Keep in mind that this communication mode is not optimal in terms of performance. Consequently, this solution is only used if cable laying is not possible or the cost is high. To understand this includes a figure in the graphical performance of the cable, the wireless bridge, obtained using the application iperf.
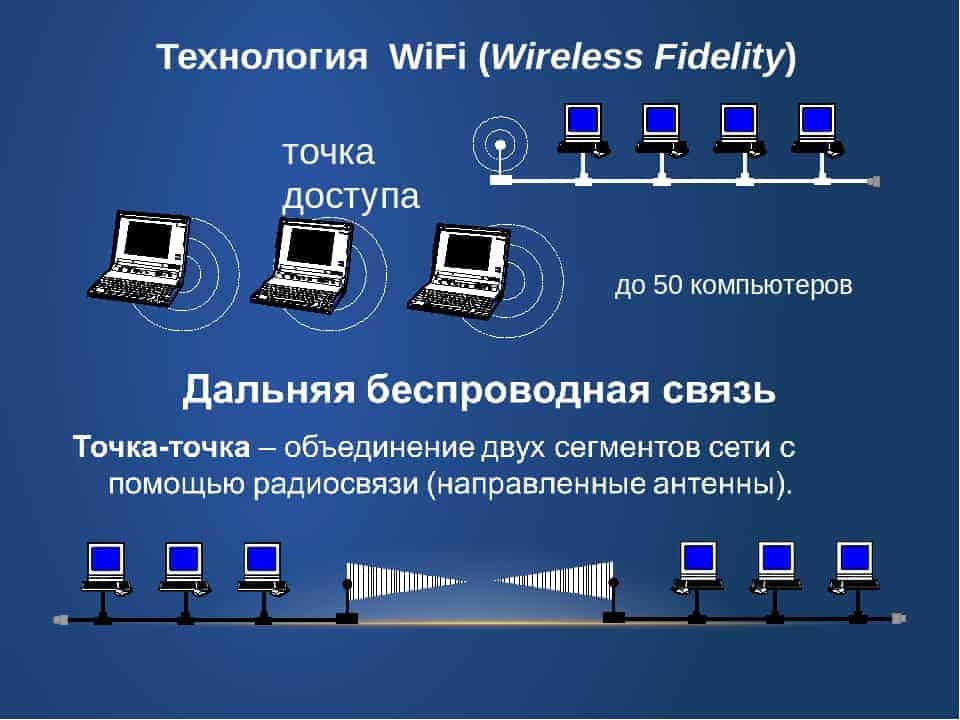
- Wi-Fi network modes of operation.
- Residential Wi-Fi
- Wireless data transfer
- What is this technology, the advantages and disadvantages of using
- Classification of wireless channels
- Wireless data transmission technologies and standards
- When did wi-fi appear
- Creation history
- Why Wi-Fi was needed
- Standards of the physical layer of Wi-Fi
- Signal representation
- Channels in the 2.4 GHz band
- Speed Adaptation
- The main standards of wi-fi
- What is a wi-fi hotspot
Wi-Fi network modes of operation.
Since the advent of consumer devices with Wi-Fi connectivity (smartphones, tablets, laptops), this wireless technology has become very popular. This has undoubtedly influenced the housing and home market, where Wi-Fi has found its niche of greatest growth. For many people, having a Wi-Fi network is associated with a router that provides an Internet connection. Nevertheless, Wi-Fi technology offers a wide range of all sorts of configurations for both professional and domestic markets, and in this article we will look at just such a range.
Technically, Wi-Fi is a technology that allows you to create a wireless local area network, that is, a wireless connection between multiple devices, that is, without cables.
The device uses Wi-Fi to connect to the network, known as a wireless access point, also called WAP – an acronym in English or simply AP. This is the device that sets the operating parameters of the Wi-Fi network and centralizes and manages all wireless communications.
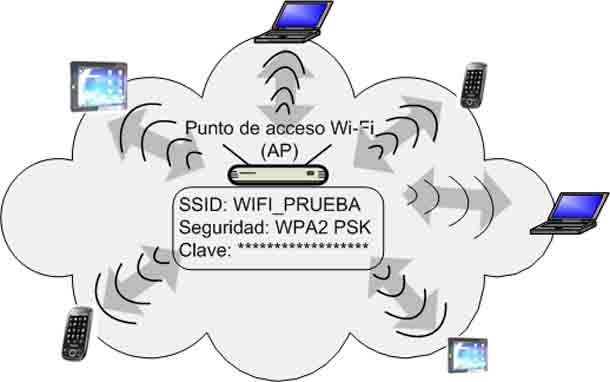
The AP is said to be a Wi-Fi network operating in infrastructure mode. Many manufacturers have called it AP mode. In this mode, the access point establishes the Wi-Fi network, basically allowing you to configure the network name (a parameter known as SSID), security type (WPA, WPA2), and if necessary the network access code.
As shown in the previous figure, the access point is a Wi-Fi network, but it does not itself provide access to the Internet. The AP, in addition to creating a Wi-Fi network, allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network. All APs have an Ethernet port for this purpose. If the AP is connected to a wired network with an Internet connection (or directly to a router), the Wi-Fi devices will have access to the Internet.
You can see the back of the AP where the Ethernet port is enabled, and on the right is the AP's connection directly to the router to allow wireless devices to connect to the Internet.
Residential Wi-Fi
In the previous section, we saw how the main way to set up a Wi-Fi network is through a Wi-Fi access point (also just called an AP). However, almost no one has an AP at home to be able to connect to a Wi-Fi network. Why?
For several years now, all Internet service providers, that is, companies that provide Internet access, have provided their users with routers with wireless access point functionality. Consequently, these users do not need an access point because the router itself already includes access point features.
Even the name of the Wi-Fi router was familiar for this type of device, as can be seen from information extracted from the web pages of several Internet service providers:
Usually (though not always) this type of Wi-Fi router only supports the mode of operation described above, known as infrastructure mode or access point mode. In this mode, Wi-Fi connectivity needs are fully covered in most cases, especially in residential networks.
But there are scenarios in which a single AP infrastructure mode (or a router that includes this feature) is insufficient to meet the connectivity needs of various devices. In the next section, we look at the most common configuration modes in Wi-Fi technology.
In fact, any device with a Wi-Fi interface and associated software can function as an access point. For example, a PC with a Wi-Fi card or a smartphone. In the case of Android smartphones, the operating system itself includes software to control the phone as if it were an access point.
Wireless data transfer
Wireless technology is a branch of computer science and information communications that allows long-distance transmission of signals in the form of text, visual or audio recordings without electrical wires as intermediaries. The best known are Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and WiMAX.
The term leads to an understanding of what wireless Internet is. It is a dedicated private network that gives the user access to a global source of world information. Such a line can work both at home and in the office. It is arranged through the selected provider.
What is this technology, the advantages and disadvantages of using
Thus, the main features of the new technology:
- The absence of an electrical cable.
- The ability to instantly exchange information between 2 or more points.
- The use of radio waves, infrared, optical, or laser radiation in order to make contact.
- Variety of implementation methods and areas of use.
- Mobility – independence of networks from additional devices in the form of cords, which reduces the overall cost of equipment.
- The frequency range provided does not require obtaining a permit.
- Wireless Internet technology protocols provide for subscriber security: encryption, MAC-address filtering (based on physical addresses of devices) and encryption.
- Ability to change access points for WLAN to find the best signal reception.
- Wide range of equipment from different manufacturers. Due to compliance to international standards purchased wireless communication devices work successfully abroad as well.
- Less reliable method of communication than via cable. Possible interruptions and temporary access disconnection.
- Limited range: in houses about 50 m, in open areas no more than 100 m. Above this mark the signal becomes weaker and disappears.
- Risk of reduced connection quality due to overlapping channels of nearby stations, electrical appliances in the apartment and physical obstacles to signal passage.
- High level of energy consumption: rapid decrease in the charge of the device, especially if it runs on batteries or rechargeable batteries.
Classification of wireless channels
There are several options for dividing the existing channels. Range is one of the most important characteristics. What wireless Internet connection technologies are available:
- Personal networks (abbreviated WPAN). An example is Bluetooth.
- Local (or WLAN). Wireless Internet is Wi-Fi.
- Urban lines (WMAN). This includes WiMAX.
- Dedicated Wide Area Networks (WWAN): CSD, GPRS, EDGE, HSPA, LTE, etc.
Wireless data transmission technologies and standards
Wireless technologies, which are more commonly grouped by the term Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity), operate under a single IEEE 802.11 protocol. The most common types of specification are:
- IEEE 802.11a: frequency bandwidth within 5 GHz, network bandwidth of 54 Mbps.
- IEEE 802.11b: 2.4 GHz bandwidth and up to 11 Mbps network bandwidth.
- IEEE 802.11g: 2.4 GHz frequency, with a maximum transfer rate of 54 Mbps.
WLAN coverage area is 50-100 meters. The line can be indoors or outdoors, with indoor or outdoor access. Initially, networks were expensive and the Internet was conducted only in large organizations. Soon the hotspots appeared in public places of large cities – through a Wi-Fi controller in a laptop or phone, any visitor could easily and quickly connect to a web resource for personal use.

