of connected clients and click Copy To ACL.
Normally, it is better not to use this function, because. password authentication provides sufficient restrictions.
Configuring Bridge mode operation
Select under Configuration operating mode Bridge ..
If you want the Wi-Fi hotspot to receive network settings from the router automatically via DHCP, then in the Bridge make the following settings:

I prefer to specify the IP address of the Wi-Fi hotspot manually, so I know exactly where to look for it later. That's why I use static network settings.
If you use static network settings, in the Bridge make the following settings:
- Address Acquisition – Select Static;
- IP Address – enter the IP address of the Wi-Fi hotspot. It must be from the same subnet as the router;
- Netmask . – enter the mask 255.255.255.0;
- Gateway – Enter the gateway IP address (the IP address of your router);
- DNS Servers – Enter the addresses of the DNS servers. You can enter your router's address or Google's DNS server address 8.8.8.8.
History
The basic Wi-Fi 802.11 standard with a radio signal reception-transmission rate of 1 Mbit dates back to 1996. The task of setting up special facilities the signal solved, but only as a start for new developments. Later, when mobile devices with Internet reception came along, new types of Wi-Fi were needed.

Router manufacturers offer a product line – a selection of routers, the technical characteristics of which require clarification to understand the capabilities of the device.
Read also: The best portable consoles for games from Aliexpress. Top 10 portable consoles 2021
Important! Standards wi-fi b, g, n are letter designations for wireless network modes, each of which provides information about the speed of the signal from the router to the adapter (Mode).
The desire of the buyer to use a new speed mode causes confusion, for what the manufacturer offers three in one – bgn Wi-Fi. The fact is that the tablet, computer or other device that a person uses may not support the new speed mode. The specifications of the adapters on older laptops (year of manufacture earlier than 2009) will not be able to accept the standard n, because at the time of manufacture there was no such thing.
Simplification of names
Computers, smartphones, netbooks, and other products with built-in Wi-Fi controllers use the IEEE standard alphabetic characters for labeling.
Please note! Such marking is understandable for specialists, but not yet for all buyers.
The names have been simplified for ease of reading. Now the major Wi-Fi standards will be publicly referred to as numbers instead of letters.

The controller icon will change when the device switches between different Wi-Fi networks, the user will be informed which versions are available. The indicator with the number 6 indicates that the device uses the most advanced version of Wi-Fi 6 to date.
Which operating mode should I set for 5 GHz wifi – ac or ax?
The question of choosing a wifi operating mode for the 5 GHz frequency range is not so acute. Because it is unlikely that the average Internet user ever got his hands on a router that supports the standard "ax". The most popular today is the "ac" mode, so most models do not even offer a choice between them. Mostly we can see the same mixed type "802.11 A + n + ac".

If the standard "AX" is supported, then again, it is more logical to choose the mixed type for the best compatibility of wifi standards between all computers, laptops, smartphones and TV set-top boxes connected to the router.
Read More: