A device that gave very slow Internet speeds. The name came from the old version of DIAL-UP modems, which functioned through the telephone network.

- What is the difference between a modem and a router, and which one is better?
- Router and its function
- The main characteristics of the device
- How a router functions
- Concept and definition
- What is an analog signal and how does it differ from a digital signal?
- The principle of ADSL
- How ADSL differs from a regular router
- The Key Characteristics of an ADSL Router
- Stationary 3G/4G router.
- What's better and what's the difference
- What is a modem?
- What is an access point?
- Choosing the Internet connection
- Strengthening the signal
- The router and its function
- The main characteristics of the device
- How a router functions
- Differences
- What is a modem
- 3G/4G modem
- ADSL model
- What to choose a modem or a router
What is the difference between a modem and a router, and which one is better?
Today, people have quite a few smart devices at home, from simple smartphones to microwave ovens, which require an Internet connection. And in general, it's hard to imagine not having Internet access in the office or home. This has become one of the main reasons why their owners should know how to use networking equipment. We are talking about devices of various types and purposes that ensure the operation of computer networks, especially the transfer of information data between united nodes, such as computers. Most often a person uses modems and routers. Even someone who has nothing to do with high technology has heard these words at least once. And if you are an active user of the World Wide Web, you probably have such devices at home. Many people don't understand the difference between a modem and a router, so we'll talk about it in simple terms. In any case – it is not the same thing, as most people think. If we are talking about the first, its main function is to direct the Internet and its traffic in the right direction.
It's not uncommon to use the devices separately, but you can find a model that combines two functions at once – this is another reason why they get confused. Before buying, it is a good idea to understand the technology of Wi-Fi, so that a quality device does not turn out low speed, "hanging" the network or at all, no signal.
Router and its function
Device, which provides access to the network for multiple users simultaneously. Since the device is not equipped with a personal radio module, you must use an additional antenna. It is usually connected to it through a wired interface.
The main characteristics of the device

Before buying, pay attention to several characteristics:
- Price tag. Usually the cheapest model costs a thousand rubles, and the most expensive – from ten to twenty.
- The list of supported models. We are talking about those with which the router will be able to function.
- Support 3/4G. Modern models work well with the first option, but do not always support the second. If you try to distribute 4G from a router that does not support this technology, you will encounter a switch to the protocol of the first option. it will happen automatically. The device will work, but at a low speed.
- The signal propagation radius.
How a router functions

The device receives the signal sent from the provider – you have a contract with him. It is he who is considered the "master" of the cable that is plugged into the connector on the router. It is otherwise called the WAN port and is blue in color. The device functions as an intermediary – it receives a signal from one source and then distributes it to consumers. All its actions are carried out strictly in accordance with the routing table, which is stored in the memory of the device.
The table is similar to an address book – it contains paths to various devices connected to the router. Each address is chosen so as to provide the shortest possible path to the device. The latter is usually checked at a set interval. Moreover, only an active user can receive a packet of Internet information. In other words, if you turn on your PC or smartphone, the router stops transmitting information to the address to which this device belongs.
Concept and definition
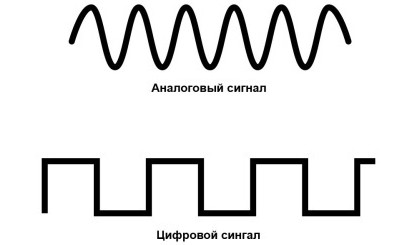
First, let's answer the question – what is it? Generally, "Modem" is an abbreviation of "MODULATOR" or "DEMODULATOR". In simple terms, such devices translates one type of signal into another. Now I will give you an example and it will become a little clearer.
Unfortunately, our computer understands only one type of information, which is encoded with zeros and ones. That is:
Morse code, invented by the great Alfred Weil, comes immediately to mind. Earlier, the task was to transmit information over a wire. But how to do this if the receiver, can only take two states: either there is voltage, or there is no voltage. As in our case 0 and 1.
And that's all I was saying, the computer only understands this kind of language. Even now you look into the computer, or into the screen of your phone, tablet or even television, and the device is endlessly adding, subtracting and transmitting a great many of these very zeros and ones.
The problem is that our whole world operates with analog data. It is precisely a modem that converts the analog signal transmitted over the wire into a digital form. You could say that a modem is a kind of translator.
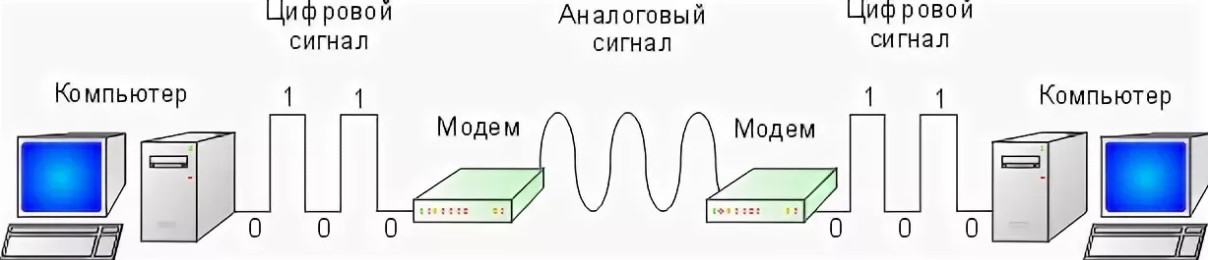
What is an analog signal and how does it differ from a digital signal?
You've probably heard this concept before in your life. Just recently in the Russian Federation, all analog broadcasting was switched to digital. That is, previously there was conventional television, but now there is digital. In fact, we are surrounded by analog information everywhere. For example, when the sun rises in the morning, we perceive information about light in different ways.
For example, it shines a little bit, shines a little more, shines a lot, barely shines (you can hardly see anything). The gradation of light intensity can be represented in an infinite number of ways. But as I said, computers, telephones and modern televisions do not understand all this and they have to transmit information only as 0 and 1.
Look at the picture above. As you can see the analog signal represented as a waveform can take different values and can be curved in different ways. But the digital one in this case takes only two values:
The modem, as I said before, translates this information in the same way. If you look at the picture below, you can see that the information is transmitted and encoded differently.
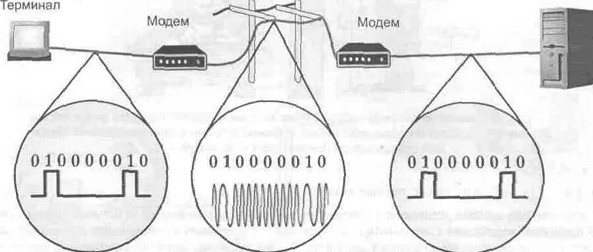
Modems were first used by the United States in air defense communications and control. Then this system was picked up by regular companies and began to develop in their fields. In our country modems came along with the Internet. If you remember the late 90's and early 2000's, you will immediately understand me.
When the Internet came to Russia and the other CIS countries, we were not ready for it. In the modern world, fiber optic connections were already in full swing. The Russian Federation was a huge country, and to connect a large number of subscribers, regions and cities would have required huge expenses, which were not available at that time.
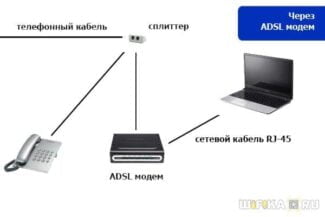
The principle of ADSL
The abbreviation ADSL stands for Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, which in Russian sounds like "asymmetric digital subscriber line". Why asymmetric? Because the amount of outgoing traffic takes a smaller fraction of the bandwidth than incoming. This is easily explained by the fact that most users download more from the Internet than they upload to the network.
To connect to the network, ADSL uses a telephone line. In order not to interfere with the telephone itself the technology sets the lower frequency limit at 25 kHz. The telephone, on the other hand, works at frequencies between 0.2 and 3.5 kHz. Thus, there is no frequency crossover, and the Internet and telephone can quite easily coexist on the same line. So you don't have to be afraid that when you connect the Internet you will have no access to the phone, like in the early 2000s.
How ADSL differs from a regular router
What is the difference between a regular router, which is connected via Ethernet cable, and an ADSL device?
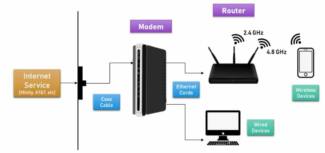
The task of a router is to receive the signal coming from an Ethernet cable (or a 3G/4G modem, which is not important to us right now) and distribute it further to all the devices connected to it in the same network. The modem receives the signal and then converts it so that the connected devices can use it.
However, nowadays there is a clear distinction between routers and modems – it is not uncommon to see routers with a modem function or, vice versa, modems with a router function. That's why in this article we are going to discuss any device that can connect using ADSL-technology, regardless of its classification.
The Key Characteristics of an ADSL Router
So what should you pay attention to when buying? There are several key characteristics on which the quality of the device depends:
- DSL technology version. Now there are three versions of ADSL – ADSL, ADSL2 and ADSL2+. They differ in the bandwidth, i.e. the maximum data transfer rate. Therefore, it is preferable to buy a modem with ADSL2+ support – it provides up to 24 Mbps of incoming traffic. For comparison, ADSL2 provides only 12 Mbit/s, while ADSL provides 8;
- Annex standards. Annex determines how the modem will work together with the phone. Annex A is the best, because it causes minimal interference and is supported by most providers. Annex L creates interference in telephony, but is able to transmit over long distances, and therefore well suited for remote areas. Annex M allows you to increase the bandwidth of the outgoing stream up to 3.5 Mbps. However not all providers support it;
- DHCP server. If the modem has a built-in DHCP server, it will make setup much easier – you will not have to manually enter IP addresses for all members of the local network when connecting. Therefore it is better to buy models with DHCP.
- The way to connect to your computer. Nowadays ADSL-modems are connected to your PC in two ways: via USB and Ethernet. The second way is more preferable. Connection via USB is notable for low stability and frequent crashes. You need to constantly monitor the firmware updates and compatibility of the modem with your PC and OS version. Another thing is Ethernet – connection to network card provides much more stable work. A USB modem may be suitable only if you want to connect only one device to the Internet and are looking for the cheapest equipment;
- The number of LAN ports. It determines how many devices you will be able to connect to the modem with an Ethernet cable. If you have only one PC at home, this point is not crucial. If you have several computers, or if you need to connect another repeater or other equipment, make sure that there are enough ports for all of them;
- wireless standard. Make sure that the modem supports 802.11n, which is the most widely used standard today and provides a stable and fast Wi-Fi connection;
- wireless speed. Here it's simple – the more the better. The standard minimum for a good wireless connection between devices is 100 Mbps. However, if you plan to use only ADSL, you can choose models with a speed of 50-60 Mbps;
- Antenna. Antennas in routers can be detachable and non-detachable. The first can be easily unscrewed and replaced by a more powerful if desired. With the latter you can not do so, so you need to initially specify their coverage area. It must be larger than the area of your apartment or office. Otherwise, there will be "blind spots" in the room, in which Wi-Fi will not catch, or the signal will be too weak.
Stationary 3G/4G router.
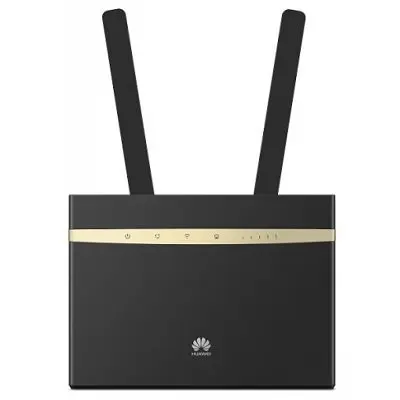

Stationary 3G/4G router is a Wi-Fi router, which has a SIM card slot, such as Huawei B593, Huawei B310, Huawei B315, Huawei B525, etc. Have a good wireless coverage radius and reliable 3G / 4G antenna connection – SMA.
Pros:
Two devices in one
Ability to connect devices via LAN cable
Great Wi-Fi range
Cons:
Price
What's better and what's the difference
Yes there is no best of them) If you care about technology, here are the differences between a modem and a router:
That is, they can also work in tandem within the same device.

But if you care to take a 3G whistle or a full-fledged WiFI router, then there look at your needs. And the usual "flash drive" can now handle quite well with a dozen connected devices. So for the home and there is not much difference. Here you should probably pay attention only to the price, appearance and the power of the antennas (to further annoy you) – otherwise do not pay attention, that's all they differ.
If you have something mixed up in your head – write in the comments. Our crazy team of writers is ready to untangle any tangle into a first-rate answer.

Master of nerdy texts and technical slog. Mr. cool glasses and a cool bowtie. Certified Wi-Fi specialist.






It's the same thing. 


What is a modem?
A modem is a device that converts a signal and adapts it to the propagation environment. When a signal is received, it is modulated. When sending a signal – demodulation. This is why a modem is also called a modulator/demodulator. A modem is always responsible for the Internet connection for a single gadget, because it is technically the simplest device.
There are two main types of modems: 3G/4G and ADSL. Connecting via 3G/4G is done with a SIM card. Here is a typical 4G (or LTE) modem.

Another popular name for a router is a router. Many users think these are different things, but they are actually the same thing. The confusion arose when Wi-Fi routers appeared, which began to include an access point in addition to a modem.
What is an access point?

In essence, it is a simple hub that provides wireless access to an existing network or the creation of a new wireless network. When several connections are made to the same access point, the bandwidth is divided by the number of connected users. You could say that an access point is a stripped down version of a router. Yes, it can work in bridge or repeater mode, but most modern routers support these modes. Again, a router is the most complex technical device of all described, which includes all the functionality of all its brethren.
Obviously, the most common and practical option is a router. Connected to the network with a cable from the provider and distributed Wi-Fi to several devices, what more do you need for home use?
A modem is fine If for some reason you don't have a fiber optic connection. This is often the case in private sectors, where providers do not lay cables. So if you can only access the World Wide Web with a telephone line, choose a modem that can convert the signal.
The access point For home use is rarely suitable. As mentioned above, its functionality is limited. But if you would like to create a seamless Wi-Fi network in your office or to set up a HotSpot in a cafe, you will need a very good access point.
Choosing the Internet connection
Earlier I thought that Wi-Fi and the Internet were the same thing, but how wrong I was. Let me tell you right away that they are different things, and they work on different standards and technologies. For example, you can have internet at home, but there will be no wifi network. And vice versa – there is no internet, but when you turn on the router around you immediately get a wi-fi network, but no internet. I don't need a regular wireless network, so I need to start by looking at options to connect to the WAN.
- Fiber optics – The most popular connection option in urban areas. It's the fastest, the most reliable, the cheapest. But here in suburban homes, it is almost impossible to connect it if there is no large population center nearby. You can ask around – perhaps in your community there is such a possibility.
- Satellite – is very expensive. As far as I know – it's still on a per-gabit basis. Plus you have to buy an expensive antenna and receiver.
- WiMAX – in the nearest large city or town there is such a tower, which transmits information by waves. It is enough to have a weak antenna and receive the signal from it. A very rare technology, but cheap.
- aDSL – The internet is transmitted via telephone wires. The connection is poor and so is the speed. Maybe it will suit someone, but I have not even considered it. I wrote it down to complete the picture.
- 3G/4G – Mobile Internet, the cheapest option, it is enough to have a modem.
I chose the latter option because there are more 3G/4G towers, the connection is improving. But most importantly, you do not need to spend a lot. This immediately raises the question of signal amplification. The fact is that if your cottage is far away from the house, the radio waves may not reach you. Or the connection will be bad.
Strengthening the signal
So, choosing mobile Internet as a primary connection I immediately bought a modem, which I should not have done – a little later I will tell you why. I came to the cottage, connected the modem to my laptop and tried to use the Internet. The quality of the connection was disgusting, the speed was constantly jumping, there were lags and interruptions. After calling the mobile operator, I was informed that the radio tower was too far away. That's what I didn't think about. The house is 10 km away from the city.
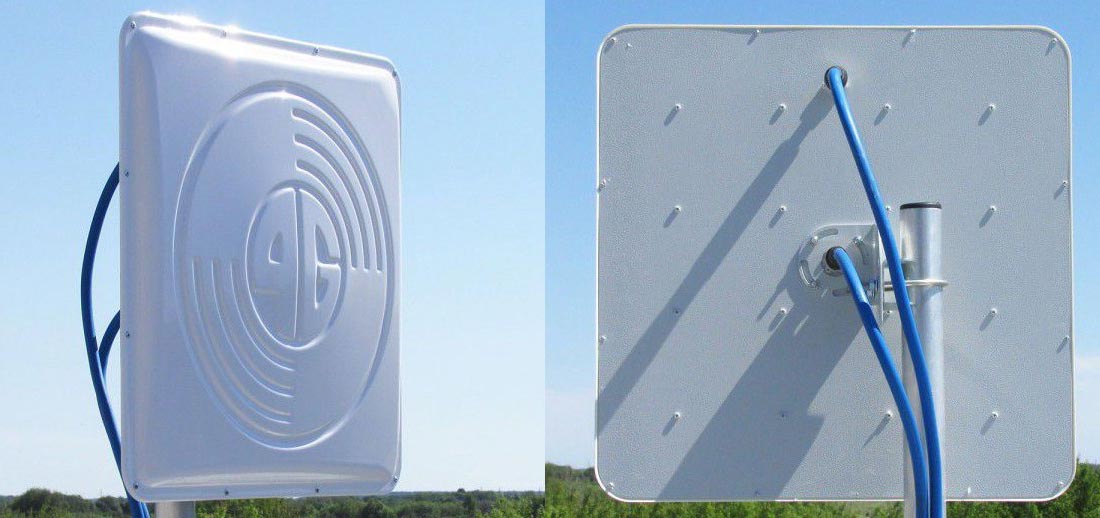

After talking to experts, I was told to buy an antenna. That is, the antenna will stand on the street on the roof and take that far away signal from the tower of the mobile provider. Bought myself a powerful 3G antenna, as in the picture above. As for the choice, you can get a professional one or a Chinese one, which is sold in a regular computer store. Here are a few models that I would recommend:
Now you have to connect it to the modem. From the antenna comes a regular cable. To connect it to the modem (flash drive) you need a special adapter – Pigtail.
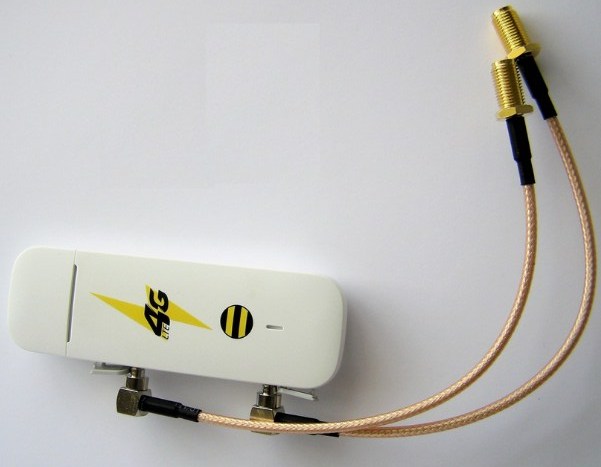

And here is where the question arose: where to plug this adapter. The thing is that there are "flash drives" that already have connections to such an antenna. But on my version, of course, there was nothing. So I had to buy another "flash drive". There is of course the option to solder the adapter directly – but it's a pain, and it's easier to just buy. Connection is quite simple – nothing complicated. Then we insert the modem into the router.

The router and its function
A device that provides access to the network simultaneously for multiple users. Since the device is not equipped with a personal radio module, you must use an additional antenna. It is usually connected via a wired interface.
The main characteristics of the device

Before buying, pay attention to several characteristics:
- Price tag. Usually the cheapest model costs a thousand rubles, and the most expensive – from ten to twenty.
- The list of supported models. We are talking about those with which the router will be able to function.
- Support for 3/4G. Modern models work well with the first option, but do not always support the second. If you try to share 4G with a router that does not support this technology, you will encounter a switch to the protocol of the first option. The device will work, but at a low speed.
- The signal propagation radius.
How a router functions

The device receives the signal sent from the provider – you have a contract with him. It is he who is considered the "master" of the cable that is plugged into the connector on the router. It is otherwise called the WAN port and is blue in color. The device functions as an intermediary – it receives a signal from one source and then distributes it to the consumers. All its actions are carried out strictly in accordance with the routing table, which is stored in the memory of the device.
The table is similar to the address book – it contains paths to various devices connected to the router. Each address is chosen so as to provide the shortest possible path to the device. The latter is usually checked at a set interval. Moreover, only an active user can receive a packet of Internet information. In other words, if you turn on your PC or smartphone, the router stops transmitting information to the address to which this device belongs.
Differences
The differences between a modem and a router (or router) are shown in the table:
| Modem | Router | |
| Presence of radio module | Yes | No |
| Ethernet support | No | Yes |
| Number of connectable devices | 1 | About 8 (model dependent) |
| Own battery | Yes | No |
| Additional features | No | Hub-mode, firewall |
As you can see, these devices are different classes of electronic devices, each of which has a specific functional purpose. In simple words a modem differs from a router in the presence of a radio module. With it, it connects to the 3G/4G network. Only one device can be connected to a modem.
What is a modem
A modem is equipment for receiving and transmitting Internet traffic. However, before we start looking at: what is the difference between a router and a modem, it is necessary to understand the types of these devices for communication.
The main distinguishing feature of the modems is the ability to work with only one connected gadget.
Modems of different kinds differ in many characteristics:
The devices are also in different price categories. Therefore, you should consider the differences between a modem and a router from the point of view of each type of equipment separately.
3G/4G modem
Models that work with 3G or 4G connectivity are a popular solution for users who are far away from fiber-optic connections. Devices of this type use mobile SIM cards to connect to the network.
On 3G/4G models, the difference between a modem and a router is more significant. For example, the appearance of the device stands out: the equipment looks like a small flash drive, while the USB port is used for connection.

Also, due to the fact that the SIM card is chosen as the source of connection to the Internet, 3G/4G modems do not have high speed and quality of connection. However, this disadvantage is compensated by the mobility of the equipment.
The price of such devices varies from 1000 to 5000 rubles. More expensive options are devices supporting 4G.

ADSL model
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) modems are used to connect to the World Wide Web via the telephone line. If the user uses the same cable for both the home phone and the Internet, then the use of this device is a must. Let's consider what is a modem of ADSL format in more detail.
What to choose a modem or a router
The difference between a router and a modem is due to the different type of Internet connection with which these types of equipment work. Moreover, you should keep in mind the different functionality of the devices. Some users use these two types of equipment to transmit the Internet signal together, because there are wifi routers that support modems of different models.
Speaking in simple words about what is better: a router or a modem, the answer will depend on the needs of the user. Therefore, when comparing the modem and router, before you understand what the difference is, you need to determine the purpose of the purchase of equipment.
If you need to create a Wi-Fi network via Ethernet cable for several devices, it is better to choose a router. However, for everyday use of the Internet you do not always need a perfect connection or excessive speed. A well-functioning modem is indispensable for trivial Internet surfing on a particular device without being tied to a specific location.
Read More:The connection speed does not always match the quality of the modem or router you bought. Sometimes it depends on the computer or other device connected to the network.