When did wi-fi appear
The first prototype was presented in 1991 by John O'Sullivanam (is the creator and embodiment of the idea), it was called "WaveLAN". The development of one universal standard for all devices was completed by 1997. It involved the American Local Area Network Standardization Committee, which introduced Wi-Fi 802.11 at that time. This invention was characterized by low bandwidth, its speed did not exceed 2 Mbit/sec.
The low competitiveness of the novelty was perceived by specialists with irony. During the same period, other offers of the same type were presented on the market, surpassing its speed by several times.

Creation history
1999 was the time of Alliance's creation, designed to increase the popularity of the new standard and increase its competitiveness figures. Companies were involved in the development:
Two prototypes were introduced to the public during the presentation:
Sales of the latter began in 2000, the standard quickly swept the market. Potential buyers appreciated its stability, bandwidth, and speed performance.
The Alliance group of members had more than 100 representatives by 2003. That same year they introduced a new standard, 802.11g. By 2003 it was the leader, leaving all competitors behind. That same year the WPA device certification program was introduced which was responsible for securing access to the World Wide Web. Twelve months later the protocol was improved and changed to WPA2.
After 14 years practically all devices started to work with wi-fi. In 2008, the 802.11n standard appeared, functioning at 600 Mbps. 2014 was the date of the introduction of 802.11ac, which operates at speeds up to 1 Gbps.

Why Wi-Fi was needed
The original Free Wi-Fi functioned slower than cable. Today, the two are nearly equal. Wireless connection is convenient for mobile equipment:
It is able to function not only within a single room, but also to cover large-scale industrial facilities. The technique is used to conduct remote or hazardous work, exchange data between different devices.
For the average user, wi-fi allows you to be not tied to one place. Experts believe that the method will soon displace the usual cellular networks. This means a rapid obsolescence of technology, considered at the moment the most modern.

Standards of the physical layer of Wi-Fi
There are several different implementations of wifi, they are described in 6 standards. The very first standard 802.11 was adopted in 1997 and had a speed of 1 or 2 Mbps, Ethernet at that time could transmit information at 10 Mbps. The current standard wifi 802.11as was adopted in 2014, the maximum transmission speed, more than 6 Gb/s.

Nowadays, wifi is used to transmit data – electromagnetic radiation or radio air, but the first version of wifi used infrared radiation, now this method is used in remotes for TV.
But since the second generation of 802.11b only electromagnetic radiation is used. Two frequencies are used, 2.4 and 5 GHz. Frequencies in this range can be used without licensing. However, other devices operate in the same range, such as a microwave oven and this interferes with the wifi signal.
Signal representation
Modern wi-fi standards use orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFMD) to transmit data. Data is transmitted in parallel at different frequencies. Although the frequencies overlap in the picture, the OFMD method allows the signals to be recognized reliably.

Channels in the 2.4 GHz band
Channels in the 2.4 GHz band use 14 channels for data transmission, their frequencies are listed in the picture. The channels are slightly shifted in relation to each other, but still partially overlap.

