Routers
- What is the difference between a Dynamic IP Address and a Static IP Address?
- Internal Dynamic IP address
- General concept of the Internet address
- Preliminary stage of router IP configuration
- Private and public numbers
- How to know your IP and what it is
- Step 3 – Select the type of connection to the Internet
- Step 7 – Save changes
- TP-Link
- Zyxel Keenetic.
- The key to successful configuration of the Wi-Fi router: a list of parameters to be checked
- What happens if the wrong type of connection is specified?
- How can you determine the connection technology used by your ISP?
- External static IP address
- What is a static IP address and what is it for?
- Option 3: ASUS
- Additional Actions
What is the difference between a Dynamic IP Address and a Static IP Address?
In one of the last articles I showed and talked about concepts such as IP address. Today we're going to dig deeper into this subject – what is a dynamic IP address, how does it differ from a static IP address, and how do you know which is better? And also how to change a static IP address from a dynamic to a wifi router and what influence to work with the Internet has a gray or white IP address.
A dynamic IP address is one that changes each time you connect to a router or access the Internet.
Internal Dynamic IP address
Let's start with an easy one. Each time your computer, laptop, smartphone, TV or any other device connects to wifi, the router gives them a separate IP address. This is a kind of identifier for the device on the network. DHCP is responsible for distributing them on the router. And every time, even when the same PC connects to the network, it is given a different IP address, that is dynamic, constantly changing from connection to connection.
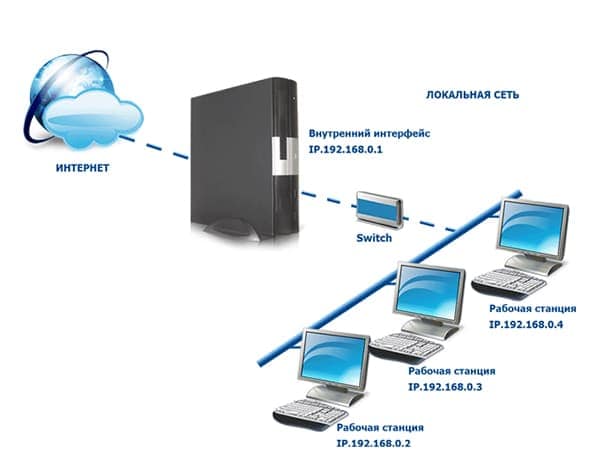
The Internet is much bigger and more complex than the home network that we create in our apartment. But the point doesn't change. Let's imagine that the provider for your area made a server (at home, his role plays the router). It has Internet access, and a whole bunch of computers connected to it from the users in your neighbourhood.

Most of the equipment of modern service providers are configured to distribute ip addresses so that to access the Internet you just need to plug the cable into the socket in the network card of your PC or laptop and open your browser. This means that the server is working in DCHP mode and you have a dynamic IP address. That is, once you have connected, you immediately assigned a free allowable value, which is assigned to you only for the duration of the current connection session.
The dynamic ip address changes either when you reconnect or at a certain time interval.
The address that you occupy will be released and assigned to someone else, and you will get a new one the next time you visit the web page. This is the same as if every time you have a new visitor, you constantly change your apartment number and you would have to report it anew each time.
General concept of the Internet address
All modern computer networks work using the Ethernet standard that assumes the use of TCP/IP protocols for data transmission. TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. Actually TCP/IP is not one protocol, but a whole family of protocols. The leading role is played here by a low-level protocol, which regulates the addressing of machines in the network – IP. This is where the concept of IP addresses comes from. The higher-level protocol, TCP, is responsible for transmitting data packets directly between software products. Several other protocols can be noted in the Ethernet structure: FTP (file transfer), SMTP (mail protocol), HTTP (transfer of hypertext information displayed by browsers), and others.

An Internet address is a numeric combination of 32 bits for the IPv4 version, or 64 bits for IPv6. The v4 version is the most common at the moment. Machine code is a number written in binary notation (a combination of zeros and ones) consisting of 32 digits. Recording the address in machine form is rather cumbersome, and not convenient for human perception. To do this it is usual to divide the number into 4 groups of 8 characters each and convert it to the decimal system, to which we are accustomed. Groups of numbers are separated by dots. This is how you get an IP address. The number in each group can be from 0 to 255. To make it clear, below is an example of writing the address in machine form, and in a more familiar to humans:
The main thing to understand here is that every device that is part of a global computer network has a unique address. There is an agreement that there are some addresses used for local networks and all others for the Internet. Internal or local addresses are never found on the Internet. Although they can be used within a huge number of private (home or office) networks. This greatly expands the LAN extension possibilities. This information is enough to understand what IP for router configuration is.
Preliminary stage of router IP configuration
To start setting up, you must meet a number of requirements on the availability of equipment. In order for everything to be successful it is necessary to prepare the equipment:
- Take the router out of the box and check the equipment set. The kit should include the router itself, the power supply unit, and a meter network cable (if it is missing, you must buy it).
- Connect the router to the power outlet.
- Connect a computer network card to the connector of the router. Connect to one of the connectors, which is labeled LAN.
- Connect the cable that comes from the provider to the WAN port.
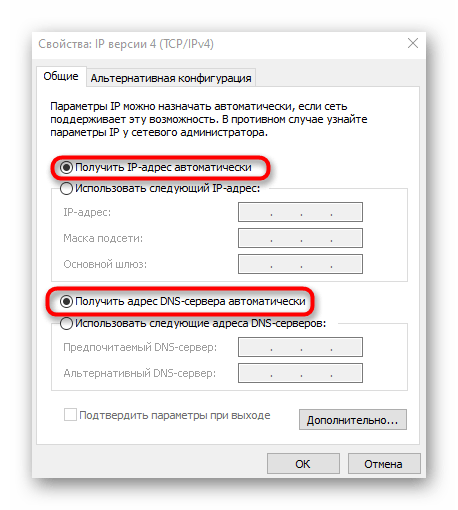
- Check on the computer that its IP address will be obtained automatically from the DHCP settings. This is done in the network adapter settings "Start – Control Panel – Network Connections (or Network Control Center – Advanced Adapter Settings) – Local Area Connection – Properties". In this properties window the "Internet Protocol (IPv4)" parameter should be set to "Obtain IP address automatically". This is needed to set your ip to configure the router.
- Let's find out the address of the router. The actions are similar to the previous point, only you need to select "Information" instead of "Properties". In the line "Default Gateway" will be the value you are looking for.
- Open any browser, and enter in the address bar the gateway that we have learned.
- Log in using your username and password. If all goes well. You will be taken to a screen where you can change or configure the router and the network.
All the connection parameters we are interested in can be viewed in another way – via the console or command line. It is even easier to do this than to browse through the many settings of the interface:
"Start – Run – cmd". Opens the command line (terminal), in which we enter the following:
"ipconfig /all", naturally without the quotes. The command will work, collect the data and display the required information in a conveniently structured form. Usually, even in the language of the operating system.
Private and public numbers
Now let's talk about the "color" of IPs, because this is the context in which they are often mentioned on the web. IPs can be white or gray (or public or private). A public IP is one that appears on the Internet. They are visible on the global network, a whole subnet can sit through one address. Anything used on local networks by ISPs, firms or users are private addresses.
Private IPs are not routable on the Internet. They are provided by the ISP to their customer immediately. You can see the address in the settings of your router or computer.
Gray addresses are not directly visible on the Internet. They are converted by NAT into public addresses, through which information is exchanged. You have a gray address by default, it is safer, because behind one public IP can be a whole network of computers and routers.
White addresses are directly visible on the Internet. They are addressed directly, bypassing most intermediaries. These include all sites, public servers, some online services and many others.
For individuals, getting a white IP is a paid service, because their number is limited, the issuance is controlled.
You'll have to actually buy the right to use from your provider, he will buy from the regional registrar, the other will buy from the higher one, and so on.
How to know your IP and what it is
Such services are not provided free of charge for any length of time. There are temporary actions, when they give such service a try, but then it comes back to the paid basis. If there is no such a box in the bill, you use dynamic IP.
If you do not know whether you have a static or dynamic IP, then it's dynamic.
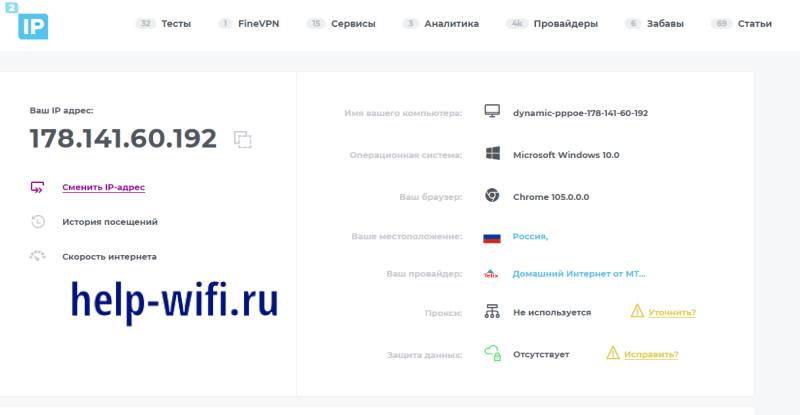
Go to the 2ip site and you will see your address on the left side of the main page. Look at the right side of the column, there in the top line is usually written the type of connection. In the example this dynamic PPPoE, in the case of a static connection the word static would be in the beginning. Write down the address from the left part of the window.
To be sure of the dynamic IP, turn off your computer and router for about 15 minutes, completely disconnected from the network. Turn it on and go to the site again, if the address has changed, then it is dynamic. This is a simple and imprecise way of diagnostics, the specific information you can get from the technical support of your provider. Contact them if you have any questions.
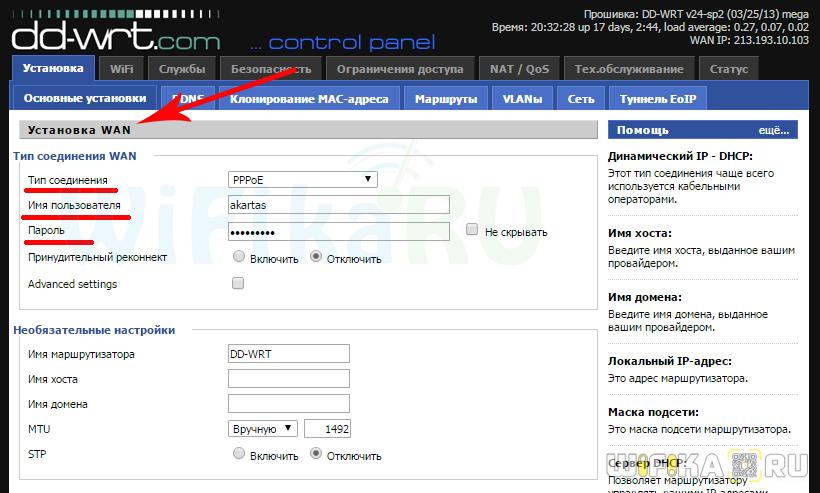
Step 3 – Select the type of connection to the Internet
In the settings of the router in the WAN or Internet section select the type of connection, which is either specified in the contract with your provider, or found out by calling technical support, and enter all the data for access, depending on this type. Again, they are all specified in the contract or accompanying explanatory materials and instructions of the provider.
Step 7 – Save changes
Save all the changes and wait for the router to reboot to apply the specified parameters.
Let's move on to setting up WiFi on the laptop. Let's consider the installation using Wndows 7 as an example, although on XP it will be the same – the only difference is the names of the menu items in the system itself. But first of all bear in mind that your notebook must have WiFi module – either built-in, which you will be informed about on a sticker on the chassis, informing about its presence, or some button to activate it.

If it is not, you must buy and install a WiFi adapter – more about choosing this device here.
Then go to the network connections section by one of the following routes:
- Windows XP: "Start > Control Panel > Switch to Classic View > Network Connections".
- Windows 7: "Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Manage Network Connections > Change Adapter Settings".
Find our wireless connection, right-click on it and go to "Internet Protocol version 4" and in the properties of the network adapter check the checkbox to get DNS automatically.

Open the laptop with the wifi module on, find the wireless icon in the lower right corner of the Windows icons panel.

Click on this icon to open the list of available WiFi networks in range. Find ours with the name you have just set on the router and enter it with the password you have set.

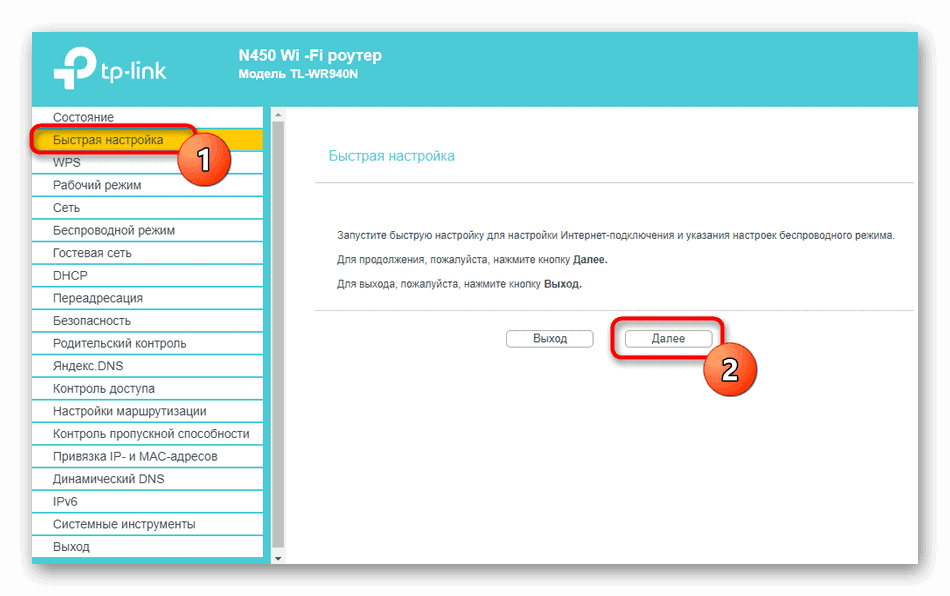
TP-Link
On the new firmware, select the "Advanced Settings" – "Network" – "DHCP-server" tab at the top. Now click "Add" and enter the data and save at the end.
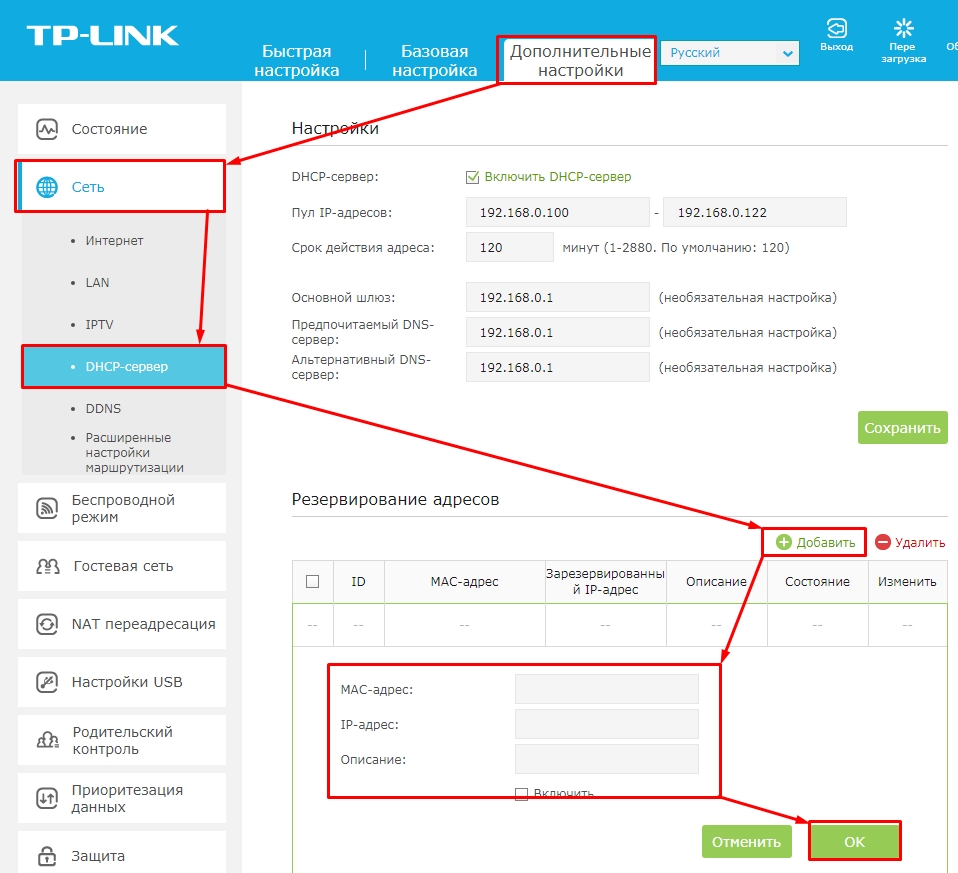
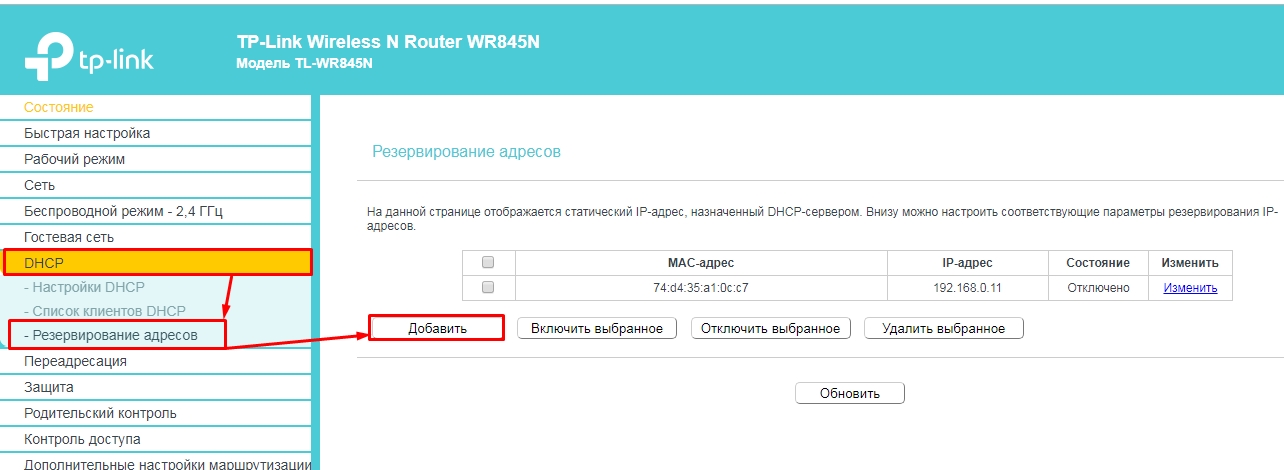
On the old firmware – "DHCP" – "Address Reservation" and press "Add".
Zyxel Keenetic.
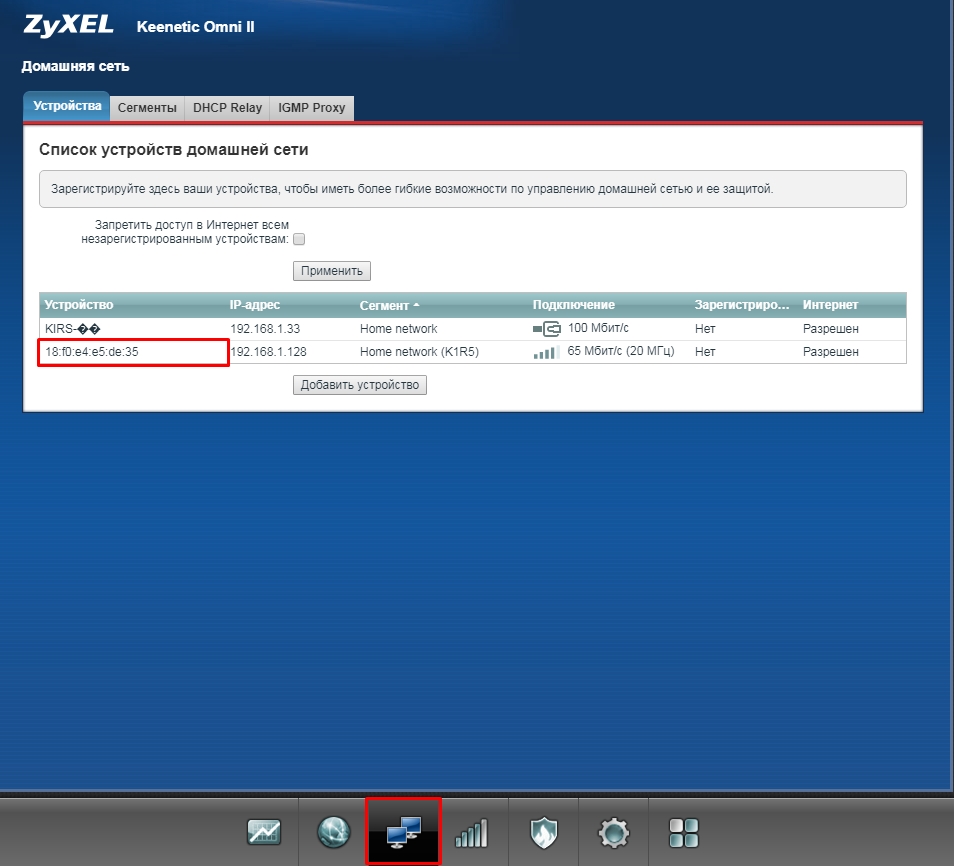
Click on the "Home network" section. Then in the tab "Devices" you will see all connected devices. You can add a device manually by clicking the button below.