Therefore the number of Wi-Fi networks which are in the same place is limited by the number of channels there cannot be more than 14. If more than 14 networks are operating in the same area, they will not have enough channels. This is known as a "wi-fi jungle" and is quite common, e.g. in apartment buildings with a wi-fi router for internet access in every apartment.
Speed Adaptation
With Ethernet the speed of the equipment is fixed, it will be the same for all devices on the network. Wi-Fi allows you to change the speed depending on the quality of the signal. If the signal quality is high, the speed increases, and if the signal quality is low, the speed decreases. In order to increase or decrease the speed, wifi changes several parameters:
- You can use different channel widths from 20 MHz to 160 MHz.
- It supports different modulations, which allow you to transmit data at different speeds and with different reliability
- It is possible to change the data interval between the characters that are transmitted via wifi.
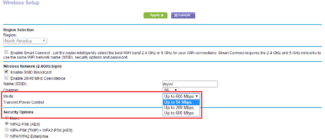
A table that shows the different speed options for the same wi-fi stream. The slowest speed of 6.5 Mbps is obtained when using a 20 MHz BPSK binary phase modulation channel and the interval between the characters is 800 ns. The highest speed of 866 Mbps is obtained by using quadrature amplitude modulation which has 256 states, the channel width of 160 MHz and the interval between the characters is 400 ns.

The data is presented for a single spatial stream, if your access point and your station have multiple antennas, you can use multiple spatial streams and thereby further increase the transmission speed.
The main standards of wi-fi
Various variations of the 802.11 standard are used for wireless data transmission using Wi-Fi technology. Let's consider the features of each of them.
- 11 – the standard is the main one, data exchange is done at low speeds.
- 11a – radio frequency 5 GHz is used for data transfer at speeds up to 54 Mbit/sec. This standard features a more efficient coding algorithm. The original signal is split into sub-signals on the transmitting device side, which minimizes the possibility of negative effects of interference.
- 11b – Not compatible with 802.11a. It is the cheapest in cost, which briefly made it the most popular standard. Along with its low cost, it is also the slowest. This standard operates at 2.4 GHz, and its bandwidth does not exceed 11 Mbit/sec.
- 11g – Runs on 2.4 GHz radio frequency with a bandwidth of 54 Mbit/sec. Since the network is often congested, the speed in reality does not exceed 24 Mbit/sec. The OFDM coding algorithm has made it possible to increase the data rate.
- 11n is the most common modern standard, operating on the 2.4 and 5 GHz frequency bands. It is compatible with the other standards and operates at speeds up to 300 Mbps.
Developers are constantly working to improve the standards. In early 2014, they adopted the 802.11as standard, which operates at speeds of up to several Gbit/sec. In addition, there is the 802.22 standard, which is designed to work in rural areas and is capable of receiving and transmitting data within a radius of 100 kilometers. Its bandwidth is 22 Mbps.
What is a wi-fi hotspot
A hotspot is a point through which you can connect to the Internet using WiFi. It can be a modem or a router. There are cell phone models that can be used as such an access point.
It is impossible to give a definite answer to the question of whether to choose in favor of Wi-Fi or connect to the Internet via cable. It depends not only on the devices, but also on what requirements the user puts forward.
- It does not require the laying of cables.
- It is possible to connect various mobile devices to the home Internet.
- The user becomes more mobile because he is not limited by the length of the cable. Access to the network is possible from any access point located in the coverage area.
- The ability to connect multiple users to the Internet within the coverage area.
- Full interoperability of all Wi-Fi Alliance certified network equipment.
- Possibility to expand the coverage area, if there is such a need.
- Most routers work exclusively on the 2.4 GHz frequency. Since this frequency is used for mobile gadgets, microwave ovens, Bluetooth and other routers, they can interfere with each other by blocking the signals coming from each other. Modern routers operate on other frequencies, which minimizes interference.
- The actual speed in most cases is lower than the manufacturer's stated speed or the speed of the cable connection. This is explained by the fact that the speed of wireless Internet depends on many different factors.
- When connecting to Wi-Fi, there is no difficulty, even with protection in the form of a password. It's okay if some person uses someone else's access point just to access the Internet for free. However, there are some hackers who hack into the network for their own criminal purposes. This mainly concerns Wi-Fi networks in public places.
- There are states that legislate restrictions on wireless access points. In Russia, Wi-Fi working outside the premises must be subject to mandatory registration procedure.