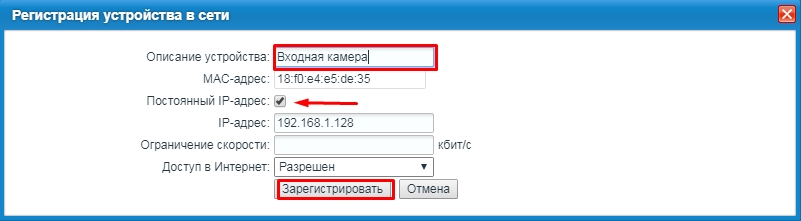
Or you can simply assign a static address to an already connected device. You just have to click on it, select "Permanent IP address". You can also write a description of the device, for convenience. At the very end, click "Register".
The key to successful configuration of the Wi-Fi router: a list of parameters to be checked
As in any other job, for a successful and problem-free configuration of the Wi-Fi router, you need to prepare in advance – find the documents received from the Internet service provider at the conclusion of the contract, and in their absence look at the official website of the company guide, how to configure the router and what network parameters to use.
If you think about it, most of the problems that arise during the setup of wireless Internet appear due to incorrectly set connection type and WAN parameters. This is the data provided by your ISP. Most companies prefer to work with dynamic IP. This is a convenient type of connection that does not require additional settings. All important functions and parameters are accepted and saved automatically, and some routers have default settings for this technology, i.e. turn on the device and use the Internet immediately.
Some users create a wireless network, give it a password and a name, but forget about the most important parameters. Even fewer subscribers know about MAC-address (what it is and why it is needed). Therefore a strong reminder(!) – check the binding and clone the MAC-address, if necessary.
These are the two main pillars on which a successful router setup rests. The main thing in the router's work is correct pairing with the ISP and network distribution, while such wireless connection data as the name or password are secondary tasks that can be easily solved after reading the device's user manual.
What happens if the wrong type of connection is specified?
Connection selection is one of the most common problems. If this setting is incorrect, but all the other data is correct, the network will appear on the computer. But Internet will not be available. Wireless connection between different devices will be available, but they will not be able to access the Internet either. On all devices that are connected to the network, the icon "no access" will be lit.
This means that the equipment cannot connect to the ISP, which means that there are some errors during configuration.
How can you determine the connection technology used by your ISP?
If we talk about technology, ISPs can use a small set of options. First of all, it is the distribution of ip address statically or dynamically, then PPPoE, PPTP, L2TP are available. To understand what these are, you should learn more about them.
- Dynamic IP. Happens most often. The address is provided automatically by your ISP. It changes with each connection. Check Dynamic IP in the router's settings. After that, no other actions are required. This is a very user friendly technology.
- Static IP. If the provider says that you have a static address, it means that he writes it exactly in the contract, as well as specifying data login and key to connect to the network. In this case, you specify the type of connection – static, then enter the value of ip-address, login / password pair. This method is less popular among the internet service providers because it requires tracking who is given which addresses.
- Technology PPPoE. It is widely used in Russia and is suitable for high speed channel connection. For it in the parameters you should specify the type of connection PPPoE. also the provider gives the login and key specified in the contract. This type often requires a static ip-address, it will be given in the contract.
- Technologies PPTP и L2TP. These technologies are similar to each other. They require a number of parameters, such as name and key for authorization, server address to which the connection will be made, static ip-address.
Before configuring the router settings, you should know. What technology is used by the provider.
External static IP address
After you have a cable to the apartment Internet, we plug it into the network socket of the computer.

If you want to set up a wireless wifi network in your home, you can also connect it to a router.

In most cases you will not need to enter any additional settings to connect to the Internet. The IP address and DNS servers are automatically detected and set up by the hardware. We discussed this type of connection in the article about Dynamic IP and DHCP settings in the router.

But there are also providers who give you specific settings for your Internet connection:
This means that your computer on their server has a separate static ip address, such as 192.168.43.1. That is, every time your computer or router will connect to the provider, it will always have the same IP address within the provider's network. But it's not that simple – here comes the concept of white and gray IP addresses. You can learn more about them in article about differences between static and dynamic addresses.
- Grey is when IP address is static inside ISP's local network only. That is inside one area you will have tied to your apartment I-p address. And it will change on the Internet.
- White is when on the Internet you will always have the same invariable identifier.
Most often under the external static IP-address is meant a white one, and we will talk about it further.
What is a static IP address and what is it for?
What are the benefits of a static IP address on the Internet? In fact, it is needed for remote access to your computer or router from the Internet. For example, if you have a file server or video surveillance system running at home, you need to be able to connect to it from any other place outside your apartment.
However, for connecting an external static white IP address any provider takes a large additional amount, which significantly increases the monthly fee for the Internet.
Today is widely developed cloud technology, which are used in literally every network device from ip surveillance cameras to wifi routers. You can find any model to your liking and for a fairly wide range of tasks. Therefore, to use for external access static ip address and pay for it I see no point.
Option 3: ASUS
The last option is suitable for owners of ASUS routers. Here, too, there are two ways you can go when configuring automatic IP. The first is to use the Setup Wizard and looks like this:
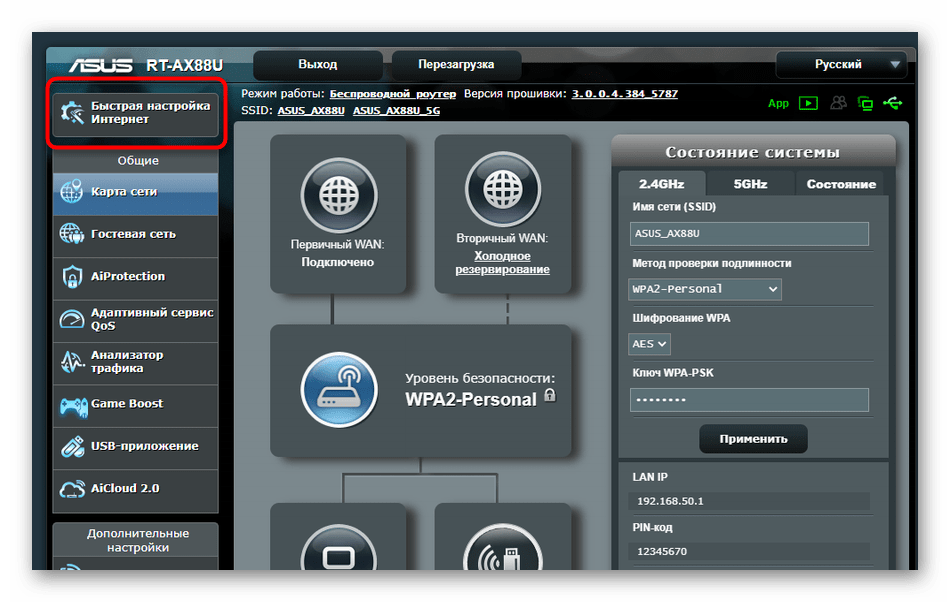
- In the web interface, click on "Quick Internet Setup.".
- Proceed to create a new network.

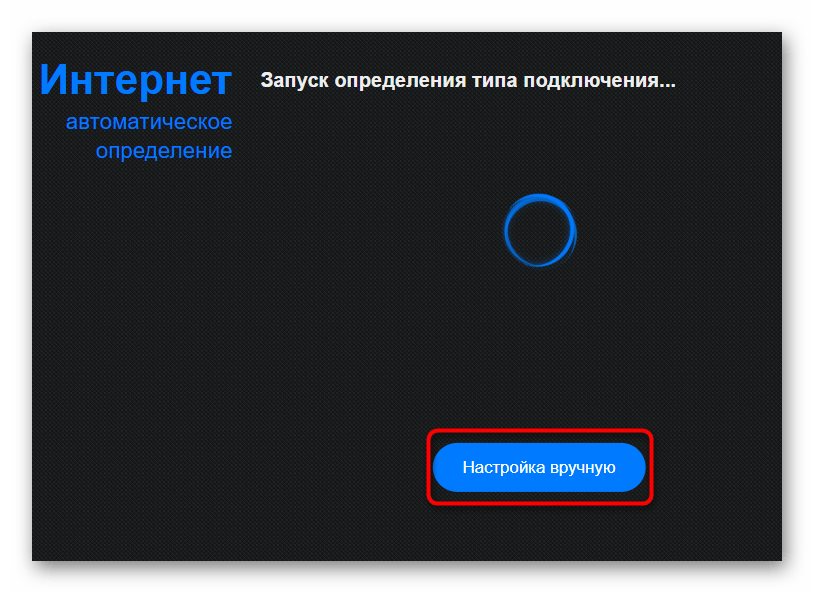
- Click on the button "Manual configuration" button.if the parameters were not automatically defined.
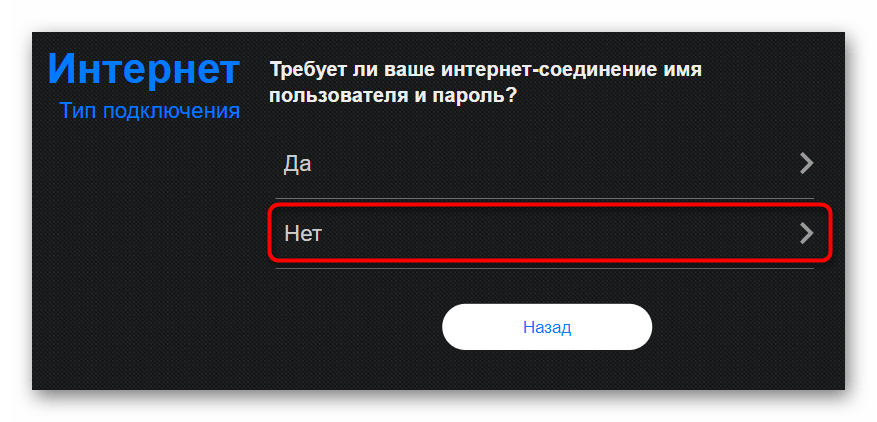
- If you are asked about username and password, answer "No".If you are asked for a username and password, answer "No" because dynamic IP does not require such data.
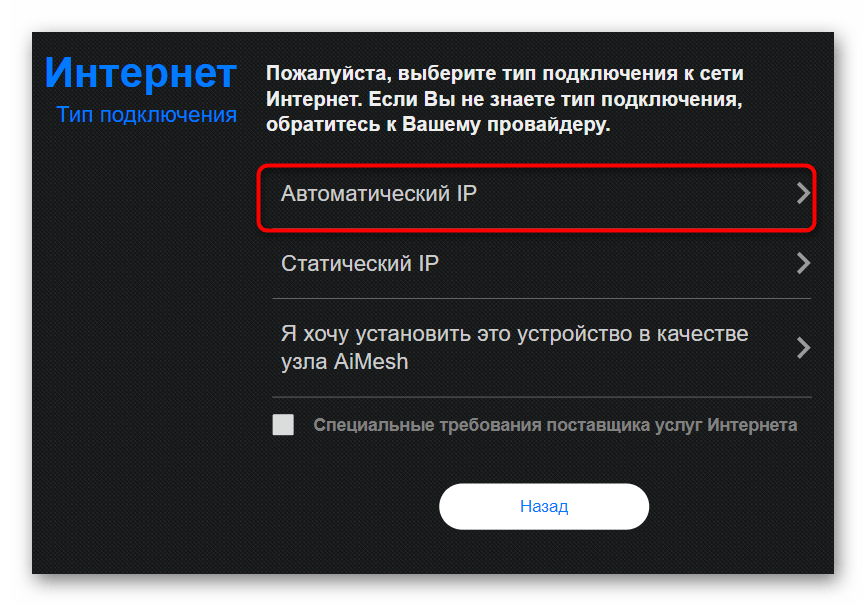
- Next, select the connection type "Auto IP.".
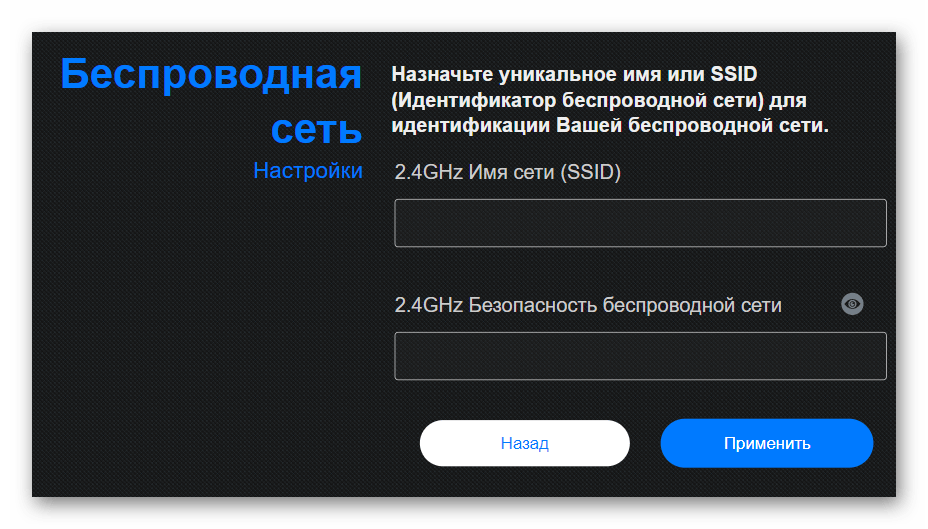
- Configure the wireless network to exit the Wizard.
Additional Actions
We would like to finish this article with a walkthrough of some extra steps of the operating system itself. They have to do with getting IP-address and DNS-servers, and the values have to be set to "Obtain automatically"so that there are no conflicts with the router settings.
- Open "Start and go to "Settings.".
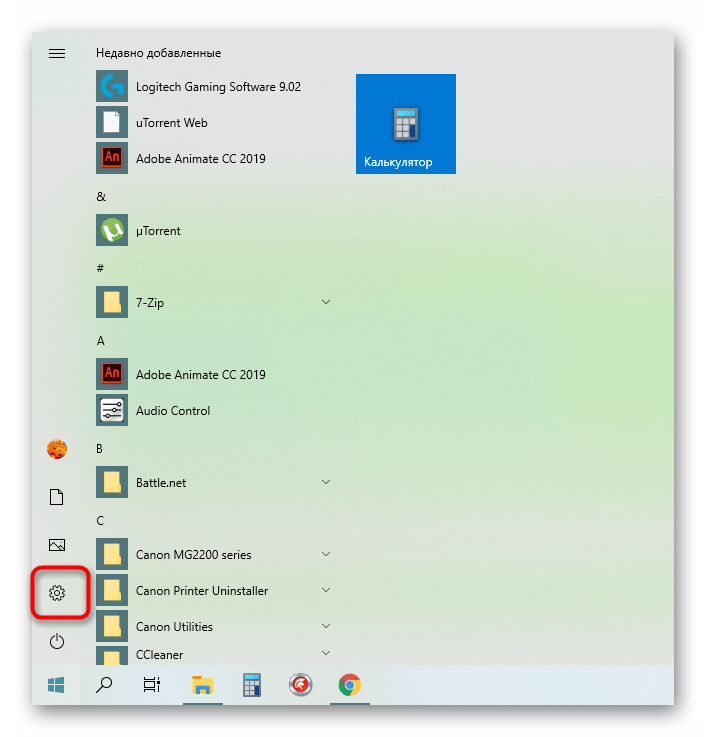
- Here, open the category "Network & Internet..
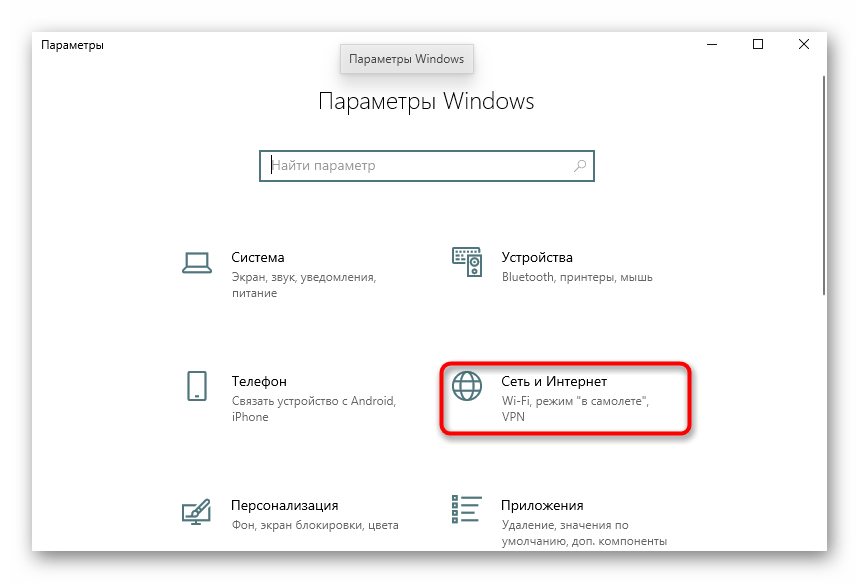
- On the first menu select "Configure Adapter Settings..
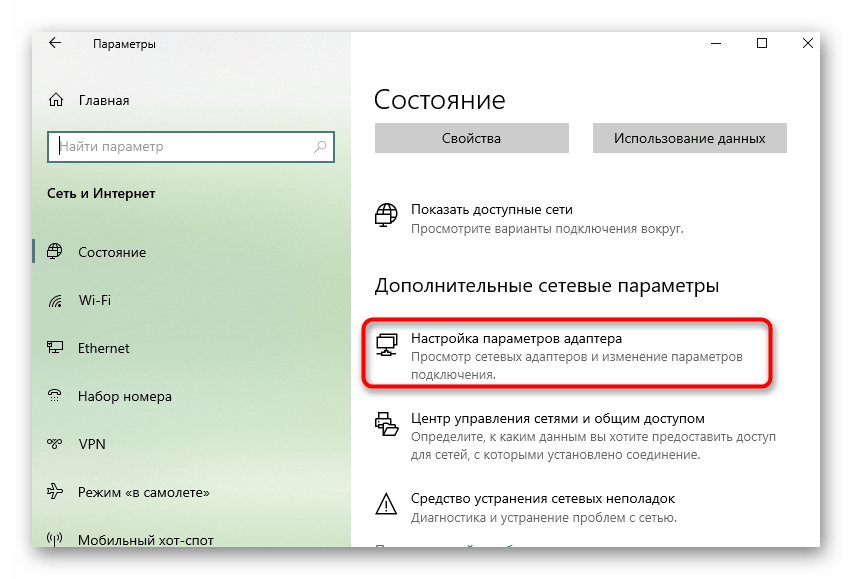
- Right-click on the active connection and use the context menu to call up "Properties" on the context menu that appears..
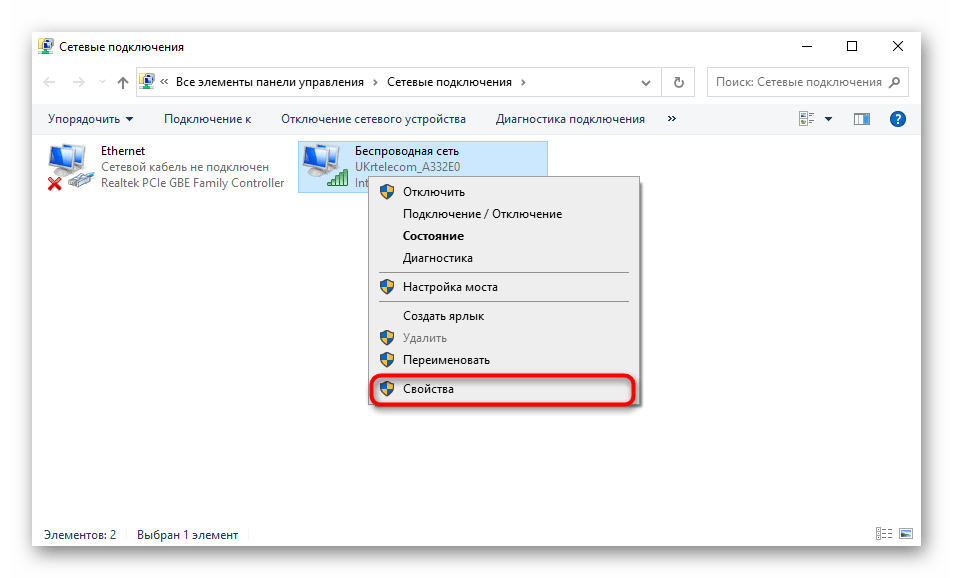
- Double-click on the line "Double-click on the line IP Version 4..
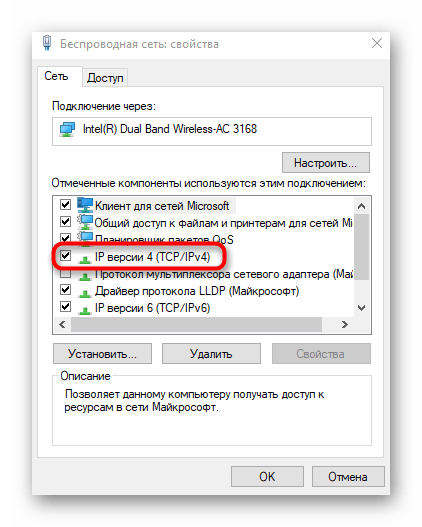
- Mark the checkboxes corresponding to automatic obtaining of IP and DNS and apply the settings.